Matrices & Determinants Questions and Answers

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsIn each circle below a 50 angle with a vertex at the center of the circle is drawn How are minor arc lengths CD and EF related A 50 8 cm C D B 50 2 cm F LL E O They are the same because the central angle measure is the same



Algebra
Matrices & Determinantspoints The matrix as three distinct real eigenvalues if and only if k 4 6 A 2 k F C

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsConsider the set of vectors S 1 k 1 k 3 3 2 1 k Determine the value s of k such that the set S forms a linearly independent set in R i ii 4 marks Suppose that k 1 and an additional vector 3 4 5 is added to the set S Using TWO different methods discuss whether the new set of vectors form a basis for R 6 marks



Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsThe nutritional content per ounce for three foods is given in the table below What combination of these provide exactly 14 grams of fat 27 grams of protein and 10 grams of fiber Food A Food B Food C Fat g oz Protein g oz Fiber g oz 2 1 8 4 2 16 1 1 5 A 4 oz of Food A 6 oz of Food B 2 oz of Food C OB No possible combination of these foods OC 3 oz of Food A 5 oz of Food B 1 oz of Food C OD 7 oz of Food A 7 oz of Food B 1 oz of Food C

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsX v ix Q Y 0 V yzo If u and v are in V is u v in V Why Find a specific vector u in V and a specific scalar c such that cu is not in V If u and v are in V is u v in V OA The vector u v may or may not be in V depending on the values of x and y OB The vector u v must be in V because V is a subset of the vector space R OC The vector u v must be in V because the x coordinate of u v is the sum of two negative numbers which must also be negative and the y coordinate of u v is the sum of nonnegative numbers which must also be nonn OD The vector u v is never in V because the entries of the vectors in V are scalars and not sums of scalars Find a specific vector u in V and a specific scalar c such that cu is not in V Choose the correct answer below 2 A U B u c u 2 2 D u 2 2 2 c 4 0 1 C c 1 c 4

Algebra
Matrices & Determinants46 A garden s length is 7 times its width It takes 66 meters of fence to enclose the garden Which equation best represents the perimeter of the garden in one variable 66 14w 66 2 7w 2w 66 21 2w EN English United States

Algebra
Matrices & Determinants38 Identify the property demonstrated in the following equation 10 7 11 10 11 7 O Distributive Property 8 O Commutative Property O None Associative Property


Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsSolve the problem below You must solve each part completely and correctly and show all your work to get the indicated points for that part Let T R R be the linear transformation given by T X1 X2 X3 x1 x2 X2 X3 X3 a Find the standard matrix of T 2 points b Show that this matrix is invertible and find its inverse 1 point c Explain why T is an invertible linear transformation and find the standard matrix of T 1 point d Find T x x2 X3 2 points

Algebra
Matrices & Determinants52 22 6 Consider the matrix A a Find an orthogonal matrix P and a diagonal matrix D such that A PDPT b Compute A77 and leave your answer as a product of 3 matrices leave numbers in calculator form

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsIII x 4 y x 1 y 2x 2 y 4 y x 1 y 2x 2 x 4 y x 1 Interim Checkpoint Algebra 2 Checkpoint 1 Part 1 WEX 543211 Simp 345 D

Algebra
Matrices & Determinants45 Solve the inequality set Graph the solution on a numberline 13 11 and x 6 5 O 2 and x 11 O 2 and x 11 O 11 O 2 O all real numbers Ono solution 46 Graph the following system on a sheet of paper or graphing utility 3 and y 5 Determine which of the following points if any satisfy the system More than one answer may be correct check all correct answers 4 9 0 1 3 9 0 5 2 11 3 1 8 11

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsFolve the system of equations to the right using matrices Use Gaussian elimination with back substitution or Gauss Jordan elimination he solution set is 0 3a 2a b b a 2b

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsThe obje A Find the value of the objective function at each corner of the graphed region B Find the maximum value of the objective function C Find the minimum value of the objective function A The value of the objective function at point A is The value of the objective function at point B is The value of the objective function at point C is The value of the objective function at point D is B The maximum value of the objective function is C The minimum value of the objective function is SEIXE

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsUse a graphing utility that gives a matrix in a row echelon form or a matrix in a reduced row echelon form if available to solve the system of equations given to the ght The solution set is 0 00 3a 2a b 2c b a 2b 13 5c 13 3c 4

Algebra
Matrices & Determinants12 6 pt Write a mail time story for 23 57 and explain what your answer means grush 91 2M to equo wasds brugernon M bris vis lois ig Are you richer poorer and by how much tog novivite rose lliw aquo ni rbum work yllcups aMM 901 staria of

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsProblem 2 Let M be an n n symmetric matrix Show that M is positive definite i e v Mv 0 for all v 0 if and only if all eigenvalues of M are positive You may and should use the result of the Spectral Theorem

Algebra
Matrices & Determinants0 a Is the set S dependent or independent Show your working labelling your Gauss reduction operations clearly 4 Handin problem Let S 12 15 b Look at your Gauss reduction again If you want an independent subset of S consisting of 3 vectors which 3 vectors could you choose

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsThe matrix A 7 B 7 5 1 has an eigenvalue 1 with algebraic multiplicity 2 and geometric 1 2 1 1 multiplicity 1 a Calculate the last eigenvalue and give your answer in the box below Number b In the essay box show that the values of a and 3 are 5 and 2 respectively c Write down a Jordan form J of the matrix A i e A PJP for some invertible matrix P and J is a Jordan matrix Hint you should not have to do any calculation for this part

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsFind a 2 x 2 matrix such that the algebraic multiplicity and the geometric multiplicity of an eigenvalue of this matrix are same while the another eigenvalue has the distinct algebraic multiplicity and geometric multiplicity

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsLet Compute Sk for k 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 S 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 00000 0

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsFind the orthogonal projection y of y W Span u 3 3 5 U Ex 1 23 5 0 3 1 3 5 onto the subspace

Algebra
Matrices & Determinantsy 0 Simplify your answer Type an expression using x as the variable CIXD

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsName the property illustrated by the following sentence 1 W 1 Choose the property that is illustrated by the sentence OA Distributive Property OB Multiplicative Inverse Property OC Associative Property OD Commutative Property

Algebra
Matrices & Determinantspose that S and S are nonzero subspaces with S contained inside S and suppose that dim S 4 1 What are the possible dimensions of S 2 If S S then what are the possible dimensions of S e In order to get credit for this problem all answers must be correct

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsA years Round to two decimal places as needed 1 Add file Question 16 Given the function P r 4r5 5r 2 0 r 10 There are at most 1 Add file Question 3 12 Find F x turning points

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsF x 1 Add file Question 4 v 0 Type an exact answer using x as needed F x 1 Add file 1 0 t 7 Find the volume of the solid generated by revolving the region bounded by the given curve and lines about the x axis y x y 5 x 0 dt

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsThe subspace P of R4 is spanned by the vectors 0 0 and P Let P be the orthogonal complement of P 5 0 0 2 Suppose that v a Your friend Ezra knows that the vector v can be uniquely expressed as v p p where pe P and pept E Find p and p and enter your answers in Maple syntax in the boxes below P is a vector in R4 a Note The vector b in Maple syntax should be entered as a b c

Algebra
Matrices & Determinants1 point Find a basis of the subspace of R4 defined by the equation 3x1 7x2 Basis 4x35x4 0

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsLet a 0 30 and 70 be real nonzero constants suc that a 3 1 Solve the system of differential equations d d dt dt 2 Solve the system of differential equations B B B a B B B Ba B B 3 3 a u u a B B Ba B u B B a u dt 3 Solve the system of differential equations a Ba Ba a a B a u u

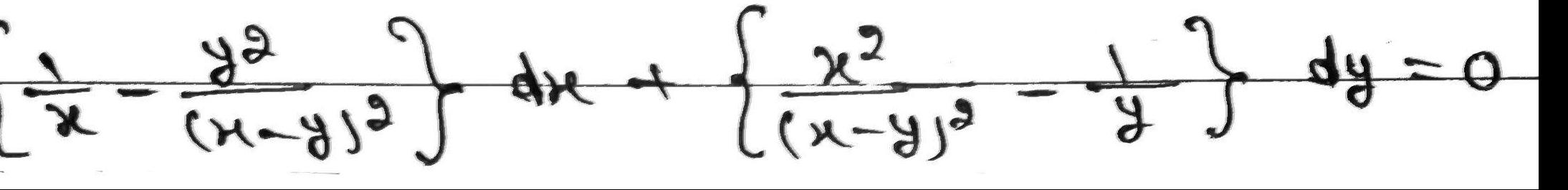


Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsLet A 1 1 0 0 1 o and B 0 1 0 0 0 ol Are A and B similar matrices f they are similar find matrices C and C such that A CBC If they are not similar show irectly that no such matrices C and C exist That is assume such matrices exist and prove 0 0 0 0 1 1 o 1 hat this assumption leads to a contradiction 1


Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsLethod Solve the following system of equations using the Gauss Jordan elimination 3x 4y z 4w 1 5x 2y 2z w 6 x y 5z 3w 2 2xy 3z2w 0

Algebra
Matrices & Determinantsc It is given that a 3 3 matrix B has the following eigenvalues with corresponding eigenvectors w A1 95 w W1 19 2 14 12 95 W2 20 Explain briefly how you know your answer is correct 5 14 A3 31 W3 Select the correct statement from the following list then use the essay box to explain briefly how you know your answer is correct B is diagonalisable because B has three linearly independent eigenvectors B is diagonalisable because B has infinitely many eigenvectors B is diagonalisable because B has three real eigenvalues B is not diagonalisable because B does not have three linearly independent eigenvectors B is not diagonalisable because the eigenvalues of B are linearly dependent B is not diagonalisable because B does not have three different eigenvalues it is impossible to tell from the given information whether B is diagonalisable or not the situation described is impossible because a 3 x 3 matrix must have three different eigenvalues 59 13 14

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsIn Problems 21 24 the given vector functions are solutions to a system x t Ax t Determine whether they form a fundamental solution set If they do find a fundamental matrix for the system and give a general solution 21 x e 22 x e 23 x 3 2e 24 X e er X X 2 2 4 X 1 0 sint COS sint X e 1 2e 1 cost sin COST

Algebra
Matrices & Determinantsa Timex c G h T kc G h Putting the dimensions in the above relation M L T LT 1 M E T PM T M L T MY x 3x 2 x 2y Comparing the powers of M L and T y z 0 x 3y 2 0 x 2y 1 1 ii iii On solving equations i and ii and iii 5 X 2 Hence dimension of time are G1 2 h1 2c 5 2

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsIf cos 50 cos 0 sin 30 and 0 0 then 2x x 7 3 11x 3 12 12 Give your exact answers as a list separated by commas Question Help Message instructor D Post to forum Submit Question Question 19 Simplify sin 10w sin 4w cos 10w cos 4w sin 10w sin 4w cos 10w cos 4w 0 1 pt100 to an expression involving a single trigonometric function

Algebra
Matrices & Determinantsssuming A is a square matrix that satisfies the condition A2 3A 21 0 find all such A and their inverses

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsExercise 4 25 marks A company produces heaters of two types called S and L The wholesale price is 40 per heater S and 88 per heater L Two time constraints result from the use of two machines A and B On machine A one needs 2 minutes for a heater S and 8 minutes for a heater L On machine B one needs 5 minutes for a heater S and 2 minutes for a heater L How many heaters of each type should one produce per hour to optimise the hourly income and what is the maximal hourly income Recall that there are 60 minutes in an hour Formulate this problem as a linear programming problem and solve it using graphical methods

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsProve the following identity without evaluating the determinants e s a b d C f e b a b c d

Algebra
Matrices & Determinants4 Solve the system of linear equations x y z w 5 2x 5y z 5w 6 3x 2 5w 1 x 3y 3z 5w 25 a b C d e inconsistent 3 4 1 5 5 4 3 1 5 1 4 3 5 4 1 3

Algebra
Matrices & Determinants4 Start with Po 0 0 0 and use Gauss Seidel iteration to find Plc for k 1 2 3 Change the order of equations if necessory to make coefficient matrix strictly diagonally dominant X 5y 2 8 ux y 2 13 2x y 62 2

Algebra
Matrices & Determinants13 10pt Find a 3 x 3 matrix U so that the matrix is diagonal 100 120 13 3 1