Anatomy and Physiology Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyWhich of the following would be an example of anxiety?
Sarah jumped when she saw the dog.
Siera dreaded walking home in the dark
Steve was certain that the food was poisoned.
The voices in John's head told him he should be afraid.

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyThe main difference between a manic episode and a hypomanic episode is the amount of social and occupational impairment
True
False

Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to PhysiologyIn order to meet the criteria for a major depressive episode, a person must have
disinterest in pleasurable activities for at least two weeks
racing thoughts for at least a week
feelings of grandiosity over a period of three weeks
ongoing intense irritability or violent outbursts

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyChecking and rechecking things is a symptom of major depressive disorder
True
False

Anatomy and Physiology
BrainWhat are the two key moods involved in mood disorders?
Anger and depression
Sadness and anxiety
Mania and depression
Anger and mania

Anatomy and Physiology
BrainWhich of the following is the most important excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain?
dopamine
glycine
glutamate
GABA

Anatomy and Physiology
CirculationOrder: GlucaGen (glucagon) 1.25 mg stat.
The directions on the package state: "For IV administration reconstitution of the 1 mg powder with 1.8 mL yields 1 mg/2 mL." How many mL will you administer?
Select one:
a. 0.625 mL
b. 0.25 mL
c. 2.5 mL
d. 6.25 mL

Anatomy and Physiology
SupexOrder: Penicillin G procaine 300,000 units IM q 12h.
The label on the vial reads 600,000 units per milliliter. How many milliliters will you administer?
Select one:
a. 0.5 mL
b. 3 mL
c. 2 mL
d. 0.25 mL

Anatomy and Physiology
CirculationOrder: Eptifibatide (Integrilin) 180 mcg/kg IV stat.
The manufacturer recommends adding 0.7 mL of sterile water for injection to each 0.75 mg vial, yielding 0.75 mg/mL. The client weighs 185 pounds. How many milliliters will you administer?
Select one:
a. 20.2 mL
b. 44.4 mL
c. 202.8 mL
d. 11.4 mL

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyOrder: Neupogen (filgrastim) 300 mcg subcut. stat. The patient weighs 132 pounds. Read the label in the figure. If the recommended dose is 5 mcg/kg/d, is the prescribed dose safe? If the prescribed dose is safe, how many milliliters will you administer?
Select one:
a. 0.5 mL
b. The prescribed dose is too small.
c. 1 mL
d. The prescribed dose is too large.

Anatomy and Physiology
CirculationOrder: Pipracil (piperacillin sodium) 8 g/day IV in four divided doses q.6h.
The directions on the package insert state, "Add 4 mL suitable diluent (sterile water or 0.9% NaCl) to yield 1g/2.5mL." How many milliliters will you administer per dosage? The patient weighs 160 pounds.
Select one:
a. 0.8 mL
b. 5 mL
c. 3.2 mL
d. 20 mL

Anatomy and Physiology
AbdomenWhich muscle flexes the thigh toward the trunk?
Adductor longus
Vastus medialis
Iliopsoas
Tensor fascia latae

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyThe physician orders potassium chloride 25 mEq p.o. q.8h. for an adult with hypokalemia. If the recommended adult dose is 10-100 mEq/d p.o. in divided doses, is the prescribed dose in the safe
range?
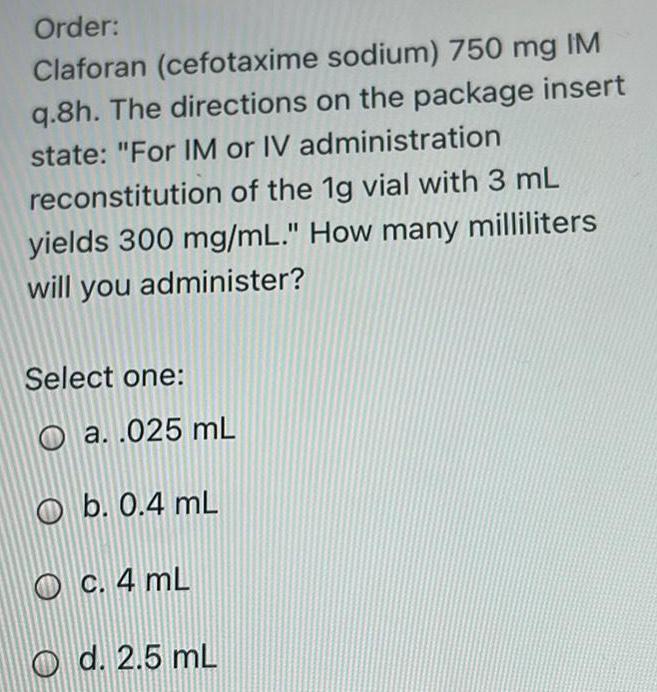
Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyClaforan (cefotaxime sodium) 750 mg IM q.8h. The directions on the package insert state: "For IM or IV administration reconstitution of the 1g vial with 3 mL yields 300 mg/mL." How many milliliters will you administer?
Select one:
a. .025 mL
b. 0.4 mL
c. 4 mL
d. 2.5 mL

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyWhich of the following best describes actin filaments?
A thick filament that looks like two golf clubs twisted together
A small, globular regulatory protein that holds another protein in place
A thin filament made of two intertwining strands whose subunits bind together like beads on a string
A long, ropelike regulatory protein that spirals around another protein, covering its active sites

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyThe physician orders 475 mg penicillin v potassium (Pen-VK). The suspension contains 250 mg per 5mL. How many mL would you administer?
Select one:
a. 23,750 mL
b. 1.9 mL
c. 0.956 mL
d. 9.5 mL

Anatomy and Physiology
SupexDamage to the glenoid labrum would affect the fit of which bone at its articulation site?
Femoral head at the hip
Humeral head at the shoulder
Ulnar head at the elbow
Clavicle at the shoulder

Anatomy and Physiology
SupexConducting a "gestural dance around the painting's perimeter," which of the following painters "would drip, pour, and splash oil paint, house and boat paint, and enamel over the surface of the canvas, determining the top and bottom of the piece only after the process was complete"?
Henri Matisse
Piet Mondrian
Jackson Pollock
Kasimir Malevich
Wassily Kandinsky

Anatomy and Physiology
Head and NeckQuestion 8
A winged sculpted figure appears as though she were alighting on the prow of a war ship. A remarkably sculpted stretch of apparently saturated material across her stomach and open wings indicate that the wind and ocean mist are blowing up against her. Her open right hand may be held high. How is the sculpture interpreted?
As an angel of mercy
As a goddess of victory
As a goddess of wrath
As an angel of death
As a mother earth goddess from an ancient cult that promoted fertility.
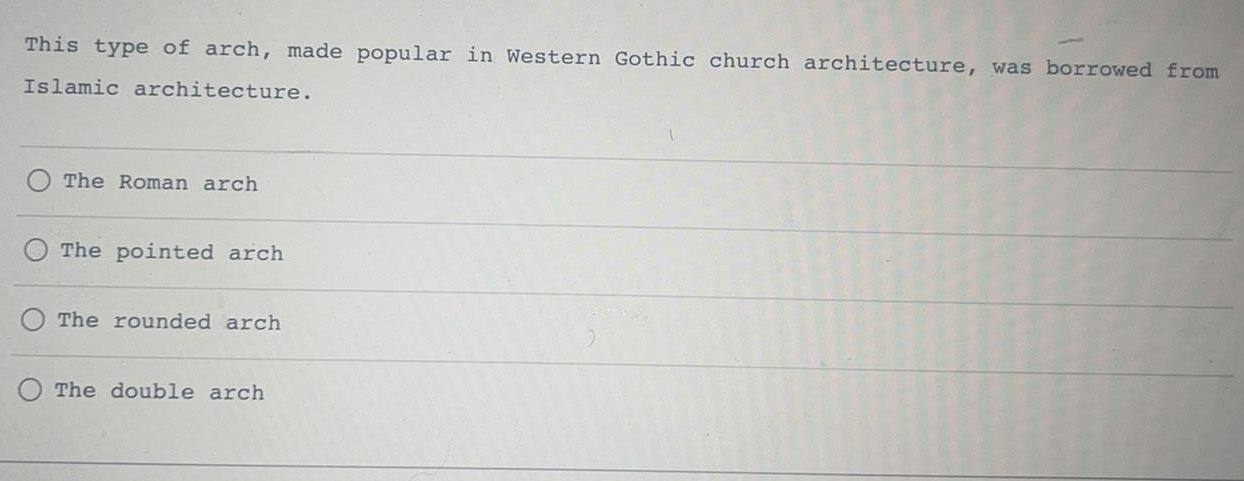
Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyThis type of arch, made popular in Western Gothic church architecture, was borrowed from Islamic architecture.
The Roman arch
The pointed arch
The rounded arch
The double arch

Anatomy and Physiology
Head and NeckThe bronze statue of Poseidon (or Zeus) depicts a god as though he were causing destruction, either throwing his trident or a lightning bolt. What expression on the face of the god is more characteristic of the Greek Classical period rather than the later Hellenistic period?
Fear, apprehension, or anxiety
Joy, delight, or happiness
Calm composure, poise, or self-control
Pain, suffering, or distress.

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyTo what does the Tutankhamon striptease refer?
The manner in which Tutankhamon instructed his priests to chisel away the name of Aten from the temples.
A painting that shows Tutankhamon's wife dancing and taking off her clothes in front of Tutankhamon.
A painting that shows Tutankhamon taking off his clothes.
The many layers of coffins archaeologists had to remove in order to get to Tutankhamon's body.

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyWhich of the following depicts a forlorn figure, out on a pier, holding his hands to the side of his ghoulish face and opening wide his eyes and mouth in the expression of a scream that is echoed behind him in wavy lines?
The Scream
Street, Berlin
Improvisation No. 30: On a Warlike Theme
The Blue Rider
Guernica

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyThe pediatric client is ordered procainamide
hydrochloride (Pronestyl) 3-6 mg/kg to a maximum of 100 mg/dose.
What would be a safe dosage for the client who weighs 35 kg?
Select one:
a. 5.8-11.67 mg
b. 100 mg
c. 8.6-17.14 mg
d. 105-210 mg

Anatomy and Physiology
G.I TractWhich statement is incorrect regarding the use of histamine-receptor blockers (H2 blockers)?
H2 blockers block histamine which causes the chief cells to decrease the secretion of hydrochloric acid
Ranitidine and Famotidine are two types of histamine-receptor blocker medications
Antacids and H2 blockers should not be given together
All the statements are incorrect

Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to PhysiologyWhich protein is produced by virally infected cells to block viral replication in neighboring cells?

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyChoose ONLY the cells which are part of the innate immune system (there may be more than one correct answer):
Eosinophils
Neutrophils
Natural Killer Cells
T-cells

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyWhat is the part of an antigen which causes immunogenicity?
MHC molecule
Antigenic determinant
T-cell receptor
CD8

Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to PhysiologyWhich antibody class crosses the placenta to give immunity to give immunity to a newborn?
IgE
IgD
IgG
IgM

Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to PhysiologyList the phases of phagocytic mobilization in correct order:
Margination - neutrophils cling to the walls of capillaries in injured areas
Chemotaxis - inflammatory chemicals attract neutrophils to the injury site
Leukocytosis - neutrophils are released from the bone marrow in response to leukocytosis-inducing
factors released by injured cells
Margination - neutrophils cling to the walls of capillaries in injured areas
Diapedesis - neutrophils squeeze through capillary walls and begin phagocytosis

Anatomy and Physiology
HistologyThe oral cavity is lined by stratified squamous epithelium. The esophagus is lined by stratified squamous epithelium. The stomach is lined by HCL secreting. The small intestine is lined with cells containing numerous simple squamous epithelium glandular mucosa stratified squamous epithelium villi and microvilli transitional epithelium goblet cells The colon's mucosa contains numerous The anal canal is lined by

Anatomy and Physiology
HistologyWhich of the following cells secrete antibodies?
T-Cells
Natural Killer Cells
B-Cells
Mast Cells

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyThe process of the thymus removing T cells that bind to strongly with self MHC peptides is called:
Natural selection
Positive selection
Negative selection
Phagocytic mobilization


Anatomy and Physiology
CirculationHow is the majority of CO2 transported in the blood?
As bicarbonate
Attached to hemoglobin
Dissolved in the plasma
Attached to platelets

Anatomy and Physiology
ThoraxWhat is the name of an activated B-cell that solely secretes antibodies?

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyBoyle's law is the inverse relationship between volume and
Diffusion
Solubility
Pressure
Oxygen

Anatomy and Physiology
SupexChoose ALL of the components of the Respiratory Membrane (need to chose all components for full credit):
Alevolar wall
Fused Basal lamina
Type II Pneumocyte
Surfactant
Capillary wall

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemThe presence of alveoli indicate that you are in the zone.
Danger
Respiratory
Conducting
Immunogenic

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyThe lungs ability to stretch and expand is called:
Lung consolidation
Elastosis
Lung motility
Lung compliance

Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to PhysiologyHow is the majority of oxygen transported in the blood?
Dissolved in plasma
Attached to hemoglobin inside the red blood cell
As bicarbonate in the plasma
Attached to Rh factor

Anatomy and Physiology
ThoraxWhich of the following is only found on the left lung?
Horizontal fissure
Oblique fissue
Cardiac notch
Middle lobe

Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to PhysiologyThe lung volume that represents the normal volume of air that is displaced between normal inhalation and exhalation is called?
Inspiratory reserve volume
Residual volume
Tidal volume
Expiratory reserve volume

Anatomy and Physiology
General AnatomyIf there is an area of diseased lung that is low in oxygen content, the traveling to that area with to match ventilation with perfusion.
nerves
vasodilate
blood vessels
depolarize
vasoconstrict


Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction to PhysiologyWhere in the digestive tract does segmentation primarily occur?
Esophagus
Small instestine
Stomach
Rectum

Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory SystemArrange the events of Inspiration in correct order:
Air flows into lungs down its pressure gradient
Thoracic cavity volume increases
Lungs are stretched and intrapulmonary volume increases
Inspiratory muscles contract
Intrapulmonary pressure decreases

Anatomy and Physiology
SupexParietal cells of the the stomach secrete. Chief cells of the stomach secrete
Pepsin
Pepsinogen
HCL
Histamine


Anatomy and Physiology
CirculationWhich of the following factors will enhance oxygen unloading from hemoglobin? (More than one answer is correct, partial credit will be given):
Increased tissue CO2
Decreased tissue BPG
Increased tissue heat
Decreased tissue pH
Increased tissue oxygen
Decreased tissue CO2
Increased tissue acidity
Decreased tissue oxygen