Vector Calculus Questions and Answers
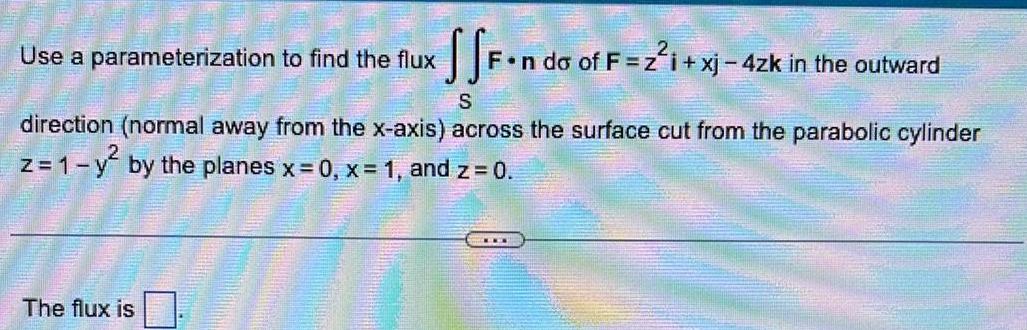
Calculus
Vector CalculusSSF n do of F 2 xj 4zk in the outward S direction normal away from the x axis across the surface cut from the parabolic cylinder z 1 y by the planes x 0 x 1 and z 0 Use a parameterization to find the flux The flux is

Calculus
Vector CalculusUse a parameterization to find the flux The flux is SSF ndoo F n do of F z i xj 2zk in the outward direction normal away from the x axis across the surface cut from the parabolic cylinder z 1 y by the planes x 0 x 1 and z 0 S EXT
Calculus
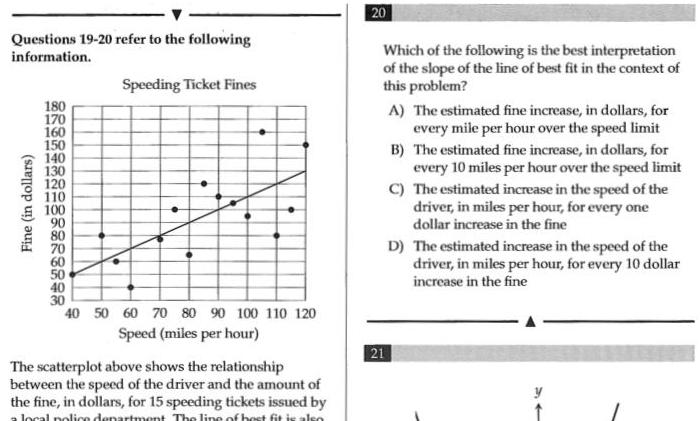
Vector CalculusQuestions 19 20 refer to the following information Fine in dollars 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 30 40 Speeding Ticket Fines 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 Speed miles per hour The scatterplot above shows the relationship between the speed of the driver and the amount of the fine in dollars for 15 speeding tickets issued by a local police department The line of best fit is also 20 Which of the following is the best interpretation of the slope of the line of best fit in the context of this problem 21 B A The estimated fine increase in dollars for every mile per hour over the speed limit The estimated fine increase in dollars for every 10 miles per hour over the speed limit C The estimated increase in the speed of the driver in miles per hour for every one dollar increase in the fine D The estimated increase in the speed of the driver in miles per hour for every 10 dollar increase in the fine

Calculus
Vector Calculus1 Determine the approximate radian measure 252 2 Determine the approximate degree measure to the nearest tenth 4 78 3 Draw both special triangles using radian measures
Calculus
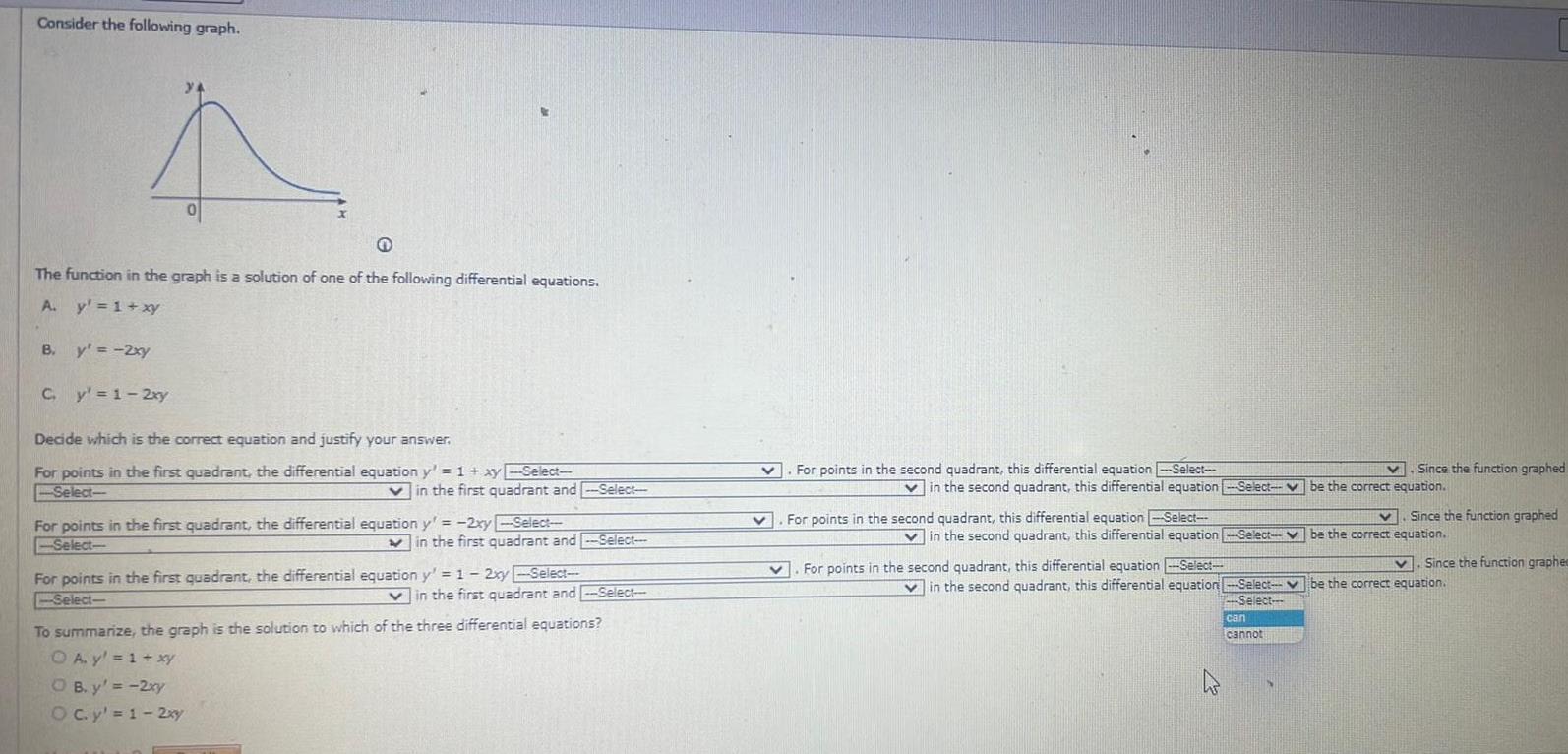
Vector CalculusConsider the following graph 4 The function in the graph is a solution of one of the following differential equations A y 1 xy B y 2xy C y 1 2xy Decide which is the correct equation and justify your answer For points in the first quadrant the differential equation y 1 xy Select Select Vin the first quadrant and Select For points in the first quadrant the differential equation y 2xy Select Select in the first quadrant and Select For points in the first quadrant the differential equation y 1 2xy Select Select OB y 2xy O c y 1 2xy in the first quadrant and Select To summarize the graph is the solution to which of the three differential equations O A y 1 xy v For points in the second quadrant this differential equation Select v v in the second quadrant this differential equation Select be the correct equation For points in the second quadrant this differential equation Select in the second quadrant this differential equation Select For points in the second quadrant this differential equation Select 4 Since the function graphed Select be the correct equation Select Since the function graphed V in the second quadrant this differential equation Select be the correct equation can cannot Since the function graphee

Calculus
Vector Calculusb Are these underestimates or overestimates of I L is an underestimate OL is an overestimate OR is an underestimate OR is an overestimate M is an underestimate OM is an overestimate c Use the graph to find T T 45 How does it compare with I T2 I d For any value of n list the numbers L R MT and I in increasing order Enter your answers as a comma separated list Enter your answer using the variables rather than numerical values I T I M Rn n n n x Enhanced Feedback Please try again For finding L R and M use Riemann sums with left endpoints right endpoints and midpoints respectively and let n 2 To find T use a Riemann sum with the mean of the left and right endpoint To list Ln R MT and I graph each one and distinguish between overestimates and underestimates Need Help Bead It Watch It

Calculus
Vector CalculusUse a parameterization to find the flux The flux is SSF n da of F z i xj 22k in the outward direction normal away from the x axis across the surface cut from the parabolic cylinder z 1 y by the planes x 0 x 1 and z 0 S GLOB

Calculus
Vector Calculus83 Navigation A plane is flying with a bearing of 302 Its speed with respect to the air is 900 kilometers per hour The wind at the plane s altitude is from the southwest at 100 kilometers per hour see figure What is the true direction of the plane and what is its speed with respect to the ground 900 km h W 32 N S E 100 km h 45

Calculus
Vector CalculusFinding a Terminal Point In Exercises 17 and 18 the vector v and its initial point are given Find the terminal point 17 v 1 3 Initial point 4 2 Answer 3 5

Calculus
Vector Calculusa Sketch the given directed line segment b Write the vector in component form c Write the vector as the linear combination of the standard unit vectors i and j d Sketch the vector with its initial point at the origin Initial Point Terminal Point 2 0 5 5 9

Calculus
Vector CalculusFinding Magnitudes In Exercises 39 40 41 and 42 find the following a u b v c u v d e IMI u v u v 39 u 1 1 v 1 2 f

Calculus
Vector CalculusWhich of the following functions grows the LEAST O A c t t 5t OB e t e O c a t t O D g t 3t t E i t In t100

Calculus
Vector CalculusFill in the table Parent Function Transformed Function a Mapping Notation b Transformation Table c Transformed Graph d Transformed Domain f x 3 g x 2 33 x 1 1 x y


Calculus
Vector CalculusThe point 5 11 is on the terminal side of the angle 8 Find the exact value of sec To get full points show your work on your scratch paper

Calculus
Vector CalculusFind the distance between the pair of points If necessary express answers in simplified radical form and then round to two decimal places 6 1 and 9 5 The distance between the points is units Simplify your answer Type an exact answer using radicals as needed Express the distance rounded to two decimal places if the exact simplified answer contains radicals Select the correct choice below and if necessary fill in the answer box to complete your choice OA The distance between the points is approximately units Type an integer or decimal rounded to two decimal places as needed B The exact simplified form does not contain radicals

Calculus
Vector CalculusWhich of the following are the most appropriate equations for the triangle O A 4 C 3 Not drawn to scale 5 3 sin A cos A sin A 3 sin A 2 cos A 4 cos 4 3 sin 4 cos 4 5 B 4 5 3 5 3


Calculus
Vector Calculus3 Match each graph in the table with the graph of its inverse Then write an equation for each function A Graph 2 0 2 Equation N 0 2x N Letter of Graph of Inverse Equation of inverse y 4 2 0 2 N 0 2 34 4 2 10 ak 0 IN

Calculus
Vector CalculusFor the following vector convert from x and y coordinates to magnitude and direction x 5 y 5 r 0

Calculus
Vector CalculusGiven the vector u 67 3j find the magnitude and angle in which the vector points measured counterclockwise from the positive x axis 0 0 2

Calculus
Vector CalculusThe Jones Company has just completed the third year of a five year MACRS recovery period for a piece of equipment it originally purchased for 295 000 a What is the book value of the equipment The book value of the equipment after the third year is Round to the nearest dollar b If Jones sells the equipment today for 175 000 and its tax rate is 35 what is the after tax cash flow from selling it The total after tax proceeds from the sale are Round to the nearest dollar c Just before it is about to sell the equipment Jones receives a new order It can take the new order if it keeps the old equipment Is there a cost to taking the order and if so what is it Explain Assume the new order will consume the remainder of the machine s useful life A Yes the cost of taking the order is the lost 50 976 in book value B No Jones already owns the machine so there is no cost to using it for the order c Yes the cost of taking the order is the extra depreciation on the machine D Yes the cost of taking the order is the lost after tax cash flow of 131 592 from selling the machine

Calculus
Vector CalculusSubstituting and combining like terms we get 4f x 2f x 2f x Part 3 of 3 Therefore f x aex 2 be x Submit Skip you cannot come back 0 ex 2 Select a solution to the differential equation 4y 2y 2y 0 0 ex

Calculus
Vector CalculusO 2 4 5 3 2 0 5 1 23 5 NOTE AB is not possible In order to multiply matrices the number of columns from the first matrix must match the number of rows from the second matrix Question Suppose C Find CD 5 4 0 BA 2 5 51 3 9 For more information on this topic look in your textbook at section 8 3 You might also want to look at the Matrix Operations presentation 6 5 6 4 1 1 c 2 3 and D 9 1 3 4 5 4

Calculus
Vector CalculusA sector of a circle has a central angle of 135 Find the area of the sector if the radius of the circle is 14 cm cm


Calculus
Vector Calculus69 The angle between 0 and 27 in radians that is coterminal with the angle Tin radians is 10


Calculus
Vector CalculusUse Cramer s rule to solve the system x y 8 x y 6 The solution set is Simplify your answer Type an ordered pair using integers or fractions

Calculus
Vector CalculusConvert 19 40 27 to a decimal number of degrees Do not round any intermediate computations Round your answer to the nearest thousandth 0 X

Calculus
Vector CalculusTriangle ABC shown below has mA 104 b 8 and c 10 Find the area of the triangle Round your answer to the nearest tenth and do not include units in your answer C A 104 a 10 B


Calculus
Vector CalculusFill in the blanks If v a i b j v w v w kv and w a i b j then the following are true i j i j j i

Calculus
Vector Calculusr 0 50 TH 4 5 2 50 77 Step 3 We are asked to find a second pair of polar coordinates for the Cartesian coordinates 5 5 We have found the following point with the required conditions are as follows We must now find polar coordinates with r 0 To find the negative value of r we choose the negative square root to solve for r r 5 2 5 2 Step 4 Recall that for a negative radius the resulting point is on the same line through the origin as the point with positive radius it is the same distance from the origin but it is on opposite sides of the origin That is r 8 represents the same point as r 0 m We found that r 8 5 2 74 are the polar coordinates of the given point with a positive radius Therefore the polar coordinates of the given point with negative radius r 5 2 and 0 8 2 is as follows r 0 Submit Skip you cannot come back

Calculus
Vector CalculusAn airplane started at point X traveled 320 miles to point Y adjusted its route and traveled another 400 miles to point Z If the airplane is currently 599 miles from its starting position at point X by how many degrees did it adjust its route at point Y Round your answer to the nearest degree if necessary Do not enter the degree symbol Z 400 Y 599 320

Calculus
Vector CalculusChris invests 15 000 at 7 simple interest for 19 years Round your answers to the nearest cent How much interest is earned over the 19 year period How much is in the account at the end of the 19 year period

Calculus
Vector Calculus4 How can we use transformations to manipulate the shape position and behavior of a polynomial function and how do these changes impact its graphical representation and algebraic properties

Calculus
Vector Calculus3 For the following function use the key points of the parent function to perform transformations Graph the parent and transformed function Write the equation of the transformed function Include a table of values for the parent and transformed function f x x g x f x 1 2 20 18 16 14 12 10 0 8 10 12 14 16 16 le


Calculus
Vector CalculusProblem 3 A QR decomposition is a decomposition of a matrix A into a product A QR of an orthonormal matrix Q and an upper triangular matrix R Write a command that takes a matrix A as input and computes a QR decomposition of the matrix Refer to Section 4 3 of the Olver text for details on a possible algorithm for decomposing A into the form QR

Calculus
Vector CalculusFind a Cartesian equation for the curve r 3 cos 8 0 x Identify the curve O circle Olima on Oline O ellipse O hyperbola


Calculus
Vector CalculusConsider the function f x x 3 6x 2 9x 1 a Find the critical points of f x and determine whether each point is a la maximum local minimum or neither b Determine the intervals where f x is increasing or decreasing c Find the points of inflection of f x and determine whether each pa corresponds to a concave up or concave down region

Calculus
Vector CalculusFind a polar equation for the parabola with focus 0 0 and directrix r cos 0 2 2
Calculus
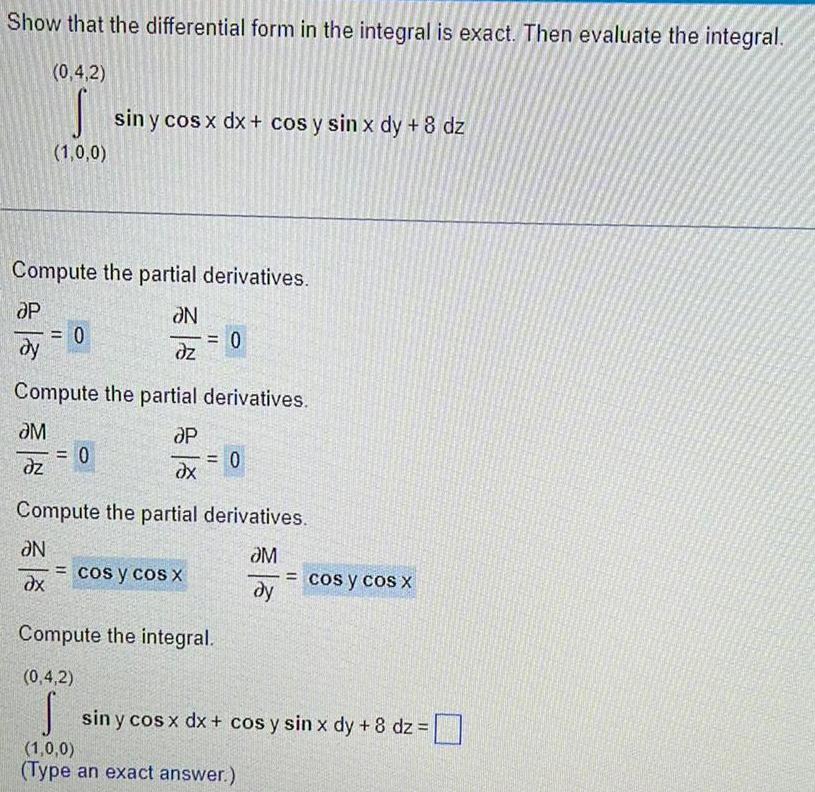
Vector CalculusShow that the differential form in the integral is exact Then evaluate the integral 0 4 2 S 1 0 0 Compute the partial derivatives OP N dy dz 0 sin y cos x dx cos y sin x dy 8 dz N ax Compute the partial derivatives M P dz dx 0 0 Compute the partial derivatives M dy cos y cos X 0 Compute the integral 0 4 2 S 1 0 0 Type an exact answer cos y cos x sin y cos x dx cos y sin x dy 8 dz

Calculus
Vector CalculusSolve the following equation for where Select the correct answer below OB OB 2 OB 5 and B and 5 sec B 1 tan B 3 3
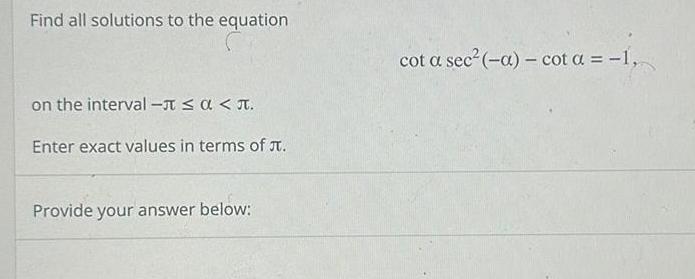
Calculus
Vector CalculusFind all solutions to the equation on the interval Enter exact values in terms of Provide your answer below cot a sec a cot a 1

Calculus
Vector CalculusLet f be a function such that f 1 2 At each point x y on the graph of f the slope is 5xy x y 5 Which of the following statements is given by da true f has a relative maximum at x 1 f has a relative minimum at x 1 f has neither a relative minimum nor a relative maximum at x 1 There is insufficient information to determine whether f has a relative minimum a relative maximum or neither at x 1

Calculus
Vector CalculusFind two positive numbers whose product is 144 and whose sum is a minimum Select the correct answer 4 36 2 72 12 12 6 24 3 48

Calculus
Vector CalculusIf y 2x 6x and 6 find dos s 0 948 836 946 928 none of these when x 5 Select the correct answer