2D Geometry Questions and Answers

Geometry
2D Geometry5 What will be the coordinates of point R if triangle RQS is rotated 90 counterclockwise 10 B 6 4 2 10 8 6 4 2 2 4 6 8 10 R 2 a 5 N 6 8

Geometry
2D Geometry3 On the set of axes below pentagon ABCDE is congruent to A B C D E Which describes a sequence of rigid motions that maps ABCDE onto A B C D E 1 a rotation of 90 counterclockwise about the origin followed by a reflection over the x axis 2 a rotation of 90 counterclockwise about the origin followed by a translation down 7 units 3 a reflection over the y axis followed by a reflection over the x axis 4 a reflection over the x axis followed by a rotation of 90 counterclockwise about the he de origin of congruence togler 16

Geometry
2D Geometry10 Which diagram shows the construction of the perpendicular bisector of AB 71 5 1 A B 3 4

Geometry
2D Geometry4 a What is a single transformation to describe the figures in the graph b What is a sequence of transformation to describe the figures in the graph 10F D 8 AA 6 4 A B 8 6 4 2 2 B 2 4 6 8 10

Geometry
2D Geometry1 Triangle TUV is shown on this coordinate plane G 3432 79 A 0 4 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 B 4 0 X Triangle TUV will be reflected over the x axis The image of TUV will then be translated 2 units up and 1 unit left What will be the coordinates of the final image of point V after the two transformations C 4 6 D 6 4


Geometry
2D GeometryGiven COS 2 sin x y 204 325 36 325 36 325 O 204 325 24 25 in Qll and Sin y 130 QIV FE



Geometry
2D GeometryIn 4 Given 1 m find the value of x and the measure of all the angles drawings are not to scale 4 6x 7 3x 17

Geometry
2D GeometryIn 2 3 Find the mL1 and justify by stating the reason drawings are not to scale 3 m 21 2 m 21 Reason 38 Reason 46



Geometry
2D Geometry26 Using the grid provided sketch the graph of the given function in the interval 5 5 and then determine the x intercepts if any y sin TCX 2 1 5 4 3 2 10 14 2 1 2 3 4 5 X
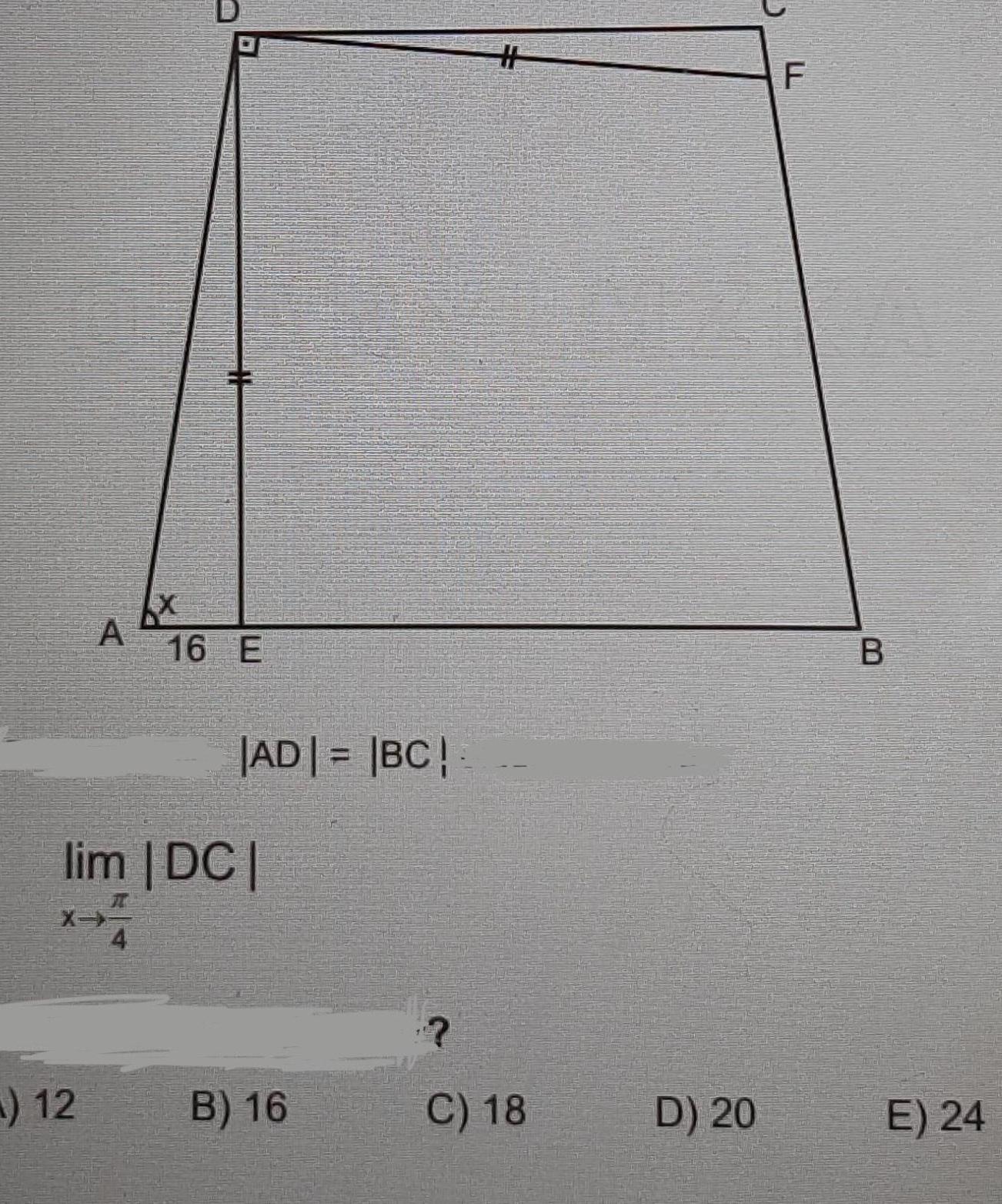

Geometry
2D Geometry1 Determine whether the Law of Sines or the Law of Cosines is needed to solve the triangle Then solve the triangle Round your answer to two decimal places A 42 B 35 c 1 4 O Law of Cosines No solution Law of Sines C 103 a 0 96 b 0 96 Law of Cosines C 103 a 0 82 b 0 96 Law of Sines No solution Law of Sines C 103 a 0 96 b 0 82

Geometry
2D Geometry28 Use the given values to evaluate if possible three trigonometric functions csc x tan x cot x 8 cos x 7 cos x 15 COS 17 17

Geometry
2D Geometry24 Evaluate the following expression 0 2an 6 where n is a whole number sec 30 1 1 cos 30 O cos 30 Osec 30 cos 30 O cos 30 O sec 30 sec 30
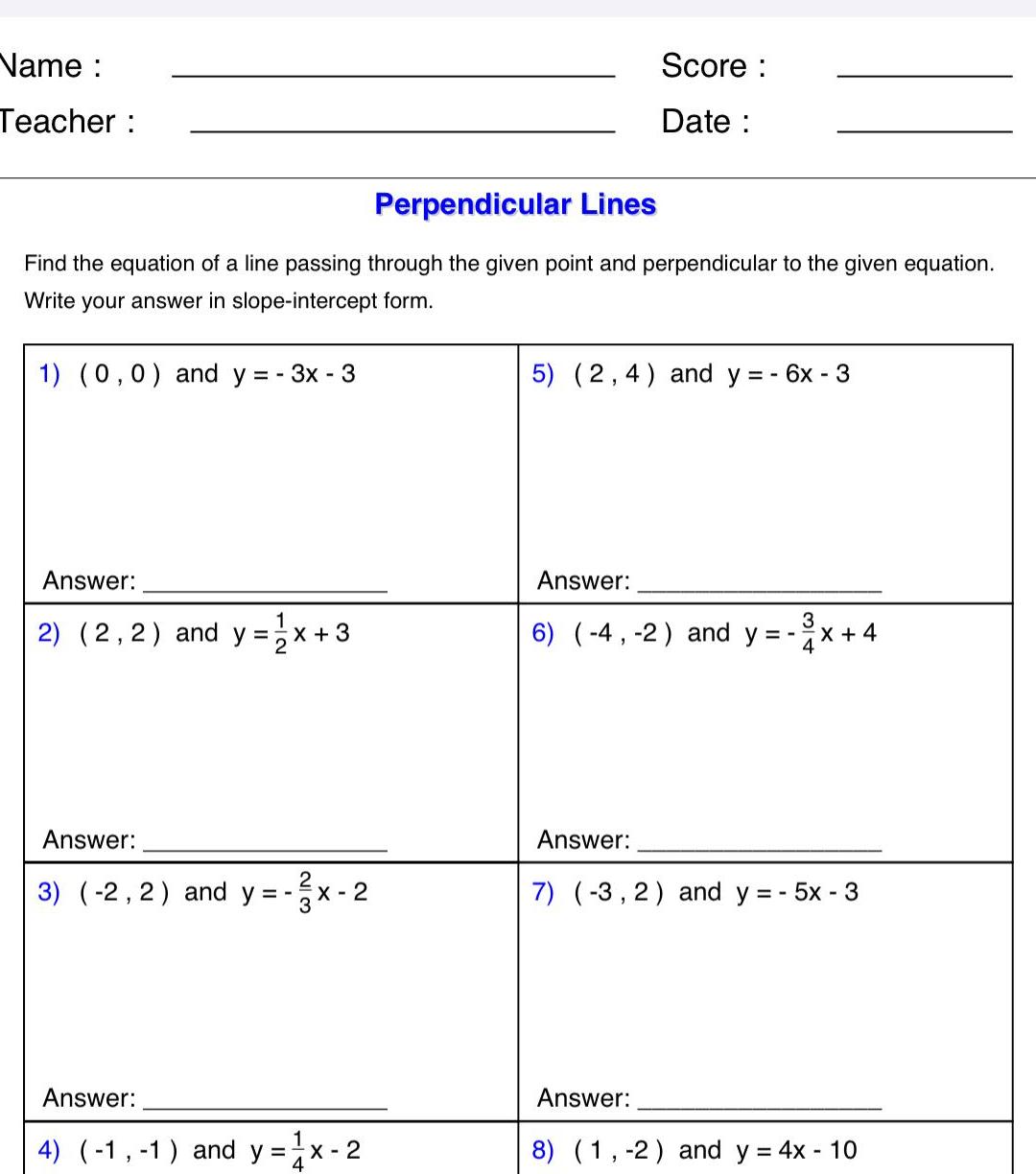
Geometry
2D GeometryName Teacher Perpendicular Lines Find the equation of a line passing through the given point and perpendicular to the given equation Write your answer in slope intercept form 1 0 0 and y 3x 3 Answer 1 2 2 2 and y x 3 Answer 3 2 2 and y 1 X 2 Answer 4 1 1 and y x 2 Score Date 5 2 4 and y 6x 3 Answer 3 6 4 2 and y Answer X 4 Answer 7 3 2 and y 5x 3 8 1 2 and y 4x 10

Geometry
2D GeometryTo find the distance across a river a surveyor chooses points A and B which are 197 ft apart on one side of the river see the figure She then chooses a reference point C on the opposite side of the river and finds that LA 47 and LB 70 A distance from A to C OOOO 208 ft 207 ft 209 ft 206 ft A A cft 8 B

Geometry
2D GeometryTwo tugboats that are 118 ft apart pull a barge as shown If the length of one cable is 206 ft and the length of the other is 227 ft find the angle formed by the two cable 37 38 28 03 31 15 DODDDDD000
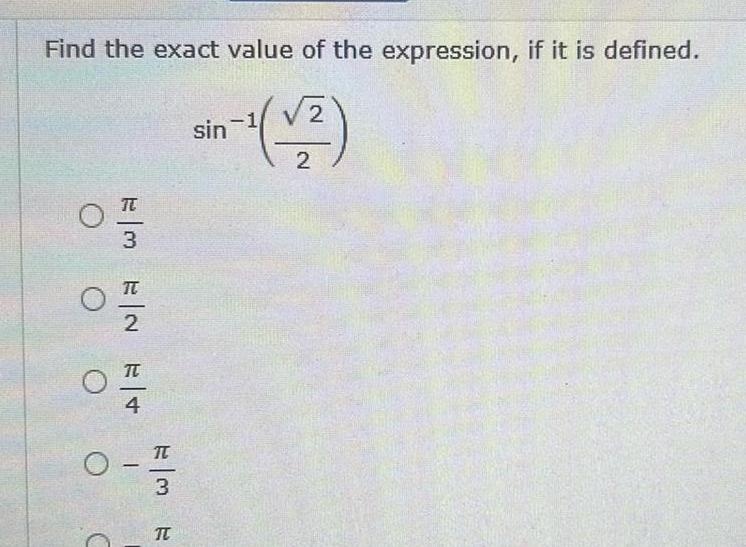
Geometry
2D GeometryFind the exact value of the expression if it is defined V2 sin 1 2 O EM EN E OOO E ME FR 3 N

Geometry
2D GeometrySimplify 1 cos 48cos 50 sin 40sin 50 A cos 8 B sin 0 C cos 90 D cos 30 2 sin 3ucos 3u cos 3usin 3u B cos 6u D sin 7u A sin 3u C sin 6u

Geometry
2D GeometryThe windshield wiper blade on Han s car is 25 inches long Each swipe of the wiper makes an angle of 125 degrees as pictured below To the nearest inch how far does the tip of the windshield wiper travel with each swipe of the blade 125 25

Geometry
2D GeometryQuestion In the diagram below of triangle TUV W is the midpoint of TV and X is the midpoint of UV If W X 53 6z and TU 46 7x what is the measure of W X U Watch Video Show Exa
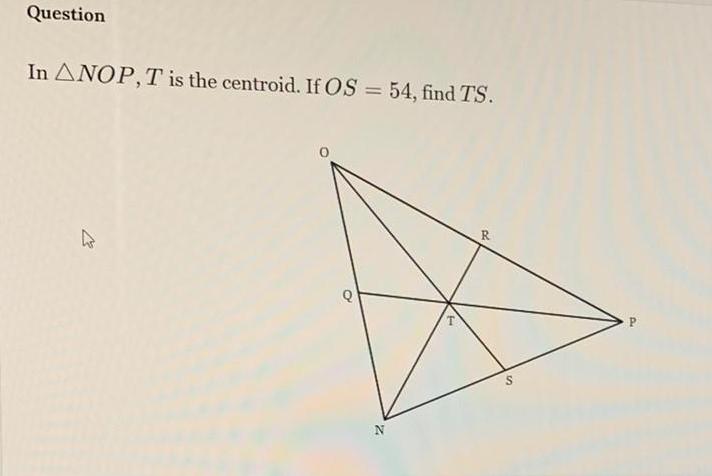

Geometry
2D Geometry9 15 Use the Laplace transform to solve the integral equation f t f sin t t f t dt sin t

Geometry
2D Geometry3 10 Use the Convolution theorem to evaluate the Laplace transform L cost cosh tt dt Do not evaluate the integral before transforming


Geometry
2D GeometryLesson HW 1 Which trigonometric function is represented by 2 Which trigonometric ratio best represents the ratio opposite leg solving a cosine function hypotenuse X DA OB C B 3 Which trigonometric ratios are equivalent to 12 Choose two 37 OA B C OD work Complete problems 1 11 below for independent practice Sine Cosine Tangent A OB C OD Y 12 11 FROHEAT Sin X Cos X Sin Z Cos Z 24 X 5 Find the correct equation to solve for x sin x cos 24 When you are finished check the solutions with your teacher 11 cos x 1 24 sin 24 11 35 37 Z A OB C OD A B C D 4 Which trigonometric ratios are equivalent to Choose two opposite leg adjacent leg hypotenuse DA B adjacent leg adjacent leg hypotenuse opposite leg hypotenuse D Z X Sin X Cos Z Sin Z Cos X 21 6 Find the correct equation to solve for x Q 55 10 R sin 55 cas 55 15 1551 51 cos 55 sin 55 10 35 28 X
Geometry
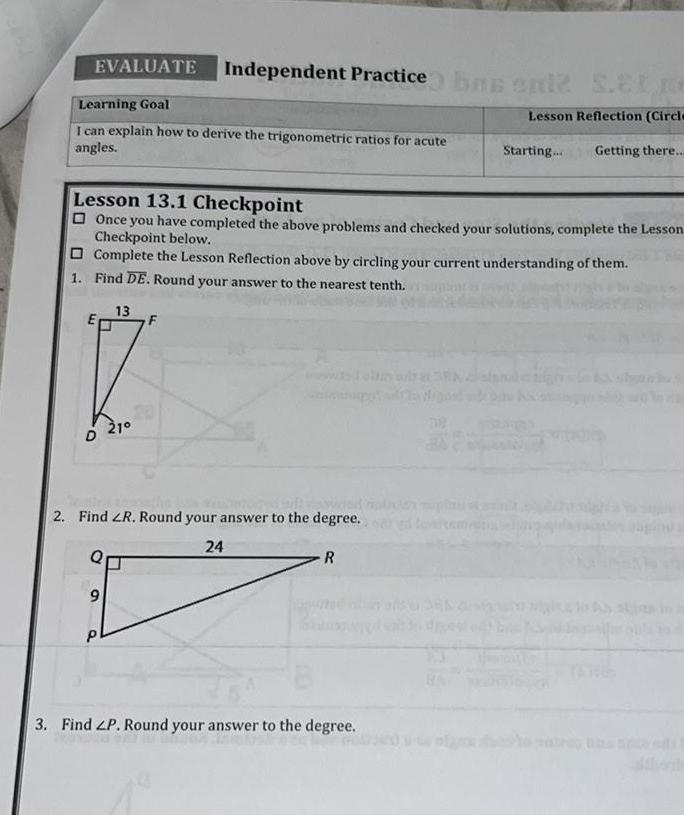
2D GeometryEVALUATE Independent Practice bas sale S Ele Learning Goal Lesson Reflection Circle I can explain how to derive the trigonometric ratios for acute angles Starting Getting there Lesson 13 1 Checkpoint Once you have completed the above problems and checked your solutions complete the Lesson Checkpoint below Complete the Lesson Reflection above by circling your current understanding of them 1 Find DE Round your answer to the nearest tenth D 13 9 210 F the 2 Find ZR Round your answer to the degree 24 R 3 Find LP Round your answer to the degree
Geometry
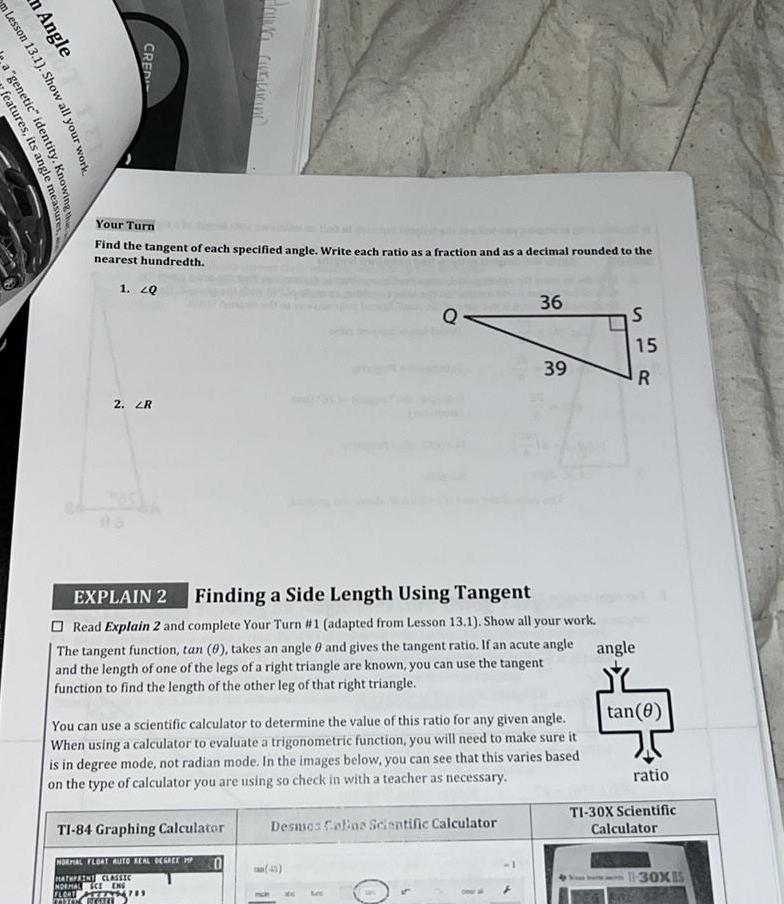
2D Geometryn Lesson 13 1 Show m Angle features its angle measures a genetic identity Knowing the CREDI Your Turn Find the tangent of each specified angle Write each ratio as a fraction and as a decimal rounded to the nearest hundredth 1 20 2 ZR EXPLAIN 2 Finding a Side Length Using Tangent Read Explain 2 and complete Your Turn 1 adapted from Lesson 13 1 Show all your work The tangent function tan 0 takes an angle 8 and gives the tangent ratio If an acute angle and the length of one of the legs of a right triangle are known you can use the tangent function to find the length of the other leg of that right triangle TI 84 Graphing Calculator You can use a scientific calculator to determine the value of this ratio for any given angle When using a calculator to evaluate a trigonometric function you will need to make sure it is in degree mode not radian mode In the images below you can see that this varies based on the type of calculator you are using so check in with a teacher as necessary NORMAL FLOAT AUTO REAL DEGREE MP MATHPAINT CLASSIC NORMAL CE ENG FLOOT YRITYS479 THE RESELL 0 36 Desmas Colias Scientific Calculator 39 45 S 15 R angle tan 0 ratio TI 30X Scientific Calculator 11 30XIS

Geometry
2D GeometryDividing Radicals 6 V100 1 5 5 3 NSSSSS 3 3 2 2 2 2 Multiply by Simplify Rational denom
Geometry
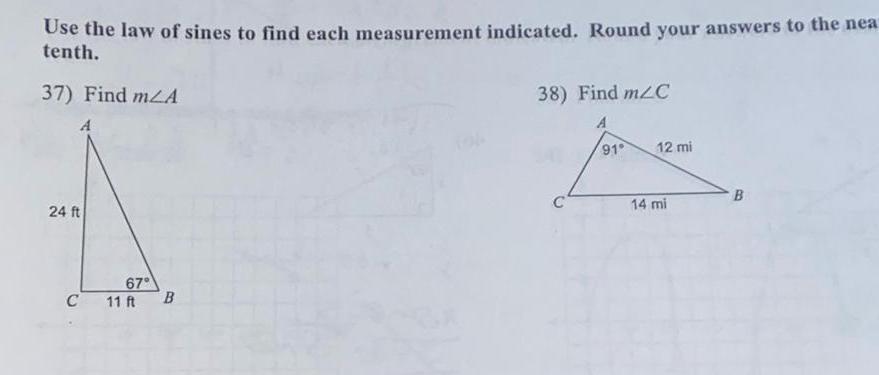
2D GeometryUse the law of sines to find each measurement indicated Round your answers to the nea tenth 37 Find mA 24 ft 67 C 11 ft B 38 Find m C 91 12 mi 14 mi B
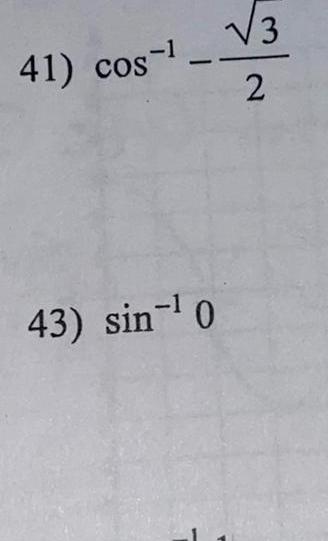
Geometry
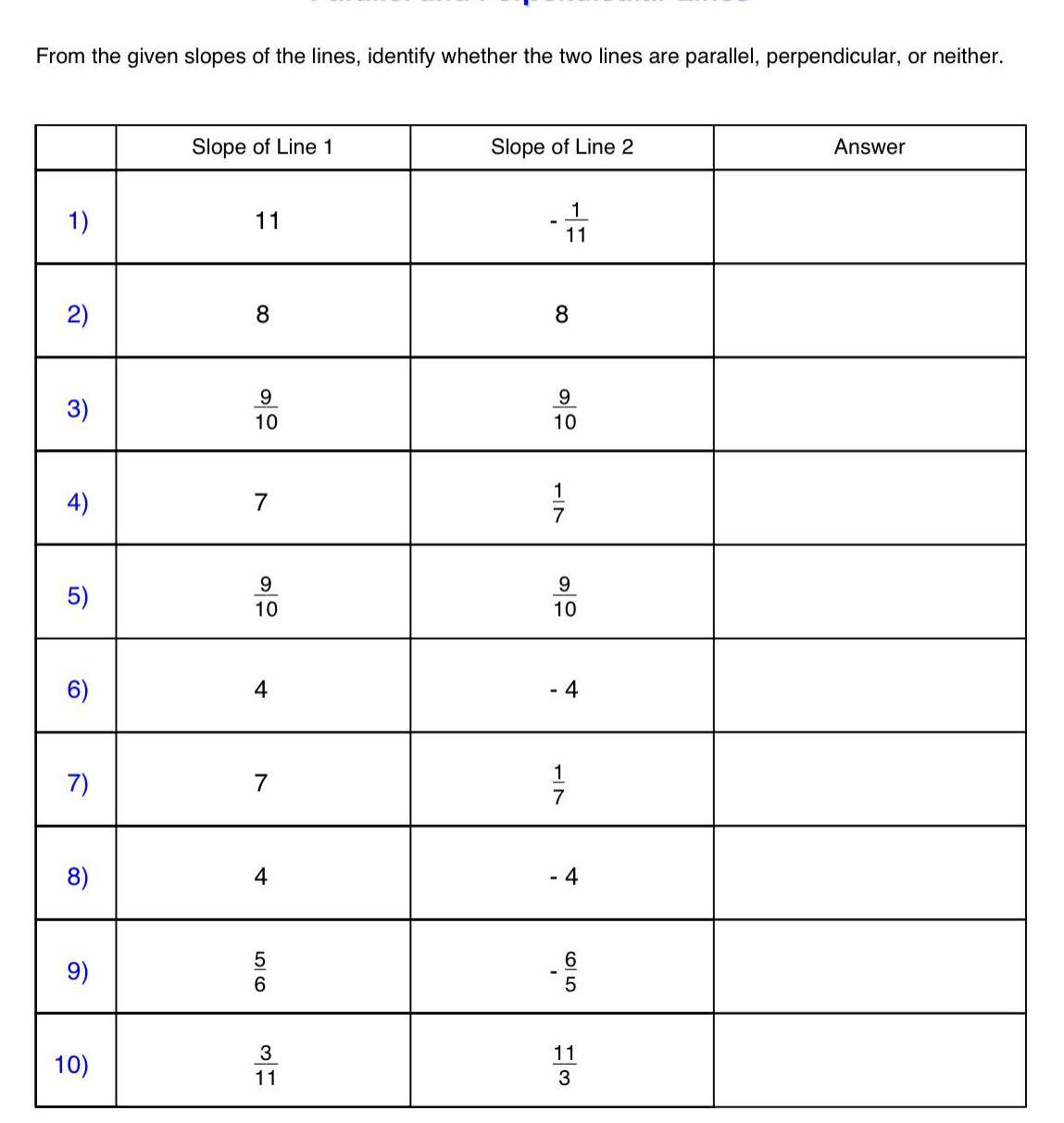
2D GeometryFrom the given slopes of the lines identify whether the two lines are parallel perpendicular or neither 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Slope of Line 1 11 8 9 10 7 9 10 4 7 4 5 6 3 11 Slope of Line 2 8 1 11 9 10 TIN 1 9 10 1 7 4 2015 6 11 3 Answer
Geometry
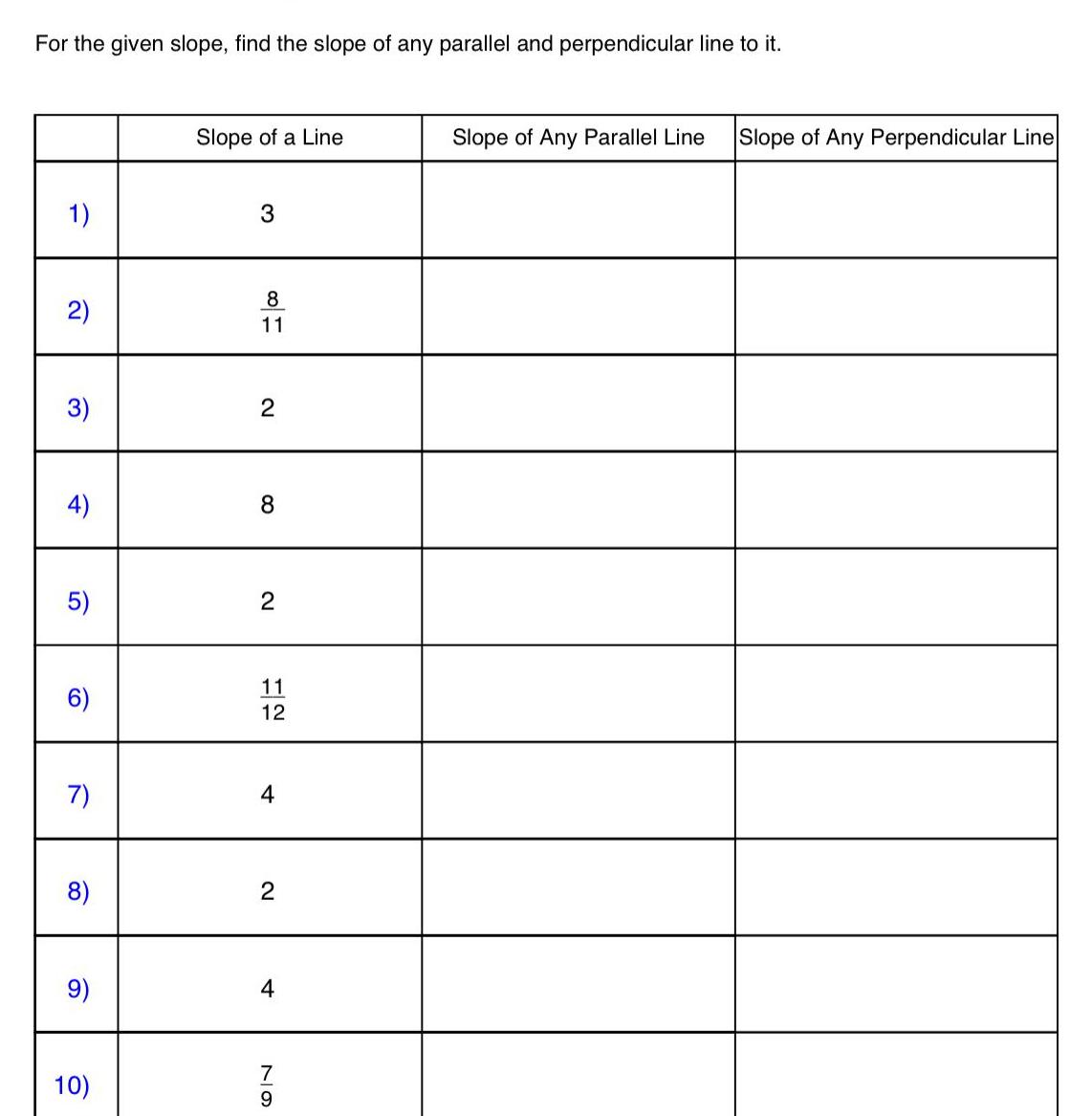
2D GeometryFor the given slope find the slope of any parallel and perpendicular line to it 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Slope of a Line 3 8 11 2 8 N 12 11 12 4 2 4 7 611 9 Slope of Any Parallel Line Slope of Any Perpendicular Line

Geometry
2D Geometry6 An obtuse angle has the point B x y on its terminal arm a Express the length of line segment OB in terms of x and y ometric ratios for the angle
Geometry
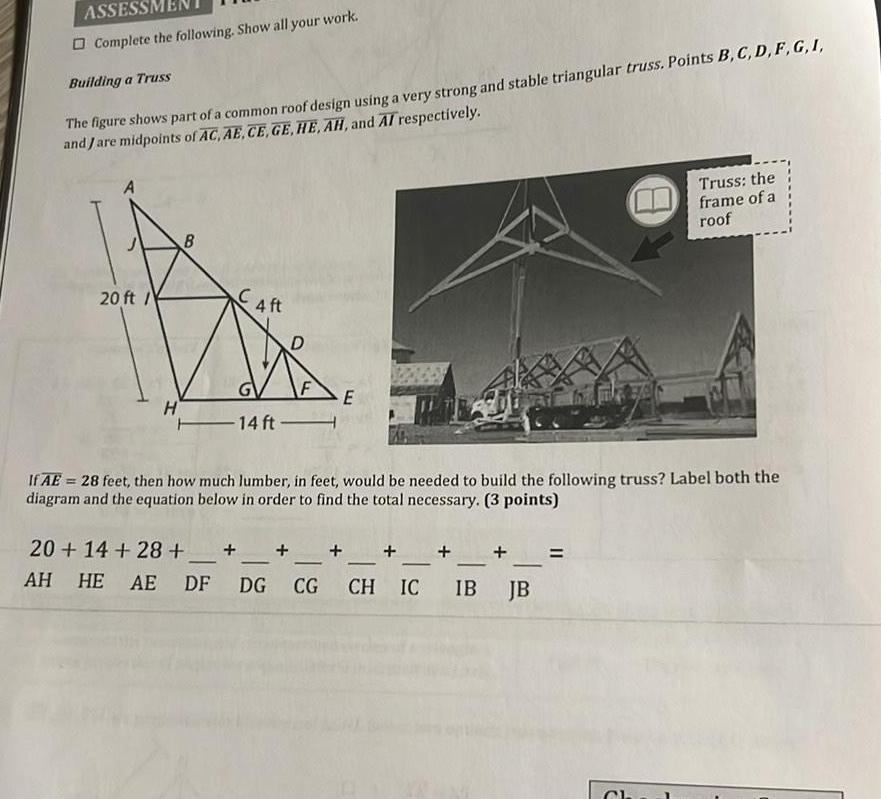
2D GeometryASSESSM Complete the following Show all your work Building a Truss The figure shows part of a common roof design using a very strong and stable triangular truss Points B C D F G I and Jare midpoints of AC AE CE GE HE AH and AI respectively 20 ft H B 4 ft F 14 ft E If AE 28 feet then how much lumber in feet would be needed to build the following truss Label both the diagram and the equation below in order to find the total necessary 3 points 20 14 28 AH HE AE DF DG CG CH IC IB Truss the frame of a roof JB
Geometry
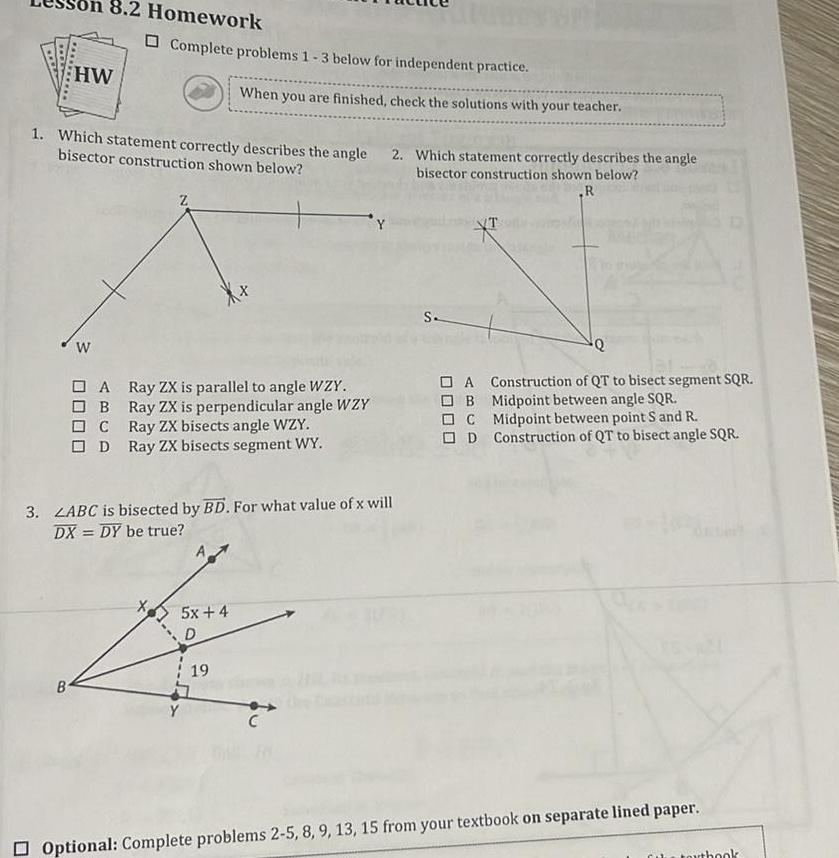
2D Geometry8 2 Homework HW B W 1 Which statement correctly describes the angle bisector construction shown below Complete problems 1 3 below for independent practice A B C OD Z When you are finished check the solutions with your teacher Ray ZX is parallel to angle WZY Ray ZX is perpendicular angle WZY Ray ZX bisects angle WZY Ray ZX bisects segment WY 3 LABC is bisected by BD For what value of x will DX DY be true 5x 4 D 19 2 Which statement correctly describes the angle bisector construction shown below R C S A Construction of QT to bisect segment SQR OB Midpoint between angle SQR C Midpoint between point S and R D Construction of QT to bisect angle SQR Optional Complete problems 2 5 8 9 13 15 from your textbook on separate lined paper book

Geometry
2D Geometry3 Consider ZF such that cos F 37 a Which quadrants can ZF be in b Find the coordinates of a point on the terminal arm of the angle in each quadrant c If you are also told that the sine of the angle is negative in which quadrant is F other primary trigonometric ratios for ZF in the quadrant identified in part c
Geometry
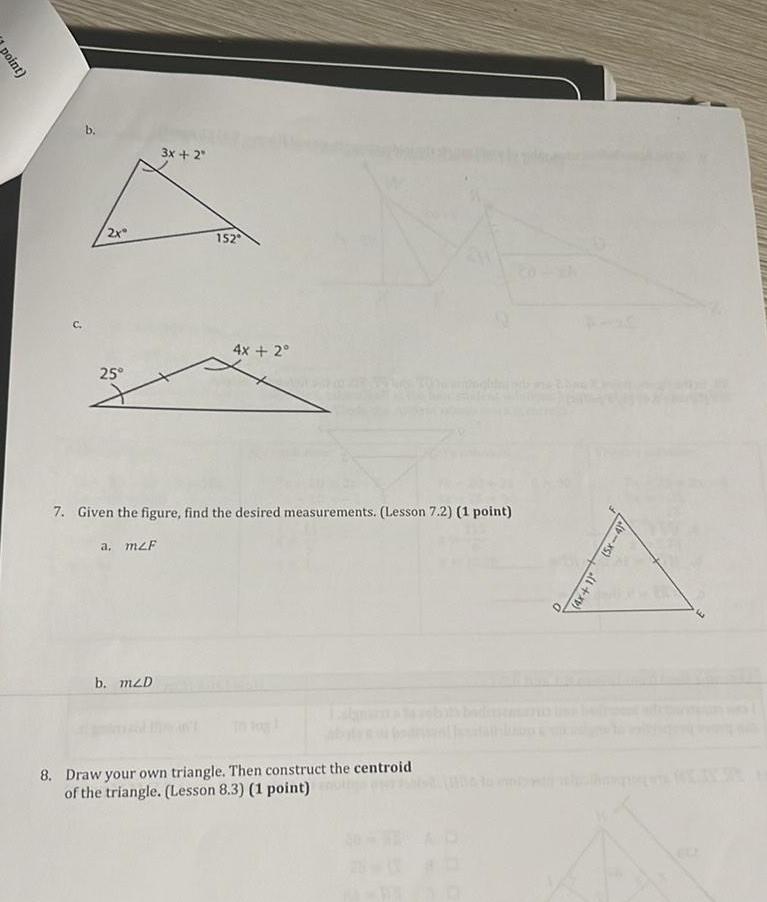
2D Geometrypoint 2x 25 3x 2 b mzD 152 4x 2 7 Given the figure find the desired measurements Lesson 7 2 1 point a mzF 8 Draw your own triangle Then construct the centroid of the triangle Lesson 8 3 1 point 4x 1 5x 4
Geometry
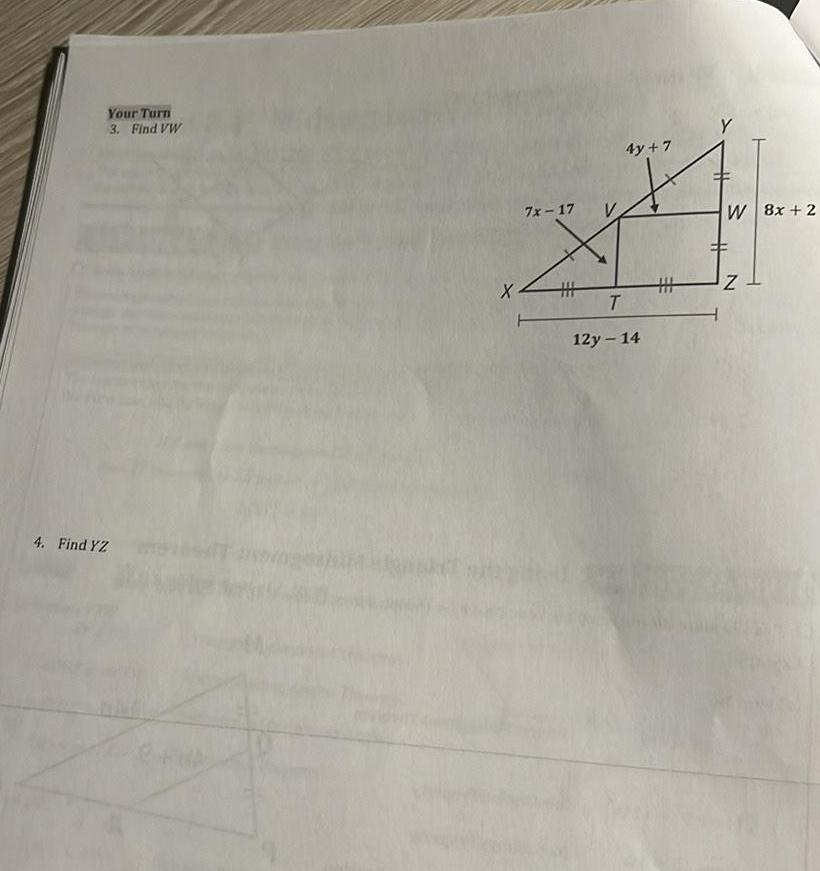
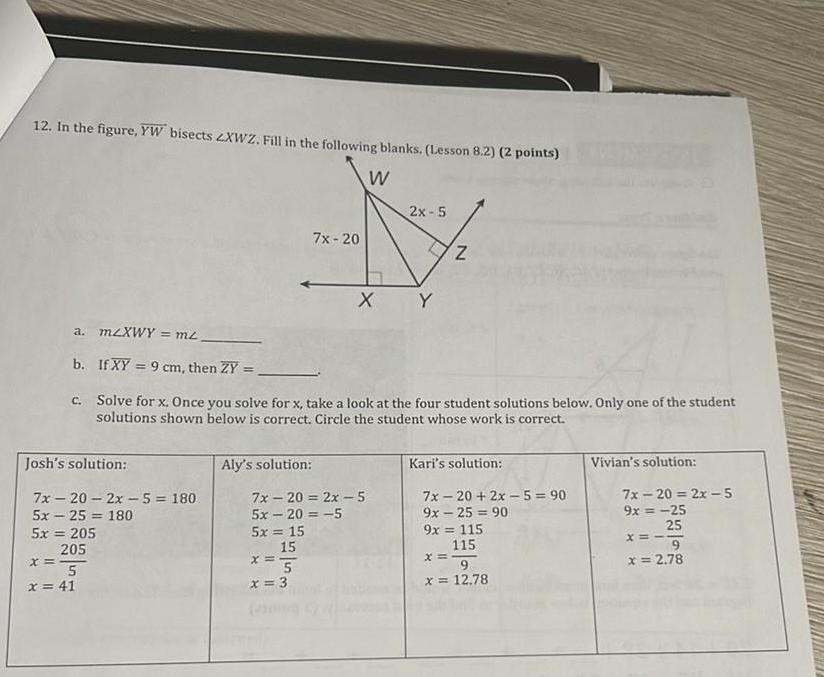
2D Geometry12 In the figure YW bisects ZXWZ Fill in the following blanks Lesson 8 2 2 points W 2x 5 7x 20 N X Y Josh s solution a m XWY m b If XY 9 cm then ZY c Solve for x Once you solve for x take a look at the four student solutions below Only one of the student solutions shown below is correct Circle the student whose work is correct 7x 20 2x 5 180 5x25 180 5x 205 205 x 5 x 41 Aly s solution 7x 20 2x 5 5x 20 5 5x 15 15 x 5 N x 3 Kari s solution 7x 20 2x 5 90 9x 25 90 9x 115 115 x 9 x 12 78 Vivian s solution 7x 20 2x 5 9x 25 25 x 9 x 2 78

Geometry
2D Geometry3 Determine whether a triangle can have the following sides with the given lengths Lesson 7 3 1 point a 5 mi 19 mi 15 mi b 4 ft 3 ft 10 ft 4 Write the angles of ADEF in order from smallest to largest Lesson 7 3 0 5 points Learning Goal from Lesson 7 1 7 2 8 3 and 8 4 I can prove the following theorems about triangles 2 25 E 1 105 D The measures of interior angles of a triangle sum to 180 The base angles of isosceles triangles are congruent The medians of a triangle meet at a point The segment joining midpoints of two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side and half the length 5 Write the sides of AGHI in order from smallest to largest Lesson 7 3 0 5 points 6 Find the value of x in each of the given figures Lesson 7 1 and 7 2 2 points a How I Did Circle one I got it 59 61 H I m still learning it

Geometry
2D Geometryn Your Turn Use the Triangle Inequality Theorem to tell whether a triangle can have the following sides with the given lengths Explain 1 12 units 4 units 17 units EXPLAIN 3 largest angle Read Explain 3 and complete Your Turn 1 2 adapted from Lesson 7 3 Show all your work In relation to each other the relative size of the side lengths of a triangle can be used to determine the relative size of the angles This means that if you are given the side lengths in order you can use them to order the angle by size largest side Ordering a Triangle s Angle Measures Given Its Side Lengths Side Angle Relationships in Triangles 2 24 cm 8 cm 30 cm Embr medium side medium angle In any triangle the larger angle is opposite the longer side AB AC BC SO mzC m2B mzA B Example For each triangle order its angle measures from least to greatest In the figure we see that the sides from shortest to longest are AB BC and AC The angles opposite these sides are LC LA and LB respectively So the order of angles from least to greatest is LC LA and LB shortest angle shortest side 2 4 15 3 A C 12

Geometry
2D GeometryLearning Goal I can prove the following theorems about triangles The segment joining midpoints of two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side and half the length X Q Lesson 8 4 Checkpoint Once you have completed the above problems and checked your solutions complete the Lesson Che below Complete the Lesson Reflection above by circling your current understanding of the Learning Goal 1 Given the figure below solve for x Then find the value of QP H x 3 x 3 3x 3 P 2 Given the figure below solve for x Then find the value of XV x 2 I V G P Starting Getting there
Geometry
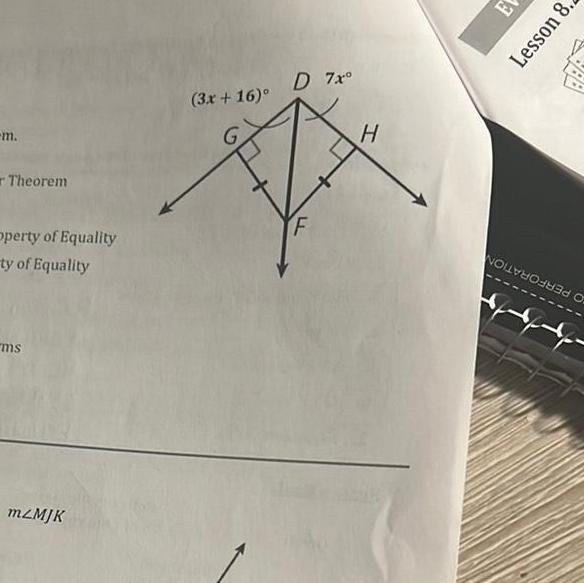
2D Geometrym Theorem Operty of Equality ty of Equality ms mzMJK 3x 16 D 7x F H E Lesson 8 NOREER O

Geometry
2D GeometryCool Down Make Your Own Invent measurements that would show triangle XYZ is similar to triangle NLM using the Side Angle Side Triangle Similarity Theorem Z N M

Geometry
2D Geometryangle DBC angle ABE angle ABC A In the diagram which angles are vertical angles Choose 2 pairs angle EBD E B C angle DBC O O O O angle ABE O O O angle ABC O OOO angle EBD O O O