Chemical Bonding Questions and Answers


Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingConsider the diagram of an aqueous solution of a soluble ionic compound Determine which ionic compound is dissolved in solution AICI NaCl MgBr Na PO4 hs 3 3 3

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingClassify the substances as electrolytes or nonelectrolytes Electrolytes M

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingWhat is true if a liquid and a gas are in equilibrium O A The number of liquid molecules and the number of gas molecules vary B The liquid molecules stay liquid and the gas molecules stay gas O C Liquid molecules are continually forming to replace escaping gas molecules OD Liquid molecules forming a gas and gas molecules forming a liquid are equal in number

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingH Br HCl CI 0 c 0 The highlighted bond is polar and the more negative atom is Br The highlighted bond is nonpolar O The highlighted bond is polar and the more negative atom is Cl The highlighted bond is nonpolar O The highlighted bond is polar and the more negative atom is O The highlighted bond is nonpolar


Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingFor each pair of compounds listed check the box next to the one with the higher boiling poin compounds Kr Xe Sn H4 PbH CH CH CH 2 CH CH higher boiling point OOO O O

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding4 points Which of the following statements are TRUE about COCI2 molecule select all that apply wrong choices will be penalized Hint Draw Lewis structure The angles between the bonding pairs are around 120 The molecular geometry around the central atom is trigonal pyramidal The central atom is carbon C The molecule is nonpolar The molecule contains pi TT bond The central atom is oxygen O The central atom contains one lone pair The molecular geometry around the central atom is trigonal planer The electron pair geometry around the central atom is tetrahedral The hybridization of the central atom is sp The electron pair geometry around the central atom is trigonal planer The molecule is polar There are 3 total electron domains around the central atom
Physical Chemistry
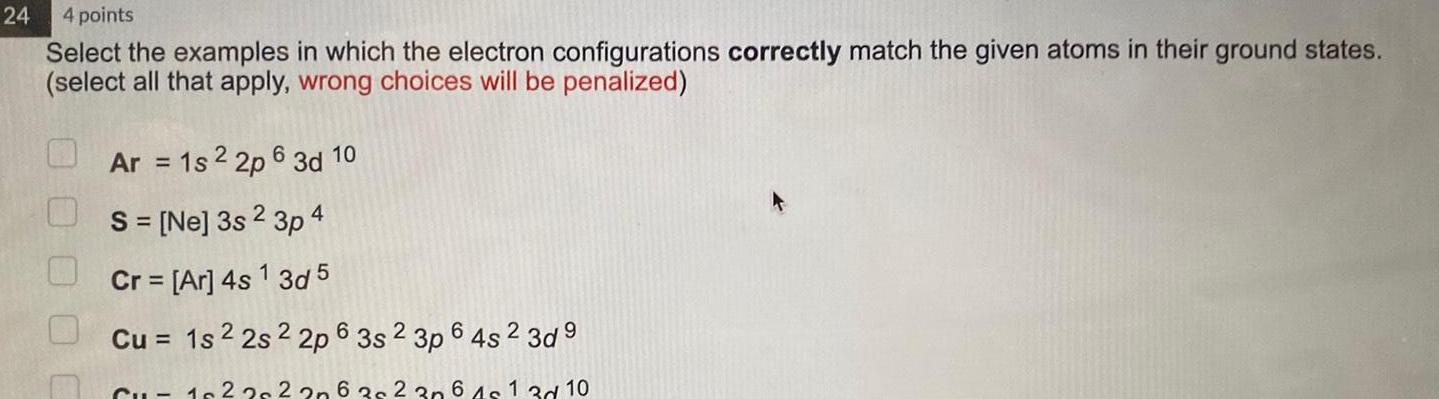
Chemical Bonding24 4 points Select the examples in which the electron configurations correctly match the given atoms in their ground states select all that apply wrong choices will be penalized Ar 1s 2 2p 6 3d 10 S Ne 3s 2 3p 4 Cr Ar 4s 1 3d 5 Cu 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d9 Cu 1622s 2 2 6 3 2 30 6 4s 1 3d 10

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding4 4 points Based on the best Lewis structure from formal charge considerations how many resonance structures if any can be drawn for the SO3 molecule 4 2 5 3

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingWhat does the ring A It means the TT electrons are delocalized around the benzene ring B It means the TT protons are delocalized around the benzene ring It means the o electrons are delocalized around the benzene ring D It means the o protons are delocalized around the benzene ring

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bondingnd sulfur in the compound Na S Tap the arrows to set the value for the oxidation state sodium sulfur

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingEl Na Mg 38 48 58 68 78 18 261 Si P C1 Ar K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe Cs Ba Lo Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At Rn Fr Ro Ro Ri Ha 88 Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Th Pa U Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No Er Using only the periodic table arrange the following elements in order of increasing atomic radius radon polonium thallium lead Smallest Largest

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingWhich of the following elements are nonmetals Z atomic numbe Choose all that apply Br Z 35 Ov Z 23 V Cs Z 55 P Z 15 None of the Above R

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding1 Write the electron configuration for the carbon atom 2 Write the electron configuration for the chlorine atom Orbital 932 a By Jo aug

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingThe structure properties and transformations of matter can best be explained by which of the following A The way in which electromagnetic radiation interacts with different substances Gravitational forces from the environment on subatomic particles B C D Attraction and repulsion between electric charges at the atomic level The number of atoms of an element in one mole of that substance

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingConsider the following electronegativity values C 2 5 O 3 5 S 2 5 F 4 0 H 2 1 Which of the following has the greater dipole dipole force A B C D H S CS2 SO OF 2

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingH C C C H LIT OH OH OH Glycerol Boiling point 290 C HHH H C C C H CI CI CI Trichloropropane Boiling point 157 C 17 The structural formulas of glycerol and trichloropropane are given above Both compounds are liquids at 25 C a For each compound identify all types of intermolecular forces present in the liquid b Explain why glycerol has the higher boiling point in terms of relative strengths of the intermolecular forces c Which one of these liquids will be more soluble in water Explain 10

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding19 At 298 K and 1 atm Br2 is a liquid with a high vapor pressure and Cl is a gas Those observations provide evidence that under the given conditions the A Forces among Br2 molecules are stronger than those among Cl molecules B Forces among Cl molecules are stronger than the Cl Cl bond C Br Br bond is stronger than the Cl Cl bond D Cl Cl bond is stronger than the Br Br bond Ne HF C H6 CH4 20 Which of the substances listed above has the highest boiling point and why A Ne because its atoms have the largest radius B HF because its molecules form hydrogen bonds C C H6 because each molecule can form multiple hydrogen bonds D CH4 because its molecules have the greatest London dispersion forces 21 Write the net ionic equations for the following two aqueous reactions a Nitrous acid HNO2 reacts with potassium hydroxide b A precipitate forms when solutions of lead II nitrate and sodium iodide are mixed

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingThe group below that shows the correct representation of the strength of intermolecular forces from weakest to strongest are A Dipole Dipole semi polar Hydrogen bonds B C D Hydrogen bonds Dipole Dipole Dispersion forces Dspersion forces Hydrogen bonds Dipole Dipole h Dispersion forces Dipole Dipole Hydrogen bonds

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingComplete the table for the complementary bases for RNA DNA interactions Be sure to use capital letters for the base abbreviations DNA RNA A G C

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingPut the following orbitals in the same atom in order from lowest energy to highest energy 3p 3d 3s C C

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingWhich of the following if any exhibits polar covalent bonding Be sure to choose all correct answers a H2 b Cl2 c HCI d SC12 e NaCl

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingWhich of the following atoms has the highest ionization energy a F b Be Oc All have the same ionization energy Od Li e Ne

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingDraw the Lewis structure for the simplest compound formed between S and F Compare your Lewis structure to the structure provided and answer the questions below F K S F F Is the Lewis structure above correct or incorrect according to what we have learned in this course Enter your answer in the space below If the Lewis structure above is incorrect also use the space below to briefly explain what is wrong with the Lewis structure drawn here

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingConsider the following Lewis structure for this compound formed between B and CI g I CI Is the Lewis structure correct or incorrect for this neutral compound Enter your answer in the space below If the Lewis structure above is incorrect also use the space below to briefly explain what is wrong with the Lewis structure drawn he

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding9 2 points Which species have delocalized molecular orbitals select all that apply wrong choices will be penalized 03 CC14 CO3

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingAtomic orbitals represent certain locations in the periodic table When elements are indicated by their atomic number which elements are represented by the 3d block Elements with atomic numbers 2 6 Elements with atomic numbers 21 30 O Elements with atomic numbers 31 36 O Elements with atomic numbers 39 48 O Elements with atomic numbers 57 80

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding11 5 points Identify the molecules with sp3 hybrid orbitals on the central atom select all that apply wrong choices will be penalized H H C Cl Cl C CI Cl Cl Sn Cl O s O O CI H O H F F S F F F F F Cl Be Cl CI O CI CI Cl Cl B C S C

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding18 Consider the molecule OCI What is the electron pair geometry around the central atom Trigonal Bipyramidal Octahedral linear Trigonal planar Tetrahedral 2 points Which species have delocalized molecular orbitals select all that apply wrong choices will be penalized

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding12 2 points Which of these examples is not one of the five basic geometries for molecules and ions Trigonal planar Tetrahedral 00000 Trigonal Bipyramidal Square Planar Octahedral Linear


Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding1 2 points According to valance bond theory select which orbitals overlap to form a bond in the following molecule HBr 1s orbital on H and 3p orbital of Br 1s orbital on H and 4p orbital of Br 1s orbital on H and 2p orbital of Br 1s orbital on H and 5p orbital of Br 4s orbital on H and 1p orbital of Br


Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingH20 CC14 Match the following shapes with the correct formulas SF6 A B C M D Figure M Figure E Figure K Figure H Figure F Figure D Figure B Figure A Figure I I

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding16 2 points Which of the following geometries has the smallest bond angle Trigonal planar Linear Tetrahedral

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingFor the covalent compound shown below list the number of covalent bonds and the total number of lone pairs of electrons CI P CI 00 CI 3 O3 covalent bonds 10 lone pairs of electrons O2 covalent bonds 3 lone pairs of electrons O4 covalent bonds 8 lone pairs of electrons O 10 lone pairs of electrons 3 lone pairs of electrons

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingLabel whether these compounds are ionic or molecular NH3 BaCl NaCH3CO CC14 O NH3 Molecular BaCl lonic NaCH3CO Molecular CCl4 Molecular O NH3 lonic BaCl lonic NaCH3CO lonic CCl4 Molecular O NH3 Molecular BaCl lonic NaCH3CO lonic CCIA Molecular O NH3 lonic BaCl lonic NaCH CO lonic

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingLabel the bond between the following elements as ionic or covalent Na 1 CHCI S O Ca F Na 1 Covalent bond C Cl lonic bond S O lonic bond Ca F Covalent bond Na 1 lonic bond C Cl Covalent bond S Olonic bond Ca F lonic bond O Na 1 lonic bond C Cl Covalent bond SO Covalent bond Ca Flonic bond Na 1 Covalent bond C C Covalent bond
Physical Chemistry
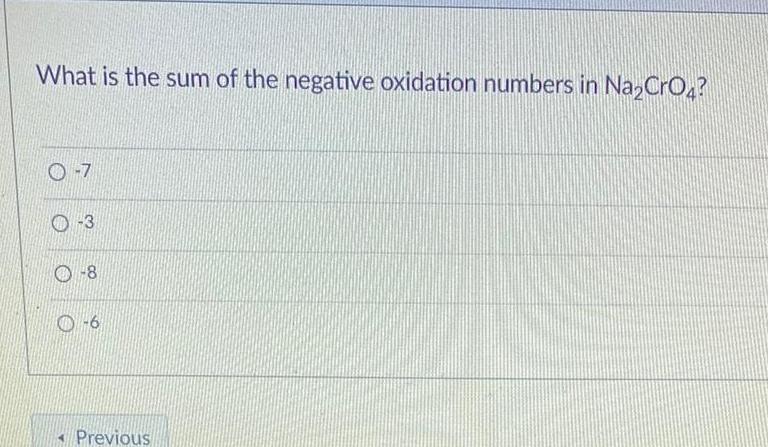
Chemical BondingWhat is the sum of the negative oxidation numbers in Na CrO4 7 3 8 6 Previous

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingElectron configuration Write the full ground state electron configuration 1s2 2s 2p3 etc for the following atoms or ions C not give the abbreviated electron configuration He 2s etc

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingPeriodic Properties Which element has the smallest ionization energy

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingPeriodic Properties Which ions have a larger radius than their parent atom

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingElectron Configuration 1 For which block s of elements are outer electrons the same as valence electrons 2 For which block are d electrons often included in the valence electrons

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingElectron Configuration What are the electron configurations for chlorine and bromine

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding1 point Name the following compound S 07 0 Bisulfur septaoxide Bisulfur heptaoxide Disulfur septaoxide



Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding4 What is the frequency of light that has a wavelength of 4 25x10 27m ah

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding70 3 points Use the following information to determine the lattice energy in kJ mol of KCI s lonization energy of K g 418 7 Enthalpy of sublimation of K s 89 2 Enthalpy of formation of KCI s 435 9 Electron affinity of Cl g 349 0 Bond energy of Cl g 240 0 Answer to 1 decimal place