Chemical Bonding Questions and Answers

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingMole fraction of benzene in the vapours over a solution of benzene and toluene is 0 4 If the ori vapour pressure of benzene is 150 mm Hg and toluene is 50 mm Hg the mole fraction of benzene i solution is 1 0 4 2 0 75 3 0 25 4 0 18

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingB12 The initial rates of reaction 3A 2B C Products at different initial concentrations are given below Initial rate Ms 1 A o M 0 010 0 010 0 010 0 005 5 0 x 10 3 5 0 10 1 0 x 10 2 1 25 x 10 3 B M 0 005 0 005 0 010 0 005 C M 0 010 0 015 0 010 0 010 The order with respect to the reactants A B and Care respectively a 3 2 0 c 2 2 0 e 2 1 0 b 3 2 1 d 2 2 1 Kerala PMT 2011

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingA 5 ampere current is passed through a solution of zinc sulphate for 40 minutes The amount of zinc deposited at the cathode is 1 0 4065 g 96500x 2 2 65 04 g 65 4 4 065 g 3 40 65 g

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bondingnitrogen after gaining 3 electron achieve noble gas config uration and ionisation potential of n 3 will be slightly less than nitrogen slightly more than nitrogen slightly less than nitrogen much more than nitrogen

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingWhat would be the pH range of the solution prepared by mixing equal volumes of10 M NaH PO4 and 102 M Na3PO4 Assume Pa 4 p 7 p 10 1 8 3 8 7 2 9 6 10 2 3 5 8 6 5 4 6 2 7 5

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingThe molar volume of liquid benzene density 0 877 g ml increases by a factor of 2750 as it vapourises at 20 C At 27 C when a non volatile solute that does not dissociate is dissolved in 54 6cm3 of benzene vapour pressure of this solution is found to be 98 88 mm Hg calculate the freezing point of the solution Given Enthalpy of vapourisation of benzene 1 394 57 Jg Enthalpy of fusion of benzene I 10 06 kJ mol Molal depression constant for benzene 5 0 K kg mol 1 177 65 K 2 277 65 K 3 517 65 K 4 237 15 K

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingThe decreasing order of the ionization potential of the following elements is 1 Ne Cl P S Al Mg 2 Ne Cl P S Mg Al 3 Ne Cl S P Mg Al 4 Ne Cl S P Al Mg USE CODE BAHUBALI FOR 10 OFF ON PLUS ICONIC S

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingEXERCISE I Conceptual Questions ELECTRIC CHARGE METHODS OF CHARGING 1 Which of the following charges can not be present on an oil drop in Millikan s experiment 1 4 0 10 9 C 2 6 0 x10 9 C 3 10 0 x 10 19 C 4 all of them 5

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingThe correct statement s regarding the binary transition metal carbonyl compounds is are Atomic numbers Fe 26 Ni 28 A Total number of valence shell electrons at metal centre in Fe CO 5 or Ni CO 4 is 16 B These are predominantly low spin in nature C Metal carbon bond strengthens when the oxidation state of the metal is lowered D The carbonyl C O bond weakens when the oxidation state of the metal is increased

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding52 The dye acriflavine when dissolved in water has its maximum light absorption at 4530 and its maximum fluorescence emission at 5080 The number of fluorescene quanta is on the average 53 of the number of YOU quanta absorbed Using the wavelength of maximum absorption and emission the percentage of absorbed energy emitted of orosco C

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding39 Bond energies of H H O O and 0 H are 105 120 and 220 kcal mol respectively then AH in the reaction 2H g O g 2H O 1 b 130 d 550 a 115 c 118 40 Given that 12x105

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding25 The rate constant for 1st order reaction is 69 3 s How much time will it take to reduce the initial 1 concentration of the reactant to its 16 2 0 02 sec 4 0 05 sec 1 0 04 sec 3 0 06 sec th value CK0223

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingIn which of the following gases at the given temperature does have the highest solubility in the liquid of CC14 O a NH3 g dissolves in CCl4 liquid at 350 K O b N g dissolves in CCl4 liquid at 350 K OC NH3 g dissolves in CCl4 liquid at 300 K d N g dissolves in CCl4 liquid at 300 K

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingThe correct order of absorbed wavelength by following complex is B CoF 4 Co H O Co CN CoF 4 Co H O Co CN c CoF Co H O J Co CN D CoF Co H O Co CN J

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingCASE BASED MCQ Q no 31 35 Read the following passage and answer the following questions Modern periodic table arranges the elements in the increasing order of atomic number It has 18 groups and 7 periods Atomic numbers are consecutive in a period and increases in the group in a pattern Elements are divided into four blocks s block p block d block and f block based on their electronic configuration 78 of elements are metals about 20 elements are non metals and few elements like B Si Ge As are metalloids Metallic character increases down the group but decreases along the period from left to right The physical and chemical properties vary periodic trends are observed in atomic size ionization valences Oxides of metals are basic some are amphoteric Non metals from acidic oxides some from netural oxides s block elements are soft highly reactive do note show variable oxidation states P block elements are metals non metals as well as metalloids show variable oxidation states exist as solids liquids and gases D block elements are metals from coloured ions show variable oxidation state have high melting and boiling points Lanthanoids and actinoids are f block elements form coloured ions All actinoids are radioactive 31 Assertion Modern periodic table contains 18 group 7 period Reason Atomic number are consecutive in a period and increases in the group 32 Assertion The highest oxidation state of Os is 5 Reason Osmium is a 5d block elements 33 Assertion Sixth and seventh periods in the periodic table contains 14 elements Reason In the periodic table 14 elements each of sixth from Z 58 to Z 71 and seventh periods from Z 90 to Z 103 respectively are known as lanthanoids and actinoids 34 Assertion Helium is placed in group 18 along with p block elements Reason Helium is much less reactive like other inert gases 35 Assertion Chemistry of actinoids is more complicated than lanthanoids Reason Actinoid elements are radioactive

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bondinglonic Equilibrium pH of a Buffer When an acid or a base is added We have just discussed that addition of H ions or OH ions to an acidic buffer HA A does not appreciably changes the pH of buffer Similarly we can analyse the same for a basic buffer BOH B In actual pH of a buffer solution changes by a small quantity Let us calculate this change in pH quantitatively Consider an acidic buffer HA A where salt A and acid HA An acidic buffer is rich in A ions Let us add x mole per litre of HCI to it This added HCI H reacts with A salt to ge undissociated acid as H A salt After adding x M H ions salt x HA acid acid x Now using Henderson s Equation pH original buffer pK log101 pH of buffer decreases Change or difference in pH pH new pH original OH HA acid salt acid Vidyamandir Classes salt x and pH new pK 1 Let us add x M NaOH to the buffer This added NaOH OH ions react with acid HA to produce salt and H O A H O salt pH of buffer increases log10 After adding x M OH ions acid x salt x pH new pK log10 acid x Change in pH pH new pH original Note 1 In exactly similar manner we can calculate the change in pH of a basic buffer BOH B Try to get a relation like this for basic buffer Remember it is not to be used as standard result salt 1 acid 1 ii A buffer solution is assumed to be destroyed if on addition of strong acid or base its pH changes by 1 unit i pH new pK 1 if the initial pH of the buffer solution was pK This means the ratio salt 10 or acid OR base ille Ho b SO

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding2 59 The following sequence of reaction occurs in commercial production of aqueous nitric acid 4NH3 g 5O g 4NO g 6H O l AH 904 kJ 1 2NO g O g 2NO g AH 1124 kJ 2 00 3NO g H O 1 2HNO3 aq NO g AH 140 kJ 3 The total heat liberated in kJ at constant pressure for the production of exactly 1 mole of aqueous nitric acid by this process is kl mol
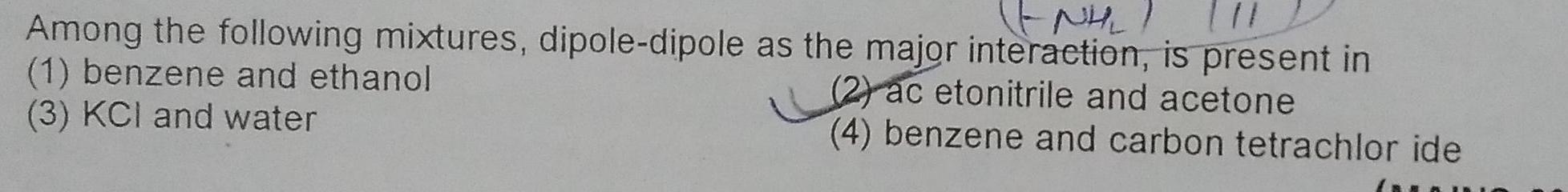
Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingNHL Among the following mixtures dipole dipole as the major interaction is present in 1 benzene and ethanol 2 ac etonitrile and acetone 3 KCI and water 4 benzene and carbon tetrachlor ide

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingWhich of the following option is incorrect regarding electrovalent bond 1 Ionic bond will be formed more easily between elements with comparatively low ionisation enthalpy high negative electron gain enthalpy 2 NH is an exception of cation because it made up of two non metallic element 3 Lattice enthalpy plays a key role in the formation of ionic compound 4 All of these

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding33 The dipole moments of CCI CHCI3 and CH4 are in the order JEE Main 2020 1 CCI CH CHCI 2 CHCI CH CCIA 3 CH CCI CHCI 4 CH CCI CHCI 4

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bondingc 450 77 Using the data provided calculate the multiple bond energy kJ mol of a C C bond in C H Given that the heat of formation of C2 H is 225 kJ mol take the bond energy of a C H bond as 350 kJ mol

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding3 550 cps 4 2200 cps 33 A wire of length one metre under a certain initial tension emits a sound of fundamental frequency 256 Hz When the tension is increased by 1 kg wt the frequency of the fundamental node increases to 320 Hz The initial tension is 1 3 4 kg wt 3 16 9 kg wt Aakash Educational 2 4 3 kg wt 4 20 9 kg wt Services Pvt Ltd Regd Office Aakash

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding3 4 27 For a certain organ pipe three successive resonance frequencies are observed at 425 595 and 765 Hz respectively Taking the speed of sound in air to be 340 m s the fundamental frequency of the pipe in Hz is 1 425 2 170 4 245 AS

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingF bond 74 The bond dissociation energy of BF in BF3 is 646 kJ mol whereas that of C F in CF4 is 515 kJ mol The correct reason for higher B dissociation energy as compared to that of C F is a stronger bond between B and F in BF3 as compared to that between C and F in CF4 significant pr p interaction between B and F in BF whereas there is no possibility of such interaction between C and F in CF4 c lower degree of p pr interaction between B and F in BF3 than that between C and F in CF4 d smaller size of B atom as compared to that of C atom The standard anthal

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding8 The theory that can completely properly explain the nature of bonding in Ni CO is JEE Main 2020 1 Crystal field theory 2 Werner s theory 3 Valence bond theory rbitol theory

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding1 4 19 127 Nitrobenzene on reduction using Zinc in alkaline medium results in X The number of sigma a and pi x bonds in X is 3055 2058 sorsos no 0 2005 1 2040 1 24 a 7 m 2 24 6 m somo Bodo X Sojos X Borg 3 27 a 7 n 4 27 a 6 x

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingOrientation Vertical Products P and Q in the following reactions respectively are Bod Bojeres sou P u Q de Jo Options 1 2 OH 3 P Zn P Cyclohexane Heat Ego P Benzene P 0 5 P Cyclohexene P 2A5 AP EAMCET 2020 P AP EAMCET 2020 OH Q Benzoquinone Q o s SS Q Cyclohexenone Q 35 JASS Q Cyclohexanol Q S Na Cr O7 H SO4 Q

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bondingstion Number 151 Question Id 8135612231 Question Type MCQ Display Question mber Yes Is Question Mandatory No Single Line Question Option No Option entation Vertical which of the following conditions the overlap of orbitals is zero do Bodards de voz ons P P 5 P

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding143 Which one of the following is a correct set 1 Diamond sp 2 3 Diamond sp Boa Do 303 38 1 5505 sp 3 50 sp Rough Work Graphite sp 4 Graphite sp 2 5 sp 4 m5 sp

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding152 Assertion A Cyclohexane is the most stable Cycloalkane Reason R Cyclopropane and cyclobutane are less stable due to angle strain and torsional strain The correct answer is Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A 2 A is true but R is not true 3 A is not true but R is truc 4 Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A 38383 A 25 5 5000 R 55 30 Barbo 2035 5 5 50 50 5 500 50 50 55 3055 1 A 35005 R 3055 530050 A 53 R 30 250 50 2 A 580358 50 R 5050 50 3 A 5850 50 50 R 30 4 A 5005 R 3052 50 A 55 R 30 550m

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingMolecular orbitalhot having any nodal plane is 625 2 0 2s 35 0 4 2py n t 2P2 3 2py Which of the following molecular species has unpaired electron s 25 204 1 N 3s 25 2P4 p3 2 Q 48 E
Physical Chemistry
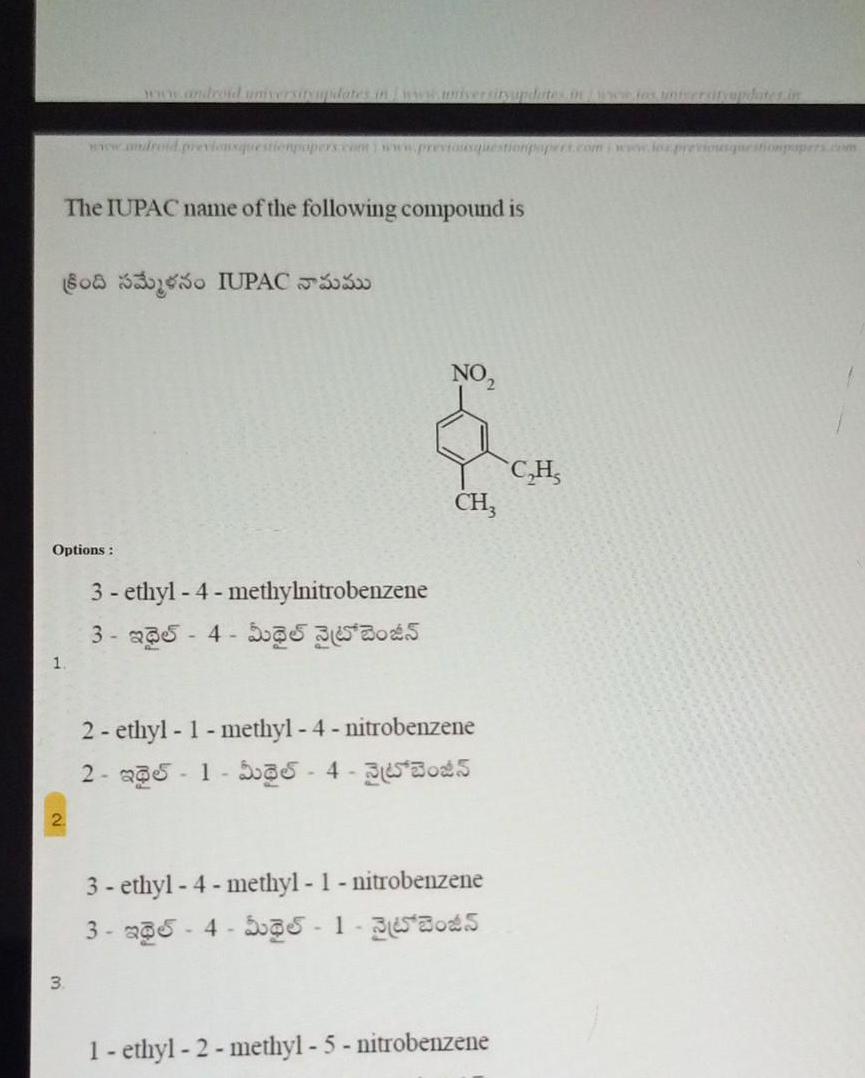
Chemical Bondingwww android previousquestionpopers com www previousquestionpapers com www loz previousquestionpapers com The IUPAC name of the following compound is 8083330 IUPAC550 1 Options 3 3 ethyl 4 methylnitrobenzene 3 235 4 55 35 3045 NO CH3 2 ethyl 1 methyl 4 nitrobenzene 2 a1 35 4 35305 3 ethyl 4 methyl 1 nitrobenzene 3 5 4 5 s 1 363045 1 ethyl 2 methyl 5 nitrobenzene C H

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding12px 47 C The maximum number of 180 angles between bond pair bond pair of electrons is observed in 1 sp hybridisation 2 sp d hybridisation 3 dsp2 hybridisation 4 sp hybridisation S Highest energy molecular orbital occupied in case of N is n

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding5 5 Which of these orbitals has two nodes 1 ols 2 o 2p 3 12px 4 20x T No 5 The maximum number of 180 angles between bond pair bond pair of electrons is observed in 1 sp hybridisation 2 sp d hybridisation 4F

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingThe rate constant for a second order reaction is 3 33x10 2 L mol s The initial concentration of the reactant is 0 5 mol L Calculate the half life of the reaction A 0 95 min B 1 95 min C 10 min D 3 45 min

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bondingcontainer is loaded in a balance as shown in figure I below In the presence of a magnetic field the pan with X is either deflected upwards figure II or deflected downwards figure III depending on the compound X Identify the correct statement s 1 Balanced Magnetic field absent m X II Upward deflection Magnetic field present N S magnet a If X is H O deflection of the panis upwards b If X is K4 Fe CN 6 s deflection of the panis upwards c If X is O g deflection of the panis downwards III Downward deflection Magnetic field present N d If X is C6H6 deflection of the panis downwards a x H O rarr Diamagnetic b x K Fe CN rarr Diamagnetic Here Fe 2 strong field ligand rarr 3d rArr t g5 eg c x 0 rarr Paramagnetic Here O g is paramagnetic due to two unpaired electrons present in pi antibonding orbitals S

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingNH gas is liquefied more easily than N Hence 1 van der Waal s constants a and b of NH that of N 2 van der Waal s constants a and b of NH3 that of N 3 a NH a N but b NH3 b N 4 a NH a N but b NH3 b N

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding1 A student mixed equal volumes of 0 2 M solutions of sulfuric acid and calcium chloride together a What precipitate forms b Write an equation for the equilibrium present and the Ksp expression c In the resulting solution does SO42 Ca2 Explain

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingIf a is the degree of dissociation of weak dibasic organic acid and y is the hydrogen ion concentration what is the initial concentration of acid POD a y 2 M EECE 0 5 2 y a M 1 is bbs sow MDH soi Insmetole toom y a 3 M 2 4 None of them

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingCH CH OH CH OH I OH CH OH X Y Here X and Y are 1 Chain isomer 2 Position isomer 3 Metamers 4 Functional group ison A first order reaction has a specific reaction rate of 10 2sor 1 How much time will it take

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingLattice enthalpy of NaCl is 788 kJ mol 1 enthalpy of solution of NaCl is 4 kJ mol Calculate hydration enthalpy of NaCl O 792 kJ mol 1 O 792 kJ mol 1 O 784 kJ mol 1 784 kl mol 1

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingThe correct statements among a to d are a Saline hydrides produce H gas when reacted with H O b Reaction of LiAIH4 with BF3 leads to B H6 c PH3 and CH4 are electron rich and electron precise hydrides respectively d HF and CH4 are called as molecular hydrides a c and d only c and d only a b and c only a b c and d

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding3 CH CH CH 0 CH 4 CH CH CH CH 0 CH A hydrogen gas electrode is made by dipping platinum wire in a solution of HCl of pH 10 and by passing hydrogen gas around the platinum wire at one atm pressure the oxidation potential of electrode would be 1 0 59V 2 0 118V 3 1 18V 4 0 059V

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingAB3 g is dissociates as AB3 g AB g B g When the initial pressure of AB is 800 torr and total pressure developed at equilibrium is 900 What fraction of AB3 g is dissociated 1 10 2 20

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bonding200ml of 0 2M solution of a weak acid HA has molar conductivity 10 Scm mol The osmotic pressure of the resulting solution obtained after dilution of original solution upto 1 litre at 500K assuming ideal solution is Given H 450 Scm mol 2 A 50 Scm mol 0 08 L atm mole K 10 3 2 A 0 4168atm B 0 3128atm

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingA solution of a metal ion when treated with KI gives a red precipitate which dissolves in excess KI to give a colourless solution Moreover the solution of metal ion on treatment with a solution of cobalt II thiocyanate gives rise to a deep blue crystalline precipitate The metal ion is 1 Pb 2 Hg 3 Cu 4 Co

Physical Chemistry
Chemical Bondingawarded 4 Marks and for WRONG answer there is a negative marking of 1 Mark No marks will be awarded if you For the reaction at 1240 K and 1 atm CaCO3 s CaO s CO g AH 176 K J per mol AE will be 1 160 KJ 3 186 4 KJ 1240 Ktm CaCO3 s CaO s CO g fe AH 176 KJAE 1 160 KJ 2 165 6 KJ 4 180 KJ 2 165 6 KJ 4 180 KI 4
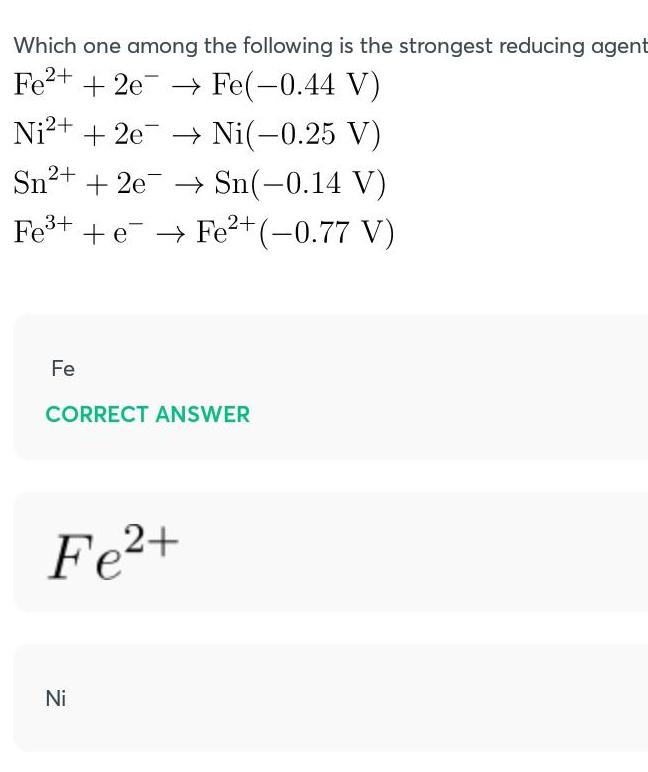
Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingWhich one among the following is the strongest reducing agent Fe2 2e Fe 0 44 V Ni 0 25 V Sn 0 14 V Fe eFe 0 77 V Ni 2e Sn 2e Fe CORRECT ANSWER Fe Ni

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingA 546 3 K B 1092 6 K C 819 45 K D 2185 2 K A mixture of solid KClO3 and KCl is strongly heated The maximum volume of evolved O2 gas is 57 2 litre at S T P and the residual mass needs 5 moles of AgNO3 for complete precipitation of AgCl The ratio of moles of KClO3 and KCl respectively in the solid mixture is KCIO KCK TO8 TI 201 S T P 67 2 litre 5 moles AgNO3 43 AC A 2 3 KCIO C B 3 2 C 11 3 D 5 2

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingDuring refining of liquid iron to steel CaO plays various roles out there which of the following is most important 1 To make a slag with SiO formed 2 To prevent oxidation of sulphur 3 To prevent higher concentration of phosphorus in steel 4 To make a very fluid slag