Solutions Questions and Answers

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsa 10 4 b 36 c 2 45 d 4 0 40 Calculate the pH of a solution with OH 2 4x10 M a 2 49 c 5 38 41 Calculate the H O if the pOH 2 75 a 5 62x10 2 M b 0 439 M c 1 78x10 M b 6 78 d 8 62 42 What product is always present in a neutralization reaction a H O b CO c 0 d H Chapter 16 Nuclear Chemistry 43 Which of the following is an example of radiation a Alpha particle c Positron b Beta particle d All are examples of radiation 44 What is the mass number of the new isotope formed when Po 218 undergoes alpha a 222 c 218 b 4 d 214 d 1 05 M 45 What form of radiation is released when a nucleus only rearranges itself to stabiliz a Alpha particle c Positron b Beta particle d Gamma Ray 46 In this form Mg 24 what does the number 24 represent for Mg b Mass Number d Type of radiation released a Atomic number c of neutrons

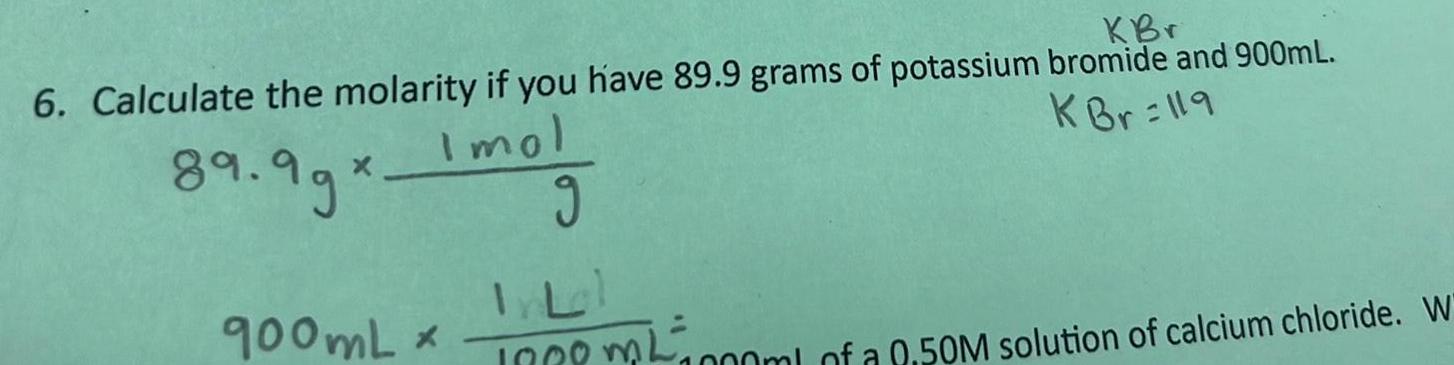
Physical Chemistry
SolutionsKBr 6 Calculate the molarity if you have 89 9 grams of potassium bromide and 900mL K Br 119 Imol 89 99 900mL g 1000ml of a 0 50M solution of calcium chloride W

Physical Chemistry
Solutions18 If a 3 0L solution has a concentration of 2 5M what will the new concentration be if the solution is diluted to 5 0L a 4 2M c 1 5M b 6 0M d 3 75M 10

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsa c 1 3M d 131 a 297g KBr c 2 98g KBr 16 How many grams of KBr are present in 100mL of 0 25M KBr solution lo non di 315 b b 119g KBr d 2 75g KBr elogna in nnm of a 350g sample of water that contains 0 041 g of lead

Physical Chemistry
Solutions21 What term is used to describe a solid that is getting dissolved to create a solution a solvent c homogenous hasd b solute d Molarity

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhat volume is needed to dissolve 78g of MgS to make a 1 43M MgS solution a 1 04L c 1 38L b 5 45L d 0 97L energy

Physical Chemistry
Solutions9 How many moles of NaCl are present in 50 mL of a 1 68M NaCl solution a 0 084 mol NaCl c 0 029 mol NaCl b 33 6 mol NaCl 4 14 d 4 87 mol NaCl lom od to vie

Physical Chemistry
Solutionschalice contains 36 45 grams ammonium chlorite in 2 36 liters of solution Cal olarity

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsC 33 apter 12 Solutions a 1 92M c 1 3M Sbned alon b 5 2M d 13M What is molarity M of a solution if 2 6 moles are dissolved in 500 mL of water Visin volloterit to Bonding 100ml of 0 25M KBr solution www um xlog rist xim do

Physical Chemistry
Solutions5 Which of the following hypothetical reactions represents a double replacement reaction O H 08 0 OH pa asp a AB CD AD BC c AB A B b A BAB d A BC B AC ealom Ta S ti bobubong ad liw HO to salom yrism w

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe rare earth metal terbium is produced from terbium III sulfate and calcium metal by the following single replacement reaction Tb SO4 3 2 Ca Ca SO4 3 2 Tb Given 27 5 g of Tb2 SO4 3 how many grams of terbium could be produced

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsShow complete calculations for each question below Use the following page if you need additional space 1 Calculate the volume mL of 0 100 M H PO required to neutralize 30 0 mL of 0 050 M Ca OH

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhy does 1 mol of sodium chloride NaCl depress the freezing point of 1 kg of water almost twice as much as 1 mol of glycerin C H O A O glycerin dissociates in water and produces twice the number of particles B O NaCl dissociates in water and produces twice the number of particles C O glycerin hydrogen bonds with the water molecules and NaCl does not D O NaCl hydrogen bonds with the water molecules and glycerin does not E O a formula unit of NaCl is more massive than a glycerin molecule F O the glycerin molecule is more massive than a formula unit of NaCl Select one answe 10 points


Physical Chemistry
SolutionsHCI H3PO4 H SO4 HBr and HC H3O2 True O False Question 4 Basic compounds release hydroxide ions OH into aqueous solution True

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhen a solute completely dissolves in a solvent it produces O an emulsion a colloidal solution O a solution a suspension

Physical Chemistry
Solutions5 Which of these is true about dissociatio a Water molecules break apart into H and O atoms b A solid breaks apart and the particles become individual ions c individual ions join together to form solids d Spectator ions form a precipitate a b Which of the following pictures show precipitation Before BEFORE Before Before After AFTER After After

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsRoom pressure in atm Room temperature in Kelvin Moles of CO required to inflate bag at room temperature and pressure Balanced equation for the reaction of NaHCO and CH COOH to produce CO Mass of NaHCO needed for the reaction 84 0 g mol Volume of vinegar required 0 833 M acetic acid ACTIVITY 2 A Testing Model Air Bags 1 Using the balance and a weigh boat weigh the grams of sodium bicarbonate that was calculated in step 8 of Activity 1 Record exact mass in Data Table 2 CAROLINA 2 Using the 50 mL graduated cylinder measure out the volume of vinegar that was calculated in step 9 of Activity 1 Data Table 2 Model Air Bag Tral 2 3 NaHCO Vinegar ml grams only data table 3 4 PIZ 2 The volume of a passenger side air bag is 160 0 L Calculate the number of moles of CO needed to inflate the air bag and the Data Table 3 80 L Driver Side Air Bag Activity Moles of CO required to inflate 80 L driver side air bag at room temperature and pressure Balanced equation for the reaction of NaHCO and CH COOH to CO 0 98a M 295 K 00494Mol Mass of NaHCO needed for the reac tion 84 0 g mol Volume of vinegar required 0 833 M acetic acid CAROLINA 4169 59 4ML ACTIVITY 3 Open a 6 x 9 inch resealable bag and hold it upright with the narrower 6 inch end over the edge of the 250 ml beaker This should create a peak and two valleys in the bag See Figure 1 4 In the valley outside of the beaker add the sodium bicarbonate powder After adding the powder hold the portion of the bag containing the powder tightly against the outside of the beaker This will help prevent a premature reaction in the next steps continued on next page www carolina com distancelearning 7 grams of sodium bicarbonate and milliliters of vinegar needed for the reaction Record all calculations in Data Table 4 ACTIVITY 3 continued Data Table 4 160 L Front Passenger Side Driver Air Bag Activity Observations Calculations www carolina com distancelearning 9 Calculations

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhat is the molality of phosphoric acid H PO4 in a solution of 14 5 g of H PO4 in 125 g of water m Question 3 What is the freezing temperature of a solution of 95 0 g of sucrose C H O in 225 0 g of water which freezes at 0 00 C when pure K of water 1 86 C m 112 Type numbers in the boxes 10 points Type numbers in the boxes 10 points

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe function of a buffer is to change color at the end point of a titration maintain the pH of a solution be a strong base maintain a neutral pH act as a strong acid OO

Physical Chemistry
Solutions24 2 points What is the solvent in my homemade pancake syrup which is 68 sugar w w Syrup Water Sugar Provicus
Physical Chemistry
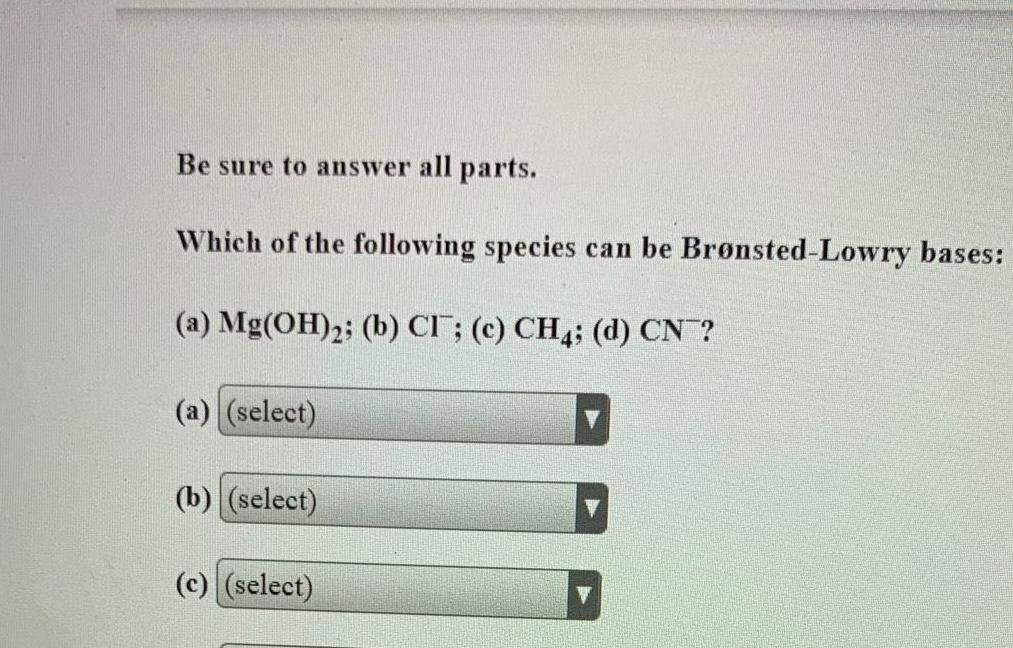
SolutionsBe sure to answer all parts Which of the following species can be Br nsted Lowry bases a Mg OH 2 b CI c CH4 d CN a select b select c select

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe cooling system in Racer Ralph s car is a mixture of 2 50 kg Compound X and 5 00 kg water This coolant solution freezes at 15 0 C Data for water H O freezing point What is the molar mass of Compound X 0 0 C K 1 86 C m g mol boiling point 100 0 C K 0 51 C m Type numbers in the boxes 10 points

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhat is the concentration of a solution formed by diluting 155 mL of 21 0 M HCI solution to 720 mL M

Physical Chemistry
Solutions6 12 6 pure water has a vapor pressure of 31 8 torr What is the vapor pressure of the solution at 30 0 C torr Question 8 10 points 147 5 g of an unknown molecular compound is added to 500 0 mL of water The freezing point Type numbers in the boxes of the solution is found to be 3 24 C What is the molar mass of the unknown compound K 10 points of water is 1 86 C m

Physical Chemistry
Solutionssolution is 100 C what is its vapor pressure atm Question 13 10 points Seawater has an osmotic pressure of 27 atm at 25 C Its density is 1 01 g mL Treating seawater Type numbers in the boxes 10 points as just NaCl dissolved in water what is the concentration of NaCl in seawater

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsQuestion 4 Solubility g salt 100 g H O Question 5 1001 80 60 40 CaCl 20 20 A solution consisting of 72 g KNO and 100 g H 0 at 40 C is A solution consisting of 65 g KClO and 200 g H 0 at 90 C is KNO3 NaCl saturated 40 60 80 80 100 Temperature C TT unsaturated KCIO3 Approximately how many grams of NaCl can dissolve in 100 g H O at 70 C Fill in the blanks by selecting one option from each menu Part 1 2 points Part 2 3 points 5 points Type numbers in the boxes

Physical Chemistry
Solutions0 15 m K CO 0 20 m NaBr 0 25 m C H OH pure H O Highest Vapor Pressure e aqueous solutions above are all at the same temperature Order these solutions from lowest to highest vapor ssure at 25 C Lowest Vapor Pressure aby Part 1 3 points ab Part 2 3 points ab Part 3 3 points aby Part 4 3 points 12 points

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA commercial mouthwash contains 3 9 g of ethanol and 0 024 g of antiseptic in each 35 mL port Calculate the weight volume percent concentration of each component w v ethanol w v antiseptic

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhat is the osmotic pressure of an aqueous solution of 3 75 g of Sr NO3 in water at 25 C The volume of the solution is 450 0 mL Assume complete dissociation atm Question 6 Type numbers in the boxes 10 points The osmotic pressure of a solution containing 7 0 g of insulin per liter is 23 torr at 25 C What Type numbers in the boxes is the molar mass of insulin 10 points

Physical Chemistry
Solutions3 Pure water freezes at 0 C When substances are dissolved in water the solute particles affect the intermolecular attractions of the water decreasing the freezing point and elevating the boiling point This is called a colligative property The magnitude of the change is determined by the number moles of solute particles dissolved in solution Which will lower the freezing point of water more one mole NaCl or one mole of CaCl Why 4 Calculate the number of moles of NaCl in your sample I

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsHow many grams of sodium are required to react with water to produce 5 0 g of sodium hydroxide Na H O NaOH H

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsConcentrated sulfuric acid is 98 0 H SO by mass and has a density of 1 83 g mL Calculate the molarity of concentrated sulfuric acid Calculate the molality of concentrated sulfuric acid M m Type numbers in the boxes ab Part 1 6 points ab Part 2 6 points 12 points

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA drink sold in a health food store contains 1 20 w v of vitamin C What volume would you have ingest to obtain 1 000 mg of vitamin C mL solution

Physical Chemistry
Solutions35 How would you classify CH3COOH in the equation below CH COOH aq H O H O aq CH CO aq a a strong base b a strong acid C d a weak base a weak acid

Physical Chemistry
Solutions4 Calculate the molarity if a flask contains 1 54 moles potassium sulfate in 125 mL of solution NH4C102 5 A chalice contains 36 45 grams ammonium chlorite in 2 36 liters of solution Calculate the molarity

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsSafrole was once used as a flavoring in root beer until it was banned in 1960 What is the vapor pressure of a solution prepared by dissolving 0 75 mol of nonvolatile safrole in 950 g of ethanol 46 07 g mol P ethanol 50 0 torr at 25 C


Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhat volume in ml of 0 254 MugCO3 solution is required to react with 64 9 mL of 0 417 MHNO3 2HNOgla LigCOglag H O LINOgled CO

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsC 0 50 M 1 50 M none of the above 5 Which of the following is a weak base calcium hydroxide b sodium fluoride f potassium hydroxide ammonia F none of the above 301029 6804

Physical Chemistry
Solutionshow you de 1 0 mol L solution you used to create the 0 1 mol L solution Give the balanced chemical equation of the precipitation reaction you did including subscripts Give the a lonic equation b Net ionic equation c Spectator lons present Using the concentration and volume of your reactants what is the limiting reagent What is the theoretical expected mass of the precipitate Calculate the yield Explain any sources of error H H H H Avey 10 53 PM OK so the compound done was CaCl2 Na2CO3 H Avey 10 53 PM all solutions to start were 1 mol L and 250 mL of a 0 1 mol L solution was made H Avey 10 54 PM The groups then combined the 75 mL of 0 1 mol L of each solution to get a precipitate

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsIf a homogeneous system has two phases that exist in equilibrium in a one component system then the system becomes bivariant univariant monovariant

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhat is the boiling point in C of a 0 743 m aqueous solution of KCI Enter your rounded answer with 3 decimal places Kb for water 0 512 C m

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe solubility of solid solutes O decreases with increase in temperature increases with surface area O decreases with surface area increases with lowered temperature

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA solution is a homogeneous mixture mixture of solute and solvent mixture of materials one of which is usually a flui all the choices

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe best example of a solution among the following is chalk powder in water muddy water table salt sodium chloride in water Ooil in water

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsdecreases the solubility of the solute in the solvent does not affect the rate of dissolution makes the solute dissolve faster decreases the capacity of the solvent to dissolve the coluto

Physical Chemistry
Solutions7 22 In which solution is the H3O less than 0 250 M di ains251991 tead g a 0 250 M HC H3O aq b 0 250 M HF aq 0 250 M HCO aq JOH HO C d all of these enone of these HO 106MS OCHS HOB HO

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA person has a 200mL solution with 13 06mol of solute dissolved in it If the solution is diluted to a total volume of 365mL how many moles of solute will be present in the new solution