Physics Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.

Physics
Current Electricity3 Figure 6 64 shows a balanced Wheatstone bridge R 5Q D Q 50 92 A S 10 22 B G P 100 S2 www C Fig 6 64 a If P is slightly increased the current in the galvanometer flows from C to A b IfP is slightly increased the current in the galvanometer flows from A to C c If Q is slightly increased the current in the galvanometer flows from C to A d If Q is slightly increased the current in the galvanometer flows from A to C Two voltmeters and two resistances are connected as

Physics
CapacitorsF a 1 F c 3 F d 4 F 93 Four capacitors are connected in a circuit as shown in the figure The effective capacitance in F between points A and B will be a 28 9 A b 4 2 F 2 F 12 F 11 2 F B c 5 V 01 d 18 98 There a capacit The e in pa 99 The W pc V

Physics
Geometrical OpticsOne face of a rectangular glass plate 6 cm thick is silvered An object held 8 cm in front of the first face forms an image 12 cm behind the silvered face The refractive index of the glass is CPMT 1999 a 0 4 c 1 2 b 0 8 d 1 6

Physics
Kinetic Theory of Gases2 The atmospheric pressure on a hill is 68 cm of mercury What do you understand from the statement 3 How does atmospheric pressure change with the change in altitude 4 Briefly describe construction of a simple barometer

Physics
KinematicsThe position time graphs of two cars A and B are straight lines making angles 30 and 60 with the time axis respectively The ratio of velocities of A and B is 1 1 3 3 3 1 2 1 3 4 3 1 on holow The

Physics
Kinematics3 Block A of mass m is to be kept at rest against a smooth vertical wall by applying a force F as shown in figure The force required is 1 mg 2 2mg 3 mg 2 mg A m 30 F

Physics
Kinetic Theory of Gases3 Which one of the following is not an assumption of kinetic theory of gases 1 The volume of a gas molecule is negligible 2 The gravitational attraction between the gas molecules is negligible 3 The density of gas is same at all points 4 The change in momentum of gas molecules is negligible

Physics
KinematicsThe graph between Ek and is P E kinetic energy and p momentum 1 Ek 3 E 1 p FL 2 Ek 4 EK 1 p

Physics
Kinematics10 An aeroplane moving horizontally from west to eas with some velocity and with an acceleration 5 m s drops a food packet at some instant Then The path of the packet is parabolic with respect to ground b A person sitting on the aeroplane shall see the packet is always vertically below the plane c With respect to plane the packet travels in straight line making an angle tan 1 2 west vertical 1 d With respect to plane the packet travels in straight line making an angle tan 1 2 east vertical e The packet moves in a parabolic path with respec to aeroplane

Physics
Wave OpticsThe distance between slit and biprism and between biprism and screen are 50 cm each The angle of biprism is 179 and its refractive index is 1 5 If the distance between successive frings is 0 0135 cm then the wavelength of light is a 5893 x 10 0 m c 5893 x 10 m b 5893 x 10 cm d 2946 x 10 cm

Physics
Kinematics7 The graph between displacement and time for a particle moving with uniform acceleration is a a Straight line with a positive slope b Parabola c Ellipse d Straight line parallel to time axis

Physics
Transmission of heatA spherical black body with a radius of 12 cm radiates 450 watt power at 500 K If the radius were halved and the temperature doubled the power radiated in watt would be NEET 2017 1 225 2 450 3 1000 4 1800
Physics
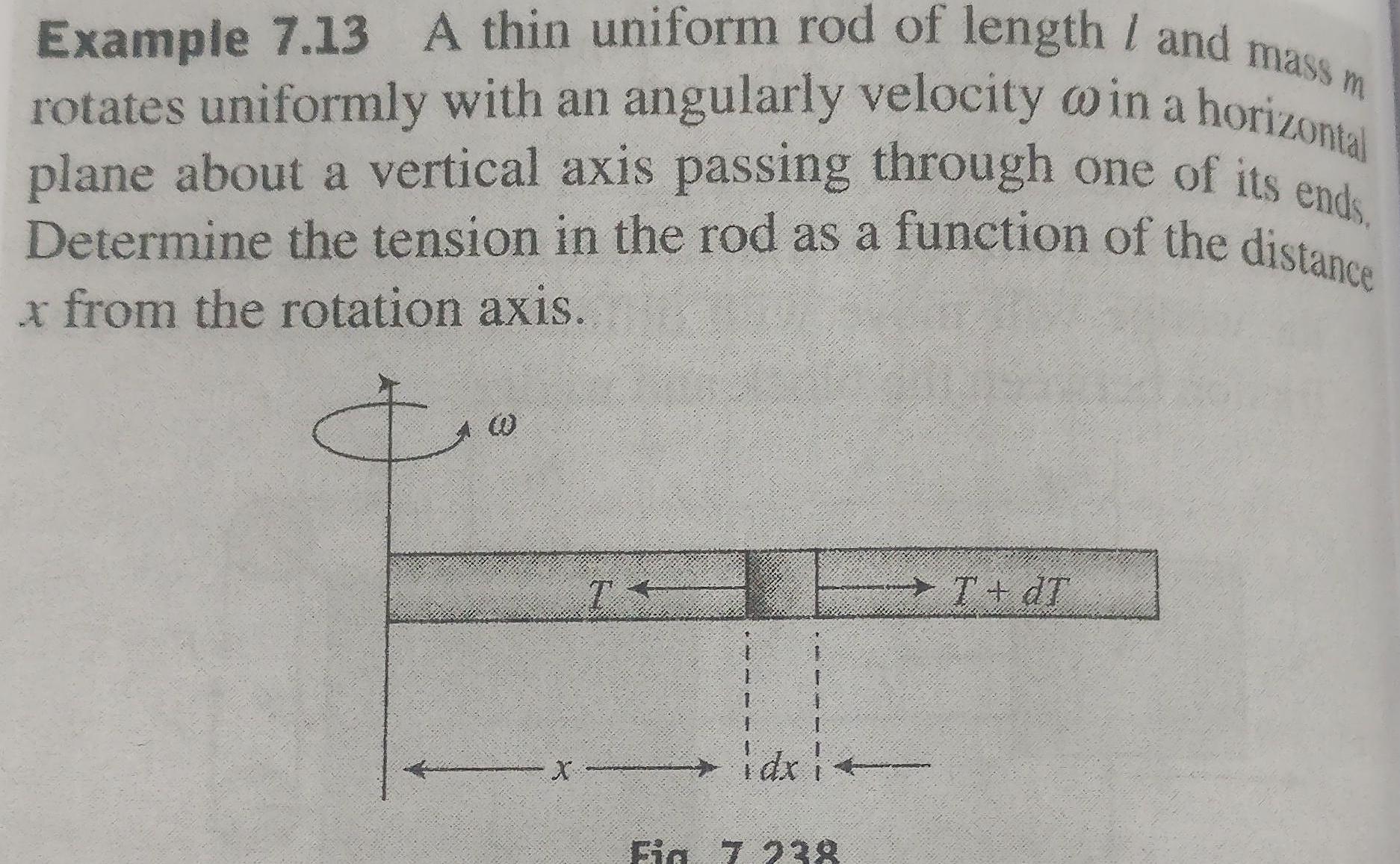
RotationExample 7 13 A thin uniform rod of length and mass m rotates uniformly with an angularly velocity in a horizontal plane about a vertical axis passing through one of its ends Determine the tension in the rod as a function of the distance x from the rotation axis X idxi Fig 7 238 T dT

Physics
Basic Physicsiv The magnitude of area of the parallelogram formed by the adjacent sides of vectors A 31 21 a nd 3 21 2k is Sol

Physics
ExperimentsThe measure of mass and volume of a body are 2 00 g and 5 0 cm respectively with possibl errors of 0 01 g and 0 1 cm What would be the maximum permissible error in its density Hint Ad Am AV Ad dx m V Am AV m V where d m V 1

Physics
AC CircuitsIn the figure shown V b at t 1 s is ab 2H a 1 30 V 202 2F b 4V www1100000 1 q 4t C 2 30 V 3 20 V 4 2 res

Physics
Fluids5 The length of one edge of a glass plate of thickness 0 2 cm is 9 8 cm If this edge of the glass plate touches the surface of a liquid of surface tension 60 dyne cm then it is pulled down with a force of Assume that angle of contact to be zero 1 1100 dyne 3 1000 dyne 2 2400 dyne 4 1200 dyne

Physics
Atomic Structure50 When the electron of a hydrogen like atom jumps from a higher energy level to a lower energy level then 1 Angular momentum of the electron remains constant 2 Kinetic energy of the electron increases 3 Wavelength of de Broglie wave associated with motion of the electron increases 1 4 Potential oporgy increases X

Physics
Current ElectricityIn Fig 5 52 connected 2 10 2 and R 20 Determine th Illustration 5 32 equivalent resistance between points i A and D and ii as shown Given R and C com B R www E www R wwww R www www R R R C
Physics
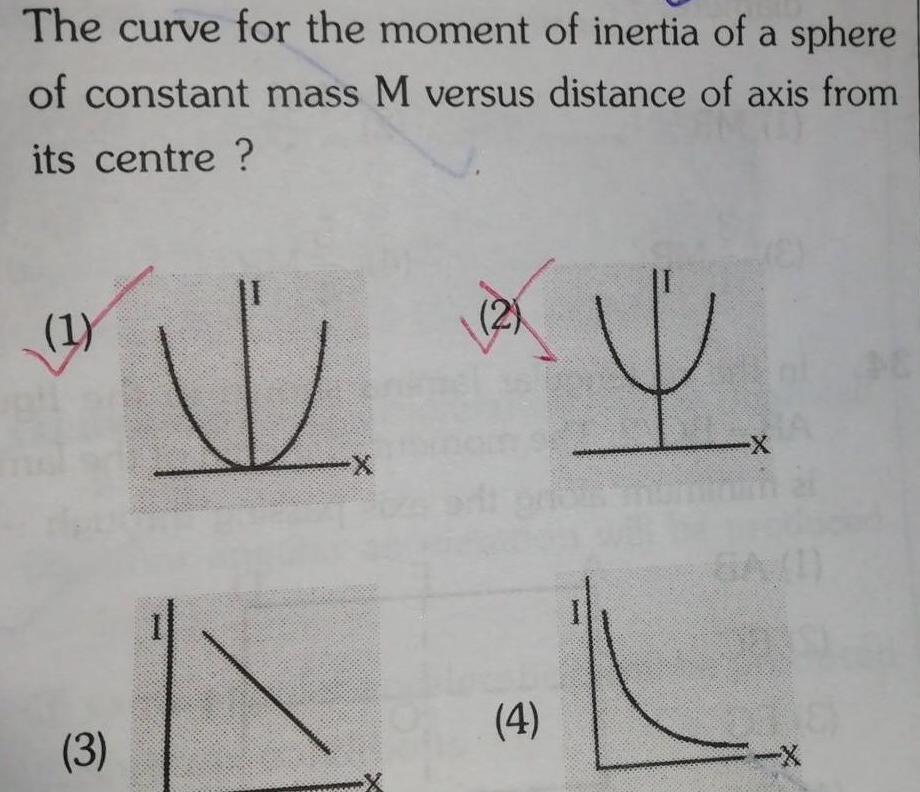
RotationThe curve for the moment of inertia of a sphere of constant mass M versus distance of axis from its centre 1 3 Hind V X 2 4 X

Physics
Electric Field and PotentialTwo thin conducting plates very large parallel to each other carrying total charges A and 20 A respectively where A is the area of each plate are placed in a uniform external electric field E as shown Find the surface charge on each surface E

Physics
Kinematics6 The acceleration a of a particle starting from rest varies with time according to relation a at B The velocity of the particle after a time t will be www a b 012 2 B Bt c at d at 2 Bt at B 2

Physics
Electric Field and PotentialFind the electric field at the origin due to the line charge ABCD of linear charge density 2 a 0 0 B y C 0 a 0 a 0 0

Physics
Current ElectricityIn the circuit shown the resistor is 1 A when the points P and M are connected to a d c voltage source The potential difference between the points M and N is 402 mir P wwwwwww 352 wwwww 0 5 www 0 52 1 0 5 volts 1 5 volts N X www 1Q M 2 3 2 volts 4 1 0 volt

Physics
AC Circuitsng emf E E cos 100 m st cos500 m st S is connected in series with a capacitor and a resistor The steady state current in the circuit is found to be i i cos 100 r s t 9 i cos 500 m st i i b i i c i i a i i d The information is insufficient to find the relation between i and i 2 An AC so

Physics
Work, power & energyThe displacement x of a body of mass 1 kg on smooth horizontal surface as a function of time t is given by 1 where x is in metres and t is in seconds Find the work done by the external agent for the first one 3 second X

Physics
FluidsChe er 1 22 A capillary tube of radius 0 50 mm is dipped vertically in a pot of water Find the difference between the pressure of the water in the tube 5 0 cm below the surface and the atmospheric pressure Surface tension of water 0 075 Nm

Physics
Kinematics11 A in a moving vertical plane At a certain when instant the link is inclined 60 to the horizontal the point A is moving horizontally at 3 m s while moving in the vertical direction What is velocity of B 1 a 55115 m s 3 m s A VB4 60 b 2 3 m s 3

Physics
Current Electricity22 What should be the current in branch BD after 22 switch S is closed Se ostrzy 152 201 1 1A 3 8A 19 B 352 S 252 402 25V 2 2A 4 Zero 3x7 4 zry 63

Physics
Magnetic Field due to current27 shows a rod PQ of length 20 0 cm and mass 200 g suspended through a fixed point O by two threads of lengths 20 0 cm each A magnetic field of strength 0 500 T exists in the vicinity of the wire PQ as shown in the figure The wires connecting PQ with the battery are loose and exert no force on PQ a Find the tension in the threads when the switch S is open b A current of 2 0 A is established when the switch S is closed Find the tension in the threads now PA S

Physics
Unit & DimensionsA dip needle vibrates in a vertical plane perpendicular to the geographical meridian The time period of vibration is found to be 2 second The same needle is then allowed to vibrate in the horizontal plane and the time period is again found to be 2 second If the angle of declination is 60 then the true angle of dip is v 1 tan 1 3 45 1 2 2 tan 2 T 22 timbe tan 2

Physics
Kinematicsin the direction During the perio is the componen low and this et along the river bank of a river flowing at a speed as shown in figure What minimum speed relative to water should the man have so that he can reach point B In which direction should he swim V 0 45 A D A Sol Let v be the speed of boatman in still water B 45 B u u b y I c For and Her rive this d t or

Physics
Newton's law of motionA sphere of mass m is held between two smooth inclined walls For sin 37 3 The normal reaction of the wall 2 is equal to 2 A 37 37 mg Correct Answer mg sin 74 mg cos 74 None of theso SWING

Physics
Electric Field and Potential5 Three concentric spherical shells have radii a b and c a b c and have surface charge densities o o and o respectively If VA V and V denote the potentials of the three shells then for c a b we have 1 Vc VB VA C 3 Vc VB VA C 2 Vc V VB A 4 V V V C B A

Physics
Wave Opticsal 81 In the given figure the angle between the 9 Dalected rays is equal to n g e r 82 1 A 2 2 A 3 3 A 4 4A

Physics
Frictionspring is 100 N m Extension produced in the spring in equilibrium is g 10 m s 1 10 cm 3 30 cm 3Kg reelle 3Kg 2 20 cm 440 cm

Physics
Transmission of heat0 Certain quantity of water cools from 70 C to 60 in the first 5 minutes and to 54 C in the nex minutes The temperature of the surroundings i AIPMT 20 1 45 C 2 20 C 3 42 C 4 10 C

Physics
Kinematics41 A skater weighing 70 kg stands on ice He throws a stone weighing 3 kg with a velocity of 8 m s in a horizontal direction Find the distance through which the skater moves back Given 0 02 Ans 0 3 m 12 A block is laid gently on a horizontal conveyor belt moving at a speed of 5 5 m s If the co efficient of friction between the block and the belt is 0 45 find how far the block will move on the belt before coming to rest on Ans 3 43 m it

Physics
Magnetic Field due to currentExample 11 11 When light of wavelength 4000 A is incident on a barium emitter emitted photoelectrons in a transverse magnetic field strength B 52x10 6 T moves in a circular path Find the radius of the circle Given work function of 31 kg barium is 2 5 eV and mass of electron is 9 1 x107 e 1 6x10 1 C h 6 6x10 34 Js

Physics
Electric Field and PotentialA parallel plate capacitor has capacitance C If the charges the plates are Q and 30 find the i charges at the inner surfaces of the plates ii potential difference between the plates iii charge flown if the plates are connected iv energy lost by the capacitor in iii v charge flown if any plate is earthed 2 d

Physics
Geometrical Opticsconvex lens of focal length f is placed in contact with a concave lens of the same foca ength The equivalent focal length of the combination is A zero B infinity C f D

Physics
KinematicsThe variation of velocity of a particle moving along a straight line is as shown in the figure given below The distance travelled by the particle in 5 s is 1 60 m 3 40 m v m s 20 10 0 12 A B bols DE C 3 4 5 t s 2 30 m 4 50 m

Physics
Atomic Structure146 Light of uniform intensity impinges perpendicularly on a totally reflecting surface If the area of the surface is halved the radiation force on it will become double a a b half c four times d one fourth

Physics
Current ElectricityThe circuit shown here has two batteries of 8 V 16 V and three resistors 30 90 and on and a capacitor of 5 F how much is current i in the circuit in steady state 1 1 6A Check all that apply 000 A B C S 2 0 67A HHM SpF 902 3 2 5A 16V 4 0 25 A

Physics
Electric Field and Potential3 Consider the situation of figure 29 Q3 The work done in taking a point charge from P to A is WA from P to B is WB and from P to C is Wc a WA WB Wc c WA WB Wc b WA WB Wc d None of these C 1 I 1 q B A P

Physics
Simple harmonic motionC 0 25 sec D 0 5 sec The maximum acceleration of a particle in SHM is made two times keeping the maximum speed to be constant It is possible when A amplitude of oscillation is doubled while frequency remains constant B amplitude is doubled while frequency is halved C frequency is doubled while amplitude is halved D frequency is doubled while amplitude remains constant
Physics
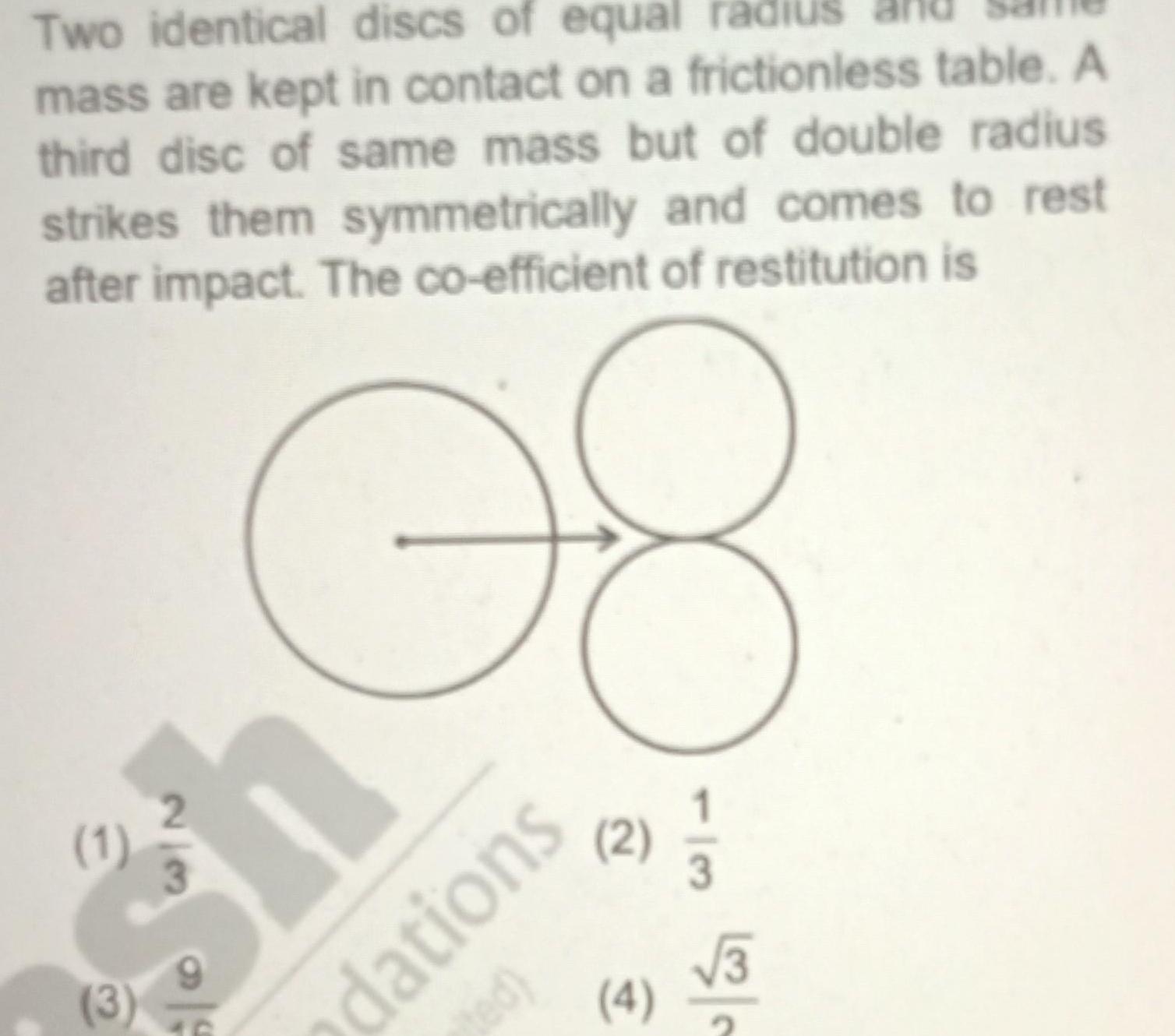
RotationTwo identical discs of equal radiu mass are kept in contact on a frictionless table A third disc of same mass but of double radius strikes them symmetrically and comes to rest after impact The co efficient of restitution is 08 1 3 3 us dations ted 2 1 1 2 3 4

Physics
Electric Field and Potentiala region sible that B region to 10 Let E and B denote electric and magnetic fields in a frame S and E and B in another frame S moving with respect to S at a velocity Two of the following equations are wrong Identify them b E E d E E vB it s a By B VE 2 C c By B vE UB

Physics
Newton's law of motionthe driver thrown e in touch we would f the bus and the owever een the sudden ictional ur feet strictly s some parts go with ere it is ore we opens of the e body opens p due lative e bus move ward e into ally hip ta the ter hat Exert hall nal the grens is Momentum Momentum of a body is defined to be the product of its mass m and velocity v and is denoted by p 5 1 Momentum is clearly a vector quantity The following common experiences indicate the importance of this quantity for considering the effect of force on motion p mv Suppose a light weight vehicle say a small car and a heavy weight vehicle say a loaded truck are parked on a horizontal road We all know that a much greater force is needed to push the truck than the car to bring them to the same speed in same time Similarly a greater opposing force is needed to stop a heavy body than a light body in the same time if they are moving with the same speed If two stones one light and the other heavy are dropped from the top of a building a person on the ground will find it easier to catch the light stone than the heavy stone The mass of a body is thus an important parameter that determines the effect of force on its motion the mos Same Sper Speed is another important parameter tout heavy consider A bullet fired by a gun can easily pierce human tissue before it stops resulting in casualty The same bullet fired with moderate speed will not cause much damage Thus for a given mass the greater the speed the greater is the opposing force needed to stop the body in a certain time Taken together the product of mass and velocity that is momentum is evidently a relevant variable of motion The greater the change in the momentum in a given time the greater is the force that needs to be applied A seasoned cricketer catches a cricket ball coming in with great speed far more easily than a novice who can hurt his hands in the Ono raggon in that the cricketer allows a both Stone tene sequire force to stopte a light stone

Physics
Unit & DimensionsIf the four forces as shown are in equilib press F F in unit vector form F 15 N 37 30 30 10 N