Physics Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.

Physics
ThermodynamicsIn the given p V diagram find a pressures at c and d b work done in different processes separately c work done in complete cycle abcd 90101 910 Solution a Line bc is passing through origin Hence po V From b to c volume is doubled Hence pressure is also 2po Po Vo Fig 21 9 2V0

Physics
Electric Field and Potential36 Determine the electric field strength vector if the potential of this field depends on x y coordinates as a a x y b axy where a is a constant Draw the approximate shape of these fields using lines of force in the x y plane

Physics
Newton's law of motion12 A horizontal force of 10 N is necessary to just hold a block stationary against a wall The coef ficient of friction between the block and the wall is 0 2 The weight of the block is a 20N c 100 N 10 N b 50N d 2 N

Physics
Magnetic Field due to currenton external magnetic 4 No field lines exists inside the magnet A magnetic needle lying parallel to a magnetic fiel requires W units of work to turn it through 60 TH magnitude of torque required to maintain t needle in same field at an angle of 30 with fielc N mis 1 2W 3 3 W 2 W W 4 3 w

Physics
Electric Field and Potentialon the bob Ans 16 4 Three charges 27 125 and 64 C are situated at the corners A B and C respectively of a rectangle ABCD having sides AB 8 x 10 2 m and BC 6 x 10 2 m Find the force on a charge 5 C placed at D Ans zero zero Find also the potential at D O 5 A spherical ball of mass m with charge q can revolve in a vertical plane at the end of a string of length on and magnitude to that

Physics
Geometrical OpticsI I T 73 Ans 1 414 i 45 r sin 1 3 4 7 The dispersive power of crown and flint glasses are 0 03 and 0 05 respectively The refractive indices for yellow light for these glasses are 1 517 and 1621 respectively It is desired to form an achromatic combination of prisms of crown and flint glasses which can produce a deviation of 1 in the yellow ray Find the refracting angles of the two prisms needed Ans 4 8 2 4 1

Physics
Electric Field and PotentialFig 3 4 40 A point dipole with an electric moment p oriented in the positive direction of the z axis is located at the origin of coordinates Find the projections and E of the electric field strength vector on the plane perpendicu to the z axis at the point S see Fig 3 4 At which points is perpendicular to p

Physics
Basic Physics30 Three forces start acting simultaneously on a particle moving with velocity v These forces are represented in magnitude and direction by the three sides of a triangle ABC as shown The particle will now move with velocity W pienst or sides letnos a Less than v b Greater than v c In the direction of the largest force BC Falm 01 B Torn

Physics
Atomic Structure6 Ionization potential of hydrogen atom is 13 6 el Hydrogen atom in ground state is excited by monochromatic light of energy 12 1 eV The spectra lines emitted by hydrogen according to Bohr s theory will be a one c three 2016 b two d four AIIMS

Physics
Simple harmonic motionD The frequency of oscillation of an electric dipole moment having dipole moment p and rotational inertia I oscillating in a uniform electric field E is given 1 1 2 I PE 3 2 PEII 2 1 2 PE I 4 2 IPE

Physics
Simple harmonic motionA particle execute S H M with frequency f Find frequency with which its kinetic energy oscilla A particle of mass 10g is placed in potential field given by V 50x 100 erg g What will be freque of oscillation of particle

Physics
Circular MotionEX Two strings of length 0 5 m each are connected to a block of mass m 2 kg at one end and their ends are attached to the point A and B 0 5 m apart on a vertical pole which T rotates with a constant angular velocity of tension in the upper string T and the lower string T Use g 9 8 m s 7 rad sec Find the ratio T 0 m 0 5 0 5 0 5 ic in moto

Physics
Atomic StructureQ 6 Two H atoms in the ground state collide inelastically The maximu amount by which their combined kinetic energy is reduced is d 27 2 eV a 10 20 eV b 20 40 eV c 13 6 eV

Physics
CapacitorsAnswer questions 11 12 and 13 by appropriately matching the information given in the three columns of the following table Three parallel plates A B C of large area carry charge Q Q and Q respectively Values of Q Q and Q are listed in Column 1 Column 2 and Column 3 respectively The separation between A and B is d whereas between B and C is 2d 11 Column 0 0 1H iv Column 2 0 2Q P Q R S Column 3 0 2Q d B II iii R D IV iv S B If plate A and C are connected by conducting wire then in which of the following case the charge flowing through conducting wire is Q 3 A 1 1 P C III ii Q

Physics
Geometrical Optics1 water medium 60 45 If refractive index of water is 3 of unknown medium is 1 1 4 3 1 43 then refractive ind 2 1 73 4 1 63

Physics
Geometrical OpticsLight from a point source in air falls on a convex spherical glass surface n and radius of curvature 20 cm The distance of the light source from the gla surface is 100 cm At what position the image is formed

Physics
Circular Motionwith macroscopic i e large When a glass rod is rubbed with a silk cloth charges appear both A similar phenomenon is observed with many other pair bodies Explain how this observation is consistent with the lat conservation of charge

Physics
Newton's law of motion3 Two blocks A and B of mass mA and mg are connected together by means of a spring and are resting on a horizontal frictionless table The blocks are then pulled apart so as to stretch the spring and then released Show that the ratio of their kinetic energies at any instant is in the inverse ratio of thei masses

Physics
Unit & DimensionsThe distance at which average radius of the earth orbi subtends an angle of 1 arc second is b Astronomical unit d Unified atomic unit J KC a Parsec c Light year

Physics
KinematicsThe equation of trajectory of a projectile is given by 40 x where y is vertically upwards If R y 4x 39 is range and 9 is angle of projection from horizontal then value of R tano is x and y are in m 2 15 6 m 4 14 2 m 1 3 9 m 3 11 7 m

Physics
KinematicsA train is moving towards east at a speed of 20 m s A bullet fired westward with a velocity of 180 m s crosses the train in 1 5 s The length of train is 1 300 m 2 240 m 3 200 m 4 270 m

Physics
KinematicsThree charges q q and q are kept at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side d Find the resultant electric force on a charge q placed at the centroid O of the triangle

Physics
RadioactivityA nuclear fusion reaction is given below H H He n 3 2 MeV A How much energy will be generated when 2 kg of deuterons are fused approx 1 1030 eV D 2 5 x 1023 MeV 2 1022 Mo 4 1033 eV

Physics
Simple harmonic motionA particle performing S H M is found at its equilibrium at t 1 s and it is found to have a speed of 0 25 m s at t 2 s If the period of oscillation is 6s Calculate amplitude of oscillation 1 3 2n m 2 m 3 3 4r 6 T m 3 4 m 8f

Physics
Waveslustration 8 A progressive wave having amplitude 5 m and wavelength 3 m If the maximum average velocity of particle in half time period is 5 m s and wave is moving in the positive x direction then find which may be the correct equation s of the wave where x in meter 1 5sin 2 2 x 3 5sin 2x 23 plution 2 4 sin 4 3 cos nt 2n 23 2 5 x 3cos 2t 3 X nt 2n 23 4 sin X 2n 2n 27 X Ans 2 3

Physics
Optical InstrumentsExample 9 12 a The near point of a hypermetropic person is 75 cm from the eye What is the power of the lens required to enable the person to read clearly a book held at 25 cm from the eye b In what way does the corrective lens help the above person Does the lens magnify objects held near the eye c The above person prefers to remove the spectacles while looking at the sky Explain why Solution a u 25 cm v 75 cm 1 f 1 25 1 75 i e f 37 5 cm The corrective lens needs to have a converging power of 2 67 dioptres b The corrective lens produces a virtual image at 75 cm of an object at 25 cm The angular size of this image is the same as that of the object In this sense the lens does not magnify the object but merely brings the object to the near point of the hypermetric eye which then gets focussed on the retina However the angular size is greater than that of the same object at the near point 75 cm viewed without the spectacles c A hypermetropic eye may have normal far point i e it may have

Physics
Basic PhysicsThe position of a particle is given by r 3ti 2t j 1k m where t is time in second and the coefficients have the proper unit for 7 to be in metre The acceleration of the particle in m s2 at t 2 sis 1 2j 3 3i 2j 2 21 4 41

Physics
Circular MotionA particle is suspended vertically from a point O by an inextensible massless string of length L A vertical line AB is at a distance L 8 from O as shown The object given a horizontal velocity u At some point its motion ceases to be circular and eventually the object passes through the line AB At the JEE 99 instant of crossing AB its velocity is horizontal Find u L L 8 u

Physics
SemiconductorsImp A red LED emits light at 0 1 watt uniformly around it The amplitude of the electric field of the light at a distance of 1 m from the diode is a 5 48 V m c 1 73 V m b 7 75 V m d 2 45 V m

Physics
Geometrical Optics3 A glass slab of thickness t 3 cm R I 2 between the object O and the concave mirror of focal lengthIf 4 5 cm It is observed that the image is formed at the object If we withdraw the slab the image will be formed at a distance of A 10 cm 11 C 80 cm 11 is placed B 30 cm 11 D 90 cm 11 Object F

Physics
KinematicsA particle is dropped from a balloon rising at 20 m s 1 at a time when the balloon is 80 m above the ground If g 10 m s 2 then the particle reaches the ground approximately in 1 5 6 s 2 6 5 s 3 4 5 s 4 4 s

Physics
KinematicsA ball is projected from a point O with some velocity Vo at an angle 30 with the horizontal as shown in the figure Consider a target at point Q The ball will hit the target then velocity vo is equal to 130 1 2 5 m s 3 4 m s Vo 3 m 2 7 5 m s 4 2 10 m s

Physics
Transmission of heatExample 22 13 A cylinder of radius R made of a material of conductivity K is surrounded by a cylindrical shell of inner radius R and outer radius 2R made of a material of thermal conductivity K The two ends of the combined system are maintained at two different temperatures There is no loss of heat across the cylindrical surface and the system is in steady state The effective thermal conductivity of the system is JEE 1998 a K K c K 3K 4 b K K K K d 3K K 4 Solution Let R and R be the thermal resistances of inner and outer portions Since temperature difference at both ends is same the resistances are in parallel Hence or bow 2R option is c Fig 22 16 1 RR R 1 R 1 KA KA 1 K R K 4 R K R K 3 R 1 1 1 ban K 3K 4 09 01 SS olgm 028 no

Physics
Capacitors12 In the given circuit charge Q on the 2uF capacitor changes as C is varied from 1pF to 3pF Q as a function of C is given properly by figures are drawn schematically and are not to scale a c Q Q Charge 1 F Charge LE C E 3 F b d luF 2 F Q Q Charge 1 F Charge 5 3 F C C

Physics
Newton's law of motionA person reaches exactly opposite point on the bank of a river if he starts swimming with a speed of 9 kmph at an angle 120 with the direction of flow of the water stream The speed of water in the stream is 1 2 5 m s 2 9 m s 3 4 5 m s 4 1 25 m s Space for Roug

Physics
Kinetic Theory of Gases17 A solid body of constant heat capacity 1 J C is being heated by keeping it in contact with reservoirs in two ways 1 Sequentially keeping in contact with 2 reservoirs such that each reservoir supplies same amount of heat ii Sequentially keeping in contact with 8 reservoirs such that each reservoir supplies same amount of heat In both the cases body is brought from initial temperature 100 C to final temperature 200 C Entropy change of the body in the two cases respectively is a In2 2ln2 c In2 4ln2 b 21n2 8ln2 d In2 In2

Physics
Thermodynamics18 Consider a spherical shell of radius R at temperature T The black body radiation inside it can be considered as an ideal gas of photons with internal energy per unit volume u U o T4 1 U V If the shell now undergoes an and pressure p 3 V adiabatic expansion the relation between T and Ris 1 1 a Toc R c Toce R b To R d Toc e 3R

Physics
AC Circuits11 An LCR circuit is equivalent to a damped pendulum In an LCR circuit the capacitor is charged to Qo and then connected to the L and R as shown below a R www If a student plots graphs of the square of maximum charge QMax on the capacitor with time t for two different values L and L L L of L then which of the following represents this graph correctly plots are schematic and not drawn to scale QMax L vooor b 2 Qax Qo For both L and L

Physics
Electric Field and PotentialTwo equal and oppositely charged particles are kept at some distance apart from each other A spherical surface having radius equal to separation between the particles and concentric with their mid point is considered Then a electric field is normal to the surface at two points only b electric field is zero at no point c electric potential is zero at every point of one circle only d All of the above
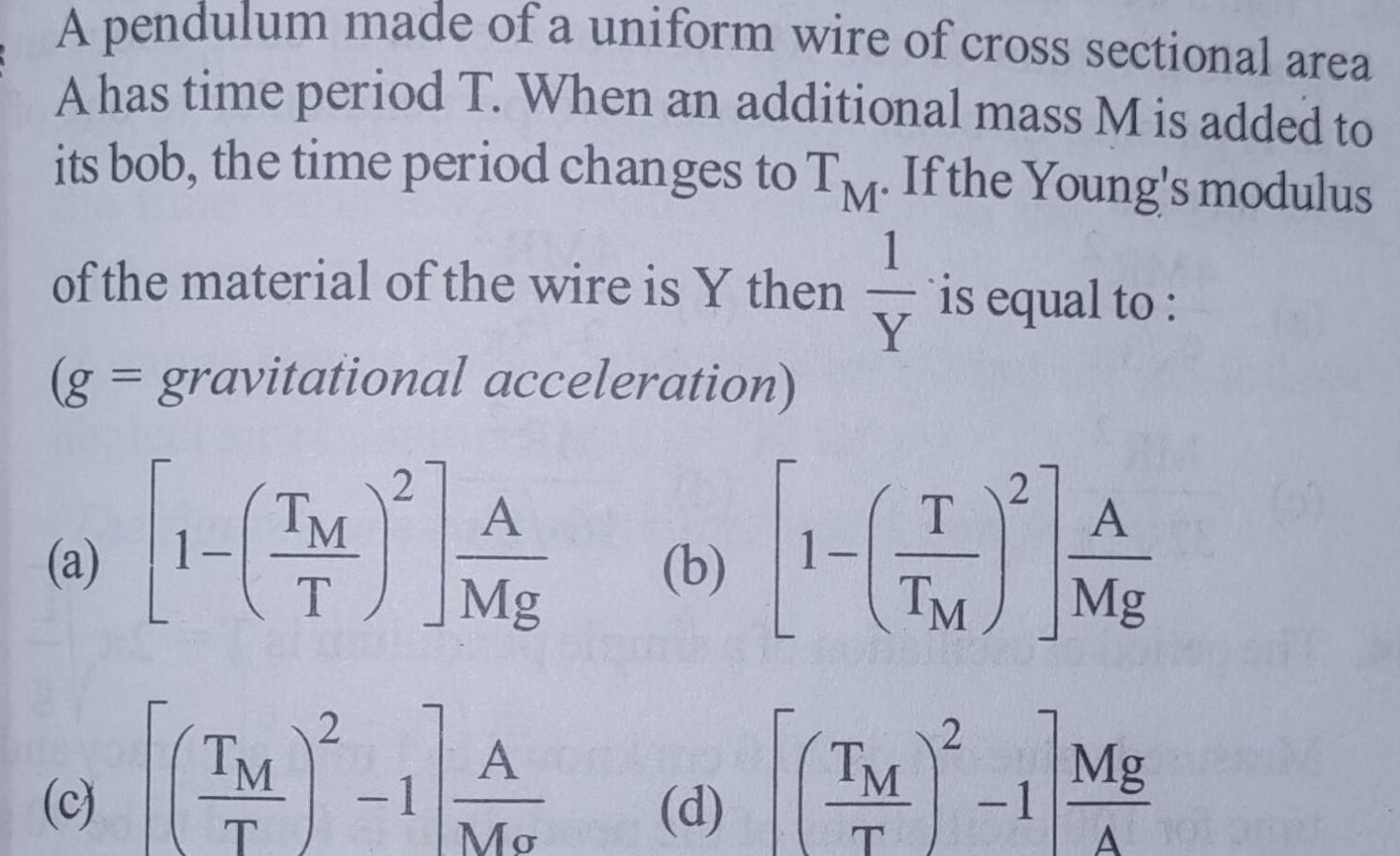
Physics
Simple harmonic motionA pendulum made of a uniform wire of cross sectional area A has time period T When an additional mass M is added to its bob the time period changes to TM If the Young s modulus 1 of the material of the wire is Y then is equal to Y g gravitational acceleration a c TM T TM 2 2 1 A Mg A Mo b T TM A Mg 2 d M 1 Mg TM T A 101 amat

Physics
Magnetic Fieldlar loop of sides 10 cm and 5 cm carrying a current 1 of 12 A is placed in different orientations as shown in the figures below A B C D xk NA FI y y y y x4 If there is a uniform magnetic field of 0 3 T in the positive z direction in which orientations the loop would be in i stable equilibrium and ii unstable equilibrium a B and D respectively

Physics
Basic Physics9 Two stones are thrown up simultaneously from the edge of a cliff 240 m high with initial speed of 10 m s and 40 m s respectively Which of the following graph best represents the time variation of relative position of the second stone with respect to the first Assume stones do not rebound after hitting the ground and neglect air resistance take g 10 m s The figures are schematic and not drawn to scale a b 240 240 y y m 8 y y m t s 12 12 t s

Physics
Electric Field and Potential5 Charges 2 Q and Q are placed as shown in figure The point at which electric field intensity is zero will be 2Q E a somewhere between Q and 2Q b somewhere on the left of Q c somewhere on the right of 2Q d somewhere and 2 Q on the right bisector of line joining Q

Physics
Magnetic FieldA conducting circular loop of radius r carries a constant current i It is placed in uniform magnetic field B such that B is perpendicular to the plane of the loop The net magnetic force acting on the loop is 1 irB 2 2 TriB 3 Zero 4 TiB

Physics
Newton's law of motionApparent weight of a man in lift Case I If the lift is at rest or moving uniformly a N mg So Wapp Wapp W actual Case II If the lift is accelerating upwards then Net upward force on man ma N mg ma N mg ma N m g a 187 or N m g a 0 then N actualmg W W app mg AN ing Lift Man d

Physics
Center of mass and momentumDistance of the centre of mass of a solid uniform cone from it If the radius of its base is R and its height is vertex is ZO then Zo is equal to 5h 8 a c 4R b d 2 3h 8R 3h 4

Physics
Current ElectricityA square wave current switching rapidly between 0 5 ampere and 0 5 ampere is passed through an AC ammeter Then the reading shown by it is A 0 25 ampere ST0 5 05 ampere 2 B 0 5 ampere D 0 5 x 2 ampere sin ot

Physics
Magnetic Field4 All of these 5 A semicircular wire PQS of radius R is connected to a wire bent in the form of a sine curve to form a closed loop as shown in the figure If the loop carries a current i and is placed in a uniform magnetic field B then the total force acting on the sine curve is x x 1 2BIR downward 3 BiR upward h Educational Services Limited Read Office 2 2BiR upward 4 Zero Aakash Tower 8 Pusa Road New Delhi 110005 Ph 011 47623456

Physics
Electricity measuring equipments7 6 Two long current ca plane as shown in the figure Magnitude of net magnetic field at centre point O is Radius of circular parts is R L 1 3 Ho 3 0 4 R Ho 4 0 k k 20 10 2 21 Ho 4 0 k 4t R 4 Zero

Physics
Center of mass and momentumMATCHING TYPE WITH 3 COLUMNS 4 ROWS he following table has 3 columns and 4 rows Based on table there are THREE questions Each question has FOUR options 4 B C and D ONLY ONE of these four options is correct 1 A ball of mass m moving with velocity vo in horizontal direction collides with a stationary ball of mass m line of impact makes an angle with horizontal choose the correct option 1 II III Column 1 Masses m m m m m m 3m 2m 3 1 m m m IV m m m 3m 0 ii Column 2 Coefficient of restitution e 0 iii iv For 0 0 which of the following is true A IV iv Q e e 1 2 1 3 e 1 m Vo Column 3 Angle between final velocities of two balls P R S R zero B 1 ii P D IV ii Q TC 2 T 3 Ji Q 70 V