Physics Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.

Physics
Basic PhysicsQ10 a State the D Alemberts principle b A plane has a takeoff speed of 88 3 m s and requires 1365 m to reach that speed Determine the acceleration of the plane and the time required to reach that speed 2 3 5M

Physics
RotationA uniform thin rod of length L is oscillating in vertical plane about a fixed horizontal axis passing through one of its end Frequency of small oscillations of the rod is Vo If bottom half of the stick were cut off then its new frequency would become 28 Vo VO 2v0 2V0

Physics
KinematicsA body of mass m collides elastically with another body of mass m at rest If the velocity of m after collision becomes 2 3 times its initial velocity the ratio of their masses is AIIMS 2018 1 1 5 2 5 1 3 5 2 4 2 5 veloci

Physics
Kinetic Theory of GasesIf Cp and Cydenoted the specific heat of unit gram mass of nitrogen at constant pressure and volume respectively then R is universal gas constant O Cp Cv R O Cp Cv 7R O 28 Cp Cv R O Cp Cy 28R

Physics
Basic Physics1 prism 2 glass slab 3 biconvex lens Light of wavelength 4000 is incident at small angle on a prism of apex angle 4 The prism has n 1 5 n 1 48 The angle of dispersion produced by the prism in this light is 1 0 2 2 0 08 0 192 3 4 None of these no goto cpectrum on the other side of the prism In the emergen

Physics
Geometrical Opticsdeviation of 1 15 2 22 5 3 0 4 12 5 The refractive index of the material of prism of 60 angle is 2 At what angle the ray of light be incident on it so that minimum deviation takes place 45 emerging Cantive index of the material of the prism is 2 60 3 30 4 75 of light is incident at angle of 60 on one face of a prism which has an apex angle of 30 The ray mi

Physics
Geometrical OpticsThe dispersion of light in a medium implies that 1 lights of different wavelengths travel with different speeds in the medium 2 lights of different frequencies travel with different speeds in the medium 3 the refractive index of medium is different for different wavelengths 4 all of the above angle of light passing from glass to air is minimum for

Physics
Geometrical Optics1 2 4 2 1 5 3 1 2 A beam of light is converging towards a point A plane parallel plate of glass of thickness t refractive index u is introduced in the path of the beam The convergent point is shifted by assume near normal incidence 1 1 1 away 2 1 away 3 nearer 4 1 1 neare t

Physics
GravitationIf at a small height h above the surface of earth acceleration due to gravity decreases by 0 2 then at depth h below the surface of earth the acceleration due to gravity will 1 Increase by 0 4 2 Increase by 0 1 3 Decrease by 0 4 4 Decrease by 0 1

Physics
Work, power & energyBody A of mass 4 m moving with speed u collides with another body B of mass 2m at rest The collision is head NEET 201 and elastic in nature After the collision the fraction of energy lost by the colliding body A is 1 5 9 2 1 9 3 8 9 4 4 9

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA ball moving with velocity 2 m s collides head on with another stationary ball of double the mass If the coefficient of AIPMT 2010 restitution is 0 5 then their velocities in m s after collision will be 0 1 2 1 1 3 1 0 5 77 4 0 2

Physics
Geometrical Optics4 It is totally reflected from all the three sides of prism and never emerges out When light rays are incident on a prism at an angle of 45 the minimum deviation is obtained If refractive index of the material of prism is 2 then the angle of prism will be 1 30 2 40 3 50 4 60 fronting angle is 60 For minimum

Physics
Optical Instruments1 20 cm 2 16 cm 3 10 cm 4 12 cm A convex lens forms a real image 9 cm long on a screen Without altering the position of the object and the screen th lens is displaced and we get again a real image 4 cm long on the screen Then the length of the object is 1 9 cm 4 36 cm 2 4 cm 3 6 cm hinnt in placed at a distance of 5 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm then the image is

Physics
Electric Field and PotentialThe electric potential decreases uniformly from V to V along X axis in a coordinate system as we moves from a point xo 0 to xo 0 then the electric field at the origin A must be equal to Xo C must be greater than V Xo V B may be equal to Xo V D may be less than Xo The anergy of electric le

Physics
Work, power & energyA ball impinges directly on a similar ball at rest The first ball is brought to rest by the impact If half of the kinetic energy is lost by impact the value of coefficient of restitution is AIIMS 2017 1 1 2 2 2 3 m Cur 3 4 3 2

Physics
Center of mass and momentum2v 2v A can of height h is filled with liquid of uniform density p If the liquid is coming out from the bottom then centre of mass of the can water in the can 1 first ascends and then descends 3 always decreases Taxa omiciranlar rings of linan V Belt Ba 2 first descends and then ascends 4 none of these 11 and of radius R each are joined to form a complete ring The

Physics
Kinetic Theory of GasesInternal energy of n moles of hydrogen at temperature is equal to the internal energy of n moles of helium at temperature 27 The value of ratio is neglect n n vibrational modes in hydrogen wo ch 314 6 8

Physics
Basic PhysicsA mass m moves with a velocity y and collides inelastically with another identical mass at rest After collision the in a direction perpendicular to the initial direction of motion Find the speed of the AIEEE 2005 Ist mass moves with velocity 2nd mass after collision Dy 2 3v 2 3 4 3

Physics
Geometrical OpticsThe critical angle between an equilateral prism and air is 45 If the incident ray is perpendicular to the refracting surface then 1 After deviation it will emerge from the second refaracting sufrace 2 It is totally reflected on the second surface and emerges out perpendicularly from third surface in air 3 It is totally reflected from the second and third refracting surfaces and finally emerges out from the first surface 4 It is totally reflected from all the three sides of prism and never emerges out When light rays are incident on a prism at an angle of 45 the minimum deviation is obtained If refractive index of the

Physics
Optical Instruments18 The ray diagram could be correct n Lens 2 If n n and n n n 1 If n n n If n n and n n 4 Under no circumstances Rafr

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA solid iron ball A of radius r collides head on with another stationary solid iron ball B of radius 2r The ratio of their speeds just after the collision e 0 5 is 1 3 2 4 3 2 In 4 1 hora kis a constant and is the
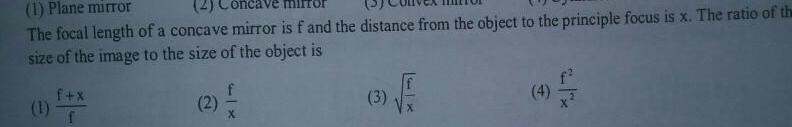
Physics
Basic Physics1 Plane mirror The focal length of a concave mirror is f and the distance from the object to the principle focus is x The ratio of the size of the image to the size of the object is f x 1 5 3 X 2 3 4

Physics
Center of mass and momentum1 1 00 J 2 0 67 J A thin rod of length L is lying along the x axis with its ends at x 0 and x L Its linear density mass length varies where n can be zero or any positive number If the position XCM of the centre of mass of the rod is plotted against n which of the following graphs best approximates the dependence of XM on n AIEEE 2008 with x as

Physics
Basic PhysicsSTATEMENT 1 Two particles moving in the same direction do not lose all their energy in a completely inelastic AIEEE 2010 collision STATEMENT 2 Principle of conservation of momentum holds true for all kinds of collisions 1 Statement 1 is true Statement 2 is true Statement 2 is the correct explanation of Statement 1 2 Statement 1 is true Statement 2 is true Statement 2 is not the correct explanation of Statement 1 3 Statement 1 is false Statement 2 is true 4 Statement 1 is true Statement 2 is false

Physics
Optical Instruments5 1 10 cm 2 20 cm 3 5 cm 4 none of these A thin linear object of size 1 mm is kept along the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm The object is at 15 cm from the lens The length of the image is 1 1 mm 2 4 mm 4 8 mm The ray diagram could be correct 3 2 mm

Physics
Basic Physics1 Violet ray 2 Green ray 4 Yellow ray 3 Red ray A spectrum is formed by a prism of dispersive power If the angle of deviation is s then the angular dispers is 1 o 8 2 8 3 1 08 4 wo When white light passes through the achromatic combination of prisms then what is observed

Physics
Center of mass and momentumWhich of the following is incorrect 1 If centre of mass of three particles is at rest and it is known that two of them are moving different non parallel lines then the third particle must also be moving 2 If centre of mass remains at rest then net work done by the forces acting on the system must be zero 3 If centre of mass remains at rest then net external force must be zero 4 None of these statement is incorrect

Physics
Center of mass and momentumAn explosion blows a rock into three parts Two parts go off at right angles of each other These two are 1 kg first part moving with a velocity of 12 ms and 2 kg second part moving with a velocity of 8 ms If the third part flies off with a velocity of 4 ms its mass would be AIPMT 20097 1 5 kg 2 7 kg 3 17 kg 4 3 kg espectively The centre of mone

Physics
Basic PhysicsThere is a small black dot at the centre C of a solid glass sphere of refractive index u When seen from outside will appear to be located 1 away from C for all values of u 2 at C for all values of u 3 at C for u 1 5 but away from C for p 1 5 4 at C only for 2 sps1 5 formed at

Physics
Basic Physics3 A prism having an apex angle of 40 and refractive index of 1 50 is located in front of a vertical plane mirror as shown A horizontal ray of light is incident on the prism The total angle through which the ray is deviated is 1 4 clockwise 2 178 clockwise M 3 2 clockwise 4 8 clockwise

Physics
Center of mass and momentum3 always decreases none of these Two semicircular rings of linear mass densities 2 and 2 and of radius R each are joined to form a complete ring The distance of the center of the mass of complete ring from its geometrical centre is 2R 3R 2 TC 2 3R 4 none of these ATC plank of length 1 which lies at rest on a frictionless horizontal surface

Physics
Basic PhysicsThe reason for shining of air bubble in water is 1 Diffraction of light 3 Scattering of light 2 Dispersion of light 4 Total internal reflection of light

Physics
Basic Physics1 60 2 100 3 180 4 240 When a plane mirror is placed horizontally on a level ground at a distance of 60m from the foot of a tower the to the tower and its image in the mirror subtend an angle of 90 at the eye The height of the tower will be 1 3 2 60 m 3 90 m 4 120 m An chinnt in at a distance of 05 m in front of a plane mirror Distance between the chient and image is

Physics
Center of mass and momentumIn the figure shown a hole of radius 2 cm is made in a semicircular disc of radius 6 cm at a distance 8 cm from the centre C of the disc The distance of the centre of mass of this system from point C is 1 4 cm 8cm 2 8 cm C 3 6 cm 4 12 cm of mass of the system of three rods of length 2a and two rods of length a as

Physics
Center of mass and momentumA heavy truck moving with a velocity of 60 km h collides with a light drum at rest If the collision be elastic then the velocity of the drum immediately after collision will be AIIMS 2014 1 zero 2 60 km h 3 120 km h 4 uncertain 11

Physics
Magnetic Field due to currentassociated with the spin where e is An electron has intrinsic angular momentum I called spin and a permanent magnetic dipole moment M the positive electron charge m is the electron mass and g is a number called g factor An electron with its spin aligned along its initial velocity in the x direction enters a region of uniform magnetic field in the z direction Due to magnetic force the torque on the spin is Mx B and perpendicular to M also perpendicular to I Since torque is perpendicular to I therefore it ensures that the spin turns with initial angular velocity wpwhich is given by the following equation 7 wp x L Due to charge on the e magnetic force also acts on the electron What is the value of wp

Physics
KinematicsA ball is thrown vertically downwards from a height of 20 m with an initial velocity v It collides with the ground loses 50 of its energy in collision and rebounds to the same height The initial velocity v is Take g 10 m s INEET 2015 1 28 ms 2 10 ms 3 14 ms 4 20 ms

Physics
Basic PhysicsTwo mirrors are inclined at an angle 9 as shown in the figure Light ray is incident parallel to one of the mirrors Light will start retracing its path after third reflection if

Physics
Geometrical OpticsA diver in a swimming pool wants to signal his distress to a person lying on the edge of the pool by flashing his water proof flash light 1 He must direct the beam vertically upwards 2 He has to direct the beam horizontally 3 He has to direct the beam at an angle to the vertical which is slightly less than the critical angle of incidence for total internal reflection 4 He has to direct the beam at an angle to the vertical which is slightly more than the critical angle of incidence for the total internal reflection dir 3500 and 7000 then the critical angle of x relative to y will be Tul

Physics
Basic Physics3 0 3 ms and 0 5 ms A moving block having mass m collides with another stationary block having mass 4m The lighter block comes to rest after collision When the initial velocity of the lighter block is v then the value of coefficient of restitution e will be NEET 2018 1 0 5 2 0 25 3 0 8 4 0 4 allide with another body B of mass 2m at rest The collision is head om

Physics
Basic Physics1 30 2 45 3 60 A parallel beam of monochromatic light is incident at one surface of a equilateral prism Angle of incidence is 55 an angle of emergence is 46 The angle of minimum deviation will be 1 Less than 41 3 More than 41 2 Equal to 41 4 None of the above

Physics
Geometrical Optics3 Concave mirror The field of view is maximum for 4 All the above can produce a vritual image 1 Plane mirror 2 Concave mirror 3 Convex mirror 4 Cylindrical mirror The focal length of a concave mirror is f and the distance from the object to the principle focus is x 1

Physics
Basic PhysicsThey co ordinate of the centre of mass of the system of three rods of length 2a and two rods of length a as shown in figure is Assume all rods to be of uniform density 1 B 28 9a 2 16 3 a M y 29 0 W 87 14 8a 4 3 3 zero placed on a smooth horizontal surface and a horizontal force F is applied on it at a distance

Physics
Geometrical Optics6 The refractive index of the material of a prism is 2 and the angle of the prism is 30 One of the two refracting surfaces of the prism is made a mirror inwards by silver coating A beam of monochromatic light entering the prism from the other face will retrace its path after reflection from the silvered surface if its angle of incidence on the prism is 1 60 2 Zero 2 45 A

Physics
Newton's law of motionA uniform sphere is placed on a smooth horizontal surface and a horizontal force F is applied on it at a dist h above the surface The acceleration of the centre 1 is maximum when h 0 3 is maximum when h 2R 2 is maximum when h R 4 is independent of h

Physics
Basic Physicsminimum deviation takes place 2 60 45 30 4 75 A ray of light is incident at angle of 60 on one face of a prism which has an apex angle of 30 The ray emerging out of the prism makes an angle of 30 with the incident ray The refractive index of the material of the prism is 1 2 3 3 1 5 4 1 6

Physics
Center of mass and momentum100 3 During the head on collision of two masses 1 kg and 2 kg the maximum energy of deformation is collision the masses are moving in the opposite direction then their velocity of approach before the collision is 1 10 m sec 2 5 m sec 3 20 m sec 4 10 2 m sec J If before

Physics
Work, power & energyTwo identical balls A and B having velocities of 0 5 ms and 0 3 ms respectively collide elastically in one dimension The velocities of B and A after the collision respectively will be NEET 2016 2 0 5 ms and 0 3 ms 1 0 5 ms and 0 3 ms 3 0 3 ms and 0 5 ms 4 0 3 ms and 0 5 ms having mass Am The lighter block com

Physics
Basic PhysicsIn the figure given the position time graph of a particle of mass 0 1 kg is shown The impulse at t 2 s is x m 4 2 2 t s 1 0 2 kg m s 2 0 2 kg m s 6 3 0 1 kg m s 4 0 4 kg m s AIIMS 2005

Physics
Simple harmonic motionA block of mass m is resting on a piston as shown in figure which is moving vertically in an SHM of period 1 s The minimum amplitude of motion at which the block and piston separate is g n 0 25 m 0 52 m O 2 5 m 0 15 m