Physics Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.

Physics
Work, power & energyA square ABCD of sides 1m rest on side AB A force of 100 N acting at 45 deg with AB acts at point C which is diagonally opposite to A The moment of this force about A is 2 Points zero 71Nm 100Nm 144Nm

Physics
Properties of matterA glass capillary tube is of the shape of truncated cone with an apex angle a so that its two ends have cross sections of different radii When dipped in water vertically water rises in it to a height h where the radius of its cross section is b If the surface tension of water is S its density isp and its contact angle with glass is the value of h will be g is the acceleration due to gravity 2014 Adv

Physics
Fluidsop 400 m s 2 600 m s 3 60 m s 4 None of these An ice berg of density 900 kg m is floating in water of density 1000 Kg m The percentage of volume of ice cube outside the water is 1 20 2 35 3 10 4 25 log of wood of mass 120 Kg floats in water The weight that can be put on the raft to make it just sink should be

Physics
Basic Physics1 20 0 A log of wood of mass 120 Kg floats in water The weight that can be put on the raft to make it just sink should t density of wood 600 Kg m 180 Kg 2 50 Kg 3 60 Kg 4 30 Kg Acylinder of height 20m is completely filled with water The velocity of efflux of water in ms through a small he

Physics
Properties of matter1 Rises 2 Falls 3 A large ship can float but a steel needle sinks because of 1 Viscostiy 2 Surface tension 3 Density The Working of an atomizer depends upon 4 None of these

Physics
Basic Physicsop 400 m s 2 600 m s 3 60 m s 4 An ice berg of density 900 kg m is floating in water of density 1000 Kg m The percentage of volume of ice cube outside the water is 38 30 1 20 2 35 3 10 4 25 A lng of wood of mass 120 Kg floats in water The weight that can be put on the raft to make it just sink should be

Physics
Magnetic Field due to currentA steady current T flows in a small square loop of wire of side L in a horizontal plane The loop is now folded about its middle such that half of it lies in a vertical plane Let u and respectively denote the magnetic moments of the current loop before and after folding Then 1 0 2 and are in the same direction 3 2 4

Physics
Basic Physics1 isochoric process 2 isobaric process The horizontal flow of fluid depends upon 1 pressure difference 2 amount of fluid In steady horizontal flow 3 isothermal process 4 adiabatic process 3 density of fluid 4 all the above

Physics
RotationTwo particles each of mass m and charge q are attached to the two ends of a light rigid rod of length 2 R The rod is rotated at constant angular speed about a perpendicular axis passing through its centre The ratio of the magnitudes of the magnetic moment of the system and its angular momentum about the centre of the rod is TH 9 2m 2 9 m 3 24 m 44 9 70m

Physics
Basic Physics3 in a straight line perpendicular to a stream line 4 for ideal lequid stream line flow on a stream line Bernoulli s equation is based upon 3 isothermal process 4 adiabatic process 1 isochoric process 2 isobaric process The horizontal flow of fluid depends upon

Physics
Basic Physics3 horizontally in line with its centre of gravity 4 may be anywhere A cork is suberged in water by a spring attached to the bottom of a bowl When the bowl is kept in an elevator moving with acceleration downwards the length of spring 1 Increases 3 Remains unchanged 2 Decreases 4 None of these

Physics
Atomic StructureDetermine the bandwidth of each of the amplifiers in Figure 12 43 Both op amps have an open loop gain of 100 dB and a unity gain bandwidth fr of 3 MHz Vin a www our Rf 220 kn R 3 3 k Vino b R www 1 0 kn R www 47 k Vout

Physics
FluidsIn order that a floating object be in a stable rotation at equilibrium its centre of buoyancy shoul 2 vertically below its centre of gravity 1 vertically above its centre of gravity 3 horizontally in line with its centre of gravity 4 may be anywhere

Physics
Magnetic Field due to currentAn infinitely long conductor PQR is bent to form a right angle as shown A current I flows through PQR The magnetic field due to this current at the point M is H Now another infinitely long straight conductor QS is connected at Q so that the current in PQ remaining unchanged The magnetic field at M is now H The ratio H H is given by IM 90 90 IR

Physics
Fluidsgl 3 5x5x5x7 gf 4 4x4x4x6 gf Two bodies are in equilibrium when suspended in water from the arms of a balance The mass of one body is 36 its density is 9 g cc If the mass of the other is 48 g its density in g cc is 1 4 3 2 3 2 3 3 4 5 In order that a floating object be in a stable rotation at equilibrium its centre of buoyancy should be

Physics
Newton's law of motion1 Point Total moment of various forces acting on the body is the vector sum of all moments Total moment of various forces acting on the body is the algebraic sum of all moments Total moment of various forces acting on the body is always zero Total moment of various forces acting on the body is the vector sum of all moments which is perpendicular to each other forces

Physics
Work, power & energy1 A collar B of mass 2 kg is constrained to move along a horizontal smooth and fixed circular track of radius 5 m The spring lying in the plane of the circular track and having spring constant 200 Nm undeformed when the collar is at A If the collar starts from rest at B the normal reaction exerted by the track on the collar when it passes through A is is e 7m B 15m C

Physics
Basic PhysicsThe time dependence of a physical quantity p is given by p po exp at2 where a is constant and t is the time The constant a a is dimensionless b has dimensions T 2 c has dimensions T d has dimensions of p

Physics
Magnetic FieldWhen a charged particle moving with velocity v is subjected to a magnetic field of induction B the force on it is non zero This implies that AIPMT 2006 1 angle between V and B is necessarily 90 2 angle between V and B can have any value other than 90 angle between V and B can have any value other than zero and 180 4 angle between V and B is either zero or 180 11 L

Physics
Basic PhysicsWhen a current of 1 ampere is passed in a coil lying in the magnetic meridian then a magnetic needle at its centre gives some deflection If the current in the coil is increased to g ampere then at what distance from the centre of the coil will the deflection of needle remains unchanged 1 2R 2 4R 3 8R 4 R

Physics
Magnetic FieldA toroid of mean radius a cross section radius r and total number of turns N It carries a current i The torque experienced by the toroid if a uniform magnetic field of strength B is applied H is zero 2 is BiN nr is iN de on the direction of mognatio fold

Physics
Fluidsddo The fraction of a floating object of volume V and density d above the surface of a liquid of density d will be 4 d do M dd 2 d do d What will be the decreasein volume when a mass M of ice melt

Physics
Current Electricityfigure the circuit is switched on and the variable resistance is adjusted such that the bulb just glows Now if the circuit is switched off www Answer A Your Attempt Rate this question Correct answer the bulb stops glowing

Physics
Magnetic Field due to currentA circular coil of radius 20 cm and 20 turns of wire is mounted vertically with its plane in magnetic meridian A smal magnetic needle free to rotate about vertical axis is placed at the center of the coil It is deflected through 45 whe a current is passed through the coil in equilibrium Horizontal component of earth s field is 0 34 x 10 T The curre in coil is 17 1 A 10t 2 6A 3 6 x 10 A 3 4 A 50

Physics
Basic PhysicsThe Reynolds number of a flow is the ratio of 1 Gravity to viscous force 3 Inertia forces to viscous force 2 Gravity force to pressure force 4 Viscous forces to pressure forces TI

Physics
FluidsBernoulli s equation is applicable to points 1 in a steadily flowing liquid 2 in a stream line 3 in a straight line perpendicular to a stream line 4 for ideal lequid stream line flow on a stream on is based upon
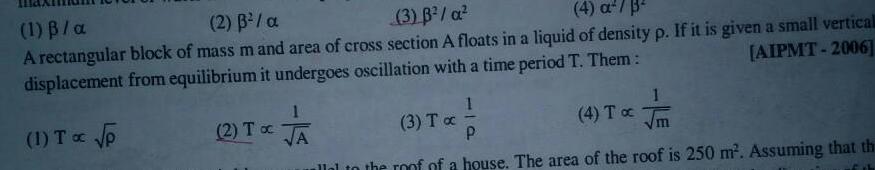
Physics
Simple harmonic motion1 B a 2 3 a 3 B a 4 a 3 A rectangular block of mass m and area of cross section A floats in a liquid of density p If it is given a small verticall displacement from equilibrium it undergoes oscillation with a time period T Them AIPMT 2006 1 T p 2 To A 1 3 Tx 4 To P allal to the roof of a house The area of the roof is 250 m Assuming that th

Physics
Basic PhysicsA combination of two simple harmonic motions with arbitrary amplitudes and phases is not necessarily periodic It is periodic only if frequency of one motion is an integral multiple of the other s frequency However a periodic motion can always be expressed as a sum of infinite number of harmonic motions with appropriate amplitudes The period of SHM does not depend on amplitude or energy or the phase constant phite under gravitation Kepler s third

Physics
NucleusIn the following fig three paths of a particle crossing a nucleus N are shown The correct path is a and c a 2 a and b N b N c 3 a b and c N 4 only a and potential difference between

Physics
Newton's law of motion1 The total momentum of a system of masses i e moving bodies in any one direction remains constant unless acted upon by an external force in that direction This statement is called A Newton s first law of motion B Newton s second law of motion C Principle of conservation of energy D Principle of conservation of momentum

Physics
GravitationA hydrogen balloon released on the moon would 1 climb up with an acceleration of 9 8 m s 3 neither climb nor fall 2 climb up with an acceleration of 9 8 x 6 m s 4 fall with an acceleration of 9 8 6 m s d R floot in water It is observed that A floats with half its volume immersed and B floats wi

Physics
Basic Physicsa Soft iron is a conductor of electricity b It is a magnetic material c It is an alloy of iron d It is used for making permanent magents State whether 1 a and c are true 2 a and b are true 3 c and d are true 4 b and d are

Physics
Circular Motion6 A section of fixed smooth circular track of radius R in vertical plane is shown in the figure A block is released from position A and leaves the track at B The radius of curvature of its trajectory just after it leaves the track at B is A 53013701 I iO B

Physics
Magnetism and MatterA proton and a deuteron moving with equal kinetic energies enter perpendicularly in a region of magnetic field B If r T and r are the radii of circular paths taken by proton and deuteron respectively the ratio T 1 2 2 2 3 2 2 4 2 would be 5552

Physics
FluidsBlood pressure is measured when the blood is pumping systolic and when the heart is resting diastolic When pressure readings are given the systolic is given first and healthy blood pressure is around 120 over 80 mm Hg Recall the density of mercury is 13 6 x 103 kg m3 a Suppose you have a blood pressure reading of 125 over 75 mm Hg What is your systolic pressure in newtons per meter squared b Suppose you have a blood pressure reading of 125 over 75 mm Hg What is your diastolic pressure in newtons per meter squared

Physics
RotationA body of mass M and radius of gyration K is rotating with angular velocity w 3t f rad s The torque acting on it at 1 1 s will be 4MK 5MK 2MK

Physics
Center of mass and momentumTwo particles of masses m and m2 are projected from the top of a tower The particle m is projected vertically downward with speed u and particle m2 is projected horizontally with speed The acceleration of centre of mass of the system is neglect air resistance same Question Type Single Correct Type 1 2 g downward m g m m2 downward

Physics
Electromagnetic InductionA starter is required for a 220 V shunt motor The maximum allowable current is 55 A and the minimum current is about 35 A Find the number of sections of starter resistance required and the resistance of each section The armature resistance of the motor is 0 4 2

Physics
FluidsIn a turbulent flow the velocity of the liquid molecules in contact with the walls of the tube is 1 Zero 2 Maximum 3 Equal to critical velocity 4 May have any value andi try and ovit

Physics
Fluidskg 3 7 5 kg Two vessels A and B of different shapes have the same base area and are filled with water up to the same height h figure The force exerted by water on the base is F for vessel A and F for vessel B The respective weights of water filled in vessels are W and W Then

Physics
Fluids3 2 time that in the other pipe Water enters through end A with speed v and leaves through end B with speed v of a cylindrical tube AB The tube is always completely filled with water In case I tube is horizontal and in case II it is vertical with end A upwards and in case III it is vertical with end B upwards We have v v for 1 Case I 2 Case II 3 Case III 4 Each case ne with a cross sectional area of 4 20 cm The water gradually 10 1 1 4 time that in the other pipe 2

Physics
ThermodynamicsTwo moles of an ideal gas undergoes the cyclic process abcda which is shown in the internal energy vs volume diagram The temperatures of the gas at b and d are 727 C and 327 C Calculate the net heat absorbed by the gas during the process a d V C 2V V

Physics
FluidsHeight of the liquid Air is steaming past a horizontal air plane wing such that its speed in 120 m s over the upper surface and 90 m s at th ower surface If the density of air is 1 3 kg per metre and the wing is 10 m long and has an average width of 2 m the he difference of the pressure on the two sides of the wing of 1 4095 0 Pascal 2 409 50 Pascal 3 40 950 Pascal water Thai 11 30 letale filled in 4 4 0950 Pascal fflux of wntor in m s through a small he

Physics
FluidsA hemispherical bowl just floats without sinking in a liquid of density 1 2 x 10 kg m If outer diameter and the density of the bowl are 1 m and 2 x 10 kgm respectively then the inner diameter of the bowl will be 3 0 98 m 1 0 94 m 2 0 97 m 4 0 99 m

Physics
KinematicsA golfer hits a shot to an elevated green The ball leaves the club with an initial speed of 16 m s at an angle of 58 above the horizontal If the speed of the ball just before it lands is 12 m s what is the elevation of the green above the point where the ball is struck k 5 8 m 4 2 m 2 m 1m

Physics
FluidsA rectangular block is 5 cm x 5 cm x 10 cm in size The block is floating in water with 5 em side vertical If it flom with 10 cm side vertical what change will occur in the level of water 2 It will rise 1 No change 3 It will fall 4 It may rise or fall depending on the density of block toal halls is floating on the surface of water in a tank If the ball are thrown into the tank one by

Physics
Basic PhysicsA siphon in use is demonstrated in the following figure The density of the liquid flowing in siphon is 1 5 gmvcc The pressure difference between the point P and S will be 1105 NIG 10 cm S R 20 cm

Physics
Basic PhysicsA body is just floating on the surface of a liquid The density of the body is same as that of the liquid The body slightly pushed down What will happen to the body 1 It will slowly come back to its earlier position position 2 It will remain submerged where it is left 3 It will sink 4 It will come out violently of the body is same as that of the liquid The bod

Physics
FluidsA bot carrying steel balls is floating on the surface of water in a tank If the ball are thrown into the tank on how will it affect the level of water 1 It will remain unchanged 3 It will fall 2 It will rise 4 First it will first rise and then fall then

Physics
Basic PhysicsA fire hose can expel water at a rate of 9 5 kg s 150 gallons minute with a speed of 24 m s How much force must the firefighters exert on the hose in order to hold it steady 0 23 KN O 0 5 KN 1 5 kN 1 2 KN