Kinematics Questions and Answers

Physics
KinematicsThe x and y co ordinates of a particle at any time t are given by x 2t 5t and y 7t where x and y are in metre and t is in second Velocity of the particle at t 2 s will be Only One Correct Answer G

Physics
Kinematics27 A particle moves in a straight line with a constant acceleration It changes its velocity from 20 m s to 40 m s while passing through a distance 270 m in t second The value of tis 1 9 2 10 4 6 3 12

Physics
Kinematics24 Two blocks A 1 kg and B 2 kg are connected by a string passing over a smooth pulley as shown in the figure 2 134 B rests on rough horizontal surface and A rest on B The coefficient of friction between A B is the same as that between B and the horizontal surface The minimum horizontal force F required to move A to the left is 25 N The coefficient of friction is g 10 m s2 Dar B A 1 kg 2 kg G bots s

Physics
KinematicsA particle is projected with speed 30 m s from the ground at an angle of 37 with the horizontal Change in speed of the particle from initial position to the instant when particle reaches its highest point is

Physics
KinematicsA ball A moving with certain velocity along positive x axis collides another stationary ball B After collision their directions of motion make angles a and B with positive x axis Which of the following values of a and B are possible Only One Correct Answer

Physics
KinematicsObjective Type Questions If the amount of charge passed in time t throug a cross section of wire is Q 8t 212 the average current from t 0 to t 2 second is 1 0 A 3 2 A 2 4 A 4 8 A

Physics
KinematicsA bullet of 4g mass is fired from a gun of mass ongo mathongo mathongo mathongo 4 kg If the bullet moves with the muzzle speed of 50 ms the impulse imparted to the gun and mathongemathongo mathongo mathongo mathongo mathongo velocity of recoil of gun are 1 0 4 kg ms 0 1 ms thongo mathongo mathongo mathongo mathongo 2 0 2 kg ms 0 05 ms matnongo 3 0 2 kg ms 0 1 ms 3 1 4 0 4 kg ms 0 05 ms thongo mathongo mathongo mathongo mathongo mathongo mathongo mathongo mathongo mathongo
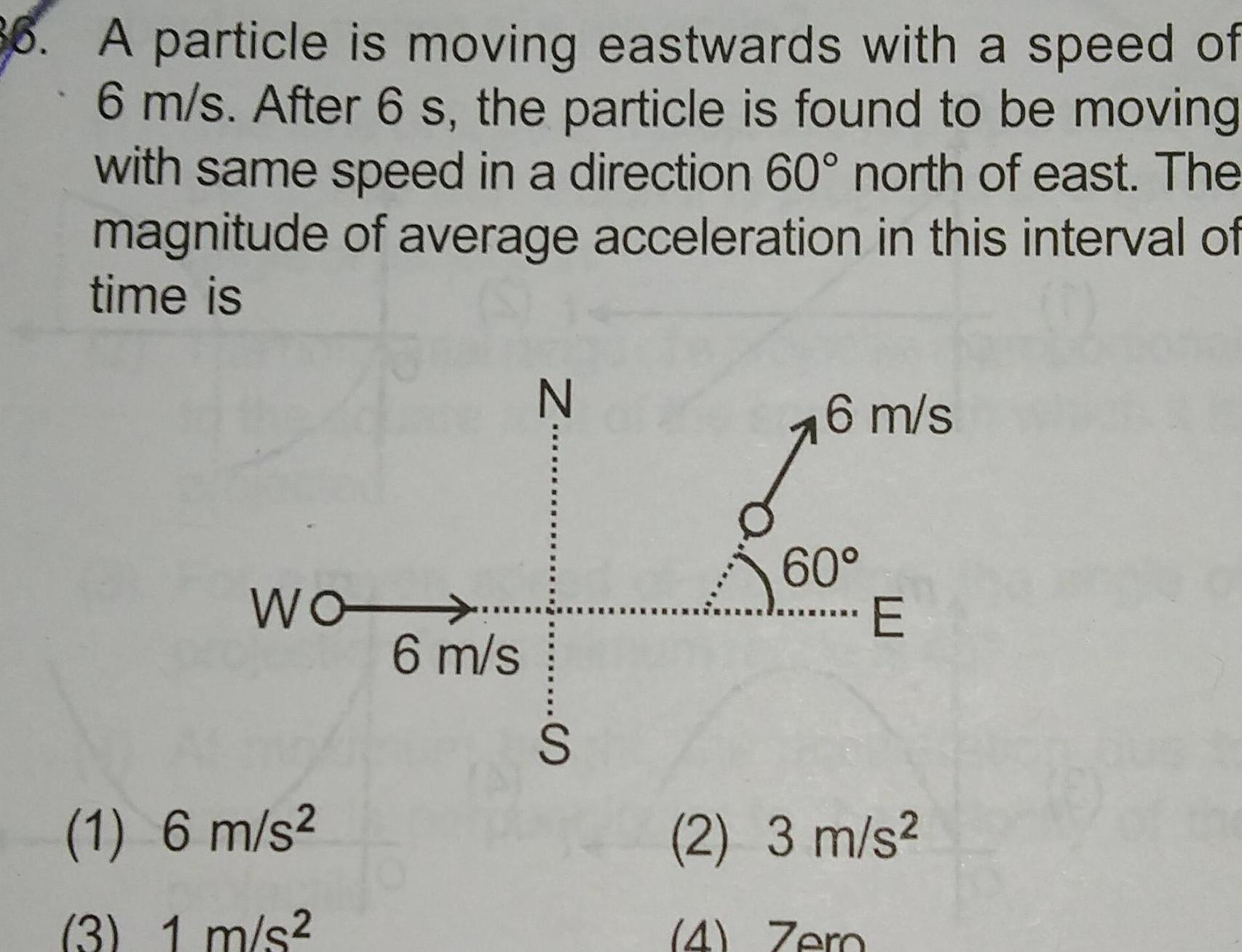
Physics
Kinematics36 A particle is moving eastwards with a speed of 6 m s After 6 s the particle is found to be moving with same speed in a direction 60 north of east The magnitude of average acceleration in this interval of time is WO 1 6 m s 3 1 m s 6 m s Z N S 6 m s 60 E 2 3 m s 4 Zero

Physics
Kinematicslock B is suspended from a cable that is attached to the block at E wraps around three pulleys and is tied to the back of a truck D If the truck starts from rest when and moves forward with a constant acceleration of a 3 2 m s is zero XD if the speed of the block at the instant x 3 m is D A m s 3 m s C 4m E B C D Figure 1 136 2 B m s m 1mla XD

Physics
KinematicsForce is applied on an object of mass 2 kg at rest on a frictionless horizontal surface as shown in the graph The speed of object at t 1 s will be F N 20 A 7 5 m s C 10 m s 10 t s 5 10 B 12 5 m s D 25 m s

Physics
KinematicsParagraph for Question 1 to 3 Rain drops are falling with a velocity 10 2m sec making an angle of 45 with vertical The drops appear to be falling vertically to a man running with constant velocity The velocity of rain drops change such that the rain drops appear to be falling vertically with times the velocity it appeared earlier to the same person running with same velocity The magnitude of velocity of man w r t ground is B 10 3 m s A 10 2 m s C 10m s D 20 m s

Physics
Kinematics1 6 points You are flying a drone in a strong wind The drone controller reports it velocity to be 50 mph 30 east of north The wind is reported to be 120 km hour due east a 2 points Sketch the situation and introduce an appropriate coordinate system b 2 points What is the velocity of the air with respect to the drone c 2 points What is the speed of the air with respect to the drone

Physics
Kinematicsd 4 ms A man walks on a straight road from his home to a marke 2 5 km away with a speed of 5 km h Finding the marke closed he instantly turns and walks back home with a speed of 7 5 km h The average speed of the man over the interva of time 0 to 40 min is equal to AMU Med 2002 a 5 km h b c 30 4 km h d 25 4 45 8 km h km h

Physics
Kinematics1 The distance travelled by a body projected upward during last second of journey is d If the velocity of projection is doubled the distance travelled by the body during the last second of its upward journey is 1 2d 2 4d 3 d 2 4 d

Physics
Kinematics26 From a suitable height two projectiles are thrown simultaneously in horizontally opposite direction with equal speed 20 m s Then the time after which the projectiles will be moving perpendicular to each other is g 10 m s 1 1 s 2 2 s 3 3 s 4 4 s 27 In the situation shown reading of the spring

Physics
Kinematics98 View In English The driver of a car travelling with speed 30 m s towards a hill sounds a horn of frequency 800 Hz If the velocity of sound in air is 330 m s the frequency of reflected sound heard by driver is ct Answer 4 Answer 2 incorrect 500 Hz 550 Hz 555 5 Hz 720 Hz d to Bookmark List Right 00 Complete Question F Peor Stat Unattempted 425 Correct 49 4 Incorrect 8 0 A and B are two thin concentric hollow conducting spheres of radii a and 2a Right Answer 3 Your Answer 1 x 1 4 76s View

Physics
KinematicsOne end of a light spring with spring constant k 1 250 N m is attached to the ceiling A second light spring is attached to the lower end with spring constant k 1 700 N m An object of mass 1 50 kg is attached to the lower end of the second spring a By how much does the pair of springs stretch in m m b What is the effective spring constant in N m of the spring system N m c What If Two identical light springs with spring constant 1 000 N m are now individually hung vertically from the ceiling and attached at each end of a symmetric object such as a rectangular block with uniform mass density In this case with the springs next to each other we describe them as being in parallel Find the effective spring constant in N m of the pair of springs as a system in this situation N m

Physics
Kinematics50 When forces F F and F are acting on a particle 3 2 3 of mass m such that F and F are mutually perpendicular then the particle remains stationary If the force F is now removed then the acceleration of the particle is 1 2 3 F E 14 E tL 2 F F m 1L

Physics
KinematicsTwo trains cross each other in the opposite direction in 40 seconds when the length of the first train is 400 meters while the length of the second train is 800 meters The ratio of the speeds of the first and the second train is 2 1 What will be the time taken by the second train to completely cross the first train when they are running in the same direction O O O 120 seconds 140 seconds 180 seconds 200 seconds

Physics
KinematicsQuestion 4 A man runs across the roof top of a tall building and jumps horizontally with the hope of landing on the roof of the next building which s at a lower height than the first If his speed is 9 m s the horizontal istance between the two buildings is 10 m and the height difference is 9 ill he be able to land on the next building Take g 10 m s

Physics
KinematicsTwo particles A and B of equal masses m are tied with an inextensible string of length 21 The initial distance between A and B is I Particle A is given speed v as shown Find the speed c particle A and B just after the string becomes taut B m

Physics
KinematicsThe surfaces are frictionless The tracks are 60 from horizontal A 494 kg mass is released from rest on a track at a height 2 8 m above a horizontal surface at the foot of the slope It collides elastically with a 591 kg mass initially at rest on the horizontal surface as shown in the figure The mass 591 kg slides up a similar track The acceleration of gravity is 9 8 m s 494 kg 60 591 kg 591 kg What is the speed of the block 591 kg im mediately after the collision Answer in units of m s To what maximum height h above the hori zontal surface will the mass 591 kg slide

Physics
KinematicsQuy A ball is projected from yount A as shown to hit the top of tower at point C buut ball siturkes at point D below the point C yind seperation between pount c and point D Soin Domis A 60 Sm B H C D 90

Physics
KinematicsA golf club and the arms of a golfer together form a lever of 1 800 m During a swing the club head reaches a linear velocity of 200 km h after traveling an arc of 210 degrees from the top of the backswing to the impact of the ball impact Assuming constant acceleration d If the golf club is 1 0 m how much farther linearly does the head of the club move than the does the club head travel than the hands

Physics
KinematicsA golfer hits a shot to a green that is elevated 2 60 m above the point where the ball is struck The ball leaves the club at a speed of 18 8 m s at an angle of 49 0 above the horizontal It rises to its maximum height and then falls down to the green Ignoring air resistance find the speed of the ball just before it lands

Physics
KinematicsThe projection of a particle on to a inclined plane is shown in the figure B is the point at which velocity is parallel to inclined plane Identify the correct options of the following t t are time intervals for the journey AB BC respectively and V V V Vare components of velocities along inclined plane perpendicular to inclined plane 2 N X

Physics
KinematicsA car travels a distance d on a straight road in two hours and then returns to the starting point in next three hours Its average speed and average velocity is 1 0 3 in 5d d 3 2 2d 5 0 4 none of these

Physics
KinematicsA ball is thrown upward with an initial velocity of100 ms After how much time will it return Draw velocity time graph for the ball and find from the graph i the maximum height attained by the ball and ii height of the ball after 15 s Take g 10 ms 2 3

Physics
KinematicsSuppose a boy is enjoying a ride on a merry go round which is moving with a constant speed of 10 m s It implies that the boy is at rest moving with no acceleration moving with uniform velocity

Physics
Kinematics17 To an underwater swimmer at depth 12 below the surface of water a bird at height 18 m above the surface c water appears at height h above the surface of water then h is equal to 2 18 m 4 36 m 1 16 m 3 24 m

Physics
KinematicsA particle of charge q and mass m is projected with velocity 200 m s at an angle of 600 with x axis At the instant speed of projectile becomes minimum a uniform magnetic field B is switched on If time of flight of particle is T then find Given m 1kg q 0 1C B 17 N E

Physics
KinematicsA body is projected with velocity 20 m s making an angle 53 with the horizontal Among the following the time after which its vertical component of velocity is equal to the horizontal component is g 10 m s O 0 2 s 01 s 0 6 s

Physics
Kinematics5 A bus is moving with a velocity 10 ms on a straight road A scooterist wishes to overtake the bus in 100 s If the bus is at a distance of 1km from the scooterist with what velocity should the scooterist chase the bus 10 m s the war and 1 50 ms 4G 436 4 Tfaria yg the HAR DU 100 1 km er at for an a 2 40 ms 3 30 ms 4 20 ms

Physics
Kinematicsre coilless cannon fires a shell with a speed at the same instant a man falls from rest from point O The shell hits a point on the wall Initially shell is aimed towards a point P as shown in figure Mark the correct option s a The falling man sees the shell move along straight line directed along initial velocity b Time taken to reach wall is b o cose c For a stationary man shell will strike below P 2 1 b tan 00 d Man falls through y 8 I PO Jon 2 bu V till the shell hits wall Tann Vo 00 b

Physics
Kinematics2 Find the initial velocity and time for a stone when it will hit a target A fixed on a wooden block P placed at coordinate 3 1 25 metres At t 0 the wooden block begins motion towards the right with an acceleration of 1 5m s2 At the same moment a stone is projected with velocity u from origin towards the falling block The hitting is seen to be occurring at 45 to the horizontal by a stationary person standing on ground for the stone during its downward motion 1 25m 3 0m A t 2 5sec u 6 32m s X

Physics
KinematicsA massless spool of inner radius r and outer radius R is placed against a vertical wall and tilted split floor as shown A light inextensible thread is tightly wound around the spool through which a mass m is hanging There exists no friction at point of contact with tilted floor but it is u with wall The angle between the two surfaces is 0 A Magnitude of force on spool with wall to maintain equilibrium is mg cot 0 R B Magnitude of force on spool from wall to maintain equilibrium is mg 1 cote cot 0 C Minimum value of u to maintain equilibrium is R r tane D Minimum value of u to maintain equilibrium is R M m 0

Physics
KinematicsC1 012 The velocity v of a particle as a function of its position x is expressed as v C C x where c and C2 are positive constants The acceleration of th particle is a C2 c C C b d 1 C2 2 G C2 C 2

Physics
KinematicsA lamp post of length and cross sectional area S 10 cm is made of material with linear expansion coefficient a 1 1 x 10 5 K and Young modulus Y 2 0 10 N m If temperature of lamp post is raised by AT 10 K what mass in kg should be put on the lamp post so tha there is no change in the length of lamp post g 10 m s

Physics
KinematicsThe x and y components of vector 4 are 4 6m respectively The x y components of vector A B are 10m 9m respectively The angle made by axis O O O tan 2 n 1 tan tan 1 4 B with X Clear Response

Physics
Kinematics8 What vertical launch speed is necessary to get a rocket to an altitude of 500 km Bonus question by how much would you overestim the launch speed if you did not account for the change of gravity with altitude

Physics
KinematicsTwo strings made of same material and have same cross sectional area are arranged as shown in the figure The pulley is ideal The wave speed of a transverse wave in the string AB is v and in CD it is vz The ratio will be V 2ny 20 v wg v 2mg 20 B VI 2 sionung ng A T 1 2 1052 ig 2 1 4 10 wwwwwww V2

Physics
KinematicsA particle of mass 1gm and charge 0 1 C is projected from ground with a velocity 10v2 at an 45 with horizontal in the area having uniform electric field 1 KVicm in horizontal direction Acceleration due to gravity is 10m s2 in vertical downward direction Select incorrect statement Time of flight for particle is 2 sec Range of particle is 20 m Total displacement of particle is om Particle will follow straight line motion 10 2 ZE vg 45

Physics
KinematicsA particle is to be projected so as to just graze each of the three identical rings of diameter 2 meter each and placed in parallel vertical planes at a distance 4 meter apart with their highest points at a height 6 meter above the point of projection If the angle of projection is 15K degree then find the value of K take g 10 m s y fur be

Physics
Kinematics75 A block of mass 5 kg is suspended by a massless rope of length 2 m from the ceiling A force of 50 N is applied in the horizontal direction at the midpoint P of the rope as shown in the figure The angle made by the rope with the vertical in equilibrium is Take g 10 m s m 5 kg S b 40 d 45 a 30 c 60 1 m P 1 m 50 N

Physics
KinematicsTwo stones projected with the same velocity but with different angles of projection with the horizontal have the same horizontal range If the angle of projection of one is 60 and the maximum height reached by it is 120 m What is the maximum height reached by the other O O O 360 m 120 m 200 m

Physics
KinematicsA stone is projected with a velocity v in the gravitational field of the earth making an angle with the horizontal A strong wind imparts a constant horizontal acceleration to the stone Which one of the following quantities associated with the stone is changed O Maximum height h O O C Vertical component of its velocity vy Horizontal range Total time of flight T

Physics
KinematicsTwo projectiles of the same mass have their maximu kinetic energies in ratio of 4 1 and the ratio of the maximum heights is also 4 1 What is the ratio of the horizontal ranges O O C 2 1 4 1

Physics
KinematicsA projectile has initially the same horizontal velocity as it would acquire if it had moved from rest with uniform acceleration of 3 m s for 0 5 minute If the maximum height reached by it is 80 m then the angle of projection is Take g 10 m s O O O tan 3 tan tan la

Physics
KinematicsA body starting from rest accelerates uniformly at the rate of 10 cm s2 and retards uniformly at the rate of 20 cm s Find the least time in which it can complete a journey of 5 km if the maximum velocity attained by the body is 72 km h Question Type Single Correct Type 1 2 3 400 sec 500 sec 300 sec

Physics
KinematicsTwo projectiles A and B thrown with speeds in the ratio 1 2 acquired the same maximum heights If A is thrown at an angle of 45 with the horizontal the angle of projection of B will be O O O 0 60 30