Molecular Basis of Inheritance Questions and Answers

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceIn terms of gene expression genes have the control to be A turned on and off B expressed genotypically C expressed without energy use D removed

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceIn terms of evolution oognesis can be to the organism as its resources can be focused towards individuals deleterious B advan tageous selected against

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritancePart 4 Mutations How does mutation in a bacterial genome contribute to the development of antibiotic resistance

Biology
Molecular Basis of Inheritance6 Describe meiosis and identify diploid to haploid cells Give the stages of the process 7 When during meiosis do you have crossing over 8 How is mitosis and meiosis different List 3 ways 9 DNA controls the cell by coding for proteins how does this information get out to the cell so it can make proteins

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceWhich of the following is NOT part of a gene A coding B stop C repair D promoter

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceThe region of the gene is where the reading of the molecule begins A operon B stop C promoter D DNA primer

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceWhich of the following is NOT a difference between DNA and RNA A number of helices B type of sugar C types of nucleotides D presence of guanine

Biology
Molecular Basis of Inheritanceon the Human Insulin and Cow Insulin charts that each of these Coded portions would produce In addition for the DNA sequences above write the complementary mRNA base sequence to the Amino Acid translations in the tables below 2 DNA Sequence mRNA Sequence Amino Acid 1 CCA 2 TAG Human Insulin 3 4 CAC CTT 5 GTT 6 ACA 7 ACG 8 TGA

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceSelect the best answer for the question 3 Cystic fibrosis is a recessive genetic disease caused by a mutation in the gene that encodes the CFTR protein which transports chloride ions in and out of cells Some populations have a relatively high rate of cystic fibrosis carriers possibly because the mutation protects against severe dehydration in diseases like cholera or typhoid What concept does this best illustrate OA Pleiotropy O B Polygenic traits OC Genetic drift O D Heterozygote advantage O Mark for review Will be highlighted on the review page

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceQ5 Humans carry a variety of non functional genetic sequences called processed pseudogenes in their DNA We can estimate how long ago these sequences first appeared in the genomes of our ancestors In humans processed pseudogenes include the three options below Which of these would be least widespread among other primate species alpha enolase psi 11 million years old AS psi7 16 million years old CALM II psi3 36 million years old

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceQ4 9 Which of the following segments of DNA would require the most energy to separate the two strands Segment A PC Ga PG CQ PG CQ PT AQ PT AQ PA TQ Segment A Segment B PA TO PT AQ PG cq PG cq PA TQ PT Ad Segment B Segment C PC Ga PA TO PC Ga PC Ga PA Ta PG Ca Segment C Segment D PG CQ PC Ga PC Ga PA TO PC Ga PG Ca Segment D

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceThe pedigrees are for a rare autosomal trait What is the chance that individual A is a carrier 2 3 O 1 4 0 1 1 2 0 5600 00000 O A B

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceQ4 2 In the diagram below showing four DNA replication bubbles RNA primers are shown as red while DNA is black Which bubble has the correct 5 and 3 labels 53 3 5 5 3 A 3 5 3 5 Bubble A Submit 3 B 15 53 Bubble B 5 C 15 3 5 Bubble C 5 13 Bubble D 3 5 5 5 3 3

Biology
Molecular Basis of Inheritancec Similar amino acid sequences for the enzyme cytochrome c are found different species The chart shows the amino acid sequences for a segment of cytochrome c found in humans pigs chickens and fruit flies What does this information suggest about the ancestry of these organisms What does it indicate about the relationships between humans and the other species listed Use mathematical comparisons in your explanation 2 points Hu ma n Pi g As Gly p Val As Gly p GI Ly Ly Ph uss lle e GI Ly Ly Val us S lle Ph e Me Ly llet s Gl Ly S Val n Cy Se sr Gl Cy n S Cy Al GI Cy sa n s

Biology
Molecular Basis of Inheritance20 This is the protein on the target cell that HIV uses for attachment A CD4 B CD8 C CXCR4 D gp16 E gp120 21 Transcription begins at a an A Operator B Operon C Promoter D Start codon E Terminator

Biology
Molecular Basis of Inheritancepassive transport mechanisms used by cells to test your understanding of active and passive transport Check All That Apply Simple diffusion Carrier mediated active transport Group translocation Facilitated diffusion

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceDuring translation a one mRNA molecule works with several rRNA molecules and many tRNA molecules to produce a protein b one tRNA molecule works with paired mRNA molecules and many rRNA molecules to produce a protein c many mRNA molecules work with one tRNA molecule and one rRNA molecule to produce a protein d strings of bonded tRNA molecules work with one mRNA molecule and one rRNA molecule to produce a protein

Biology
Molecular Basis of Inheritancevbout 50 of cases of viral hepatitis in US are caused by HBV which is one examp eveloped DNA virus Why is then HBV classified as a reverse transcribing virus HBV infections range from acute to chronic how do chronic infections can affect the population

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceRNA polymerase adds an RNA nucleotide complementary to strand s of the DNA molecule during transcription A the lagging and leading B one C both D the lagging

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceSE 7 How do the catabolite activator and lac repressor proteins contribute to regulating lac o expression in E coli

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceHow many different codons code for serine SER 38 Arg R Ser 5 Lys 8 D 80 U G A 32 A chaubre 0 00 0 13 C Mac M C Phe GU AC Levi 25 NOU GUC 16 chacho FE A UG JUGA CUCA ar A G U C 10 05 Cye 1 Tep Wy Law B Stop First letter UUU UUUC UUA UUG C G Speed 1x CUU CUC CUA CUG Phe QUU GUC GUA GUG Leu AUU AUC lle AUA AUG Met Val Second letter C UCU UCC Ser UCA UCG CCU CCC CCA CCO ACU ACC ACA ACG OCU GCC GCA GCG Pro Thr Ala UAU UAC CAU CAC CAA CAG Tyr Cys UAA Stop UGA Stop UAG Stop UGG Trp AAU AAC AAA AAG GAU GAC GAA GAG His Gin Asn Lys G Asp Glu UGU UGC COU CGC CGA CGG AGU AGC AGA AGG GGU GOO GGA GGG Arg Ser Arg Gly Paus

Biology
Molecular Basis of Inheritance21 Two genes in a genetic cross appear to be unlinked when A crossing over occurs during second meiotic anaphase B the frequency of parental types exceeds that of recombinants in the test cross C the centromere is located between them on the chromosome D alleles pair during S phase E chromosomes align during telophase I of meiosis 22 We used A polyacrylamide SDS gel electrophoresis B Qiaquick DNA cleanup to purify a genomic DNA digest from RE EcoRI C Ni chelate spin column and elution with imidazole D PCR and DNA sequencing to detect SNPs E Reverse Transcription and Western blotting to detect Alu polymorphism

Biology
Molecular Basis of Inheritance8 is the molecule that causes translational miscoding A kanamycin B NNRTI C ddNTP D HIV1 protease inhibitor E puromycin 9 The best example of R group covalent bonding in protein is A Asp Lys B Ser Gin C A U base pair D Phe Leu E S S in Cys Cys SE 1 What do rheumatoid arthritis systemic lupus erythematosus multiple sclerosis and Type I diabetes have in common and what general treatment is used for the first two ailments 10

Biology
Molecular Basis of Inheritance15 would be a result of his A transcription activation B selective degradation of mRNA via ubiquitination C Alu transposition D chromatin compaction E repression of lactose operon 16 are most commonly used in CODIS A STDs B STRS C LINES D SINES E SNPs

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceLagging stand A DNA polymerase B shown in the diagram below XII 0 00 0 13 Leading stand DUN C transcription Original DNA translation Okazaki fragment RNA primer Primase Helicase Speed 1x Topoisomerase XD Parent DNA 00 Paused

Biology
Molecular Basis of Inheritance10 Electrophoresis gels containing polyacrylamide and SDS are most often be used to A affinity purify recombinant cholesterol B sequence RNA segments C translate DNA from mRNA D separate DNA fragments based on size E separate unfolded polypeptides based on size 11 2 pt each 36 Q total 45 pts answer all Qs on Exam remains the same between alleles in a single locus STR or VNTR A Resistant retrovirus arising from lack of proofreading activity B Length and sequence within the repeat C Non Mendelian epistasis D Hardy Weinberg E The number of repeats equilibrium 12 BLASTn could be used to A determine mitochondrial haplotype defining SNPs B determine the sequence of a lipopolysaccharide fragment C find H sapiens homolog of S cerevisiae protein D clone cut DNA fragments E visualize puffs in polytene chromosomes

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceV Arg R Ser K A Aan NO AND JDS C A 66 CHOUCHOUCAGUCA 6U343 The Lex P 2 GUC G U A C 16 UG CACES proek ERS 51 Oco CHP 105 Hs EHS tw C C Hig P Tre W Lau 2 Start Stop First letter JUU UUUC UUA UUG CUU CUC CUA CUG Phe GUL GUC GUA GUG Leu Leu Second letter Val UCU UCC UCA UCG AUU ACU AUC lle ACC AUA ACA AUG Met ACG COU CCC CCA CCG GCU GCC GCA GCO Ber Pro Thr Ala UAU UAC Tyr Cys UAA Stop UGA Stop UAG Stop UGG Trp CAU CAC CA CAG AAU AAC AAA AAG GAU GAC GAA GAG His Gin Aan Lys Asp UGU UGC Gl CGU CGC CGA CGG AGU AGC AGA AGG GGU GGC GGA GGG Arg Ser Arg Gly JURG 5040 5040 5040 Third letter

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceCH 0 00 0 05 tRNA codon mRNA Speed 1x a sequence of three bases Pa b brings the genetic code from the cleus to the cytoplasm

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceRetrotransposons are A STRS B intermediately repetitive and tandemly repetitive C LINES D single copy E Alu elements 14 Sugar and nitrogenous base in a nucleoside are covalently linked by the A alpha helix B peptide bond C beta strand D N glycosidic bond E phosphodiester bond

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceDL A Normal Mutation is a change in DNA sequence Insertion CTTGTAGTAS GTGAACATCAT GG C CACTTGT AGG TACC GTGAA CATCCATGG Mutation is changge n DNA sequence C insertion CACTTGTATAC CGA Deletion GTGAA CATATGGCT Mutation is chanen DNA sequence
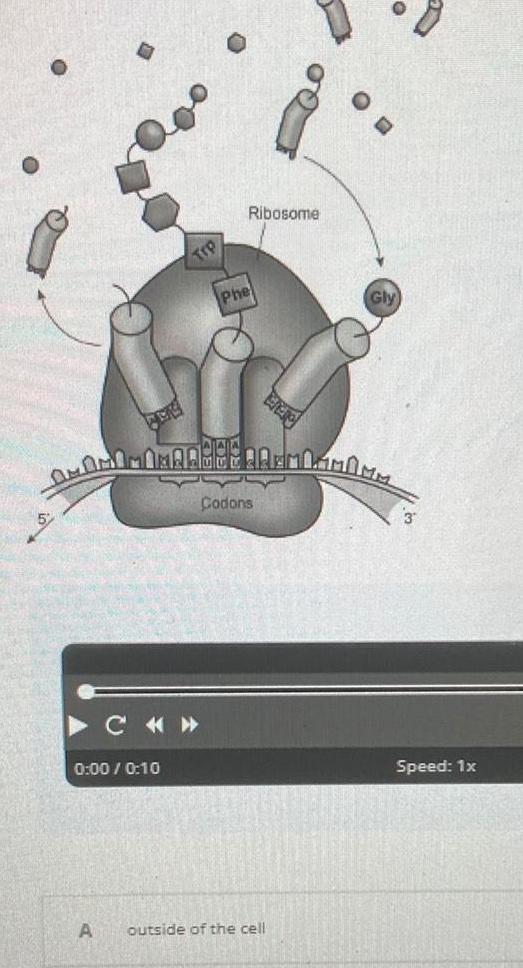
Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceC AHOO AREM LMMMM 0 00 0 10 Ribosome Phe DINA Codons A outside of the cell Speed 1x

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceWhat is the corresponding mRNA sequence from the DNA strand Remember the base pair rule shown below C G A U CGA TTA CAG produced as a result of transcription

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceQuril 0 00 0 23 A C H B Cas Abelone Speed 1x The transfer of the instructions from the nucleus to the cytoplasm The process in which the genetic code in mRNA is read to make a protein The transfer of genetic instructions in DNA to mRNA

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceC 0 00 0 21 A B RNA ANNAR Speed 1x DNA is being transcribed into mRNA mRNA is being translated into amino acids DNA Paused

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceDNA RNA PROTEIN A B C EE GLU NORMAL PROTEIN NORMAL HEMOGLOBIN MUTATION GUG VAL MUTANT PROTEIN CLUMPED HEMOGLOBIN It will have no effect on the organism It will probably be beneficial to the organism It will affect the shape of the hemoglobin protein

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceThe graphic below shows the central dogma of molecular biology Press the hotspot that indicates which portion represents transcription C 0 00 0 11 Speed 1x Paused

Biology
Molecular Basis of Inheritanceheterozygous genotype homozygous dominant genotype homozygous recessive genotype phenotype a b C aa AA black fur d Aa

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceCH 30 0 09 genotype Homologous pair chromosome 1 Homologous pair chromosome 2 Paternal copy from father Maternal copy from mother Speed 1x Pau

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceMultiple Choice O O O Uracil Adenine Thymine Cytosine All of these are pyrimidines

Biology
Molecular Basis of Inheritance25 66 Refer to Problem 25 65 What sequence appears on the mRNA molecule transcribed from the DNA sequence T A C C C T Label your answer with 3 and 5 ends what dipeptide is 7367 Keter To ProDICION synthesized from the informational DNA sequence T A C C C IY

Biology
Molecular Basis of Inheritance5 77 A normal hemoglobin protein has a glutamic acid at posi tion 6 in sickle cell hemoglobin this glutamic acid has been replaced by a valine List all the possible mRNA codons that could be present for each type of hemoglobin Can a single base change result in a change from Glu to Val in hemoglobin

Biology
Molecular Basis of Inheritance5 out of 5 points How can Humans get over 80 000 different mRNA sequences which is how much we are known to make from just 20 000 genes roughly all we have in are genome Question 27

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceExons AND Introns which can be spliced are found in O Non coding intergenic DNA only O The genes of Eukaryotes O The genes of Bacteria O The non coding intergenic dna of Bacteria

Biology
Molecular Basis of Inheritance25 63 What anticodon sequences are complementary to the codons listed in Problem 25 62 Remember that the anticodons are opposite in direction to the codons so label the 3 and 5 ends codons for Remember trees are complementary to the 1 anticodone are rec

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceWhy do we say that DNA replication is semiconse ive on and leic acid is it found It found son What kind of sucher dis

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceExons AND Introns which can be spliced are found in stion 18 When DNA is used to make a complimentary strand of mRNA this is called

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceX 0 out of 3 points Which of the following is a disfunctional remnant of a retrovirus that was inserted into a genome and continues to excise remove and reinsert itself throughout the genome Xover generations uestion 20 estion 21 3 out of 3 points

Biology
Molecular Basis of Inheritancex Parental population Offspring population FIX S Xf R p Xp Phenotipic values Phenotipic values

Biology
Molecular Basis of Inheritance0 00 0 24 A C B Speed 1x Pau Genetic drift can occur due to the bottleneck effect when a few individuals start a new population Genetic drift can occur due to the bottleneck effect which may happen after a forest fire

Biology
Molecular Basis of InheritanceOrganisms inherit specific traits and characteristics from their parents Albinism is an inherited disorder that occurs when an organism is unable to produce or distribute melanin Melanin is a substance in the body that helps determine skin color hair color and eye color Which is the basic unit of heredity that carries the trait of albinism from parent to offspring base pairs genes 59 55 proteins