2D Geometry Questions and Answers
Geometry
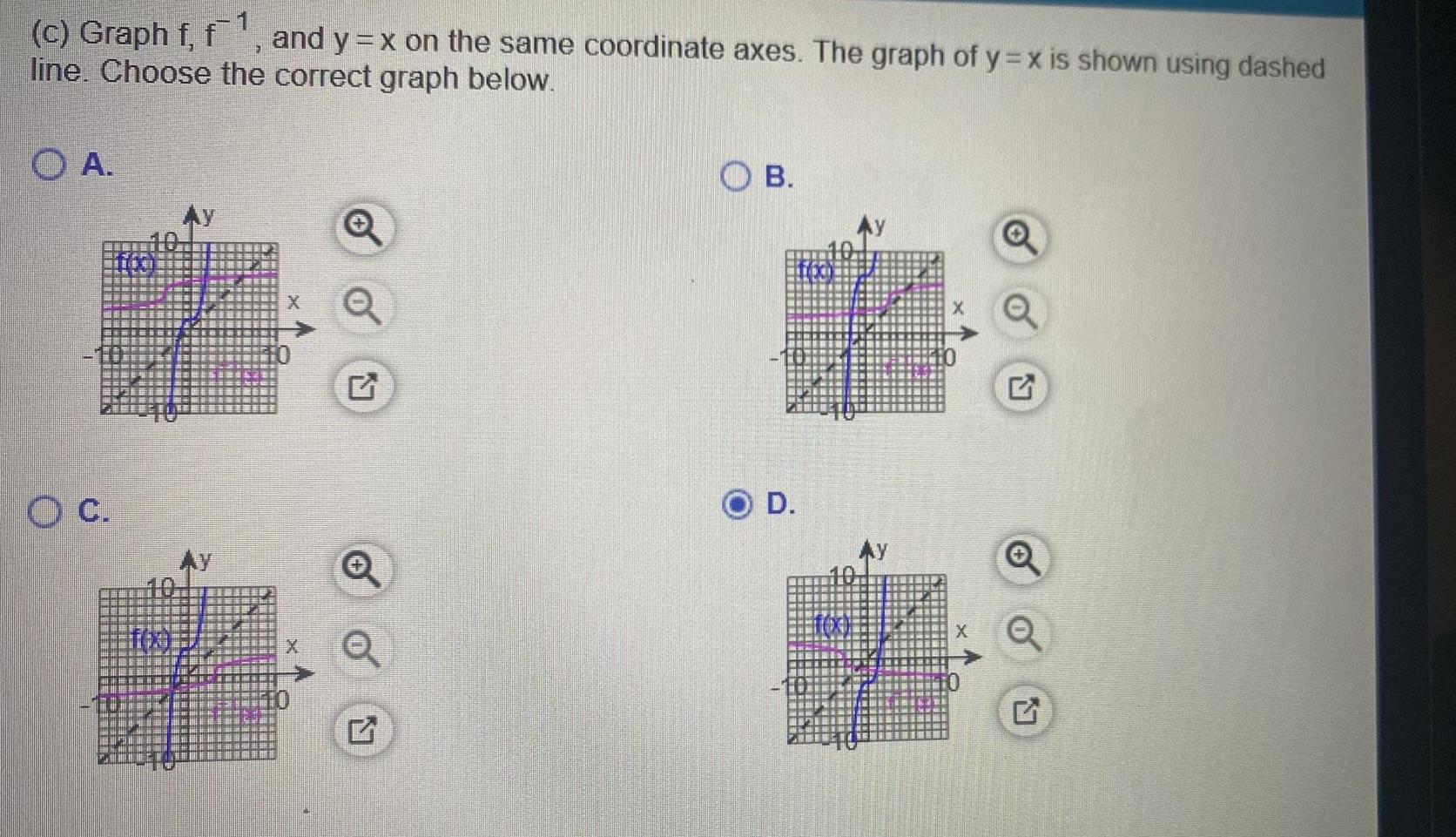
2D Geometryc Graph f f and y x on the same coordinate axes The graph of y x is shown using dashed line Choose the correct graph below A OC O Q B D L

Geometry
2D GeometryD G N PR 9 A AV 77 Congruence Stmt 250 Congruence Stmt h Congruence Stmt A Reason Reason Reason 7 10 U V W A Y X Congruence Stmt A Reason 8 11 M Congruence Stmt A Reason K 12 D Congruence Stmt 4 Reason F E LE AN


Geometry
2D GeometryDirections You will be designing a city map using the guidelines listed below You will be graded on content creativity and neatness Guidelines 1 Your city must have two streets that are parallel to each other and one street that intersects the parallel streets You must name all of these streets after streets in your city 2 Your city has a hospital that is on one of the exterior angles Draw and name the hospital 3 The school is alternate exterior to the hospital that is in your city Draw and name the school 4 The school and the pet shop are at corresponding locations Draw and name the pet shop gas station 5 The pet shop and the gas station are at alternate interior locations Draw and name the 6 The gas station and the park are at same side interior locations Draw and name the park 7 The park and the grocery store are at alternate interior locations Draw and name the grocery store 8 The grocery store and the restaurant are at vertical locations Draw and name the restaurant 9 The restaurant and your house are at alternate exterior locations Draw and name your house ric ent ivity ess 50 points 25 points 25 points 5 points for each guideline that was correctly followed Does your drawing look like a city Did you take the time to make your buildings look good and your streets look good Are they origi Is it colorful Did you use a straightedge to draw your streets Did you write neat and spell correctly

Geometry
2D GeometryA cruise ship maintains a speed of 12 knots nautical miles per hour sailing from San Juan to Barbados a distance of 600 nautical miles To avoid a tropical storm the captain heads out of San Juan at a direction of 38 off a direct heading to Barbados The captain maintains the 12 knot speed for 11 hours after which time the path to Barbados becomes clear of storms a Through what angle should the captain turn to head directly to Barbados b Once the turn is made how long will it be before the ship reaches Barbados if the same 12 knot speed is maintained a The captain should head through an angle of Do not round until the final answer Then round to one decimal place as needed Barbados 600 O 38 San Juan

Geometry
2D Geometry5 2 determine the exact value coS X COS X Simplify your answer including any radicals Use integers or fractions for any numbers in the expression Rationalize all denominators

Geometry
2D GeometryProblem A ship is sailing east At one point the bearing of a submerged rock is 47 20 After the ship has sailed 16 4 miles the bearing of the rock has become 380 40 Find the distance of the ship from the rock at the latter point ZA N G Rock LI

Geometry
2D Geometryhorizontal plane non horizontal plane circular cylinder parabolic cylinder ellipsoid elliptic paraboloid hyperbolic paraboloid cone hyperboloid one sheet hyperboloid two sheets 2 z 6x 2y 3 z y 3x 4 z 3 5 3x 6y 22 4 6 6y z 4

Geometry
2D GeometryK Write the expression as a product of trigonometric functions cos 10x cos 4x cos 10x cos 4x

Geometry
2D GeometryThe following data lists the number of correct and wrong dosage amounts calculated by 32 physicians In a research experiment a group of 19 physicians was given bottles of epinephrine labeled with a concentration of 1 milligram in 1 milliliter solution and another group of 13 physicians was given bottles labeled with a ratio of 1 milliliter of a 1 1000 solution If one of the physicians is randomly selected what is the probability of getting one who calculated the dose correctly Is that probability as high as it should be Correct Dosage Calculation Wrong Dosage Calculation 15 4 Concentration Label 1 milligram in 1 milliliter solution Ratio Label 1 milliliter of a 1 1000 solution P physician calculated the dose correctly Round to three decimal places as needed SLICA Points 0 of 2 3 10 C

Geometry
2D Geometrysin 5x 12 5x Choose the correct expanded form of sin using the sum or difference formula for sine 12 5x A sin sin 12 5x B sin sin 12 5x c sin 12 OD sin 5x 12 sin sin K4 3x 54 K4 3x 96 W 3 R6 73 T K sin cos 6 cos 4 sin 6 IS COS sin 3x 4 I os 3 sin 4 COS 3x sin T T T I 4 cos 6 cos 4 sin 6 3x COS cos sin 4 3x 4 W 3 sin 3 5x The exact value of sin 12 Simplify your answer including any radicals Use integers or fractions for any numbers in the expression

Geometry
2D GeometryThe expression below simplifies to a constant a single function or a power of a function Use fundamental ident to simplify the expression sin x 2 COS X sin x 2 cos x secx cos x secx

Geometry
2D GeometryEach of the regions A B and C bounded by the graph of f and the x axis has area 3 y B W 12 2 A C 4 Find the value of L r x 2x 4 dx

Geometry
2D GeometryClick here to watch the video 40 Given that cos 0 and sin 8 0 determine the values of the sine and cosine functions for 20 41 sin 20 Type a simplified fraction

Geometry
2D GeometryWatch the video that describes expressing cos A B as a function of a single variable Click here to watch the video Write the expression as a function of a alone cos 270 a

Geometry
2D GeometryThree atoms with atomic radii of 4 0 5 0 and 5 9 are arranged as in the figure Find the measure of the angle at the center of atom B inside the triangle 4 0 5 0 B A 5 9


Geometry
2D GeometryEXPLAIN 1 Using Vertical Angles Read Explain 1 and complete Your Turn 1 3 adapted from Lesson 4 1 Show all your work You can use the Vertical Angles Theorem to find missing angle measures Example A Find the angle measures 1 What is the measure of ZDEB Find the value of x mzAEC m2DEB 101 4x 3 104 4x Vertical angles are congruent 26 x So the value of x is 26 and m DEB 101 mLAED mLDEB 180 x 101 180 x 79 mLAED 79 mLAED m2CEB mLCEB 79 Substitute angle measures Add 3 on both sides Your Turn 1 Find the value of x 2 What is the measure of LAED What is the measure of ZCEB LAED and LDEB form a linear pair so they are supplementary Divide by 4 on both sides Definition of supplementary angles Substitute angle measures Subtract 101 on both sides Substitute x for its angle measure Vertical angles are congruent Transitive Property S D 2 The measure of two verticle angles are 58 and 3x 4 Find the value of x 101 4x 3 5x 11 P T 4 x 6 B R

Geometry
2D GeometryTWO 0 10 C so P T L A 44 y Show Transcribed Text Calculate the angle delta theta CA 23 98

Geometry
2D GeometryQuestion 3 of 5 3 A particular vehicle gets an average of 35 mpg on the highway Is 35 mpg a parameter or statistic Q Parameter Statistic Continue Reset answer

Geometry
2D GeometryHW When you are finished check the solutions with your teacher Convert the following vector into coordinate notation rule 3 1 2 Convert the following vector into coordinate notation rule 4 7

Geometry
2D GeometryFind the Reference Number t bar and the Terminal Point for each value of t To receive full credit you must clearly show how you got these numbers by drawing Unit Circle and showing what it is 5 d t 5

Geometry
2D GeometryA 16 ft ladder leans against the side of a house The bottom of the ladder is 6 ft away from the side of the house Find x the angle of elevation of the ladder Round your answer to the nearest tenth of a degree 16 XA X 68 0 X

Geometry
2D Geometryrag each equation to the correct location on the table Not all equations will be used etermine which equations represent lines that are parallel or perpendicular to the linear equation provided on the graph y y 4 5 y 8 y 2x 2 8 6 4 2 Parallel Line x 3 8 6 4 S 2 2 4 6 0 to 2 A 4 y 6 8 2x 1 Perpendicular Line


Geometry
2D Geometry8 AS A M is the result of rotating ASAM by 50 about Point C If the length of S C is 6 then the lengths of SC is 6 What is the measure of LA CA What is the measure of ZMCM

Geometry
2D GeometryT 8 The circle at right has its center at 1 2 instead of 0 0 The radius is still 5 Move the purple point to a point on the circle whose x value is 4 What is the horizontal distance between these points VE Submit

Geometry
2D Geometry3 Determine if the triangles can be proven to be congruent If so complete the congruence statement and provide reasoning SAS SSS or HL If they can t be proven congruent write CBD Cannot Be Determined b X AARC BA Reasoning W AYZW A Reasoning APSQ A Reasoning


Geometry
2D Geometry5 The function g has a zero at 4 with multiplicity 2 a zero at x 1 with a multiplicity 3 and a zero at x 4 with multiplicity 1 Sketch a possible graph of g x 3 2 5A 4 3 2 1 0 1 3 6 3 4 5 x

Geometry
2D Geometry2 Write a proof Given CA a CD B is the midpoint of AD Prove ACAB ACDB B Statements Reaso

Geometry
2D GeometryConsider the following y 4 cot Find the period Give the equations for two consecutive vertical asymptotes for the graph of the function Enter your answers as a comma separated I X TX 5 Consider the following y 3 tan 2x Find the period Give the equations for two consecutive vertical asymptotes for the graph of the function Enter you

Geometry
2D GeometryUse the parent function f x b and transformation techniques to graph g x e 1 Also indicate which transformation s is are applied Determine the domain range and horizontal asymptote of 9 Select all transformations that apply Vertically compress the graph of f by a factor of 6 Shift the graph of f 1 unit up Shift the graph of f 1 unit down Reflect the graph of f about the z axis Reflect the graph of f about the y axis Horizontally stretch the graph of f by a factor of 1 Vertically stretch the graph of f by a factor of 1 Shift the graph of f 6 units to the right Horizontally compress the graph of f by a factor of 6 Shift the graph of f 6 units to the left

Geometry
2D GeometryUse the parent function f x b and transformation techniques to graph h z 2 1 Also indicate which transformation s is are applied Determine the domain range and horizontal asymptote of h Select all transformations that apply Reflect the graph of f about the z axis Shift the graph of f 1 unit down Reflect the graph of f about the y axis Shift the graph of f 1 unit up Vertically compress the graph of f by a factor of 1 Horizontally compress the graph of f by a factor of 1 Vertically stretch the graph of f by a factor of 1 Shift the graph of f 1 unit to the right Shift the graph of f 1 unit to the left Horizontally stretch the graph of f by a factor of 1

Geometry
2D GeometryAB FE In 3 4 find the length of indicated sides d x x y y and use a protractor to measure the indicated angle Mark congruent angles and sides If the triangles are congruent write a triangle congruency statement by SAS 3 E 8 F 6 4 D 2 8 DE 4 6 2 BC ongruence Statement 81 2 6 4 A B 02 4 6 8 m B m E 4 8 6 4 2 D BR AD 8 6 4 2 2 10 4 R 6 8 2 BG 4 AM B 6 Congruence Statement G 8 m B m A


Geometry
2D GeometryComplete the process of solving the equation Fill in the missing term and select the missing description Simplify any fractions 8 x 5 16 X 5 2 X Add 8 to both sides Subtract 8 from both sides Multiply both sides by 8 Divide both sides by 8 Combine like terms

Geometry
2D GeometryRuby is visiting San Francisco From her hotel she walks 1 block east and 2 blocks north to a coffee shop Then she walks blocks west and 3 blocks north to a museum Where is the museum in relation to her hotel The museum is block s and block s of her hotel

Geometry
2D GeometryEcologists surveying a location often need to calculate the area of irregular regions For example they may need to find the area of the home range of a marked animal with known multiple locations This calculation is done by recording certain lengths and angles associated with the region An example of such a region is shown in the figure The lengths are measured in meters b 110 az 40 A 20 a 200 F 70 C Macmillan Learning ration for Calculus 102022 Find the unknown sides and angles in the figure Use decimal notation Give your answers to one decimal place where needed Include the degree symbol in your answers where needed m C m

Geometry
2D GeometryOne of the two sets of functions f1 fa f3 or g1 92 93 is graphed in the figure to the left below the other set is graphed in the right figure Points A and B each have x 0 Taylor polynomials of degree 2 approximating these functions near x 0 are as follows fi x 4 x 2x 91 x 2 x x f2 x 4 x 2x 92 x 2 x x f3 x 4 x x 93 x 2 x 2x 11 a Match the functions to the appropriate figure f matches C g matches C b What are the coordinates of the points A and B A B 2 O B c Match each function with the graphs a c in the appropriate figure f f fs O 91 O 92

Geometry
2D Geometry2 a Sketch the polar graph of r 0 the interval 0 2 How many petals do you see sin 20 in b Which values of 0 correspond to the petal in the first quadrant c Experiment with the polar graphs for r 0 sin k0for other integer values of k Make a conjecture about the connection between the integer k and the number of petals in the polar graph for values of 0 in the interval 0 2 Fill in the blanks When k is odd the number of petals equals When k is even the number of petals is
Geometry
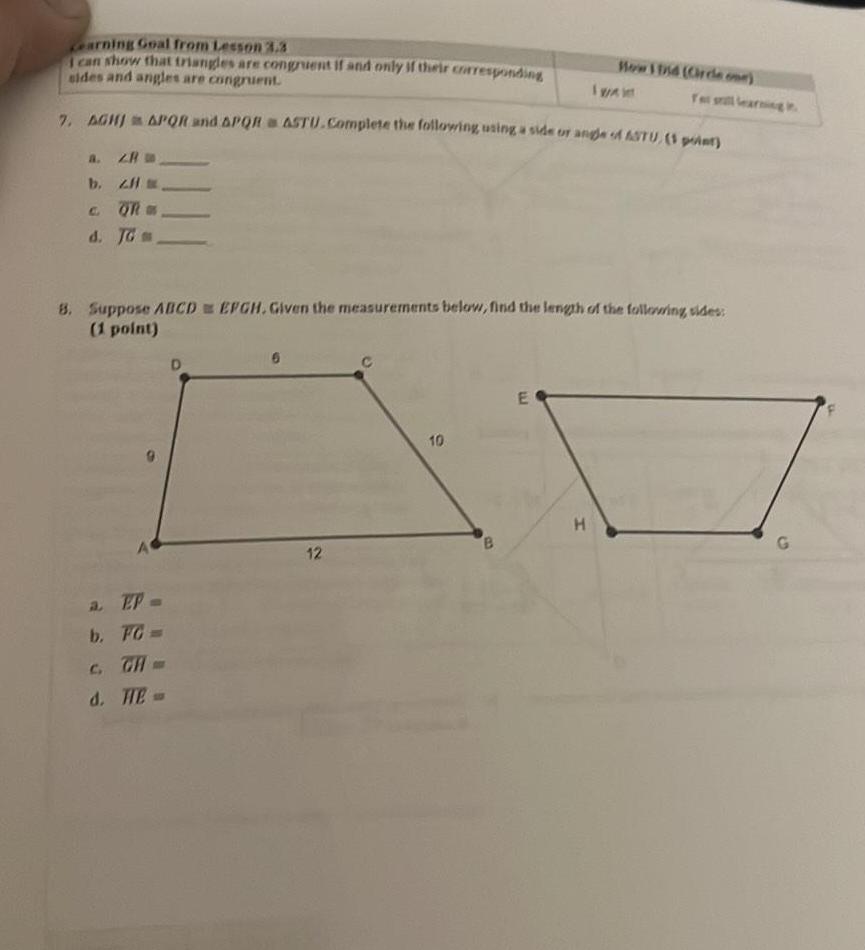
2D Geometryearning Goal from Lesson 3 3 I can show that triangles are congruent if and only if their corresponding sides and angles are congruent 7 AGHJ APQR and APQR a ASTU Complete the following using a side or angle of ASTU 1 point a ZR b z H C QR d JG a EP b FG C GA d HE 8 Suppose ABCDEFGH Given the measurements below find the length of the following sides 1 point D 6 12 10 B E How I Did Circle Te still learning H I wai

Geometry
2D Geometry9 Use the following triangles to answer the following Assume AABC ADEF 2 points B 3x 6 ft A a 6y 12 a What is the length of AB 3x 20 25 ft B y 7 C 10 AABC AEFG Solve the following problems below 2 points A F 14 ZD 18 C By 2 4x ft E b What is mLEDF 3y 7 E 5x 80 Solve for x Then using that information find the measure b Solve for y Then using that information find the measure of FE and AB of LA Checkpoint Score Total

Geometry
2D GeometryLearning Goal from Lesson 3 2 Given two figures I can determine if they are congruent using properties of rigid motion a 6 In each graph determine which type of transformation was used to make AABC and AMNP congruent 1 2 point each O C A Rotation OB Reflection DC Translation OD The two shapes are NOT congruent N 43 A Rotation by 180 about the origin B Reflection across the y axis OC Translation of x y x 4 y OD The two shapes are NOT congruent b d How I Did Circle one I m still learning it B I got it N e A Rotation B Reflection OC Translation OD The two shapes are NOT congruent 43 R r A 90 rotation clockwise around the origin B Reflection across the y axis C 90 rotation counterclockwise around the origin OD The two shapes are NOT congruent

Geometry
2D GeometryEXPLAIN 1 Determining if Figures are congruent Read Explain 1 and complete Your Turn 1 2 adapted from Lesson 3 2 and complete the following A way to determine if two geometric figures are congruent is to show that one figure maps onto the other by a sequence of rigid motions such as a sequence of reflections translations and or rotations This was practiced in Lesson 3 1 Sequences of Transformations First practice with just one transformation Example The figures shown are congruent Find a rigid motion that maps one figure to the other Give coordinate notation for the transformations you use 2 AABC AXYZ CDEF JKLM The answer is B D 8 4 8 E L 0 4 y M 8 4 8 Part 1 Figure CDEF can be mapped onto JKLM by A Rotation B Reflection C Translation OD The figures are not congruent Part 2 The coordinate notation is x y x y a reflection across the y axis 8 Y 0 4 ty X 8 N C B A Part 1 Figure ABC can be mapped onto XYZ by A Rotation The answer is A Part 2 The coordinate notation is x y y x a rotation of 90 B Reflection DC Translation OD The figures are not congruent

Geometry
2D Geometry6 for independent practice inished check the solutions with your teacher ven rotation Create a table to find the coordinates of the image 2 rotation 180 about the origin C D



Geometry
2D GeometrySuppose f x 12x Determine and graph four distinct antiderivatives of f 10 10 8 6 4 2 8 6 4 2 2 4 6 8 10 2 4 6 8 16 Clear All Draw IEE
