Geometry Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.








Geometry
Coordinate systemWrite a two column proof 1 Given EF FH ZE ZH Prove HG DE D G E F H Statement Reason


Geometry
2D Geometrythe object and the image congruent or not con Explain your answers The diagram shows triangle B on a coordinate grid Make four copies of the diagram On different copies of the diagram draw the image of B after each combination of transformations a b C d 5 1 followed by reflection in the x axis Translation Rotation of 180 centre 3 2 followed by reflection in the x axis Translation 3 5 clockwise centre 2 1 followed by rotation 90 Reflection in the line y 1 followed by rotation 90 anticlockwise centre 2 2 Think like a mathematician 6 5 4 3 2 B 6 5 4 3 2 1 2 3 4 5 6

Geometry
Heights & Distances0 157 1 65 0 0108 0 0028 Z 0 157 1 65 0 0108 0 0028 1 1 solving for T The equation 1 is in quadratic form solving for by evaluating the roots of the quadratic equation Rewring the equatin 1 3 Solving for root Z 1 2 concentration Discarding the negative root 0 06 0 0 0556 0 05 0 04 0 03 0 02 0 82572 0 157 0 008 0 0 04315 0 01 ax bx c 0 T 0 root 0 root T 0 03 b b 4 a c 2 a 0 15 0 152 4 0 825 0 008 2 0 825 0 15 0 0225 0 0264 2 0 825 0 5 0 15 0 2211 2 0 825 1 0 4311 Distance Z 1 5 y 0 0128x 0 0557 R 0 9998 2 2 5

Geometry
Heights & DistancesDesign a relational schema and SQL quenes to iStore the basis functional dependencies i Check Fa functional dependency is part of the closure of besis set of functional dependencies stored in your relations designed above

Geometry
3D GeometryStep 1 We want to find the exact value of sin From the text the quadrants are numbered counter clockwise from the upper right I II III IV This angle lies in quadrant III III K T sin 27 Step 2 Sketching the angle we draw the triangle formed with the terminal side and the x axis Looking at this triangle we see triangle that it is a 71 632 2 2 To find that value we first have to draw the angle 3 y Likewise the opposite side should be labeled 2A 3 From the text we know that the side lengths are 1 2 3 To label the sides with the proper lengths we note that 2 being the longest side length must be the hypotenuse The smallest angle will be opposite the shortest side Looking at the triangle and taking into account the quadrant so that the sign is correct the adjacent side should be labeled 3 x
Geometry
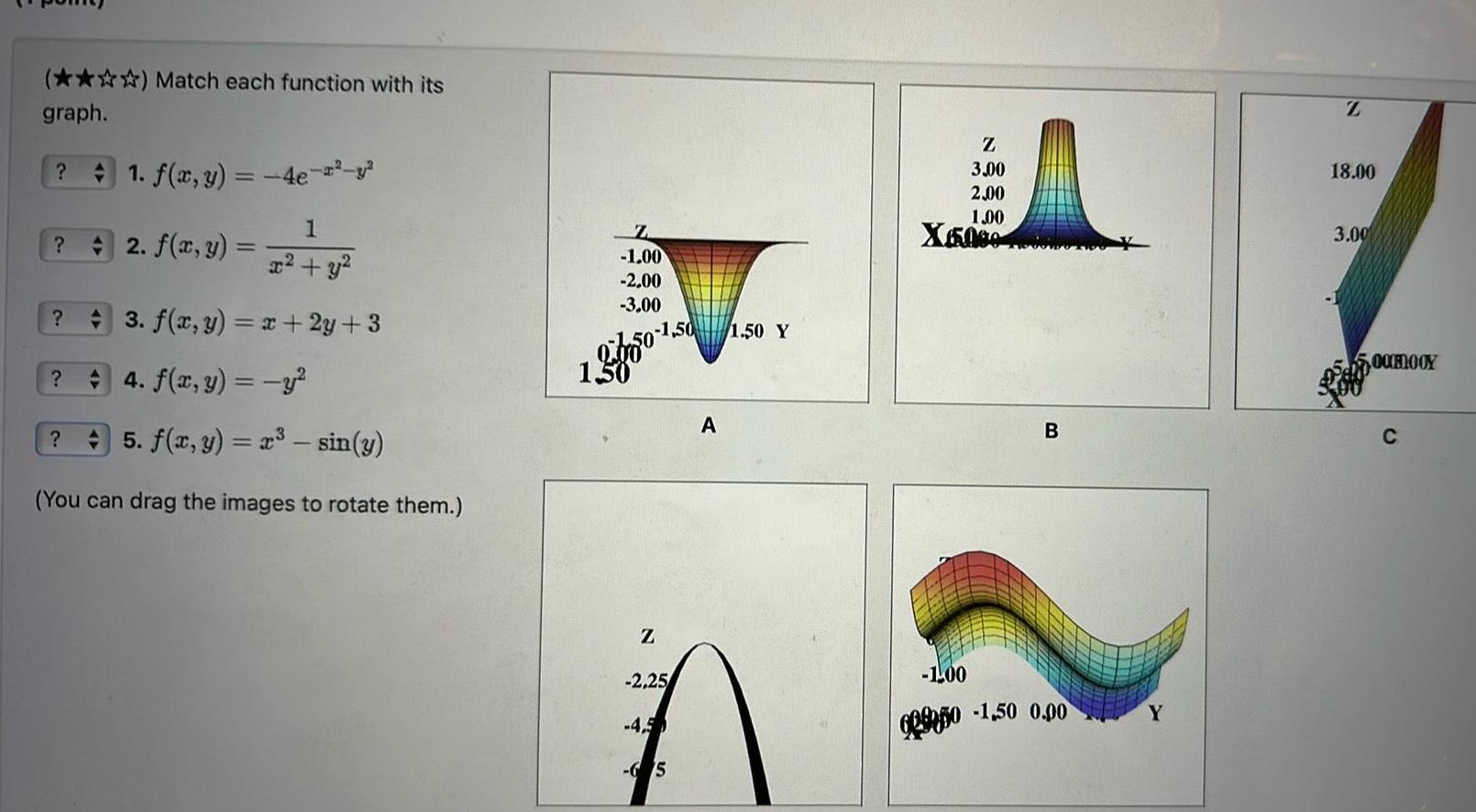
2D GeometryMatch each function with its graph 1 f x y 4e 1 x y 3 f x y x 2y 3 42 f x y 4 f x y y 5 f x y x sin y You can drag the images to rotate them Z 1 00 2 00 3 00 1 50 1 50 Z 2 25 4 5 65 A 1 50 Y Z 3 00 2 00 1 00 X5000 B 1 00 6950 1 50 0 00 Y Z 18 00 3 00 5 00ROOY C
Geometry
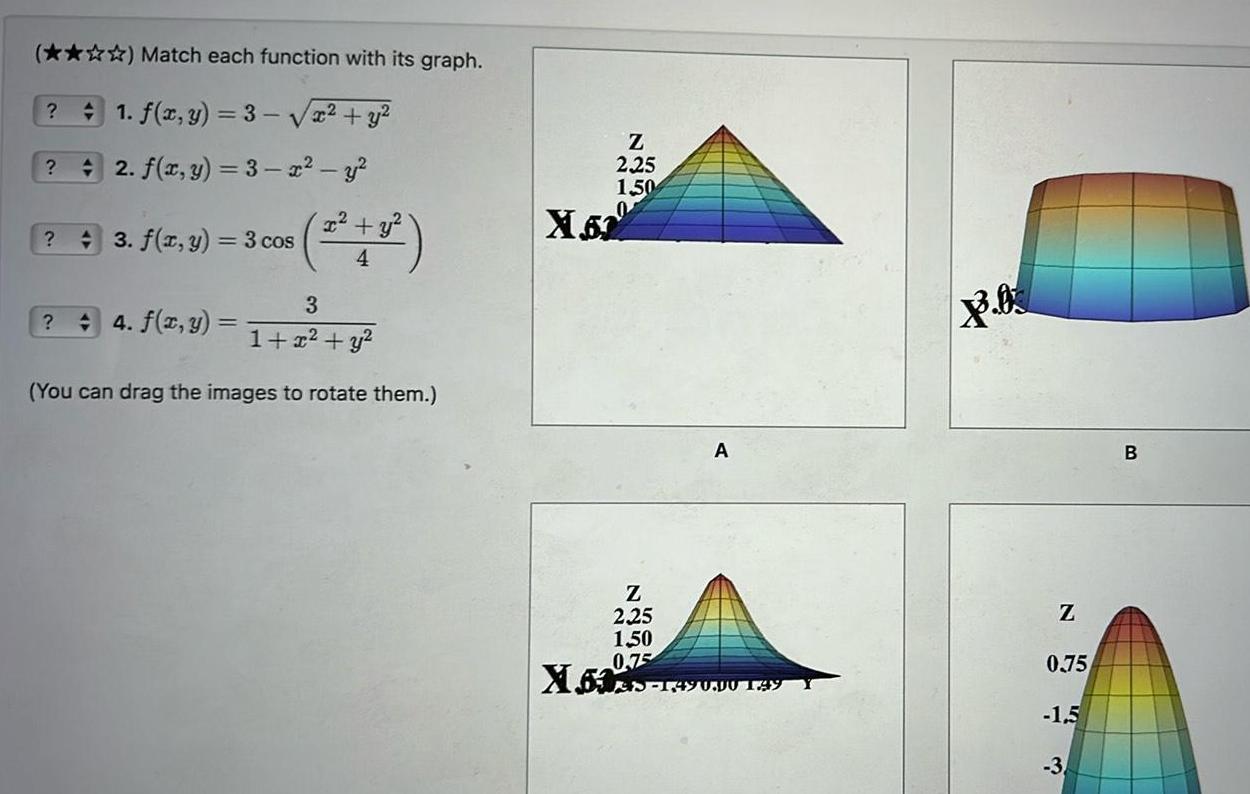
2D GeometryMatch each function with its graph 1 f x y 3 x y 2 f x y 3 x y 3 f x y 3 cos 4 3 2 4 f x y 1 2 y You can drag the images to rotate them Z 2 25 1 50 X 52 Z 2 25 1 50 0 75 X603 149 A 1 490 00 149 Z 0 75 1 5 3 B

Geometry
Coordinate systemStep 1 We want to find the exact value of sin 3r From the text the quadrants are numbered counter clockwise from the upper right I II III IV This angle lies in quadrant 111 III 11 4 3 To find that value we first have to draw the angle Step 2 Sketching the angle we draw the triangle formed with the terminal side and the y axis Looking at this triangle we see that it is a triangle xxx Likewise the opposite side should be labeled 3A From the text we know that the side lengths are 2 2 2 To label the sides with the proper lengths we note that 2 being the longest side length must be the hypotenuse The smallest angle will be opposite the shortest side Looking at the triangle and taking into account the quadrant so that the sign is correct the adjacent side should be labeled
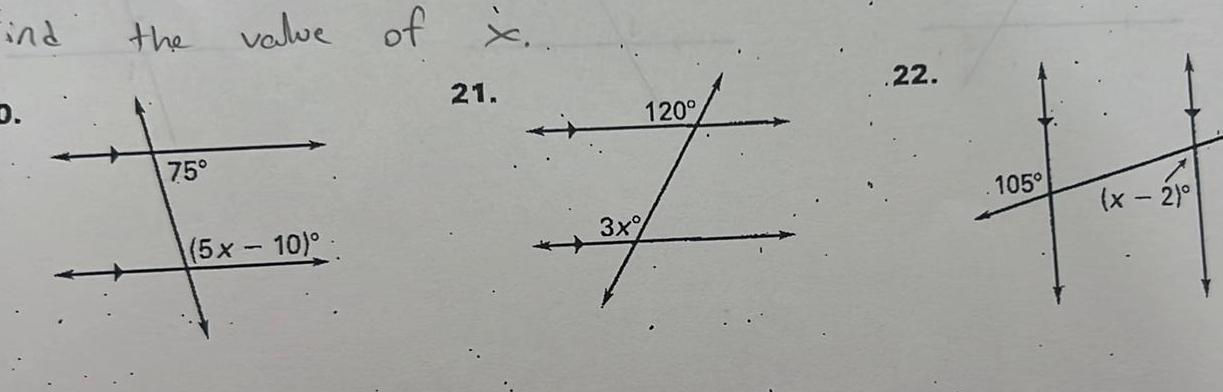
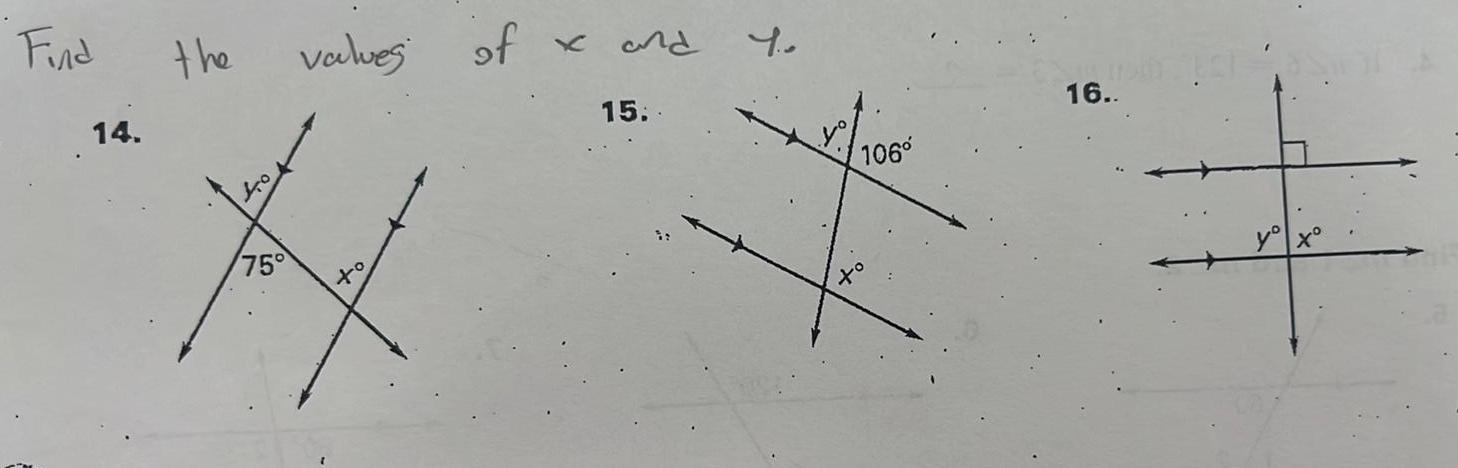

Geometry
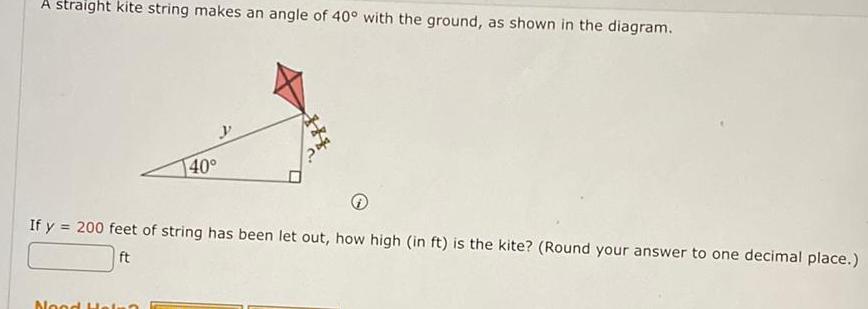
2D GeometryA straight kite string makes an angle of 40 with the ground as shown in the diagram 40 If y 200 feet of string has been let out how high in ft is the kite Round your answer to one decimal place ft Nood Hein
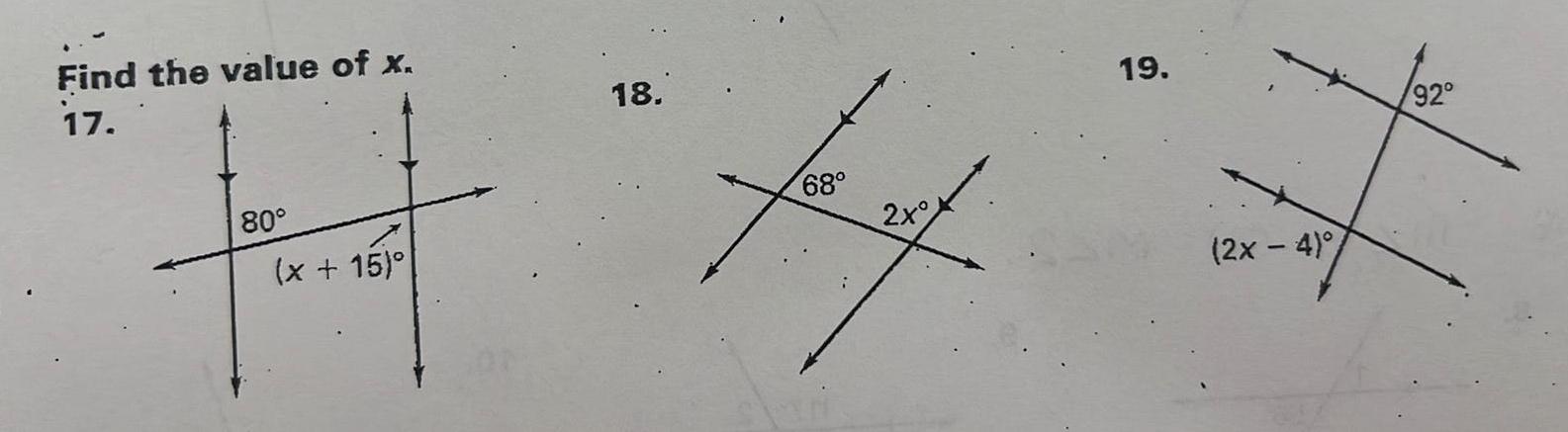

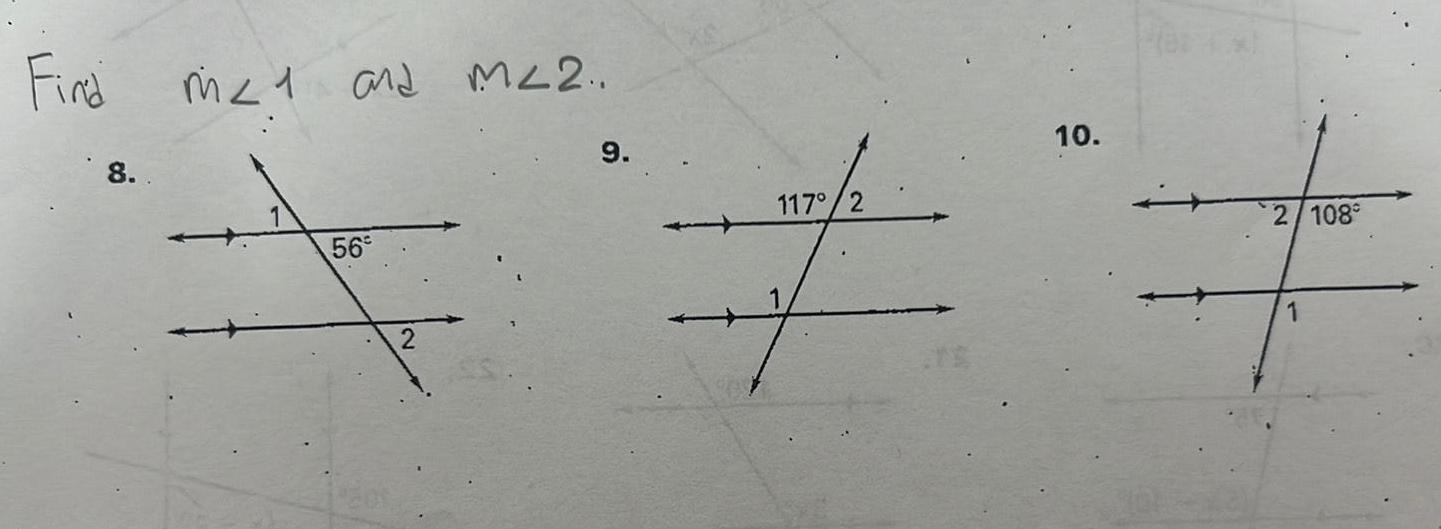

Geometry
Coordinate systemFor use with pages Find the angle measure Tell which postulate or theorem you use 1 If m1 50 then m 5 2 If m 4 45 then m26 3 If m 2 130 then m 7 4 Ifm 6 123 then m 3 2 3 4 519 7 6 8

Geometry
Solution of triangles3 Solve the triangle below Round each answer to the nearest tenth 24 a C 36 16

Geometry
Coordinate system4 A pilot is flying over a straight highway He determines the angle of depression to two mile posts 2 1 km apart to be 25 and 49 as shown in the figure below Find the distance of the plane from point A and find the elevation of the plane 125 49 A B

Geometry
Heights & Distancesr 8 Give two other polar coordinate representations of the point one with r 0 and one with r 0 2 2 3 smaller r value r 0 Need Help Read It 2 X 0 larger r value 2 0


Geometry
Coordinate systemFor the following exercises assume a is opposite side a is opposite side b and is opposite side c Solve each triangle if possible Round each answer to the nearest tenth 1 B 50 a 105 b 45

Geometry
2D Geometry7 Given quadrilateral TRAP with T 5 7 R 3 4 A 9 5 and P 1 10 Show TRAP is an isosceles trapezoid 3 4
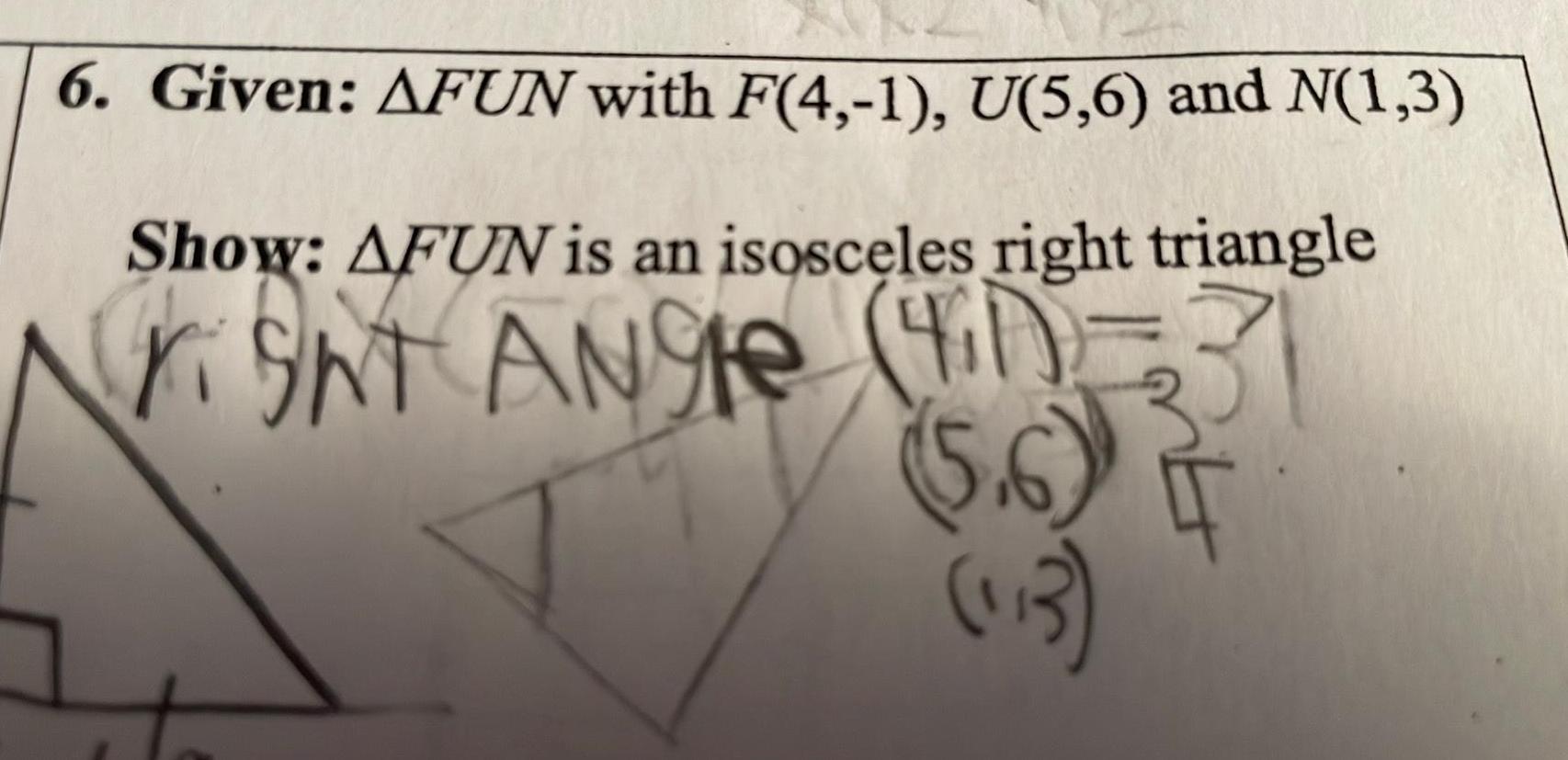
Geometry
2D Geometry6 Given AFUN with F 4 1 U 5 6 and N 1 3 Show AFUN is an isosceles right triangle righT ANgle 41 5 6 113

Geometry
Coordinate systemFind all of the solutions to the equation in the interval 0 2 2 sin r1 esc z

Geometry
Coordinate systemFind the standard form of the equation of the hyperbola with the given characteristics Vertices 3 5 3 11 Asymptotes y x 6 y x

Geometry
Coordinate systemFind the center vertices and foci of the hyperbola y 3 x 4 x 4 9 center x y vertices x y foci x y x y x y 1 smaller y value larger y value 2 smaller y value Find the asymptotes of the hyperbola Enter your answers as a comma separated list of equations 4 larger y value Sketch its graph using the asymptotes as an aid Use a graphing utility to verify your graph y 8 6 4 2 2 X 6 8 X X 2 6 4 2 2 4 2 8 8 X

Geometry
Coordinate systemConsider the following 4x 9y 24x 90y 198 0 a Find the standard form of the equation of the hyperbola If the hyperbola is degenerate enter NONE b Find the center vertices foci and asymptotes of the hyperbola If the hyperbola is degenerate enter NONE in each answer blank Center Vertices Foci Asymptotes y negative slope positive slope c Select the correct graph of the hyperbola using the asymptotes as an aid Use a graphing utility to verify your answer A 4 10 6

Geometry
Solution of triangles9 Given APQR with P 1 4 Q 3 0 and R 2 3 Prove APQR is NOT a right triangle 11 1 4 R 2 3 W Q 3 0 Mainita com
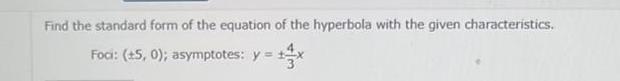
Geometry
2D GeometryFind the standard form of the equation of the hyperbola with the given characteristics Foci 5 0 asymptotes y x


Geometry
Coordinate systemFind the standard form of the equation of the hyperbola with the given characteristics Vertices 14 0 foci 7 0

Geometry
Coordinate systemHan invests 13 000 into a fund that combines stocks and bonds The return varies from year to year The balance at 5 year intervals is given in the table below The goal of this exercise is to find constants a and b such that the model y ae best fits the data In order to do that we apply the natural logarithm to both sides of the model This yields In y n a and using properties of logarithms weet T lex be and the problem now reduone to finding the Pcjwey In y In a In ee In y In a bt If we let Y In y c In a and c b the problem now reduces to finding the linear fit Y q c the set of dats points Part b t 0 5 10 15 20 25 y Balance 1 000 13 14 5 16 18 2 19 9 22 3 5 10 FLO 18 31 115 11451 lec16 In 1821 In 199 Find the cheskydecompcation of S and store in U Soke thener system w me sing the backataah command Solve the langur system cw using the backslash command Compute the best fit use 25 2231 art a The sectors and y have already been created for you Compute the sector by evaluating the natu ofy note that the natural logam entered a lng in MATLAB Create the mote X for the rear Create the tor 2 Create the magic I Plot the date pents and upper case Use o to plot points by the original data polts Use Lindth 2 und is that you por Use Inestyle and color the line back gure by tyckig hold off Computand where and are the values you found in part 4 Se the wi coobies a widespectively Ente figure to open a new gu plot the original data points and lower cass no toplot points
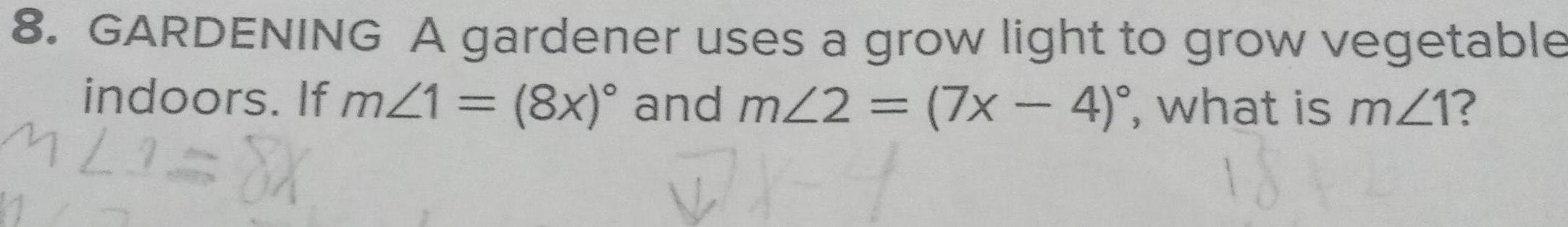
Geometry
2D Geometry8 GARDENING A gardener uses a grow light to grow vegetable indoors If m 1 8x and m 2 7x 4 what is m 1 M21 8X 7 1846 11

Geometry
2D Geometry13y 17 1 2 3 Given m27 38 and mz10 102 find the measure of each missing angle 4 3 5 6 29 x 3 15x 7 9 10 12 11 8 7 m 13 14 16 15

Geometry
2D GeometryThis is just a practice with some of the applications Please make sure you study all of the vocabulary for the unit too A large portion of the quiz is based off of the vocab Find the value of each variable 1 Note pl m P m 120 Co e d a b C d e


Geometry
Heights & DistancesA property is bing transported through a fluidat steady state trough a content cros sectional area at point the concentration is 278 x 10 amount of roperty m and 1 50 x 10 at point 2 t a distanceof 20 m away Thedificity depends on concentraion l as 8 0 150 1651 a calculate the teadystate fut if he two points were separated by 35 m but with he same concentrations How does the flux vary with the distance between the points Calculate the steady state fut if the concentration at point 2 was 150 x 10 amount of property using the right stance 20 to do the way with he diference in concentration b

Geometry
Coordinate systemComplete the proof of the identity by choosing the Rule that justifies each step sec x tan x 1 To see a detailed description of a Rule select the More Information Button to the right of the R Statement sec x tan x 1 tan x tan x Rule Rule

Geometry
2D GeometryA1 November 21 03 m2SUT 34 Find mz1 Find x if m2 4x 5 and A2 m151 A3 Find BD T A4 Solve for x 12 1 1 21 16 15 35

Geometry
Solution of triangles20 21 8 40 Q 43 75 For 19 21 find the values of x and y 19 Jo 77 96 R 1 y 35 2 xo st 4 S 3 64 7 5 6 mz1 mz2 mz3 m24 x x x m25 mz6 m27 m28 y y y

Geometry
Solution of trianglesSection 5 1 Worksheet 1 The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two interior angles For 2 5 classify the triangle by its sides and by its angle measures 2 X 3 M For 8 For 6 and 7 classify AABC by its sides Then determine whether it is a right triangle 6 A 2 3 B 6 3 C 2 7 7 A 3 3 B 6 9 C 6 3 Classify by sides Is it a right triangle N find m21 Then classify the triangle by its angles 78 319 4 J Classify by sides Is it a right triangle mz1 Classify by its angles 5 B A