Organic Chemistry Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryCellulose is a polysaccharide which has
A. only beta-1,4-bonds between glucose units
B. only alpha-1,4-links bonds glucose units
C. hemiacetal links joining glucose units
D. both alpha-1,4- and bonds between glucose units

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionShow the molecular equation, ionic equation and the net ionic equation for the following equations. If all species are spectator ions, please indicate that no reaction takes place. Note: Be sure the original equation is balanced before proceeding!
1. AgNO3(aq) + KCl(aq) → AgCl(s) + KNO3(aq)
2. Mg(NO3)2(aq) + Na₂CO3(aq) → MgCO3(s) + NaNO3(aq)
3. strontium bromide (aq) + potassium sulfate(aq) → strontium sulfate(s) + potassium bromide (aq)
4. manganese (II) chloride (aq) + ammonium carbonate(aq) → manganese(II)carbonate(s) + ammonium chloride (aq)
5. chromium(III)nitrate(aq) + iron(II)sulfate(aq) → chromium(III)sulfate(aq) + iron(II)nitrate(aq)

Organic Chemistry
AminesHumans cannot digest cellulose because they
A. lack the necessary enzymes to digest beta-glcosides
B. cannot digest chlorophyll
C. are poisoned by beta-glycosides
D. are allergic to beta-glycosides
E. have intestinal flora which use up beta-glycosides

Organic Chemistry
BiomoleculesA monosaccharide that contains six carbon atoms, one of which is an aldehyde group, is classified as a(n)
A. ketotetrose
B. aldohexose
C. aldopentose
D. ketopentose
E. aldotetrose

Organic Chemistry
BiomoleculesIn the L-isomer of a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide, the -OH group furthest frm the carbonyl is written
A. on the left of the bottom chiral carbon
B. on the right of the bottom chiral carbon
C. on the right of the top chiral carbon
D. on the left of the top chiral carbon
E. on the left of the middle chiral carbon

Organic Chemistry
BiomoleculesWhat are antibodies?
Y-shaped proteins that recognize and help destroy foreign substances
proteins on cell surfaces that identify the cell as self
cells that engulf pathogens that were marked for destruction
foreign substances whose presence triggers an immune response

Organic Chemistry
IsomerismKetones typically have a carbonyl stretching frequency around 1715 cm-¹.
a. Provide an explanation why the C-O group of 4-methoxychalcone has a stretching frequency of 1650 cm-¹

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionWith respect to the Na+/K+ ATPase,
it is not an antiport
it helps balance a cell's osmotic pressure
it is electroneutral
it uses a proton gradient for energy
all of the above are true
none of the above are true

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryIdentify the neutral element represented by this excited-state electron configuration, then write the ground-state electron configuration for that element.
excited state: 1s22s²2p⁰3s¹

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryDraw the skeletal ("line") structure of methylcyclopropane.

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryPlease provide a mechanism for the following transformation. You may use general base, B, and general acid H+ in your answer.
note: tributyl phosphine is a catalyst in this reaction

Organic Chemistry
IsomerismSuppose all the hydrogen atoms in this molecule are replaced by chlorine atoms:
Draw a skeletal ("line") structure of the new molecule.
Be sure you follow all the usual rules for drawing skeletal structures.

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistrySuppose all the chlorine atoms in this molecule are replaced by hydrogen atoms:
Draw a skeletal ("line") structure of the new molecule.
Be sure you follow all the usual rules for drawing skeletal structures.

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryPredict the product(s) when each of the following are reacted with mCPBA, making sure to indicate the relative stereochemical outcome. Indicate any racemic mixtures by drawing both enantiomers.

Organic Chemistry
Aldehydes & KetonesSelect all the solvents/solutions in which you would expect this compound to dissolve:
Ethyl acetate
Dilute aqueous sodium bicarbonate
Dilute aqueous NaOH
Dilute aqueous HCI


Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryWhich of the following sets of elements contain all transition elements?
Cobalt, Rhodium, Gold, and Mercury
Silicon, Germanium, lodine, and Lead
lodine, Xenon, Antimony, and Indium
Helium, Calcium, Radium, and Beryllium

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionPredict the number of signals expected in the H NMR spectrum of each molecule below
Ignore signal splitting.

Organic Chemistry
BiomoleculesAn unknown compound is not symmetric, has a molecular formula of C5H10O and contains a functional group attached to a 3º carbon.
It has broad absorption band in the 3200 - 3550 cm-¹ region and no absorption in the 1620 - 1690 cm-¹ region. What is the structure for this compound?

Organic Chemistry
BiomoleculesWith respect to electron transport,
the Q cycle requires both cytochrome C and complex II
protons are pumped out of the matrix in four places
oxidation of Cu+2 produces Cu+1
all of the above are true


Organic Chemistry
IsomerismWith respect to metabolites made from cholesterol
estrogens are derived from androgens
it includes vitamin D, but not vitamin A
they do not include the prostaglandins
all of the above are true
none of the above are true

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryWhy is the ammonium salt of lidocaine used rather than the amine?
The ammonium salt (lidocaine hydrochloride) is in water and body fluids than the amine lidocaine.

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryIonic nomenclature introduces the idea of a cation and anion. Ionic compounds like barium chloride, BaCl2 or aluminum sulfate, Al2(SO4)3 are partnership between opposite charges where all "+" cations and "-" anion charges balance to equal zero.
Ba²+ + CI- + Cl- has a net charge of zero and Al³+ + Al³+ + SO42- + SO4²- + SO4²- has a net charge of zero
BaCI2 Al₂(SO4)3
Question 1: why would BaCl not be a netural compound?

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryWhich of the following is the major product of the reaction of 1-propanol with a strong oxidizing agent?

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryA student weighs out 4.66 g of benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO) to react with sodium borohydride (NaBH₂) according to the following chemical equation:
C6H5CHO + NaBH4 → C6H5CH₂OH
To ensure complete consumption of benzaldehyde, 1.5 equivalents of NaBH4 are used. Calculate how many grams of NaBH, are needed.
(MW_C6H5CHO = 106.12 g/mol; MW_NaBH4 = 37.83 g/mol)

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryWhat is the IUPAC name of the following ether?
CH3-CH2-CH₂-CH2-O-CH3
2-methoxybutane
1-butoxymethane
butyl methyl ether
1-methoxybutane

Organic Chemistry
BiomoleculesWith respect to regulation of cholesterol synthesis,
when cholesterol is high, HMG-CoA reductase is allosterically inhibited
it is allosterically controlled by ketone bodies
it is controlled by regulating oxidation of acetyl-CoA
all of the above are true
none of the above are true

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryHow many molecules of SO3 can be formed from 0.74 moles of O₂
(assuming excess SO₂) from the following UNBALANCED equation?
SO₂(g) + O₂(g) → SO3(g)

Organic Chemistry
Aldehydes & KetonesPredict the aldol product that would result when
the following aldehyde is allowed to react under
the following conditions:
HCl, H₂O, heat
Draw the molecule on the canvas by choosing buttons from the Tools (for bonds and charges), Atoms, and Templates toolbars.

Organic Chemistry
IsomerismStep one of glycolysis is irreversible in muscle cells, meaning that glucose-6-phosphate
is not easily converted back to glucose. Why would this beneficial to muscle cells?
(optional) Glucose-6-phosphate is an allosteric inhibitor of hexokinase, the enzyme that
catalyzes reaction 1 of glycolysis. Review the section in your text about enzyme
inhibitors.
a. How does an allosteric inhibitor work?
b. Why would this enzyme be a good target for regulation by inhibition?

Organic Chemistry
AminesWhat is the name of this compound?
A) 1-methyl-5-bromoaniline
B) N-methyl-3-bromoaniline
C) N-methyl-p-bromoaniline
D) 1-bromo-3-N-methylamine benzene
E) 1-brotno-3-N-methyl aniline

Organic Chemistry
HydrocarbonsThe IUPAC name for this compound is
A) N-ethylpropanamide.
B) N-ethylacetamide.
C) pentanamide.
D) N,N-diethylacetamide.
E) ethylpropionamide

Organic Chemistry
BiomoleculesThe net chemical equation for the first step of glycolysis is:
Glucose + ATP glucose-6-phosphate + ADP
Write a similar equation for the following steps of glycolysis:
a. Step 7:
b. Step 4:
c. Step 10:
d. Step 6:
e. Step 3:
![What is the rate law for the following mechanism in terms of the overall rate constant k?
Step 1: A+B = C (fast)
Step 2: B+C → D (slow)
Express your answer in terms of k and the necessary concentrations (e.g., k* [A]^3* [D]).](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/56688773-1659465675.0283806.jpeg?w=256)
Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryWhat is the rate law for the following mechanism in terms of the overall rate constant k?
Step 1: A+B = C (fast)
Step 2: B+C → D (slow)
Express your answer in terms of k and the necessary concentrations (e.g., k* [A]^3* [D]).

Organic Chemistry
IsomerismHydrazine reacted with oxygen according to the (unbalanced) equation
N₂H4 (1) + O₂(g) → NO2 (g) + H₂O (g)
pe un lf 25.00 kg of hydrazine are reacted with 150.0 kg of oxygen, which is the limiting
reagent?
1905 19
How many kg of NO2 are produced from the reaction of the limiting reagent?
If 36.00 kg of NO2 are obtained from the reaction of the limiting reagent, what is
the % yield? Suser (20

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionA certain reaction with an activation energy of 165 kJ/mol was run at 535 K and again at 555 K. What is the ratio of f at the higher temperature to f at the lower temperature?
Express your answer numerically using one significant figure.

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryA certain reaction has an activation energy of 70.0 kJ/mol and a frequency factor of A₁ = 5.00x1012 M-¹s-¹. What is the rate constant, k, of this reaction at 29.0 °C ?
Express your answer with the appropriate units. Indicate the multiplication of units explicitly either with a multiplication dot (asterisk) or a dash.


Organic Chemistry
IsomerismWhat are the moles of each element in 100.0 g of vinegar? (Enter your answers to three decimal places.)

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryThe empirical formula for vinegar is CH₂O. Determine the molecular formula of vinegar if the molar mass is known to be about 60 g/mol.
What is the molar mass of your molecular formula, C₂H4O2? (Enter your answer to two decimal places.)

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryA canister of chlorine gas contains 2,270 mL under a pressure of 0.836 atm. Assuming
unchanging temperature and amount of gas, what is the pressure when the volume is decreased
to 1.00L?
a. 0.368 atm
b. 1.90 atm
C. 2.72 atm
d. 1,900 atm
e. 2,720 atm


Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryCopper (Cu) is element 29 on the periodic table. Calculate the mass, in grams, of 1.46 mol of Cu.

Organic Chemistry
PolymersGadolinium (Gd) is element 64 on the periodic table. Calculate the amount (mol) Gd in 2.54 g Gd.
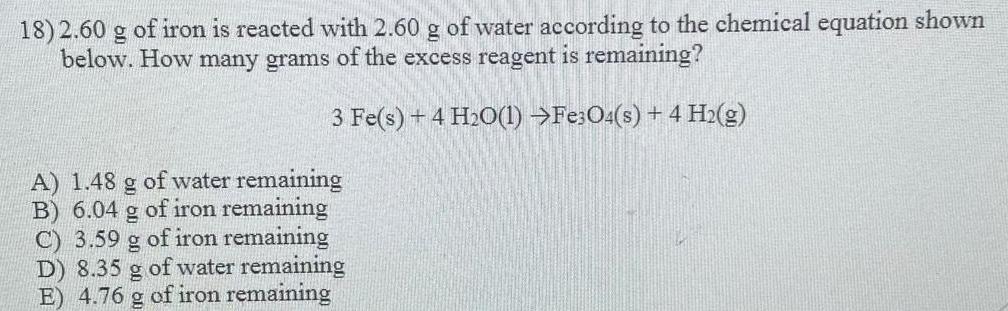
Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistry2.60 g of iron is reacted with 2.60 g of water according to the chemical equation shown
below. How many grams of the excess reagent is remaining?
3 Fe(s) + 4H₂O(l) ---> Fe3O4(s) + 4 H₂(g)
A) 1.48 g of water remaining
B) 6.04 g of iron remaining
C) 3.59 g of iron remaining
D) 8.35 g of water remaining
E) 4.76 g of iron remaining

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryA sample of Xe weighs 20.5 grams. Will a sample of Ca that contains the same number of atoms weigh more or less than 20.5 grams?
Calculate the mass of a sample of Ca that contains the same number of atoms.

Organic Chemistry
Isomerism(S)-2-hydroxypropanoic acid (lactic acid) is produced in the fermentation of milk to make yogurt. Some bacteria produce a mixture of stereoisomers and some produce solely the (R)-isomer. (S)-lactic acid. is shown below. Draw the (R)-isomer. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, where applicable.

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryThe following reaction steps are shown using conventional electron pushing. (a) Draw the
second product whose formation would have been rationalized with this same arrow. (b)
Use the bouncing arrow formalism to illustrate the formation of only the product shown.

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionThe activation energy of a certain reaction is 35.2 kJ/mol. At 24 °C, the rate constant is 0.0160s-¹. At what temperature in degrees Celsius would this reaction go twice as fast?
Express your answer with the appropriate units.