Practical Detection Questions and Answers

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionA scientist expects to get 5.9g of sodium chloride based on their calculations. In the lab, they collect 5.5g of sodium chloride. What is the percent yield for their reaction?
2Na(s) + Cl2(g) --> 2NaCl(s)
107%
93.2%
72%
0.9%
89%
![Calculate the K, for the following hypothetical reaction, using the given equilibrium
concentrations: [A] = 0.020 M, [B] = 0.030 M and [C]=7.74 M
A (g) + 2B (g) = C()
a. 4.3 x10³
b. 1.3x10*
c. 7.7 x10³
d. 2.3x10€](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/80376686-1659894415.6000364.jpeg?w=256)
Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionCalculate the K, for the following hypothetical reaction, using the given equilibrium
concentrations: [A] = 0.020 M, [B] = 0.030 M and [C]=7.74 M
A (g) + 2B (g) = C()
a. 4.3 x10³
b. 1.3x10*
c. 7.7 x10³
d. 2.3x10€
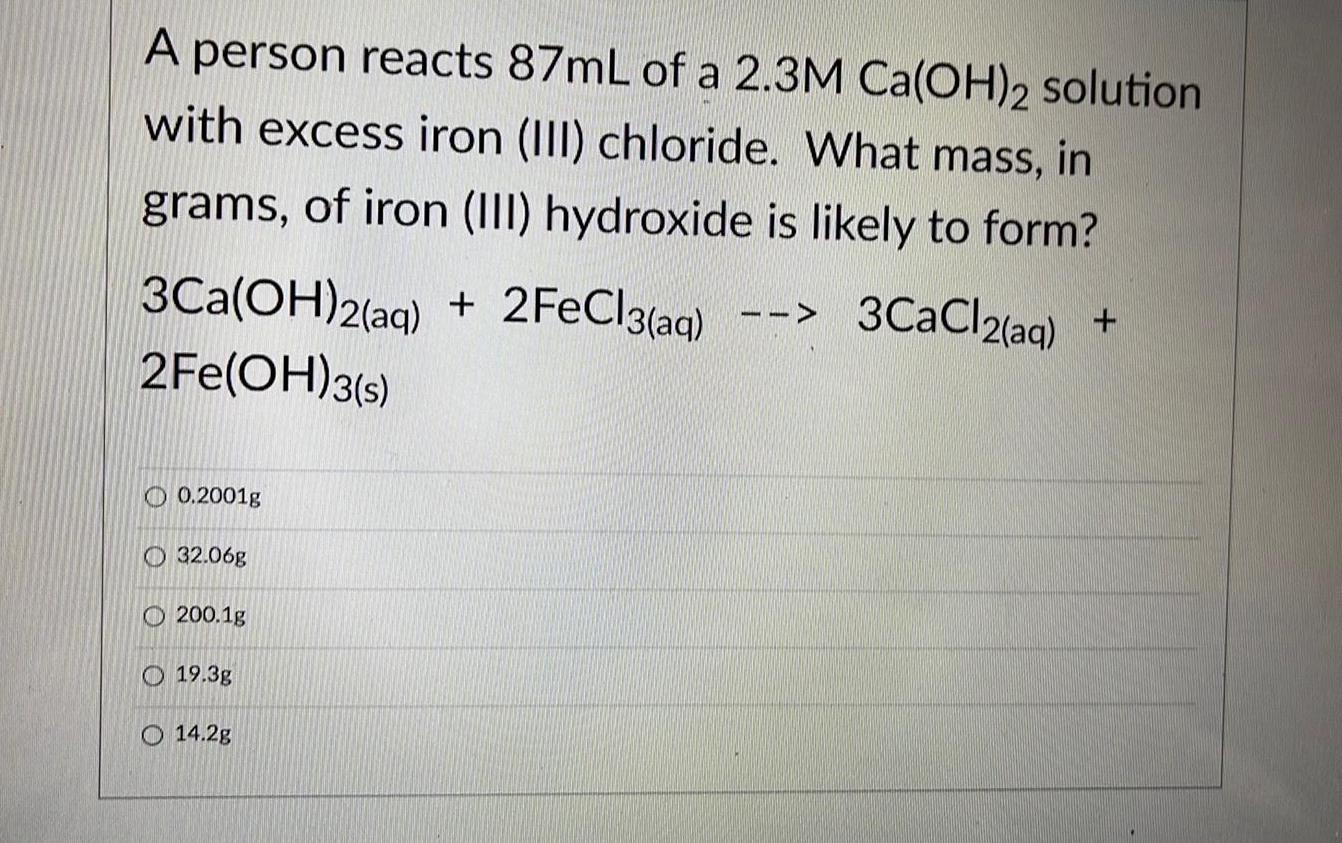
Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionA person reacts 87mL of a 2.3M Ca(OH)2 solution with excess iron (III) chloride. What mass, in
grams, of iron (III) hydroxide is likely to form?
3Ca(OH)2(aq) + 2FeCl3(aq) --> 3CaCl2(aq) +2Fe(OH)3(s)
0.2001g
32.06g
200.1g
19.3g
14.2g

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionA person creates a 0.5L solution using 164.25g of solid HCI. What will the concentration (molarity) of the solution be?
328.5M
9M
15.6M
4.5M
10.25M

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionWhat type of reaction is below?
Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) --> MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Synthesis
Combustion
Decomposition
Double Replacement
Single Replacement

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionWhich of the following statements is most accurate?
Energy is stored in chemical bonds and released when the bonds are broken.
Energy is absorbed when chemical bonds are broken and released when new bonds form.
More energy is required to form a chemical bond than the energy required to break a chemical bond.
Answers A and C are both true.

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionWhat are the original and final oxidation numbers for iron in the smelting of iron
from iron oxide?
Fe₂O3(s) + 3CO(g) → 2Fe(s) + 3CO₂(g)
No Change
+3 --> 0
0 -- +2
+2 --> 0

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionWhat is the oxidation number for carbon in the ionic compound potassium carbonate (K₂CO3)?
-6
+4
-4
+3

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionWhich of the following statements about electrochemical cells is true?
Only oxidation half-reactions are useful
Oxidation occurs at the anode
Reduction occurs at the anode
An element with a strong attraction to electrons will be easily oxidized

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionWhich of the following statements is true about redox reactions?
Oxidation reactions always occur with reduction reactions because if one
element is losing electrons, another has to be gaining them.
An oxidizing agent is a species that is reduced.
An atom is reduced when it gains electrons.
All of the above are true.

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionIt required 66.66 mL of 2.000 M Al(OH)3 to titrate (neutralize) 100.00 mL of an HBrO3 solution. What is the molarity. M, of the HBrO3 solution?
3 HBrO3+ Al(OH)3 --> 3 H₂O + Al(BrO3)3
A. 0.4000 M
B. 1.333 M
C. 2.000 M
D. 4.000 M

Organic Chemistry
Practical Detection25.0 g of HI(g) is injected into a 4.00 L reaction vessel that contains 20.0 g of l₂(g). When the system comes to equilibrium at 400°C, what will be the total pressure inside the reaction vessel?
2HI(g) H₂(g) + 12(g), K = 0.0156 at 400°C
a 2.43 atm
b. 3.78 atm
c.0.815 atm
d. 2.70 atm
e. 13.0 atm

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionLook at the formula for the Heat of Reaction (ΔH).
ΔH is equal to the -
heat content of reactants minus the heat content of the products
Hydrogen reactants minus the Hydrogen products
heat content of the products minus the heat content of the reactants
Hydrogen products minus the Hydrogen the reactants
K

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionGiven the reaction at equilibrium:
NaCl(s) <--> Na+ (aq) + Cl-¹ (ag)
The addition of KCI to this system will cause a shift in the equilibrium to the
right, and the concentration of Na+(aq) ions will decrease
right, and the concentration of Na+(aq) ions will increase
left, and the concentration of Na+(aq) ions will increase
left, and the concentration of Na+(aq) ions will decrease

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionChoose the correct agent in each of these reactions:
Mg(s) + O2(g) → MgO Select the oxidizing agent:
CuO (s) + H2(g) →→ Cu(s) + H₂O(g) Select the reducing agent:
2 Na(s) + Cl2(g) →→→ NaCl(s) Select the reducing agent:

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionSodium hydroxide, NaOH, is a strong base that is used in industrial synthesis and processes such as making paper. What is the mass of 2.30×1022 formula units of NaOH (Molar mass = 40.0 g/mol)? Express the mass in grams to three significant figures.

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionHow will the presence or absence of the NH4+ ion be
detected in fertilizer?
Add hydrochloric acid (HCI) and look for a color
change with red litmus paper.
Add hydrochloric acid (HCI), followed by BaCl₂ and
look for the formation of a white precipitate.
Add silver nitrate (AgNO3) and look for a white
precipitate.
Add sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and look for a color
change with red litmus paper.
Add hydrochloric acid (HCI) and look for the
presence of bubbles.

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionIn the following reactions, indicate if the species is oxidized or reduced
Mg2+ becomes Mg
O becomes O²-
Fe2+ becomes Fe³+
F becomes F-
Cu becomes Cu+
H becomes H+

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionA sample of helium gas has a volume of 6.5 L at a pressure of 1.11 atm and a temperature of 25 °C. What is the pressure of the gas in atm when the volume and temperature of the gas sample are changed to 1850 mL and 325 K, respectively?
0.235 atm
0.300 atm
4.25 atm
173.5 atm

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionThe atomic mass of hydrogen is 1.01 g/mol. What percentage of H atoms have an atomic mass of
1.01 amu?
66 %
100 %
33 %
None
More information is needed to determine this.
(you only have one attempt on this question)

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionIn order to neutralize 25.0mL of sulfuric acid (H₂SO4), 33.3mL of 1.0M sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is needed. Calculate the molarity of the acid.
a. 0.38M
b. 0.66M
c. 0.76M
d. 1.32M
e. 1.50M

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionThe reaction between Na2CO3 and CaCl2 actually produced 25.6 g of CaCO3. If the theoretical yield is 30.15 g, What is the percent yield for this reaction?
Na2CO3 + CaCl2 ---> CaCO3 + 2NaCl
100.%
58.0 %
84.9%
73.196
37.9 %

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionYou have a gas at 35°C that is confined to a 7.5 L cylinder with pressure of 952 torr.
a. What volume will the gas occupy if the pressure is decreased to 805 torr?
8.9 L
6.3 L
It will remain unchanged.
5.5 L

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionA mixture containing 0.550 mol Cl₂,
0.443 mol Br2, and 0.520 mol I2 are
confined to a 10.00 L vessel at 50°C.
a. What is the partial pressure (in atm)
of Br₂ in the mixture?
b. What is the total pressure (in atm) of
the mixture?
4.01 atm
0.621 atm
1.51 atm
40.1 atm

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionIn lab you need to measure out 0.84 mol of C3H6O3 for an experiment. How many grams should you weigh out?
Give your answer to 2 decimal spaces.

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionThe following reaction is first order in
respect to NO and second order in
respect to O₂. With this in mind, what
is the rate constant for the reaction?
Be sure you choose the answer with
the right units.

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionDuring kinetic studies, the following reaction was determined to be second order in respect to NO and zeroth order in respect to O₂. What is the overall order for the reaction?
2 NO (g) + O₂ (g) ⇒ 2 NO₂ (g)
first order
third order
second order
zeroth order

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionHow many moles of Fe₂O3 are in 211 g of the compound?
number of moles:

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionDimensional Analysis 1: Unit Conversions:Question 8
Convert 80 hours into seconds (60 seconds = 1
minute; 60 minutes = 1 hour). Round to two decimal
places when necessary (5.05).
Enter answer below
Enter your response

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionAllyl sulfide, C6H₁0S, in the substance that gives garlic, onion and leeks their characteristic odor. Some studies indicate that garlic may beneficial for the heart
and in lowering cholesterol.
a. How many moles of H are in 0.75 moles of C6H10S?
b. How many moles of S are in 23.2 g of C6H10S?
c. How many grams of C are in 44.0 g of C6H10S?

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionA 1.5% KBr (w/v) solution in water is produced by mixing...
1.5 moles of KBr in 100 moles of water.
1.5 moles of KBr with 100 ml of water.
1.5 g of KBr in a solution of 100 ml.
1.5 g of KBr with 100 ml of water.

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionWrite the balanced chemical equations for the reactions in which sodium phosphate is added to copper(II) sulfate and iron(III)
chloride, respectively. Include states of matter.
copper(II) sulfate and sodium phosphate:
iron(III) chloride and sodium phosphate:
These are examples of reactions.

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionLiquid octane (CH₂(CH₂) CH3) will react with gaseous oxygen (0₂) to produce gaseous carbon dioxide (CO₂) and gaseous water (H₂O). Suppose 4.6 g of octane is mixed with 8.48 g of oxygen. Calculate the maximum mass of water that could be produced by the chemical reaction. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.

Organic Chemistry
Practical Detection4 HCl(aq) + MnO₂ (s) ⇒ MnCl, (aq) + 2 H₂O(1) + Cl₂(g)
A sample of 43.9 g MnO₂ is added to a solution containing 43.1 g HCI.
What is the limiting reactant?
HCI
MnO₂
What is the theoretical yield of Cl₂?
theoretical yield:

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionA researcher studying the nutritional value of a new candy places a 5.70 g sample of the candy inside a bomb calorimeter and combusts it in excess oxygen. The observed temperature increase is 2.69 "C. If the heat capacity of the calorimeter is 42.70 kJ-K-¹, how many nutritional Calories are there per gram of the candy?
Calories per gram of candy: Callg

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionAcetylene (C₂H₂) gas and oxygen (O₂) gas react to form carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas and water (H₂O) vapor. Suppose you have 11.0 mol of C₂H₂ and 3.0 mol
of O₂ in a reactor.
What would be the limiting reactant? Enter its chemical formula below.

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionCalculate the number of moles of solute in 37.05 mL of 0.1155 M K₂Cr₂O, (aq).
moles of solute: mol

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionA nurse decides to move from England to India. The nurse currently makes 46,800 Euros as their annual salary. How much is this salary in Indian Rupees every month?
The conversion factor you will need is: 1 Euro = 95.12 Indian Rupees
The nurse's salary will be Indian Rupees per month.

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionGiven the following balanced equation, determine how many moles of O2 are needed to completely react with 8 moles of K: 4K+0₂ > 2K₂0
4.0 moles
1.0 moles
2.0 moles
3.0 moles

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionA 0.515 g sample of steam at 103.2 "C is condensed into a container with 4.97 g of water at 15.5 °C. What is the final temperature of the water mixture if no heat is lost? The specific heat of water is 4.18, the specific heat of steam is 2.01, and A Hvap = 40.7 kJ/mol.
T₁ =

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionIn the month of August, your electric bill was $145.68. What is the hourly cost of electricity in your home? The hourly cost for August was cents per hour. (Round to 5 decimal places) I

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionMatch each orbital with a description of its general shape.
d orbitals
s orbitals
f orbitals
p orbitals
a. dumbbell shaped
b. clover shaped
c. spherical
d. none of these

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionWhich of the following correctly summarizes the
Hund's Rule?
Matter can neither be created nor destroyed.
It only changes form during chemical
reactions.
It is fundamentally impossible to know both
the location and velocity of an electron at the
same time.
Each electron within an atom will have its
own unique set of four quantum numbers.
Electrons orbiting an atom fill the lowest
available energy levels prior to filling higher
energy orbitals.
The ground state or lowest energy state of an
atom is the one that contains the maximum
number of unpaired electrons.

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionWhat are the sublevels of the 3rd energy level (n=3)?
3s, 3d, 3f
3s, 3p, 3d
3s, 3p, 3f
3p, 3d, 3f
3s, 3p, 3d, 3f

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionWhich of the following correctly summarizes the Aufbau Principle?
Each electron within an atom will have its own unique set of four quantum numbers.
Matter can neither be created nor destroyed. It only changes form during chemical reactions.
It is fundamentally impossible to know both the location and velocity of an electron at the same time.
The ground state or lowest energy state of an atom is the one that contains the maximum number of unpaired electrons.
Electrons orbiting an atom fill the lowest available energy levels prior to filling higher energy orbitals.

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionA chemist adds 210.0 mL of a 2.68 × 10-5M zinc oxalate (ZnC₂04) solution to a reaction flask. Calculate the micromoles of zinc oxalate the chemist has added to the flask. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.
Organic Chemistry
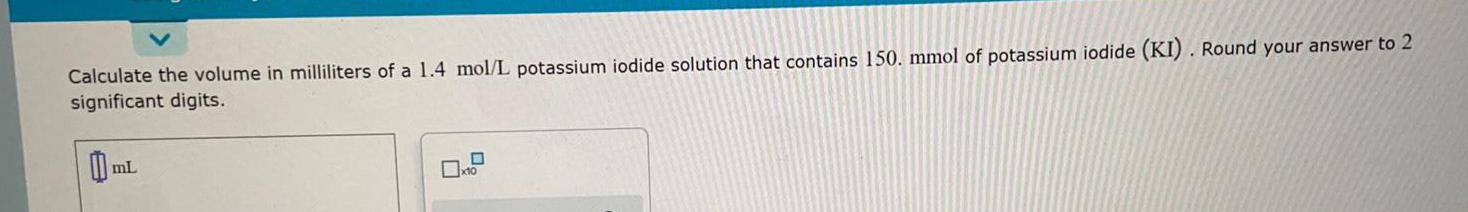
Practical DetectionCalculate the volume in milliliters of a 1.4 mol/L potassium iodide solution that contains 150. mmol of potassium iodide (KI). Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
Organic Chemistry
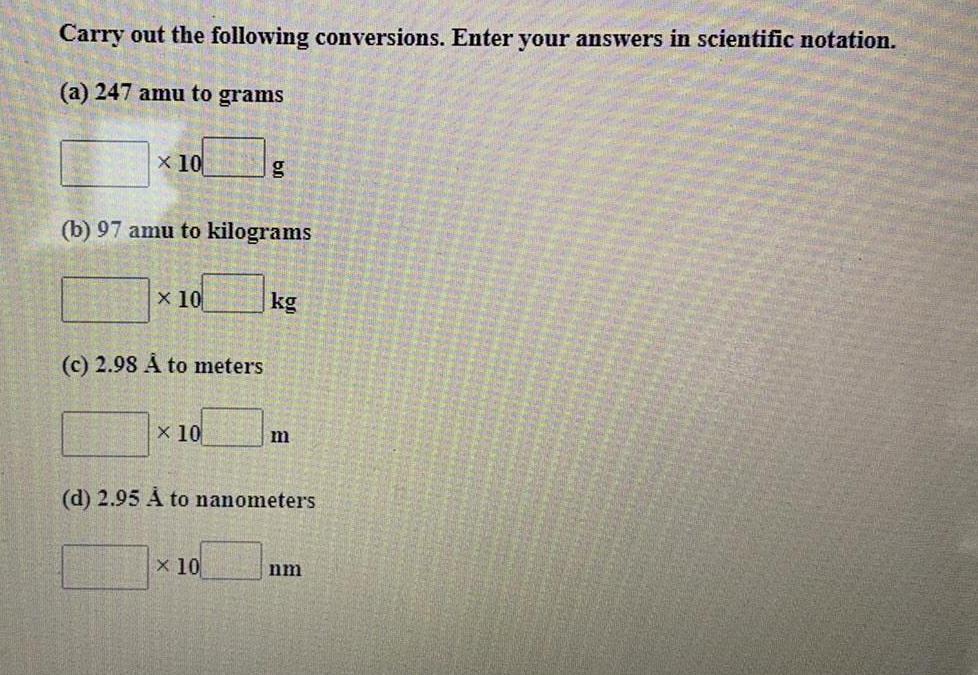
Practical DetectionCarry out the following conversions. Enter your answers in scientific notation.
(a) 247 amu to grams
(b) 97 amu to kilograms
(c) 2.98 A to meters
(d) 2.95 À to nanometers

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionIf the flask is open to the atmosphere, the mercury levels are equal. For each of the following situations where a gas is contained in the flask, calculate the pressure in the flask in torr,
atmospheres, and pascals.
with atmospheric P= 652 torr, height in tube 140. mm greater on side of flask

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionThe measured dipole moment of hydrobromic acid, HBr, is 0.82 D and the H-Br bond distance is
1.41 Å. Determine the percent ionic character of the bond in HBr.