Energetics Questions and Answers

Physical Chemistry
Energeticsa A phototube in a photoelectric device has a photosensitive element When light of wavelength 574 6 nm is shone on this surface electrons are emitted with a maximum kinetic energy of 1 958 x 10 19 J electron What wavelength of light would emit electrons with a maximum kinetic energy of 2 345 x 10 19

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsQ2 15 Points The feed gas contains 12 SO2 8 02 and 80 N enters the converter at 25 C The SO is completely converted to SO3 for the following reaction SO O SO3 and the product gas leaves the converter at 25 C 1 20 How much heat is transferred to the cooling coils from the converter per 100 g mole of the feed gas Consider basis of 100 g mole of the feed gas The enthalpy of SO2 and SO3 at 25 C and 1 atm are 296 9 and 395 2 kJ g mole respectively

Physical Chemistry
Energetics9 If one mole of an ideal gas C p m 5 R Ris expanded isothermally at 300 until it s volume is tripled then change in entropy of gas is a zero b infinity 5 R ln 3 d R ln 3 2 In previous problem if expansion is carried out freely Pext 0 then AS is b infinity a zero c R ln 3 d None When one mole of an ideal gas in

Physical Chemistry
Energeticsa 278 7 C b 278 7 K 78 AS for freezing of 10 g of H O l enthalpy of fusion is 80 cal g at 0 C and 1 atm is d 12 25 J K a 12 25 J K c 2 93 J K b 0 244 J K 79 Chloroform has AH vaporization 29 2 kJ mol and boils at 61 2 C What is the value m

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsHow many kj of heat will be evolved in making 22 4 L at STP 1 00 mol of H S from Fes and dilute hydrochloric acid The enthalpies of formation of FeS s H aq Fe2 aq CI aq H S g are 95 4 0 87 9 167 0 20 6 kcal mol respectively 180 1 kl mol 180 1 kg mol 13 1 kcal mol 13 1 kg mol

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsThe enthalpy of combustion of carbor hydrogen and sucrose are 393 5 286 2 an 5644 2 kJ mol respectively Calculate th enthalpy of formation of sucrose 1 6323 9 kJ 2 2226 kJ 3 2226 kJ 4 can t predict

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsFor the following reaction The thermodynamic parameters are Parametes AH kJ mol 2H g O g 2H 0 1 ASO j mol H O 1 285 9 70 H g 0 130 6 O g 0 205 Calculate at T 298K a Heat released by direct combustion b Maximum electrical work can be performed c Heat released in fuel cell during electrical work

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsPb NO3 2 aq Na2S aq PbS s 2 NaNO3 aq When a 50 0 mL sample of 0 20 M Pb NO3 2 aq and a 50 0 mL sample of 0 20 M Na2S aq are mixed in a calorimeter a reaction occurs according to the equation above If the temperature of the mixture increases from 23 0 C to 26 0 C what is the experimental value of AH ran for the reaction Assume that the mixture has a total mass of 100 g and a specific heat of 4 2 J g C

Physical Chemistry
Energetics0 5 mole each of two ideal gases A Cv m R R and B Cv m 3R are taken in a container 2 5 and expanded reversibly and adiabatically during this process temperature of gaseous mixture decreased from 350 K to 250 K Find AH in cal mol for the process a 100 R b 137 5 R c 375 R d None of these

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsWhen 0 16 g of glucose was burnt in a bomb calorimeter the temperature rose by 4 deg Calculate the calorimeter constant water equivalent of the calorimeter given that AH 2 8 x 106 J mol 1 molar enthalpy of combustion Molar mass of glucose 180 mol 1 5 73 x 10 J deg 2 7 53 x 10 J deg 3 6 22 x 10 J deg 4 3 57 10 J deg X

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsFor a given reaction DS 69 0 J mol K and the reaction is spontaneous at temperature above the crossover temperature 439K The value of DI kl mol assuming that DH and DS do not vary with temperature DS Delta Entropy DH Delta Enthalpy Select one O a 6 36 x 10 3 O b 30 3 O c 1 57 x 10 4 O d 1 57 x 10 4 Oe 30 3

Physical Chemistry
Energetics41 20 g Ar gas is allowed to expand reversibly and isothermally at 300 K from 5 L to 10 L Calculate the approximate value of work done Take R 25 3 J K mole at wt of Ar 40 u a 862 5 J b 375 J c 1437 5 J d 1250 J

Physical Chemistry
Energeticstemperature and low pressure 1 The value of AG for the phosphorylation of glucose in glycolysis is 13 8 kJ mol What would be the value of K at 298 K for the above process a e 55 69 b e 5 569 C e 0 5569 d e 556 9

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsExpansion of ideal gas takes place from 10 L in vacuum isothermally at 300 K Which of the following is correct 1 H 0 3 w 0 2 q 0 famonin Vaccino All of these a Pusa Road New Delhi 110005 Ph 011 47623456 AH W

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsKoq gener A aq The AG of the reaction is 9 770 kJ mol Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction at 25 C enzyme AG B aq What is AG for the reaction at body temperature 37 0 C if the concentration of A is 1 8 M and the concentration of B is 0 45 M kJ mol

Physical Chemistry
Energeticsf 10 Assertion The heat absorbed during the isothermal expansion of an ideal gas against vacuum is zero Reason The volume occupied by the molecules of an ideal gas is zero

Physical Chemistry
Energeticshydration 8 The heat of combustion of benzene determined in a bomb calorimeter is 870 k Cal mol at 298 K The value of AE for the reaction is a 1740 k Cal mol b 870 k Cal mol c 870k Cal mol d 1740 k Cal mol

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsOne mole of a real gas is subjected to heating at constant volume from P V T state to P2 V2 T state Then it is subjected to irreversible adiabatic compression against constant external pressure of P3 atm till syatem reaches the final state P3 V3 T3 If the constant volume molar heat capacity of real gas is Cy Find out correct expression for AH from state 1 to state 3 1 C T3 T P3V P V 2 Cv T2 T1 P3V2 P V 3 Cv T2 T1 P3V P V 4 Cp T2 T1 P3V P V

Physical Chemistry
Energetics3 Assertion A reaction which is spontaneous and by decrease of randomness must be accompanied exothermic Reason All exothermic reactions are accompanied by decrease of randomness

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsThe molar enthalpies of combustion of C H g C graphite and H g are 1300 394 and 286 kJ mol respectively The standard enthalpy of formation of C H g would be Options 226 kJ mol 1 626 kJ mol 1 226 kJ mol 1
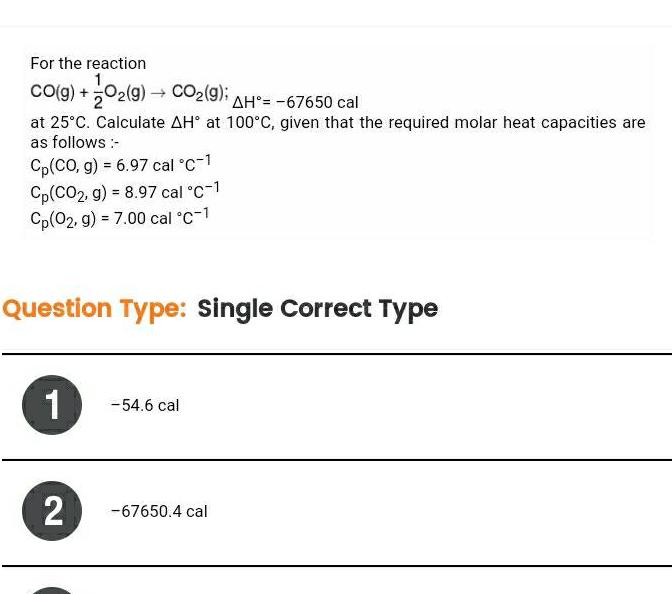
Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsFor the reaction 1 CO g O2 g CO 9 AH 67650 cal at 25 C Calculate AH at 100 C given that the required molar heat capacities are as follows Cp CO g 6 97 cal C 1 Cp CO2 g 8 97 cal C 1 Cp 02 g 7 00 cal C 1 Question Type Single Correct Type 1 2 54 6 cal 67650 4 cal

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsThe bond enthalpies of H H Cl Cl and H Cl are 435 243 and 431 kJ mol respectively The enthalpy of formation of HCl g will be Options 92 kJ mol 92 kl mol 1 247 kJ mol 1

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsQuestion No 42 If the temperature of the gas molecules is increased then which is an incorrect statement about Maxwell Boltzmann distribution curve O The most probable speed increases O The fraction of molecules having higher speed decreases O The fraction of molecules having most probable speed decreases The entire curve shifts towards right

Physical Chemistry
Energetics30 For a certain reaction the change in enthalpy and change in entropy are 40 63 kJ mol and 100 JK What is the value of AG at 27 C and indicate whether the reaction is spontaneous or not a 10630 J mol spontaneous b 10630 J mol non spontaneous c 7990 J mol spontaneous d 7900 J mol spontaneous

Physical Chemistry
Energeticsd Constant temperature pressure and composition 6 The heat of combustion of solid benzoic acid at constant volume is 321 30 kJ at 27 C The heat of combustion at constant pressure is R a 321 30 300 b 321 30 300 R c 321 30 150 R d 321 30 900 R

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsC 33 4 Calculate the enthalpy change in kcal for the reaction XeFXe F F F The average Xe F bond enthalpy is 34 kCal mol first I E of Xe is 279 kCal mol electron gain enthalpy of F is 85 kCal mol and the bond dissociation enthalpy of F is 38 kcal mol a 292 kCal mol b 383 kCal mol c 521 kCal mol d 528 kCal mol

Physical Chemistry
Energetics3 Aerial 01 2 ethyl anthraquinol 4 Electrolysis Hay high current density One mole of a non ideal gas undergoes a change of state 2 0 atom 3 0L 95 K 4atm 5L 245K with a change internal energy AE 30 0L atm The change in enthalpy AH of the process in L atom is 1 40 0 3 44 0 1 CH MgBr 3 HLA 2 42 3 4 not defined because pressure is not constant Product

Physical Chemistry
Energetics34 The volume of a gas decreases from 500 cc to 300 cc when a sample of gas is compressed by an average pressure of 0 6 atm During this process 10 J of heat is liberated The change in internal energy is a 2 16 J b 12 156 J c 2 16 J d 101 3 J

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsWhich of the following statements is are incorrect Options Absolute value of enthalpy cannot be determined Absolute value of internal energy cannot be determined Absolute value of entropy can be determined Internal energy enthalpy and

Physical Chemistry
Energeticsc 676 5 kJ d 676 5 kJ 54 When 50 cm of 0 2 N H SO is mixed with 50 cm of IN KOH the heat liberated is a 11 46 kJ b 57 3 kJ c 573 J d 53 J 55 The correct relationali

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsThe following information is given for antimony at 1 atm AHvap 1440 00 C 1 605 10 J g T 1440 00 C Tm 631 00 C Specific heat solid 0 2090 J g C Specific heat liquid 0 2590 J g C AHfus 631 00 C 161 1 J g A 34 20 g sample of solid antimony is initially at 611 00 C If 5 179 x 10 J of heat are added to the sample at constant pressure P 1 atm which of the following is are true Select all that apply The sample is a liquid The sample is at a temperature greater than 631 00 C The sample is a solid The sample is a solid in equilibrium with liquid The sample is at a temperature of 631 00 C

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsThe standard reaction enthalpy of the reaction Zn s H O g ZnO s H g is 223 kJ mol and the standard reaction Gibb s functions is 33 kJ mol at 1520 K Assuming that both AH and AS remain constant estimate the minimum temperature in Kelvin above which the equilibrium constant becomes greater than one

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsThe diamonds high pressure are formed from graphite under very Given that the densities of graphite and diamond are respectively 2 4 and 3 6 g cm and are independent of pressure AGO values for graphite and diamond are zero and 3 0 kJ mol respectively If the equilibrium pressure at which graphite is converted into diamond at 25 C is P bar then the value of 0 01P is

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsOne mole of a monatomic gas at pressure 2 atm 279 K is taken to final pressure 4 atm by a reversible path described by P V constant Calculate the magnitude of process AE W for the

Physical Chemistry
Energetics5 a The diagram to the right represents a diver s motion from the top of a high diving board into a pool of water At what point does the diver have the greatest kinetic energy and the least potential energy

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsOne mole of a gas changed from its initial state 15L 2 atm to final state 4L 10atm reversibly If this change can be represented by a straight line in P V curve maximum temperature approximate the gas attained is x K Then find the value of x x 700 value is in hundreds

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsFor the reaction CO g O2 g CO g AH 67650 cal at 25 C Calculate AH at 100 C given that the required molar heat capacities are as follows C CO g 6 97 cal C C CO g 8 97 cal C Cp O2 g 7 00 cal C 1 54 6 cal 3 67681 1 cal 2 67650 4 cal 67762 5 cal

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsFor an exothermic reaction following two steps are involved Step 1 A B 1 slow Step 2 1 AB fast Which of the following graphs correctly represent this reaction 3 Potential energy Potential energy A B Reaction coordinate a A B AB Reaction coordinate c AB 2 Potential energy A B Potential energy Reaction coordinate b A B Reaction coordinate d AD AB

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsQ For a reaction ALP the plots of A and P with time at temperatures T and T are given below 10 A mol L Time T 2 T 10 A P mol L If T2 T1 the correct statement s is are Assume AH and AS are independent of temperature and ratio of In K at T to ln K at T2 is greater than 1 T2 TT Here H S G and K are enthalpy entropy Gibbs energy and equilibrium constant respectively A AH 0 AS 0 B AGO 0 AH 0 C AGO 0 AS 0 D Time FF T T LIFE Adu 20181

Physical Chemistry
Energetics2Ca s O2 g 2CaO s AHorxn 1269 8 kJ ASorxn 364 6 J K For this problem assume that all reactants and products are in their standard states Calculate the free energy change for the reaction at 29 C

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsIn a particular chemical reaction at 500 C and 1 atm pressure in the presence of catalyst V 205 the energy released is 182 kJ We can say about this reaction that it is a an O O exothermic reaction endothermic reaction neither exothermic reaction nor endothermic reaction data insufficient

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsA gas phase recombination reaction is first order in each of the reactants The energy of activation for the reaction is 49 6 kJ mol At 55 C the rate constant is 0 23 m s1 Calculate the entropy of activation at 55 C Select one a 79 J K 1 mol 1 b 87 J K 1 mol 1 Oc 112 J K 1 mol 1 O d 78 J K 1 mol 1 e 93 J K 1 mol 1

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsConsider the combustion of liquid methanol CH OH 1 O2 g CO g 2H O l AH 726 5 kJ If the reaction were written to produce H O g instead of H O l the magnitude of AH increase decrease O remain unchanged O can t be predicted

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsCalculate the quantity of energy produced per gram of reactant for the fusion of H 3 atomic mass 3 016049 amu with H 1 atomic mass 1 007825 amu to form He 4 atomic mass 4 002603 amu Express your answer using five significant figures WAZ Pa G P C ww 2

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsIdentify which of the following is correct about the below given reaction 2 H O g 2 H2 g O2 g At low temperature the reaction is nonspontaneous and AG 0 and at high temperature the reaction is nonspontaneous and AG 0 At low temperature the reaction is nonspontaneous and AG 0 and at high temperature the reaction is spontaneous and AG 0 At low temperature the reaction is spontaneous and AG 0 and at high temperature the reaction is nonspontaneous and AG 0 O At low temperature the reaction is spontaneous and AG 0 and at high temperature the reaction is spontaneous and AG 0 O It is not possible to determine without more information

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsWhen a liquid molecular mass 378 that is immiscible with water was steam distilled at 95 C at a total pressure of 750 torr the distillate contained x gm of liquid per gm of water Calculate the value of x Where vapour pressure of water is 630 torr at 95 C

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsUse the collision theory of gas phase reactions to calculate the theoretical value of the second order rate constant for the reaction D2 g Br2 g 2 DBr g at 450 K assuming that it is elementary bimolecular Take the collision cross section as 0 30 nm the reduced mass as 3 930 u and the activation energy as 200 Kj mol Select one a 1 7 X 10 2 dm mol s1 b 4 7 X 1013 dm mol st c 4 6 X 1013 dm mor s1 d 6 4 X 10 2 dm mol s1 e 3 5 X 10 1 dm mol g

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsPhotoelectric effect supports quantum nature of light because a the energy of released electron is discrete b the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons depends only on the frequency of light and not on its intensity c even when the metal surface is faintly illuminated the photoelectrons leave the surface immediately d electric charge of the photoelectrons is quantised

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsIf an ideal gas expands isothermally from 50 L to 100 L against 2 atm external pressure then values of W AU and Q respectively will be NCERT Pg 166 1 100 L atm zero and 100 L atm 2 50 L atm zero and 50 L atm 3 100 L atm zero and 100 L atm 4 50 L atm zero and 50 L atm

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsWhat is bond enthalpy Calculate C Cl bond enthalpy from following reaction CH4 g Cl2 g CH3Cl g HCl g AH 104 KJ mol if C H Cl Cl and H Cl bond enthalpies are 414 243 and 431 KJ mol respectively