Energetics Questions and Answers

Physical Chemistry
Energetics03 A liquid confined inside an adiabatic container is suddenly taken from state 1 to state 2 by single stage process as shown then AH is A AH 2P Po 2yPo Vo 0 Y 1 C AH 3P V Vo 2 4V B AH PoVo 00 D AH 3yP Vo 0 0 V 1

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsMoving to the next ques on 7 Then a sample of aqueous hydrochloric acid was neutralized with aqueous sodium hydroxide in a calorimeter the temperature of 9 1 e reaction increased from 25 0 C to 31 5 C If the specific heat of water is 1 00 cal g C calculate the quantity of energy in calories involved in this eutralization reaction

Physical Chemistry
Energeticsg sample of NH4NO3 is heated in bomb calorimeter The temperature of the AT calorimeter increases by 6 32 K the heat capacity of the system is 1 23 kJ g deg The molar heat of decomposition for NH4NO3 is 1 16 1 kJ mol 3621 89 kJmol 2 7 53 kJmol 4 498 1 kJ mol

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsOut of the following properties how many are extensive properties 1 Resistance 2 E M F 3 lonic Mobility 4 Dipole Moment 5 Heat Capacity 6 Specific Heat 7 Densit 8 Specific volume A reversible reaction is carried out at 500k where its equilibrium constant in unity If AH at 500K is 4 K I The

Physical Chemistry
Energeticssir how pressure in intensive property if i have 1 mole of of gas in a container then pressure be P if i leave 1 2 moles now wont the pressure become P 2 at cons volume and temperature as per PV nT

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsQ Given the following entropy values in JK mol at 298 K and 1 atm H g 130 6 Cl g 223 0 HCl g 186 7 The entropy change in JK mol for the reaction H g Cl g 2HCl g is CBSE AIPMT 1996 a 540 3 b 727 0 c 166 9 d 19 8

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsObtain the parameters of the Lennard Jones potential from the second virial coefficient of carbon dioxide assuming that the van der Waals EOS is applicable jo U r k T 1 r dr b 3 B 2 NA 2 Explain this B integration and how to get this final coefficient 03

Physical Chemistry
Energeticse cyclic process for an ideal gas is shown below Here P V and T are pressure volume and temperature respectively The thermodynamic parameters q w H and U are heat work enthalpy and internal energy respectively JEE 2018 The correct option s is are Volume V A 9AC C AHCA AUCA and ar A P V T 19 AUBC and WAB P V V and Ac 9AC AUBC B P V T C 58001 bar C P V T Temperature T D 1450 bar B WBC P V V and BC AHAC D ABC AHAC and AHCA AUCA
Physical Chemistry
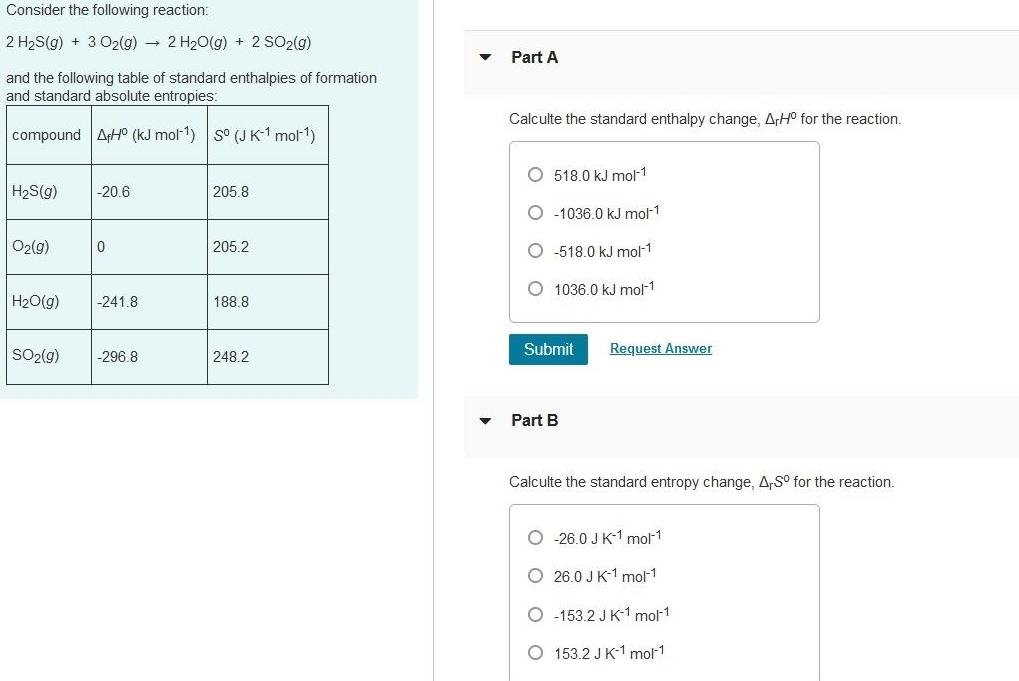
EnergeticsConsider the following reaction 2 H S g 3 O2 g 2 H O g 2 SO2 g and the following table of standard enthalpies of formation and standard absolute entropies compound AHO kJ mol 1 S J K 1 mol H S g O2 g H O g SO g 20 6 0 241 8 296 8 205 8 205 2 188 8 248 2 Part A Calculte the standard enthalpy change ArH for the reaction O518 0 kJ mol 1 O 1036 0 kJ mol 1 O 518 0 kJ mol 1 O 1036 0 kJ mol 1 Submit Request Answer Part B Calculte the standard entropy change A S for the reaction O 26 0 J K 1 mol 1 O26 0 J K 1 mol 1 O 153 2 J K 1 mol 1 O 153 2 J K 1 mol 1

Physical Chemistry
Energetics8 The rate of reaction decreased by 3 555 times when the temperature was changed from 40 C to 30 C The activation energy in kJ mol of the reaction is Take R 8 314 J mol K and In 3 555 1 268 JEE Main 2020

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsFor a zero order reaction which of the following statement is false uestion Type Single Correct Type 1 2 3 4 The rate is independent of temperature of the reaction The rate is independent of concentration of the reactants The half life period depends on initial concentration of reactants The rate constant has the unit mol litre 1 sec 1

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsElectrical work done in one second is equal to electrical potential multiplied by total charge passed If we want to obtain maximum work from a galvanic cell then charge has to be passed reversibly The reversible work done by a galvanic cell is equal to decrease in its Gibbs energy and therefore if the emf of the cell is E and nF is the amount of charge passed and AG is the Gibbs energy of the reaction then

Physical Chemistry
Energetics7 At 25 C the ionic mobility of CH COO H are respectively 4 1 x 10 4 3 63 10 cm sec The conductivity of 0 001M CH COOH is 5 10 5S cm Dissociation constant of CH COOH is a 1 64 10 5 c 3 10 5 b 3 10 4 d 3 x 10 6
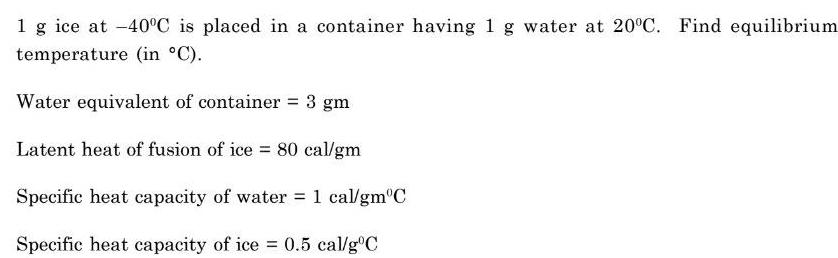
Physical Chemistry
Energetics1 g ice at 40 C is placed in a container having 1 g water at 20 C Find equilibrium temperature in C Water equivalent of container 3 gm Latent heat of fusion of ice 80 cal gm Specific heat capacity of water 1 cal gm C Specific heat capacity of ice 0 5 cal g C

Physical Chemistry
Energetics1 4 2 16 3 Which of the following are not a constant value 55 fth f ax for face between two given thermodynamic states of a omfafine seat given system 0 q iii U PV 1 i and iv 2 iii and iv 3 ii only 4 i only The relative lowering of vapour pressure of an 56 ii q w iv H TS 1 q iii U PV D q w iv HI TS 4 4 face from 1 i iv 3 ret ii an averafter fad re and safa farzan 2 i iv

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsA ground state H atom absorbs a photon with a frequency equal to 3 20 x 1015 sec The atom then emits two photons one at a time two successive jumps one of wavelength 2626nm to reach an intermediate level and a second to reach the ground state a What higher level n did the electron reach b What intermediate level n did the electron reach c What was the wavelength of the second photon emitted

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsIf S 0 50 SO 1 2O SO3 SO3 H O H SO4 AH 298 2 kj AH 98 7 kJ AH3 130 2 kJ H 1 2O2 H O AH4 287 3 kj Then the enthalpy of formation of H SO4 at 298 K is 814 4 kJ 650 3 kJ

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsA 1 0 mol of Ideal gas initially at 10 atm and 300K is allowed to expand isothermally to 1 0 atm Calculate the net work done by the system P V diagram is given P 1 1247 1 J 3 1247 1 J 10atm S W 5atm rev W V 1atm 2 3741 3 J 4 3741 3 J

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsConsider the reactions given below On the basis of these reactions find out which of the the algebraic relationship given in options a to d is correct i C g 4H g CH 9 AH a kJ mol 1 ii C graphite 2H 9 CH4 AH y kJ mol 1 1 x y 2 x 2y 3 x y 4 x y

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsIf enthalpy of neutralization of a weak monobasic acid HA with NaOH is 7 7 kcal eqv them ionization enthalpy of HA is Enthalpy of neutralization of HCI with NaOH is 13 7 kcal 2 17 eqv 1 21 4 kcal eqv 3 19 7 kcal eqv 2 6 kcal eqv 4 12 kcal eqv 8

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsIn the reaction BrO 3 aq 5Br aq 6H 3Br 1 2H O 1 The rate of appearance of bromine Br is related to rate of disappearance of bromid ions as following 1 d Br dt 3 5 d Br dt 2 d Br dt 5 3 d Br dt 3 d Br dt 5 3 d Br dt 4 d Bral dt 3 5 d Br1 dt
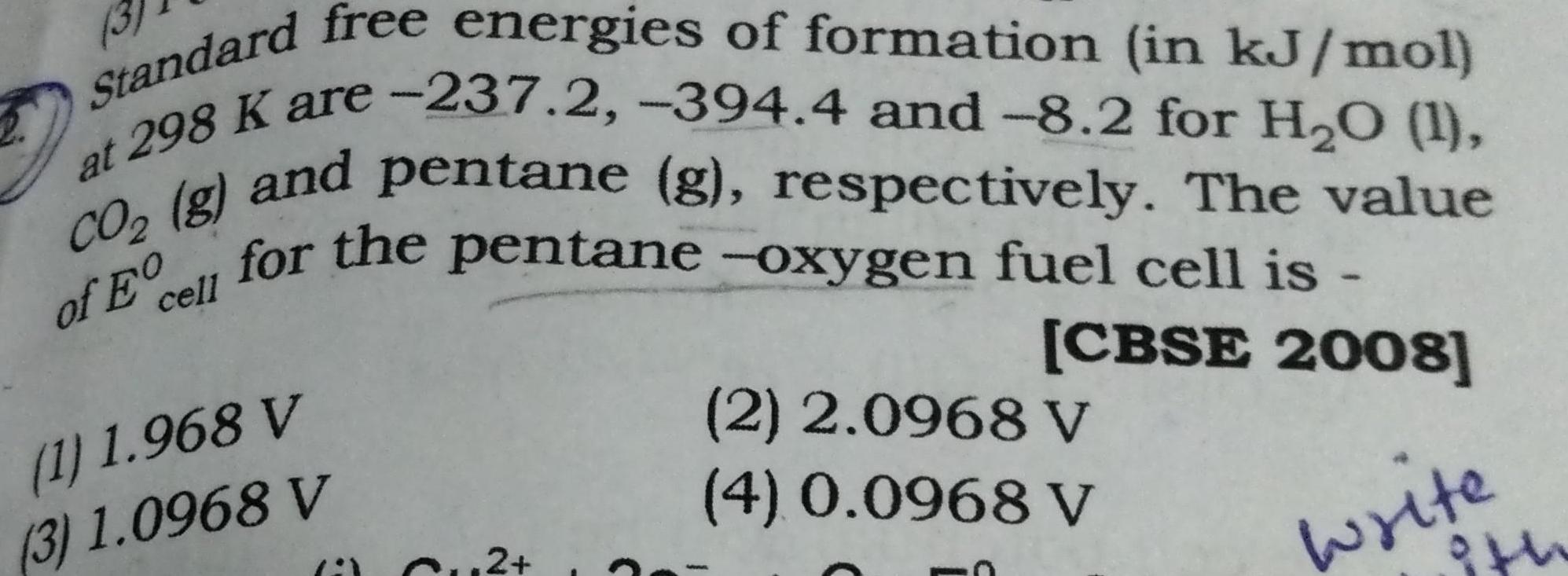
Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsStandard free energies of formation in kJ mol at 298 K are 237 2 394 4 and 8 2 for H O 1 of Ecell for the pentane oxygen fuel cell is CO g and pentane g respectively The value CBSE 2008 write 1 1 968 V 3 1 0968 V Cu2 2 2 0968 V 4 0 0968 V

Physical Chemistry
Energetics14 The lattice enthalpy of KI will be if the enthalpy 1 AH KI 78 0 kcal mol 1 II lonisation energy of K to K is 4 0 eV III Dissociation energy of l to 1 is 28 0 kcal mol IV Sublimation energy of K is 20 0 kcal mol V Electron gain enthalpy for I to 1 is 70 0 kcal mol 1 VI Sublimation energy of 12 is 14 0 kcal mol 1 1 eV 23 0 kcal mol 1 14 1 kcal mol 2 14 1 kcal mol 3 141 kcal mol 1 A

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsFollowing process is used in welding metals C H g O g H O g 2CO g 5 2 If 39 gm of acetylene undergo combustion at 25 Take R JK mol 3 A q for process 1197 5 kJ C AS 3000 J K 4H 1200 kJ mol 1 atm and 327 C then B Work done 2 5 kJ D AS is negative

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsThe enthalpy of combustion of benzoic acid C6H5COOH is commonly used as the standard for calibrating constant volume bomb calorimeters its value has been accurately determined to be 3226 7 kJ mol When 3 2017 g of benzoic acid are burned in a calorimeter the temperature rises from 21 84 C to 26 67 C What is the heat capacity of the bomb Assume that the quantity of water surrounding the bomb is exactly 2250 g

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsThree moles of an ideal gas at 200 K and 2 0 atm pressure undergo reversible adiabatic compression until the temperature becomes 250 K for the gas C is 27 5 JK mol in this temperature range 1 0 3 Calculate q w AU AH and final V and final P Given 1 4 2 1 5 4 13 3 2 61

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsWhich one is correct among the following 1 A H CH g AH comb C grap AH AHO comb H g AH CH g comb 2 AH comb CH g A H CO g A H H O C AH CH g 3 A H CH g AH ublimation C graphite 2BE H 4BEC H 4 AH com CH g 4BEc x 4BEC BEO o 2BEC o AH H O 4BE o

Physical Chemistry
Energetics2 The molar heat capacity Cpm of SO g is described by the following equation over the range 300 K 1700 K Cp m 3 093 6 967 10 45 81 10 7 1 035 10 In this equation T is the R T K 7 K T K Th absolute temperature in Kelvin The ratios ensure that Cpm has the correct dimension K Assuming ideal gas behavior calculate q w AU and AH if 1 mol of SO g is heated from 75 to 1350 C at a constant pressure of 1 bar Explain the sign of w

Physical Chemistry
Energetics4 Glycerol 2 moles of an ideal gas monoatomic is subjected to isothermal compression upto half of its initial volume and then allowed to undergo isothermal expansion upto 2 3rd of its original volume The value of AU change in internal energy in the entire process is 1 2J 3 6J 2 3J 4 O relation is are correct for the

Physical Chemistry
Energetics2 When a 50 0 mL volume of a 0 858 mol L solution of H O decomposes in the presence of 10 0 mL of a Fe NO3 3 catalyst the temperature of the solution rises 16 7 C Assuming 1 0 g mL density for the 60 0 mL of solution a specific heat of 4 18 J g C for the solution and a heat capacity of 10 0 J C for the calorimeter a Calculate the total heat released by the decomposition of the 50 0 mL of the H O solution b Calculate the enthalpy heat change for the decomposition of H O in units of kJ mole ve for 2a and 2b

Physical Chemistry
Energetics97 If S O SO SO 0 SO AH 298 2 AH 98 7 SO3 H O H SO AH 130 2 H 0 H O AH 287 3 Then the enthalpy of formation of H SO4 298 K is 1 814 4 kJ 3 320 5 kJ 2 650 3 kJ 4 433 5 kl

Physical Chemistry
Energetics27 16 gm of O expand at constant pressure and 273 15 K to occupy double its original volume The work done during the process will be A w 260 cal B w 180 cal C w 130 cal D w 273 15 cal

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsWhen one mole of C6H5COOH s is burnt completely in sufficient oxygen in closed rigid vessel then it liberate 2kJ heat at 300K Find magnitude of enthalpy change of reaction in Joules at 300K when 12 2gm C6H5COOH s is reacted with 48 grams of oxygen R 8J mol K

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsOne mole of a real gas is subjected to a process from 2 bar 30 L 300 K to 2 bar 40 L 500 K The molar heat capacity of gas at constant volume and constant pressure are 25 and 40 J K mol respectively What is the change in internal energy of the gas in this process a 5000 J c 8000 J b 6000 J d 10 000 J

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsFive moles of an ideal gas expand isothermally and reversibly from a pressure of 10 atm to 2 atm at 300 K What is the largest mass approx which can be lifted through a height of 1 m in this expansion A 20 48 g C 20 48 kg B 204 8g D 2048 kg

Physical Chemistry
Energetics7 Use the Maxwell distribution of speeds to estimate the fraction of N molecules at 400 K that have speeds in the range 290 to 300 m s Ans 1 023 10 8 In the following questions calculate the final volume of gas in Litre at the specified conditions assuming the temperature and mass remain constant Ans a 0 15 I b

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsThe enthalpy of combustion of carbon hydrogen and sucrose are 393 5 286 2 and 56442 kJ mol respectively Calculate the enthalpy of formation of sucroso 1 3 4 6323 9 kJ 2226 kJ 2226 kJ can t predict

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsWhen a system is taken from A to C through path ABC 10 J of heat flows to the system and 4 J of work is done by the system B C A D How much heat flows into the system in path ADC if the work done by the system is 3 1

Physical Chemistry
Energetics7 Choose the reaction s from the following options for which the standard enthalpy of reaction is equal to standard enthalpy of formation JEE Adv 2019 Paper A S8 s O g SO g 8 C 2C g 3H g C H g B 2H g O g 2H O 1 D 0 9 03 9

Physical Chemistry
Energetics2 59 At 500 kilobar pressure density of diamond and graphite are 3 g cc and 2 g cc respectively at certain temperature T The value of AH AU is kJ mol kJ mol for the conversion of 1 mole of graphite to 1 mole of diamond at temperature T

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsAn ideal gas is allowed to expand both reversib irreversibly in an isolated system If T is the initial temperature and Tis the final temperature which of the following statements is correct a Trev Timev b TT for both reversible and irreversible processes c Tirrev Trev d TT for reversible process but T T for irreversible process

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsConsider the conversion of O into O as 1 0 0 0 fast 11 O 0 20 slow One doubling the concentration of Os the rate of overall reaction becomes 1 1 times 3 3 times 2 2 times 4 4 times

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsWhat is the amount of heat in Joules absorbed by 18 g of water initially at room temperature heated to 100 C If 10 g of Cu is added to this water than decrease in temperature in Kelvin of water was found to be C p m for water 75 32 J mol K C p m for Cu 24 47 J mol K a 5649 369 c 5278 342 b d 5544 324 3425 425

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsWhat is the AG f Cr3 given AG following unbalanced reaction O g Cr s 197 5 kJ mol 214 5 kJ mol 287 1 kJ mol 351 3 kJ mol f H 0 1 Cr aq 237 19 kJ mol and AG acidic solution f H 0 kJ mol and the

Physical Chemistry
Energetics4A n factors n n and n respectively During titration with an oxidizing agent Let at t 0 volume used of reagent be V Let at t t volume used of reagent be V Let at t volume used of reagent be V The rate constant for above action if only and Care participa C K 78 is taking place 28 3C following first order kinetics if all A B and C are oxidisable with 14 2 302 BK V C K The rate constant for above reaction if all are participating in titrations 2 303 V A K log V t 2 303 t 2 303 log log Mitrations REVIEW BOOKLET 2021 JEEA PART 4 CHEMISTRY V 4n 2n 3n V 3n 2n 3n V n MEGACOSM

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsCorrect for the following graph is are AG AI O ALO 2Mg O 2MgO 1673 T K 1 Mg will be good reducing agent below 1673 2 Al will be good reducing agent below 1673 3 Al O3 will be good reducing agent after 1673

Physical Chemistry
Energetics30 Three mole of an ideal gas is taken through the process ABC as shown in the figure The total work done by the gas is T 27 T P 1 2 RTo In2 3 12 RTo In2 B 2P 8P P 2 4 RT In2 4 4 RTo In2 1 3 35 Am firs pip OV res 1

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsEnthalpy of the reaction 1 O g CH OH is negative I 2 enthalpy of combustion of CH3OH 1 and CH4 g a and b respectively then select the correct relationship are 1 a b 3 a b CH4 g 2 a b 4 a b

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsWhat is the energy change when 25 0 g of water is cooled from vapor at 100 0 C to liquid water at 40 0 C Water H O Physical Data Molar Mass 18 02 g mol Enthalpy of Vaporization AHvap 40 7 kJ mol Specific Heat C 4 184 J g C 1 O 6 27 kJ O 6 27 kJ O 62 7 kJ

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsMaximum change in temperature is observed on mixing which of the following One litre each of 0 01 M HCI and 0 01 M KOH x 500 mL each of 0 02 M HCI and 0 02 M KOH One litre of 0 01 M HCI and 500 mL of 0 02 M KOH 100 mL of 0 1 M HCI and 50 mL of 0 2 M KOH Solution Answer 4 Enthalpy change is same in all but volume is minimum in