Limits & Continuity Questions and Answers

Calculus
Limits & ContinuityA football player punts a ball at an angle of 45° at 1.5 feet off the ground, with an initial velocity of 78 feet per second. How far away does the ball land, in feet, when hitting the ground?
Calculus
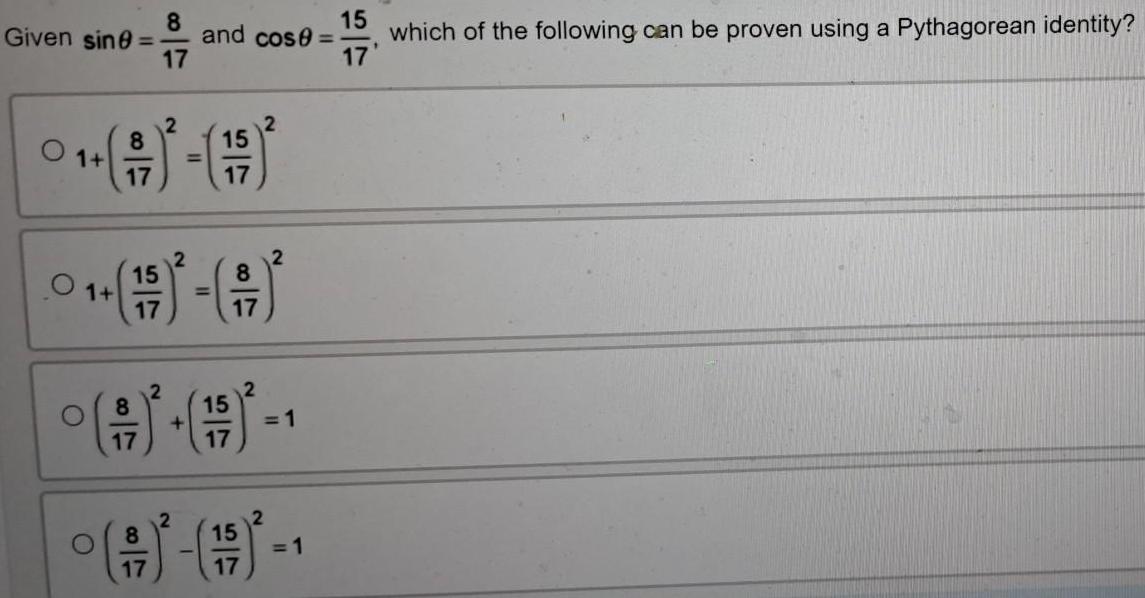
Limits & ContinuityGiven sinθ = 8/17 and cosθ = 15/17 which of the following can be proven using a Pythagorean identity?
1 + (8/17)^2 = (15/17)^2
1 + (15/17)^2 = (8/17)^2
(8/17)^2 + (15/17)^2 = 1
(8/17)^2 - (15/17)^2 = 1


Calculus
Limits & ContinuityThe concentration, C, of phenylbutazone, in micrograms per milliliter (µg/mL), in the plasma of a calf injected with this anti-inflammatory agent is given approximately by C(t) = 42.06 e^ -0.01042t, where t is the number of hours after the injection and 0 st≤90.
a) Given that the model is accurate for 0 st≤ 90, what is the initial dosage?
b) What is the average amount of phenylbutazone in the calf's body for the time between 15 and 90 hours?
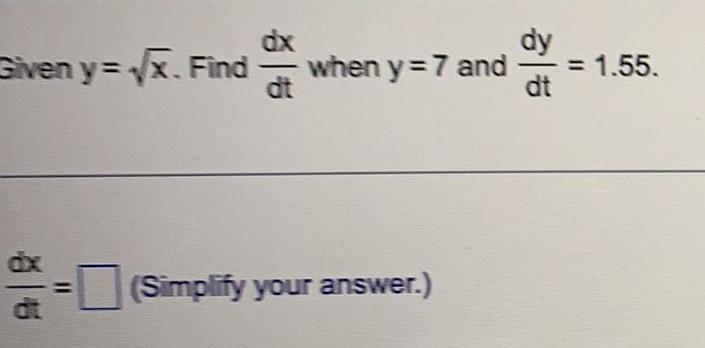
Calculus
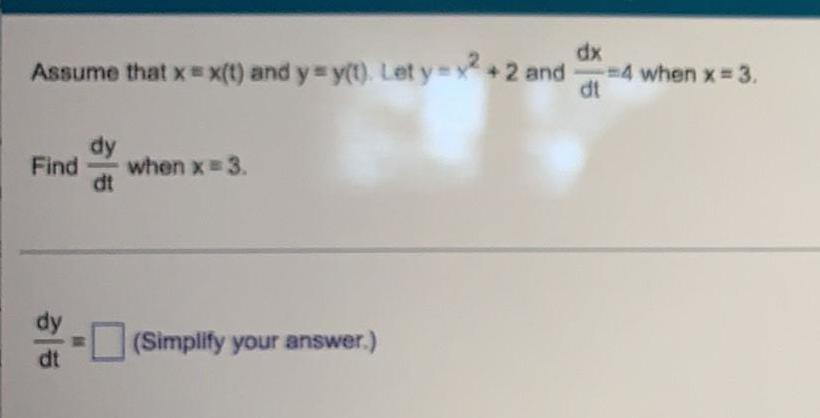
Limits & ContinuityAssume that x = x(t) and y=y(t). Let y = x² +2 and dx/dt = 4
Find dy/dt when x = 3.


Calculus
Limits & Continuityf(x) = 3x+12/x-4
Finds
a. relative maximum and minimum
b. vertical and horisontal asymptotes
c. Graph
Calculus
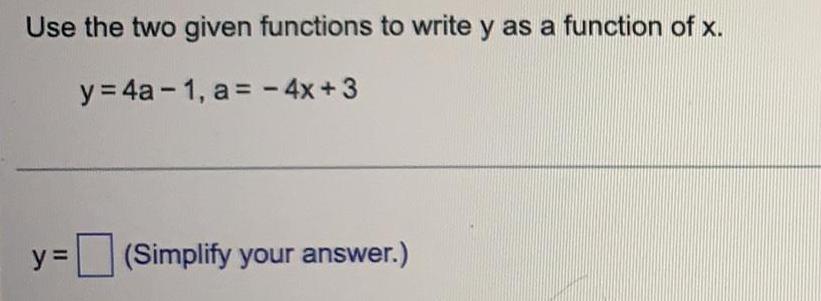
Limits & ContinuityUse the two given functions to write y as a function of x.
y = 4a-1, a = - 4x +3
y =
(Simplify your answer.)
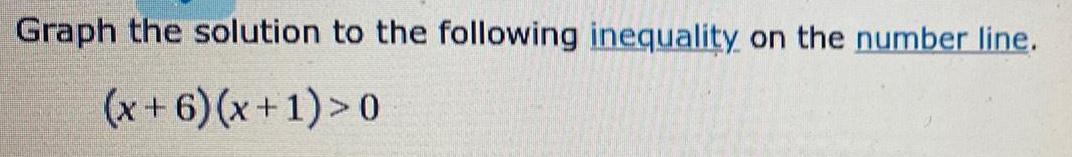
Calculus
Limits & ContinuityGraph the solution to the following inequality on the number line.
(x+6) (x+1)>0

Calculus
Limits & ContinuityLet f(x) = x/2 - sin πx/6. Find all values of c in the interval (-1, 0) such that f'(c) =
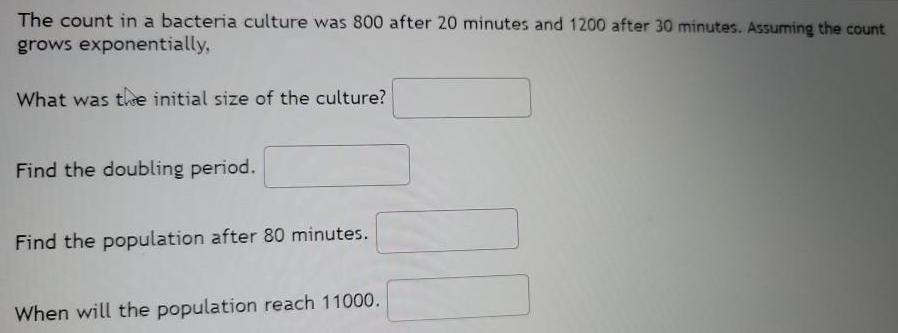
Calculus
Limits & ContinuityThe count in a bacteria culture was 800 after 20 minutes and 1200 after 30 minutes. Assuming the count grows exponentially,
What was the initial size of the culture?
Find the doubling period.
Find the population after 80 minutes.
When will the population reach 11000.


Calculus
Limits & ContinuityLet f(x) = 1/x-6 and g(x) = 7/x + 6
Find the following functions. Simplify your answers.
f(g(x)) =
g(f(x)) =
![Consider f(y) = -13y - 26 sin(y) on [0, 2π].
Determine the intervals on which f is decreasing.
f is decreasing on:
f is decreasing nowhere.
Determine the intervals on which f is increasing.
f is increasing on:
f is increasing nowhere.
Determine the value and location of any local minimum of f. Enter the solution in (y, f(y)) form. If
multiple solutions exist, use a comma-separated list to enter the solutions.
f has a local minimum at:
f has no local minimum.
Determine the value and location of any local maximum of f. Enter the solution in (y, f(y)) form. If
multiple solutions exist, use a comma-separated list to enter the solutions.
f has a local maximum at:
f has no local maximum.](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/84288903-1657650125.3784556.jpeg?w=256)
Calculus
Limits & ContinuityConsider f(y) = -13y - 26 sin(y) on [0, 2π].
Determine the intervals on which f is decreasing.
f is decreasing on:
f is decreasing nowhere.
Determine the intervals on which f is increasing.
f is increasing on:
f is increasing nowhere.
Determine the value and location of any local minimum of f. Enter the solution in (y, f(y)) form. If
multiple solutions exist, use a comma-separated list to enter the solutions.
f has a local minimum at:
f has no local minimum.
Determine the value and location of any local maximum of f. Enter the solution in (y, f(y)) form. If
multiple solutions exist, use a comma-separated list to enter the solutions.
f has a local maximum at:
f has no local maximum.
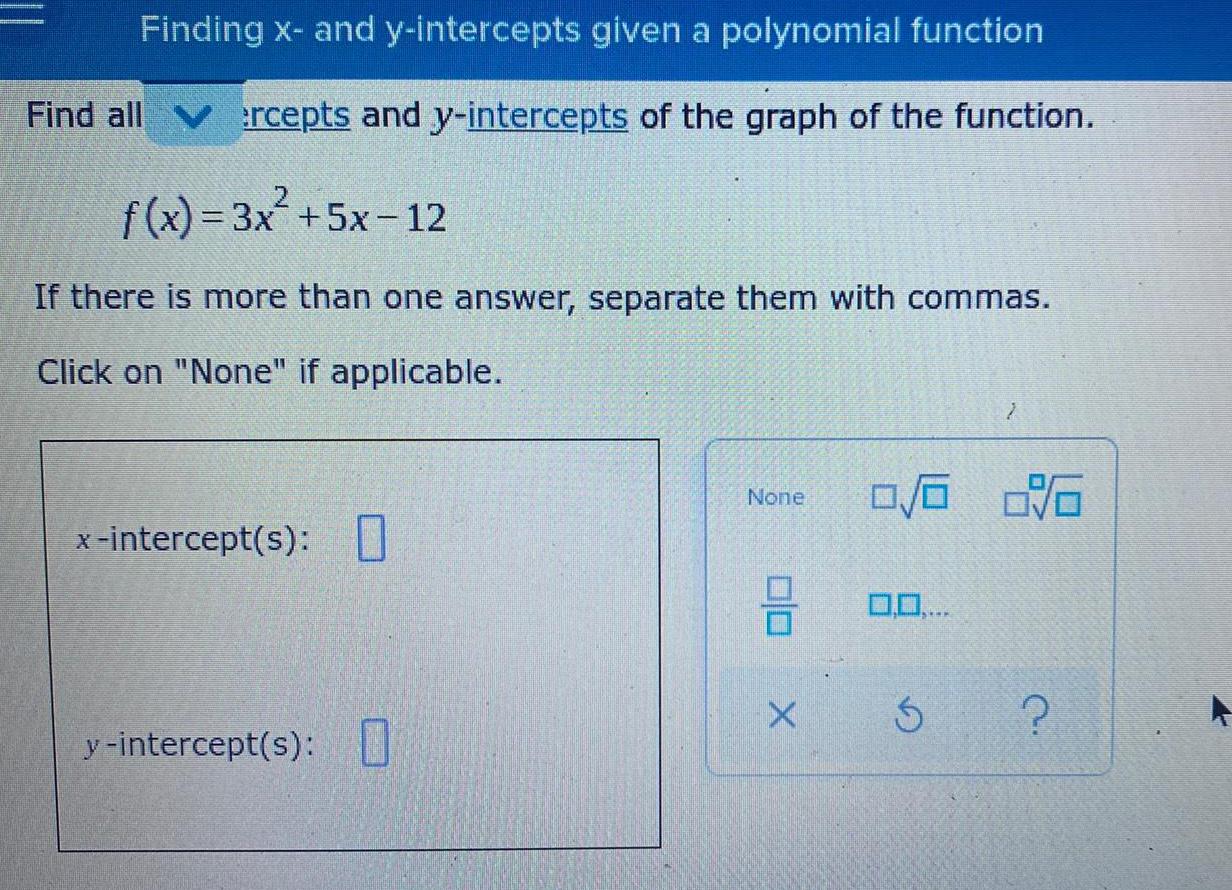
Calculus
Limits & ContinuityFinding x- and y-intercepts given a polynomial function
Find all ercepts and y-intercepts of the graph of the function.
f(x) = 3x² +5x-12
If there is more than one answer, separate them with commas.
Click on "None" if applicable.
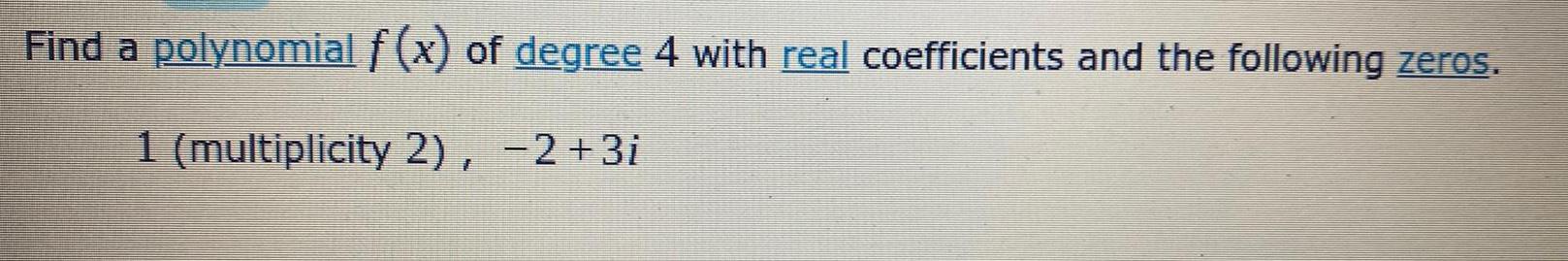
Calculus
Limits & ContinuityFind a polynomial f (x) of degree 4 with real coefficients and the following zeros.
1 (multiplicity 2), -2+3i

Calculus
Limits & ContinuityDetermining the end behavior of the graph of a polynomial...
(a) f(x)= = -2x + 2x - 7x + 4
Falls to the left and rises to the right
Rises to the left and falls to the right
Rises to the left and rises to the right
Falls to the left and falls to the right
(b) f(x) = 2x3 + 9x2 - 6x-4
Falls to the left and rises to the right
Rises to the left and falls to the right
Rises to the left and rises to the right
Falls to the left and falls to the right
(c) f(x) = -5x (2x - 5)²
Falls to the left and rises to the right
Rises to the left and falls to the right
Rises to the left and rises to the right
Falls to the left and falls to the right

Calculus
Limits & ContinuityFor the polynomial below, 2 is a zero.
g(x)=x²
=x² + 4x²
Express g (x) as a product of linear factors.
www.
10x - 4
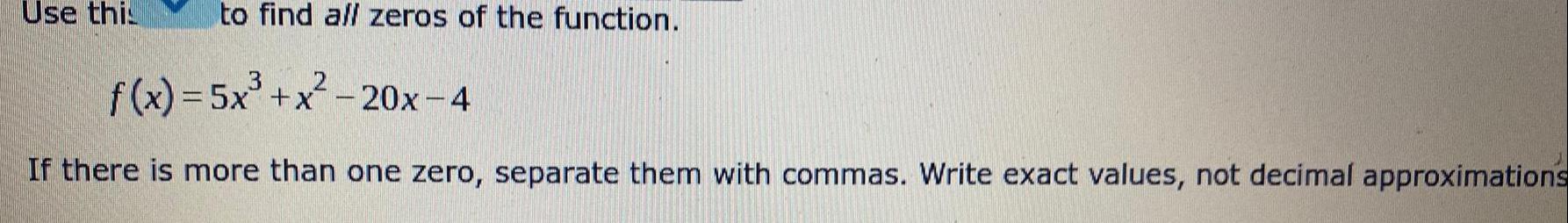
Calculus
Limits & ContinuityUse this
to find all zeros of the function.
f(x) = 5x³+x²2-20x-4
If there is more than one zero, separate them with commas. Write exact values, not decimal approximations

Calculus
Limits & ContinuityFor the polynomial below, -2 is a zero.
f(x)=x² + 3x² - 4x - 12
Express f(x) as a product of linear factors.

Calculus
Limits & ContinuityFind a
mla
-4, 3, 2-i
f(x) = 11
degree 4 with real coerricle
and the following zeros
0²
x
5
U
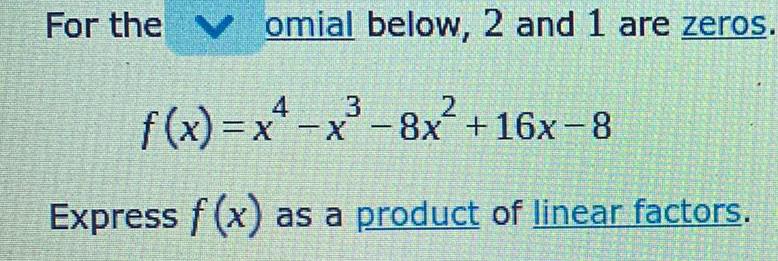
Calculus
Limits & ContinuityFor the
omial below, 2 and 1 are zeros.
4
3
f(x)=x²-x³-8x² +16x-8
Express f(x) as a product of linear factors.
2
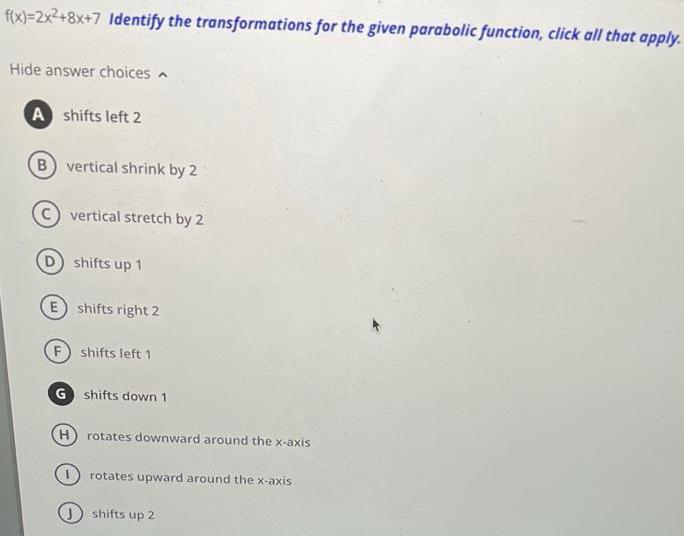
Calculus
Limits & Continuityf(x)=2x²+8x+7 Identify the transformations for the given parabolic function, click all that apply.
Hide answer choices
A shifts left 2
B) vertical shrink by 2
vertical stretch by 2
D) shifts up 1
E shifts right 2
(F) shifts left 1
G shifts down 1
(H) rotates downward around the x-axis
rotates upward around the x-axis
shifts up 2

Calculus
Limits & ContinuityConsider f(x) = -12 arcsin (625)
Determine the intervals on which f is decreasing.
Of is decreasing on:
Of is decreasing nowhere.
Determine the intervals on which f is increasing.
Of is increasing on:
Of is increasing nowhere.
Determine the value and location of any local minimum of f. Enter the solution in (x, f(x)) form. If
multiple solutions exist, use a comma-separated list to enter the solutions.
of has a local minimum at:
Of has no local minimum.
Determine the value and location of any local maximum of f. Enter the solution in (x, f(x)) form. If
multiple solutions exist, use a comma-separated list to enter the solutions.
of has a local maximum at:
Of has no local maximum.
Calculus
Limits & ContinuityQuestion 6 of 10 (1 point) | Attempt 1 of Unlimited View question in a popup
Car inspection: Of all the registered automobiles in a city, 11% fail the emissions test. Fourteen automobiles are selected at
random to undergo an emissions test. Round the answers to at least four decimal places.

Calculus
Limits & Continuity(a) Find the largest number 6 such that if Ix - 3| < 6, then [5x - 15| < &, where & = 0.5.
d≤
(b) Repeat part (a) and determine & with & = 0.05.
d≤
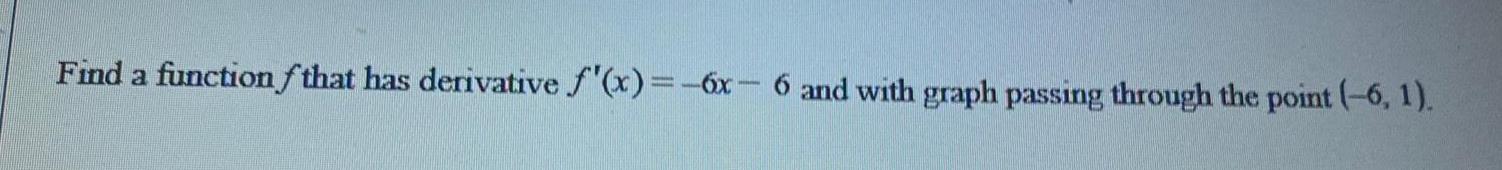
Calculus
Limits & ContinuityFind a function that has derivative f'(x) = -6x-6 and with graph passing through the point (-6, 1).
![Locate the absolute extrema of the function g(x)=
3x +5
on the closed interval [0, 5]](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/84267184-1657635093.5064716.jpeg?w=256)
Calculus
Limits & ContinuityLocate the absolute extrema of the function g(x)=
3x +5
on the closed interval [0, 5]
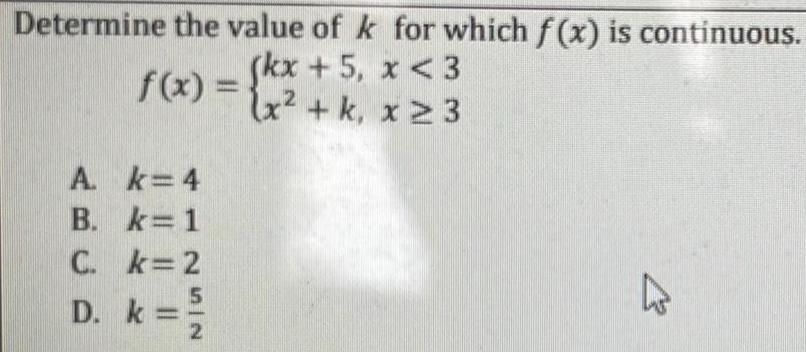
Calculus
Limits & ContinuityDetermine the value of k
5,
f(x) = {kx + 5₁
A
k=4
B. k=1
C. k=2
D. k=
5
IN
2
for which f(x) is continuous.
x <3
(x² + k, x ≥ 3
K

Calculus
Limits & ContinuityFind the length and width (in feet) of a rectangle that has the given area and a minimum perimeter.
Area: 25 square feet
ft (smaller value)
ft (larger value)

Calculus
Limits & ContinuityFind c> 0 such that the area of the region enclosed by the parabolas y = x² - c² and
y = c² - x² is 190.
C =
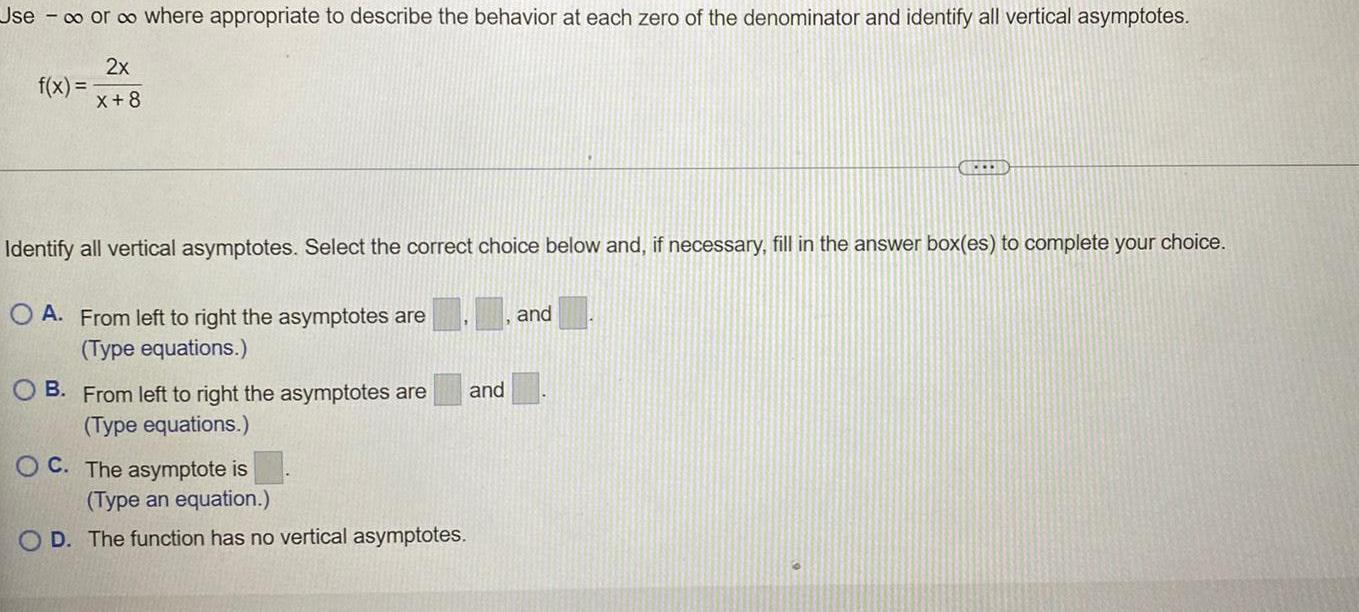
Calculus
Limits & ContinuityUse - ∞o or ∞o where appropriate to describe the behavior at each zero of the denominator and identify all vertical asymptotes.
f(x) = 2x/x+8
Identify all vertical asymptotes. Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box(es) to complete your choice.
A. From left to right the asymptotes are___,____and____
(Type equations.)
B. From left to right the asymptotes are___and_____
(Type equations.)
C. The asymptote is____
(Type an equation.)
D. The function has no vertical asymptotes.

Calculus
Limits & ContinuityUse - ∞ or ∞ where appropriate to describe the behavior at each zero of the denominator and identify all vertical asymptotes.
f(x) = 2x/x+8
Locate all zeros of the denominator and describe the behavior of the function at those values. Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer boxes to complete your choice.
As x approaches the smaller zero from the left and right, f(x) approaches and
respectively. As x approaches the
A. There are two zeros. The smaller zero is x= and the larger zero is x =
larger zero from the left and right, f(x) approaches and respectively.
B. There is one zero, at x = As x approaches this zero from the left and right, f(x) approaches and respectively.
C. There are no zeros of the denominator.
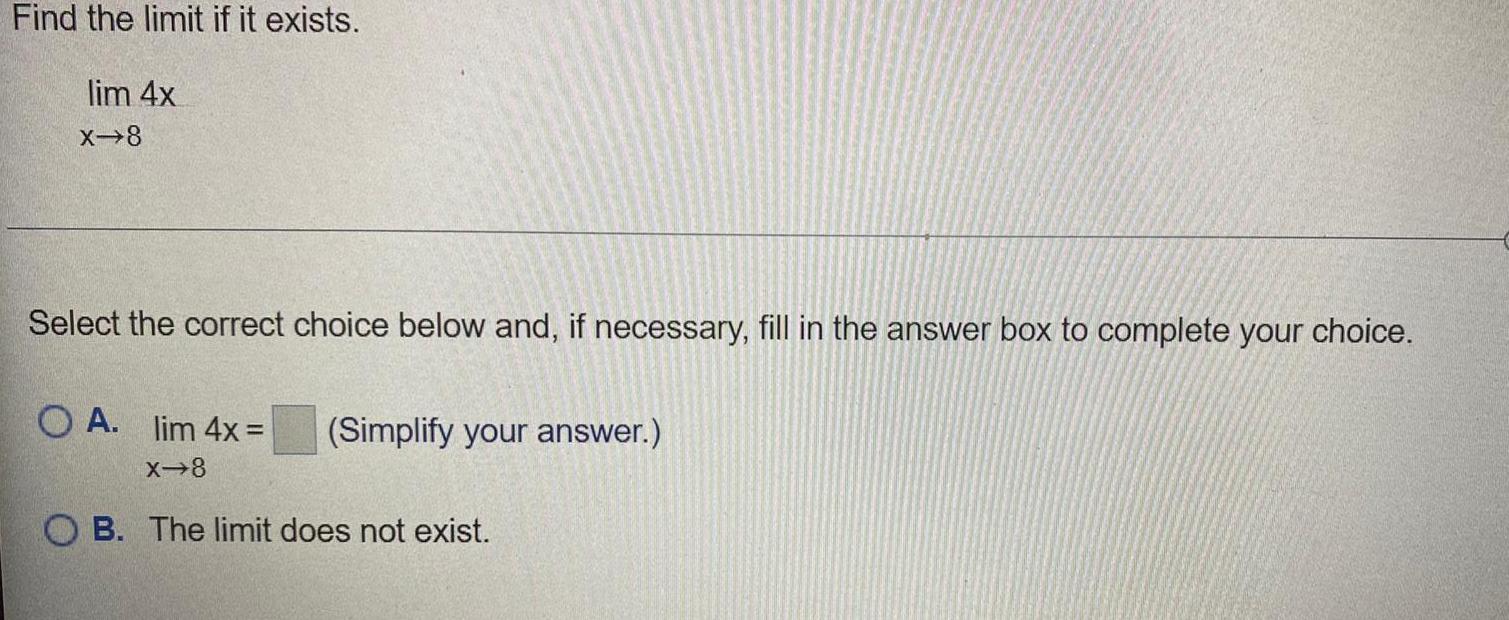
Calculus
Limits & ContinuityFind the limit if it exists.
lim 4x
X→8
Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice.
A. lim 4x =
X→8
(Simplify your answer.)
B. The limit does not exist.

Calculus
Limits & ContinuityFind lim f(6 +h)-f(6)/h if f(x) = 4x - 1.
h→0
lim f(6 +h)-f(6)/h if f(x) = 4x - 1.
h→0
(Simplify your answer.)
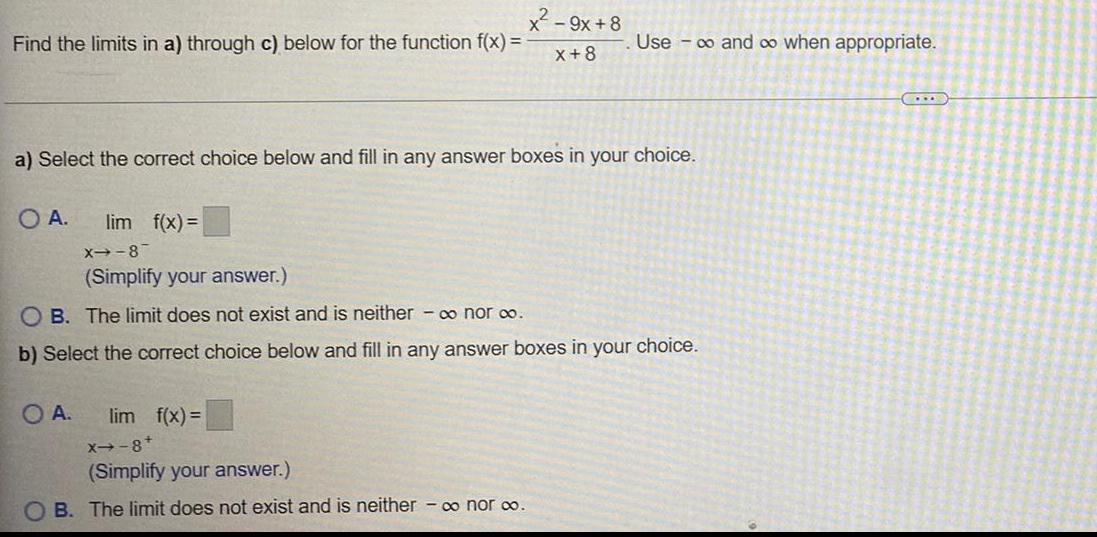
Calculus
Limits & ContinuityFind the limits in a) through c) below for the function f(x) =x²-9x+8/ x+8 Use ∞ and ∞ when appropriate.
a) Select the correct choice below and fill in any answer boxes in your choice.
A. lim f(x)=
X--8-
B. The limit does not exist and is neither - ∞ nor ∞.
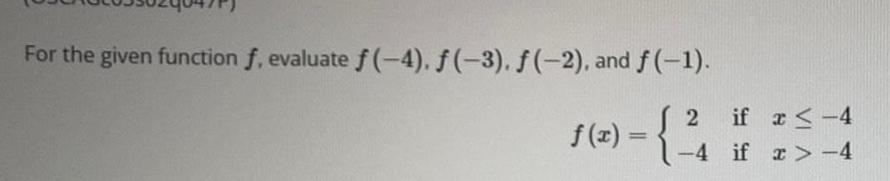
Calculus
Limits & ContinuityFor the given function f, evaluate f(-4), ƒ (-3), ƒ (-2), and f(-1).
f(x) = 2 if x≤-4
-4 if x>-4

Calculus
Limits & ContinuityFor the given function f. evaluate f(-3), f(-2). f(-1), and f (0).
f(x) =-2x²+3 if x < -1
4x-2 if x>-1
f(-3) =
f(-2)=
f(-1) =
f(0) =
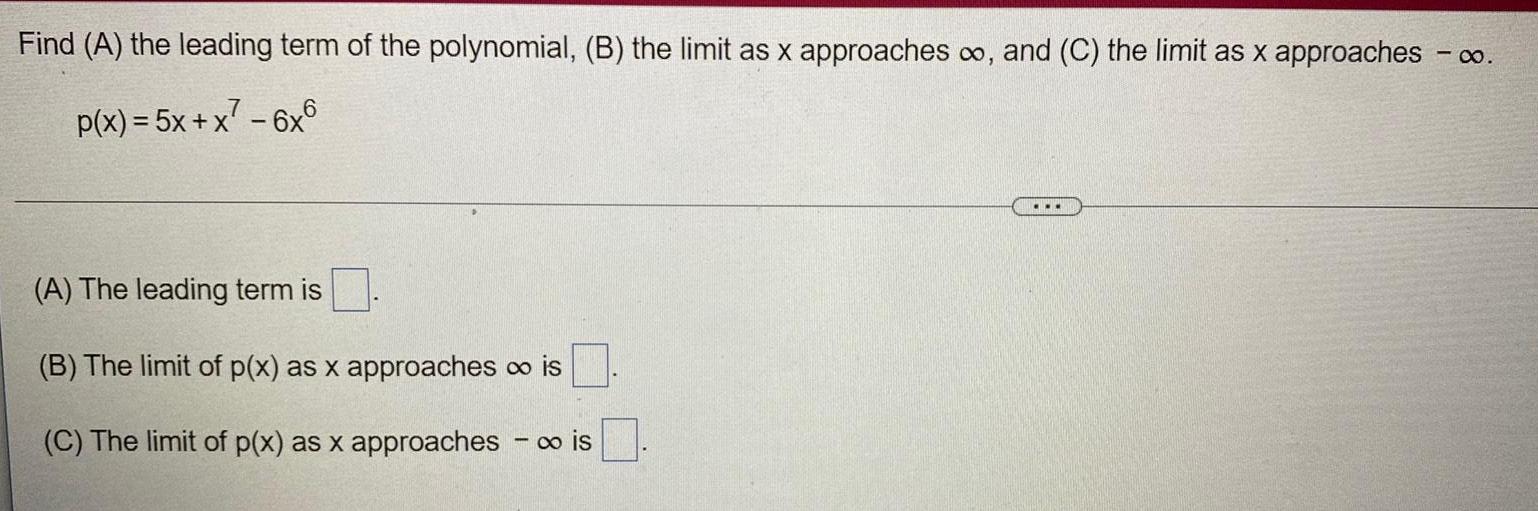
Calculus
Limits & ContinuityFind (A) the leading term of the polynomial, (B) the limit as x approaches ∞o, and (C) the limit as x approaches - ∞
p(x) = 5x + x² - 6x6
(A) The leading term is
(B) The limit of p(x) as x approaches ∞ is
(C) The limit of p(x) as x approaches-∞ is

Calculus
Limits & ContinuityWhat is the area of the sector of a circle who's radius is 43.5 cm and is bounded by an arc of π/12 radians?
A. 247.7 cm2
B. 5.69 cm²
C. 946.13 cm²
D. 495.39 cm²

Calculus
Limits & ContinuityThe position of an object is given by s(t) = In(t³).
What is the displacement of the object between t = 1 and t = 4?
A. 3
B. 4.159
C. 4.328
D. 16.87
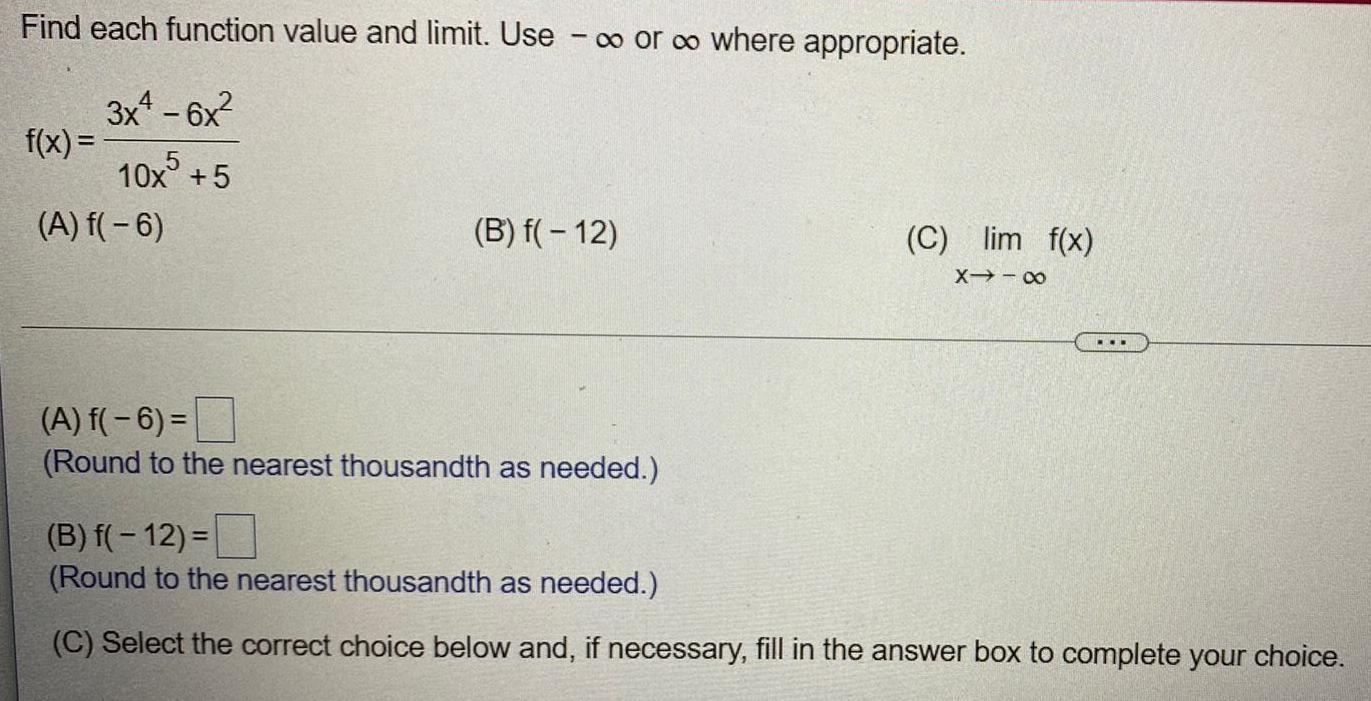
Calculus
Limits & ContinuityFind each function value and limit. Use - ∞o or co where appropriate.
f(x) = 3x² - 6x² / 10x⁵ + 5
(A) f(-6)
(B) f(-12)
(C) lim f(x)
(A) f(-6)=
(Round the nearest thousandth as needed.)
(B) f(- 12) =
(Round to the nearest thousandth as needed.)
(C) Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice.

Calculus
Limits & ContinuityLet f(y) = -4-3y² + 8y
Determine the critical values of f. If multiple such values exist, enter the solutions using a comma-separated list.

Calculus
Limits & ContinuityFor the polynomial below, -3 is a zero.
h(x)=x³ + 9x² + 25x + 21
Express h (x) as a product of linear factors.

Calculus
Limits & ContinuityUse the Factor Theorem to determine whether x + 3 is a factor of P(x) = x³ + 2x² +7.
Specifically, evaluate P at the proper value, and then determine whether x + 3 is a factor.

Calculus
Limits & ContinuityFor f(x) = 1/6+x², the slope of the graph of y = f(x) is known to be -2/49 at the point with x-coordinate 1. Find the equation of the tangent line at that point.

Calculus
Limits & ContinuityUse the Factor Theorem to determine whether x +2 is a factor of P(x) = -2x⁴-2x³+4x+24.
Specifically, evaluate P at the proper value, and then determine whether x + 2 is a factor.

Calculus
Limits & ContinuityFor the polynomial below, 2 is a zero.
g(x)=x³ - 8x² + 16x - 8
Express g (x) as a product of linear factors.

Calculus
Limits & ContinuityFind all asymptotes (vertical, horizontal, and/or slant) for y = x³ / (x²-16 )