Vector Calculus Questions and Answers
Calculus
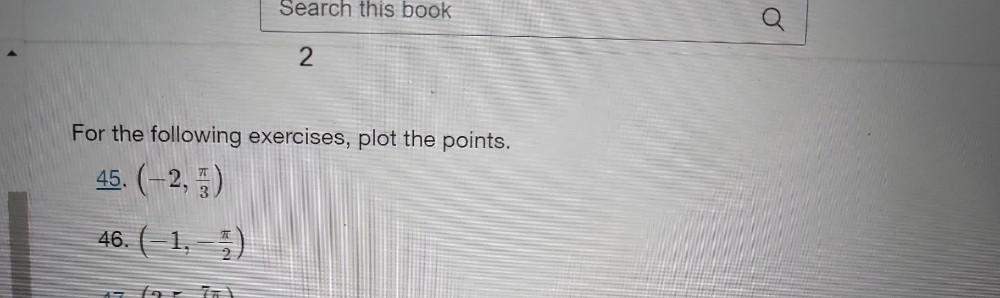
Vector CalculusThe magnitude and direction of vectors t, u, and v are shown in the table.
Vector Magnitude Direction
t 7 240⁰
u 10 30⁰
v 15 310⁰
What is the direction of t + u + v? Round to the nearest degree.
Calculus
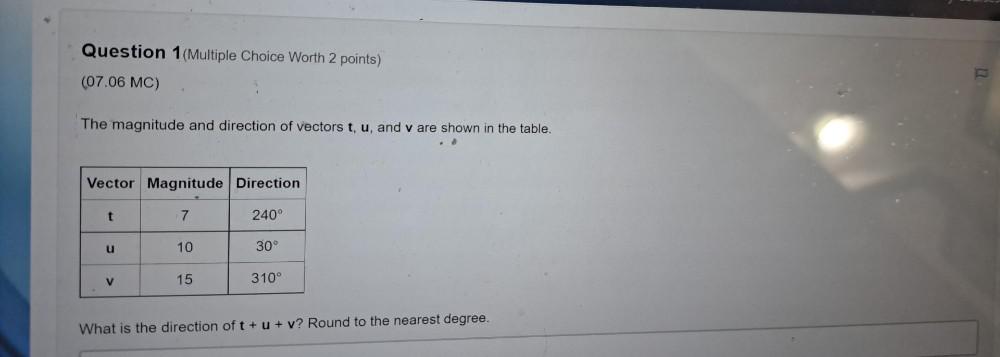
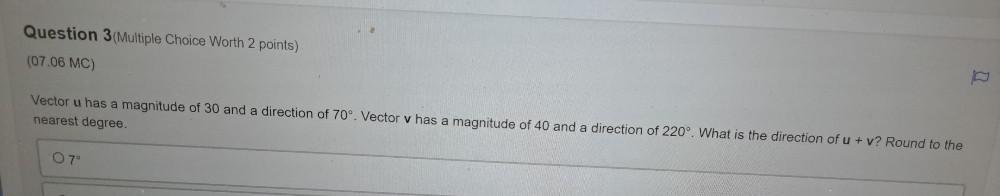
Vector CalculusVector u has a magnitude of 30 and a direction of 70°. Vector v has a magnitude of 40 and a direction of 220°. What is the direction of u + v? Round to the nearest degree.
Calculus
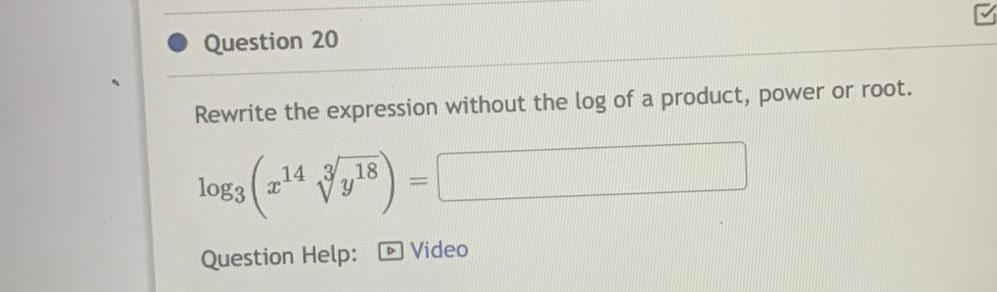
Vector CalculusRewrite the expression without the log of a product, power or root.
log₃(x¹⁴ ∛y¹⁸) =_______________

Calculus
Vector CalculusMatch the words with their definition.
1. simple interest
2. principal
3. compound interest
a. When you deposit money into a savings account
b. interest paid only on the principal
c. the bank pays on the principal and the interest already earned

Calculus
Vector CalculusComplete the square for the following in order to rewrite the equation of the conic in standard
form. State any applicable characteristics, including center, vertex (vertices), focus (foci), directrix
and/or equations of asymptotes. Provide your calculations. (8pts each)
i. 9x² - y² - 14y - 58 = 0
ii. 16y2 - 56y - 16x +81 = 0

Calculus
Vector Calculusa) Explain the difference between a positive angle and a negative angle.
b) Consider the time 11:30 where the initial side is the hour hand and terminal side is the minute hand. Draw the angle between the two hands in standard position. State the angle in positive degrees and then restate the angle as a negative angle.
c) Draw a picture depicting the definition of a radian and in your own words, write a definition.
d) Draw a circle. Show approximate radian and degree values for every 1/8 of the circle. Show approximate values for 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 radians.
Calculus
Vector CalculusAlgebraically find the inverse of f(x) = 3 cos (2x), showing your steps. State the domain and range of both f(x) and f-¹(x).

Calculus
Vector CalculusA club with nine members is to choose three officers: president, vice-president, and secretary-treasurer. If each office is to be held by one person and no person can hold more than one office, in how many ways can those offices be filled?
Calculus
Vector CalculusA 5-digit phone number cannot start with 0. Assume that there are no restrictions on the remaining 4 numbers. How many telephone numbers are possible in which all 5 digits are different?
The possible number of 5-digit telephone numbers where all the digits are different is ___.

Calculus
Vector CalculusAssume A and B are independent events with P(A) = 0.8 and P(B)=0.5. Find (a) P(A ∩ B), (b) P(AUB), (c) P (A' ∩ B'), (d) P (A'∩B), and (e) P (A ∩ B').
(a) P(A ∩ B)=
(b) P(A U B) =
(c) P (A' ∩B') =
(d) P (A' ∩ B) =
(e) P (A ∩ B') =

Calculus
Vector CalculusLet x be a continuous random variable with a standard normal distribution. Using the accompanying standard normal distribution table, find P(0 ≤x≤2.23).

Calculus
Vector CalculusThe population of a colony of rabbits grows exponentially. The colony begins with 10 rabbits; 5 years later there are 340 rabbits. Using your solution from question 19, find and interpret R−¹(y).
![For the probability density function f defined on the random variable x, find (a) the mean of x, (b) the standard deviation of x, and (c) the probability that the random variable x is within one standard deviation of the mear 1 f(x)=2x. (5.7] a) Find the mean. p= (Round to three decimal places as needed.) b) Find the standard deviation. G= (Round to three decimal places as needed.) c) Find the probability that the random variable x is within one standard deviation of the mean. The probability is (Round to three decimal places as needed.)](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/84762244-1659863694.1531553.jpeg?w=256)
Calculus
Vector CalculusFor the probability density function f defined on the random variable x, find (a) the mean of x, (b) the standard deviation of x, and (c) the probability that the random variable x is within one standard deviation of the mear 1 f(x)=2x. (5.7] a) Find the mean. p= (Round to three decimal places as needed.) b) Find the standard deviation. G= (Round to three decimal places as needed.) c) Find the probability that the random variable x is within one standard deviation of the mean. The probability is (Round to three decimal places as needed.)

Calculus
Vector CalculusYour parents have a credit card with a balance of $2,748.56. The interest rate is 10.5% APR. A late payment fee of $40.00 is added to the principal if they pay after 6/1. They make a payment for $300.00 on 6/1. How much interest did they pay?
$24.05
$288.60
$24.40
$297.00
Calculus
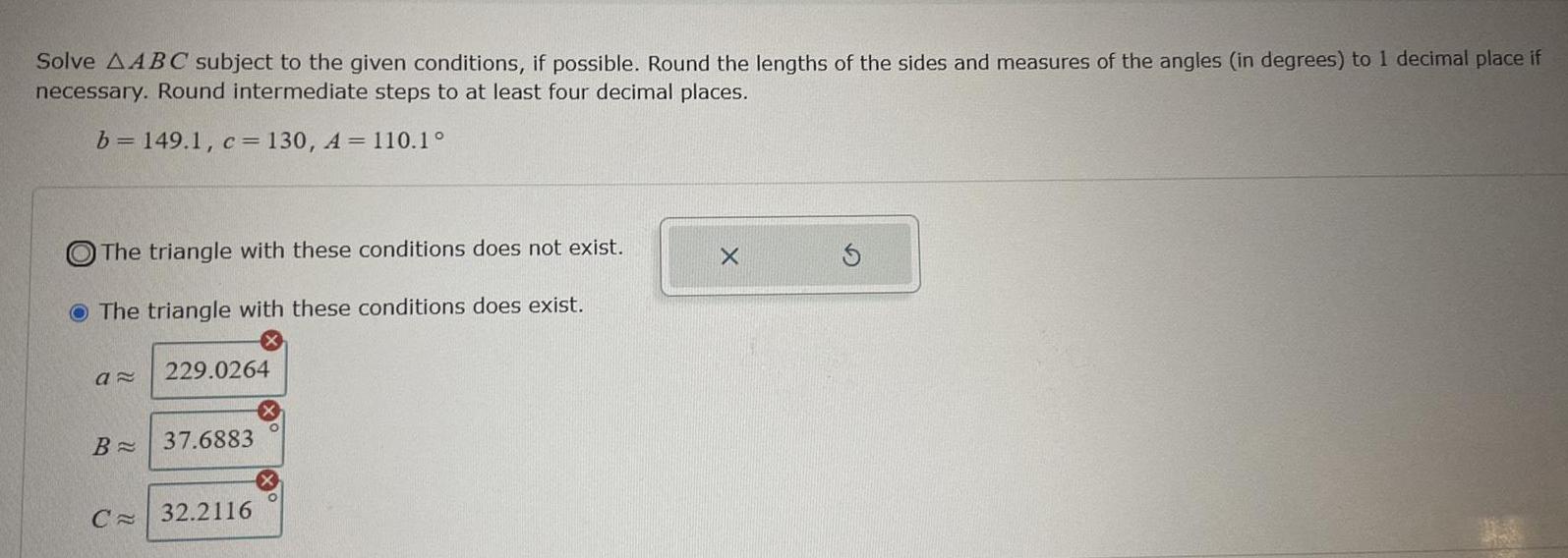
Vector CalculusSolve AABC subject to the given conditions, if possible. Round the lengths of the sides and measures of the angles (in degrees) to 1 decimal place if necessary. Round intermediate steps to at least four decimal places.
b = 149.1, c = 130, A = 110.1°
The triangle with these conditions does not exist.
The triangle with these conditions does exist.
α≈
B=
C

Calculus
Vector CalculusSuppose f(x) = 4* and g(x) = -3x - 2. Find a simplified formula for the function:
h(x) = (g(f(x)))²


Calculus
Vector CalculusWrite the linear function whose graph passes through the points
(4, 5) and (2, 13).
Write the answer in the form f(x) = mx + b.
Do not enter any spaces in the answer.
f(x) =__________A
Calculus
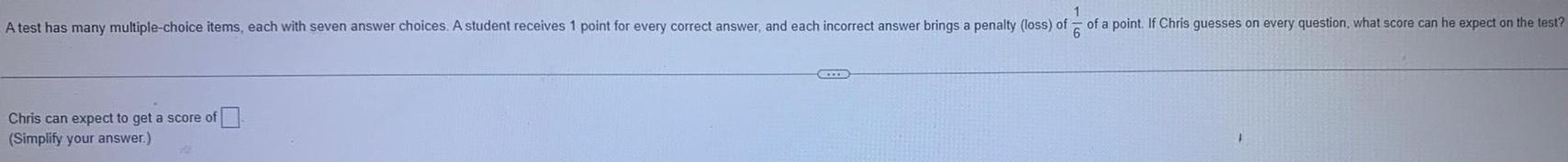
Vector CalculusA test has many multiple-choice items, each with seven answer choices. A student receives 1 point for every correct answer, and each incorrect answer brings a penalty (loss) of a point. If Chris guesses on every question, what score can he expect on the test

Calculus
Vector CalculusFind the length and width of a rectangle that has perimeter 48 meters and a maximum
area.
12 m; 12 m.
16 m; 9 m.
1m; 23 m.
13 m; 11 m.
6 m; 18 m.


Calculus
Vector CalculusA student was asked to prove the trigonometric identity tan1/2x + cot1/2x = 2cscx. Which of the following could be the first step in proving the identity?
I. 1-cosx/sinx + 1-cosx/sinx = 2cscx
II. 1+cosx/sinx + sinx/1-cosx = 2cscx
III. sinx/ 1+cosx + 1+cosx/sinx = 2cscx

Calculus
Vector CalculusFind the directional derivative of the function f(x, y) = x²e^-y at the point P(-2,0) in the direction v = (2, -3).

Calculus
Vector CalculusFind the area of the surface S, where S is the part of the paraboloidz 1 -x²-y² that lies above the plane z = -2.
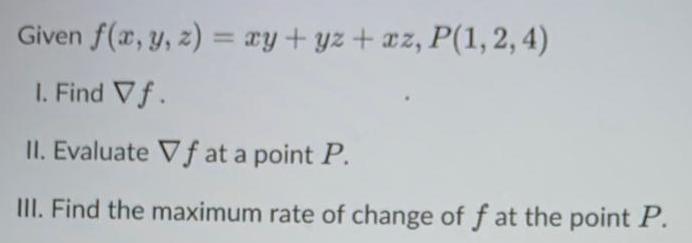
Calculus
Vector CalculusGiven f(x, y, z) = xy + yz + xz, P(1, 2, 4)
I. Find Vf.
II. Evaluate Vf at a point P.
III. Find the maximum rate of change of f at the point P.

Calculus
Vector CalculusFind v*v for the given vector.
v=-4i +2j + 4k
Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box(es) within your choice.
A. The answer is a vector. v*v = ai + bj + ck where a =
(Type integers or simplified fractions.)
B. The answer is a scalar. V*V=
(Type an integer or a simplified fraction.)
,b= and c =
![Write the given rule as an equation using function notation. Find the output when the input is 1, 2, 3, and 4.
Rule: raise 2 to the power of the input. Use b for the function and n for the input.
[Note: Do not use any space in your answer.]
Function:
b(1) =
b(2) =
b(3) =
b(4) =](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/84676996-1659041641.2279992.jpeg?w=256)
Calculus
Vector CalculusWrite the given rule as an equation using function notation. Find the output when the input is 1, 2, 3, and 4.
Rule: raise 2 to the power of the input. Use b for the function and n for the input.
[Note: Do not use any space in your answer.]
Function:
b(1) =
b(2) =
b(3) =
b(4) =
Calculus
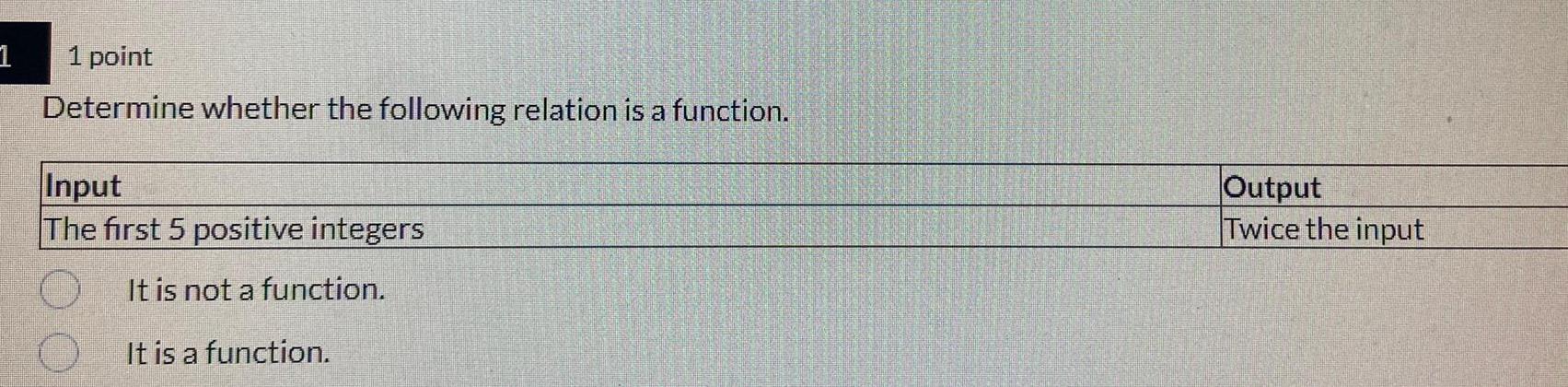
Vector CalculusDetermine whether the following relation is a function.
Input Output
The first 5 positive integers It is not a function.
It is a function.
Twice the input

Calculus
Vector CalculusSolve the linear programming problem.
Maximize
P = 40x+ 50y
Subject to
2x+y ≤ 16
x+y ≤ 9
x+2y = 14
x, y ≥ 0
What is the maximum value of P?
Select the correct choice below and fill in any answer boxes present in your choice.
A. P=
(Type an integer or a fraction.)
B. There is no maximum value of P.



Calculus
Vector CalculusFind the common difference for the arithmetic sequence.
{4, 12, 20, 28, 36,...}

Calculus
Vector CalculusThe first term of a geometric sequence is 5 and the common ratio is 3. Find the 6th term.
Calculus
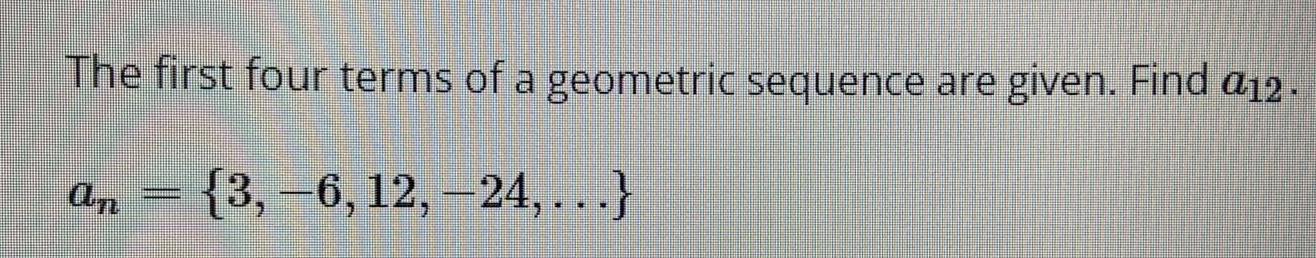
Vector CalculusThe first four terms of a geometric sequence are given. Find a12.
an = {3, -6, 12, -24,...}

Calculus
Vector CalculusFind the first five terms of the arithmetic sequence given the first term and common difference.
a₁ = −35, d = -9

Calculus
Vector CalculusFind the first term a₁ of the arithmetic sequence in which a9 = 23 and a17 = 95.
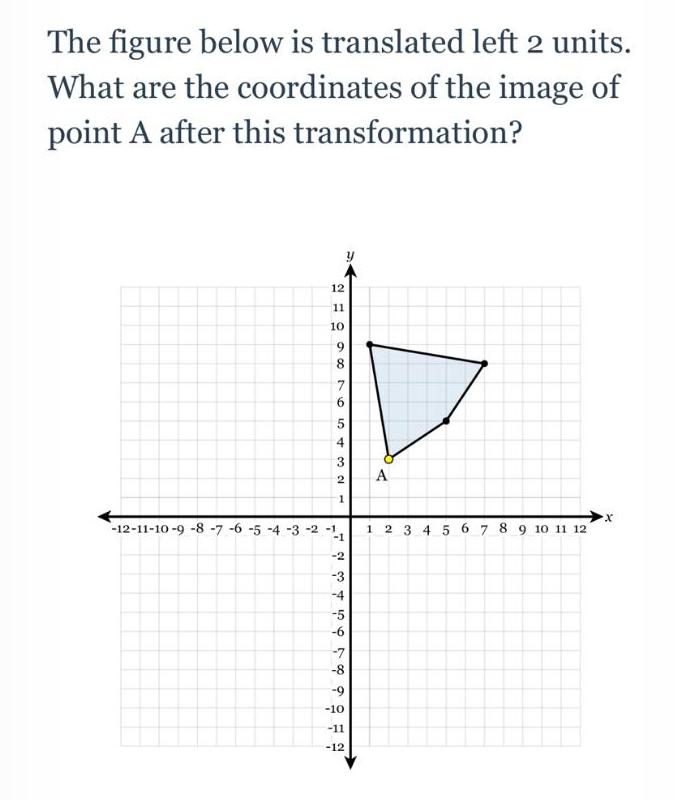
Calculus
Vector CalculusThe figure below is translated left 2 units. What are the coordinates of the image of point A after this transformation?

Calculus
Vector CalculusWhat is the end behavior of the function f(x)=-1 4x²?
As a →∞, f(x) →-∞
As →-∞, f(x) →-∞
As x→∞, f(x) → ∞
As →-∞. f(x)→-∞
As x→∞, f(x) → ∞
As x→-∞, f(x) → ∞

Calculus
Vector CalculusFind the vertex, focus, and directrix of the parabola. Then sketch the parabola.
(x + 5) + (y-2)² = 0
vertex (x, y) = (
focus (x, y) = (
directrix
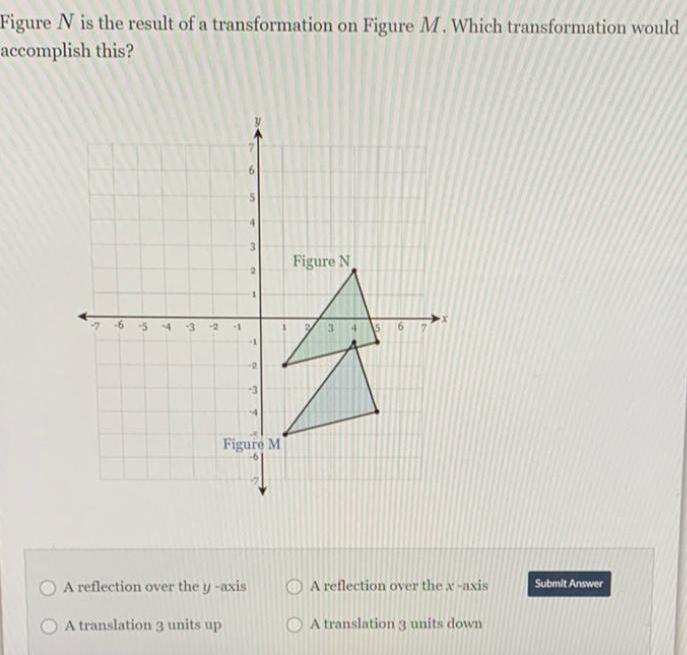
Calculus
Vector CalculusFigure N is the result of a transformation on Figure M. Which transformation would accomplish this?
A reflection over the y -axis A reflection over the x-axis
A translation 3 units up A translation 3 units down
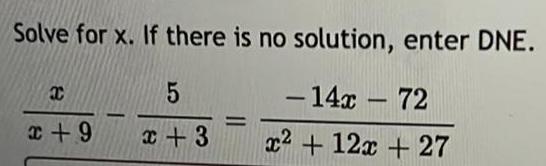
Calculus
Vector CalculusSolve for x. If there is no solution, enter DNE.
x 5 - 14x - 72
x + 9 x + 3 x² + 12x + 27

Calculus
Vector CalculusSuppose f(x) = √2x and g(x) = x2 2. Show that f(x) and g(x) are inverse functions using algebra.
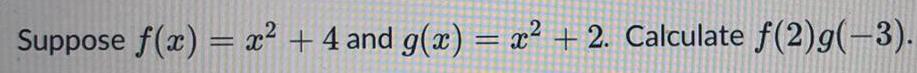

Calculus
Vector CalculusThe vector < 18,5> has initial point (-10,-4).
The terminal point of the vector is:

Calculus
Vector CalculusThe unit circle can alternatively be parametrized by the equations:
x(t) = -t² + 1 / t² + 1
y(t)= t² + 1 / 2t
Everyone point on the unit circle except (-1,0) can be described using the above parametrization. Find a possible way to obtain the missing point (-1,0) from this parametrization.

Calculus
Vector CalculusWhere do the graphs of f(x) = cos(x/2) and g(x) = √3-cos(x/2) intersect on the interval [0, 360°)?

Calculus
Vector CalculusGiven the following information about two spherical tanks that are connected,
calculate the work required to fill both tanks from the ground.
The first tank: Radius = 1m
The second tank: Radius = 0.5m
The first tank is on the ground and the second tank is 2m above the top of the first tank. The tanks are connected by a tube that is of negligible width. The tube goes through the top of the first tank and the bottom of the second tank. If p > 0 is the density (in kg/m^3) of the liquid in both tanks, calculate the work required to deliver the liquid to fill both tanks from the ground.
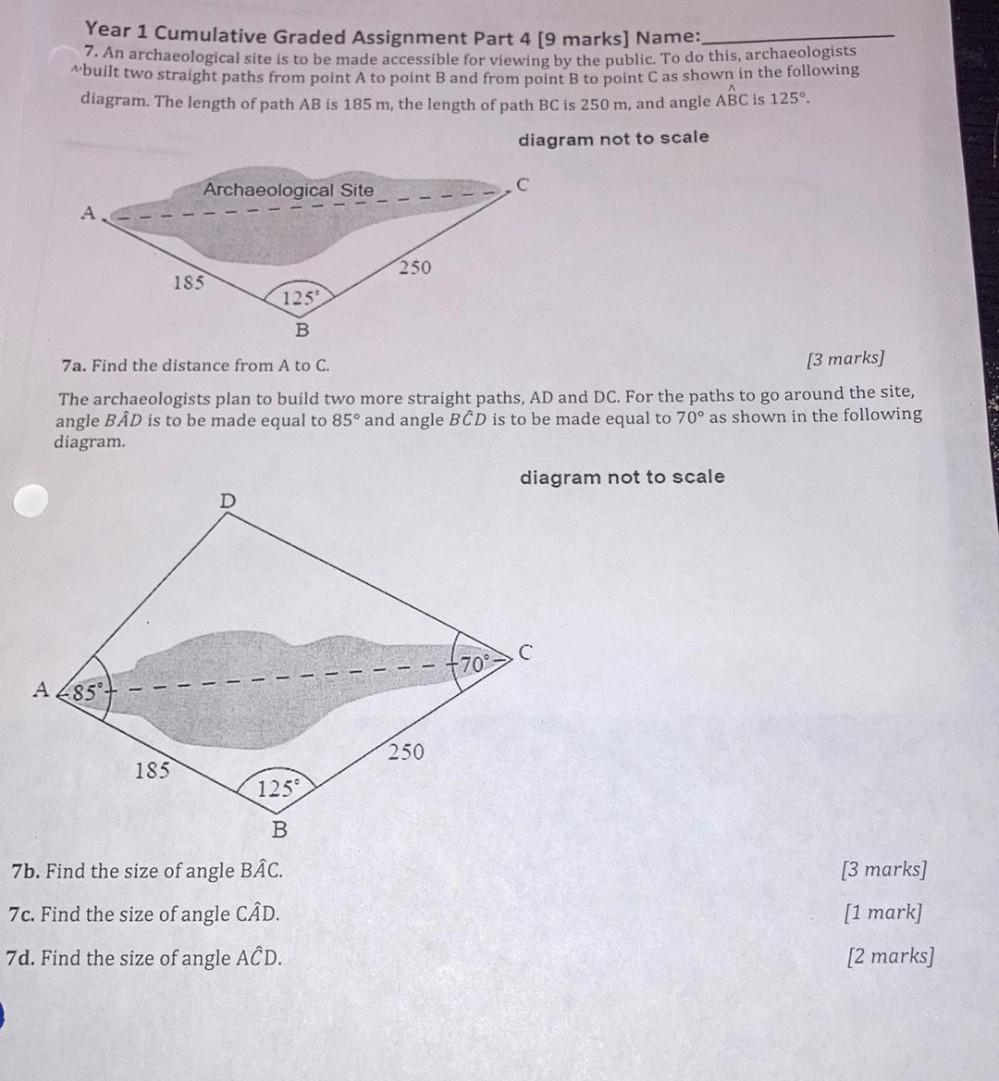
Calculus
Vector CalculusAn archaeological site is to be made accessible for viewing by the public. To do this, archaeologists built two straight paths from point A to point B and from point B to point C as shown in the following diagram. The length of path AB is 185 m, the length of path BC is 250 m, and angle ABC is 125°.
7a. Find the distance from A to C.
The archaeologists plan to build two more straight paths, AD and DC. For the paths to go around the site, angle BÂD is to be made equal to 85° and angle BCD is to be made equal to 70° as shown in the following diagram.
7b. Find the size of angle BÂC.
7c. Find the size of angle CÂD.
7d. Find the size of angle ACD.