Solutions Questions and Answers

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsState and explain the van t Hoff s factor i A sample of camphor K 40 melts at 176 C A solution of 0 0205gm of a hydrocarbon in 0 261gm camphor melts at 156 C The hydrocarbon contains 92 3 carbon Determine the molecular formula of the hydrocarbon 2 2

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsIdentify the incorrect statement s Assume no change in volume of solution On adding HCI to NaOH aqueous solution the boiling point of the solution decreases initially and then gradually increases On adding NaOH to Ca OH 2 aqueous solution the freezing point increases initially On adding HCI to NaOH aqueous solution the relative lowering in vapour pressure increases initially then decreases On adding water to a solution containing 0 1 M NaOH and 0 1 M HCl boiling point of solution will decrease

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsFor the following reaction the equilibrium constant K at 298 K is 16 x 10 7 C 2 Fe aq S aq FeS s 2 When equal volumes of 0 06 M Fe aq and T 0 2 M S aq solutions are mixed the equilibrium concentration of Fe aq is found by Y x 10 7 M The value of Y is IDE

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsskipp Moles of CO obtained on complete oxidation of 22 g of propane in presence of excess of oxygen is Options 1 5 2 2 5 0 5

Physical Chemistry
Solutions35 The nature of graph for effect of concentration on rate of reaction between 0 1 M Na 2S 20 3and 1 M HCI is a straight line with a decreasing slope b increasing slope c increasing slope intersecting to y axis d decreasing slope intersecting to x axis 1 pc

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsConsider the following diagram P J Solution SPM P 2 Solvent Container 1 Container 2 SPM is the semi permeable membrane P and P are the pressure applied Identify the incorrect statement If P P then liquid will flow from container 2 to container 1 To stop the osmosis P must be equal to osmotic pressure To carry out osmosis P must be lesser than P2 If P is greater than P then reverse osmosis will occur 2

Physical Chemistry
Solutions0 005 mol of Kl react with excess of CuSO and PRE 4 form 12 The 1 requires x L of 1 M Na S O 3 2 solution The total moles of sulphur atom in zero oxidation state in product are y mol The value of 1000 2y 2x is 14

Physical Chemistry
Solutions100 ml solution of FeC O and FeSO is completely oxidised by 60 ml of 0 02 M KMnO in acidio medium The resulting solution is then reduced by Zn and dil HCL The reduced solution is again oxidised completely by 40 ml of 0 02 M KMnO4 What is molarity of FeC 0 in solution

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsIf the density of ethanol is 0 78 kg L then volume of ethanol he making 2 L of 0 5 M solution is Options 45 2 mL 58 97 mL 71 4 mL 25 5 mL Solution Answer 2 NCERT Reference Some basic concepts of chemistry XI Part 1 Page No 26

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe low boiling azeotrope is a mixture of two miscible liquids that when boiled produce the same composition in the vapor phase a is a vertical line form the vapor phase to the liquid phase O b OC is a mixture of two miscible liquids that when boiled produce the different composition in the vapor phase O d 1s is a mixture of two immiscible liquids that when heated becomes completely miscible

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAssuming the vapour pressure of water is increased from 30 to 31 mm Hg at 25 C against an external pressure of 10 atm If the vapour pressure is to be maintained at 30 mm Hg for 1 L of water 55 5 moles at 25 C and 10 atm pressure how much NaCl in moles is to be added to the water 0 765

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA 0 002 molar solution of a complex Pt NH3 4C14 in water had a freezing point depression of 0 0108 C Given K for H 0 1 86K molality Considering 100 ionization of the complex how many ions are produced after ionization

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsConsider the following diagram 1 Solution SPM Solvent Container 1 Container 2 SPM is the semi permeable membrane P and P are the pressure applied Identify the incorrect statement If P P then liquid will flow from container 2 to container 1 To stop the osmosis P must be equal to osmotic pressure To carry out osmosis P must be lesser than P If P is greater than P then reverse osmosis will occur

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA liquid solution is formed by mixing 10 moles of aniline with 20 moles of phenol at a temperature T If vapour pressure of pure phenol and pure aniline are 90 87 mm of Hg respectively at the temperature T then identify what could be the possible value of vapour pressure of the solution Question Type Single Correct Type 1 89 mm 2 80 mm 3 93 mm 4 90 mm

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsConsider the following curve P 40 mmHg x X 1 mp E mole fraction y 50 mmHg 19 X 1 The above graph can be for which of the following mixture OCHCl H O On hexane n heptane Aniline phenol Read Las

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe specific conductivity of N 10 KCl solution at 20 C is 0 012 2 cm and the resistance of the cel containing this solution at 20 C is 56 2 The cell constant is 1 4 616 cm 2 0 672 cm 3 2 173 cm 4 3 324 cm

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsSulfur trioxide is not directly dissolved in water to form sulfuric acid because Sulfur trioxide is insoluble in water due to its covalent nature The reaction with water is so exothermic and evaporates the SO3 as dense fog which is difficult to condense SO3 does not react with water to form the acid SO3 could be converted to H SO3 when dissolved in pure water

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsConsider the following diagram P P Solution SPM Solvent Container 1 Container 2 SPM is the semi permeable membrane P and P2 are the pressure applied Identify the incorrect statement O If P P2 then liquid will flow from container 2 to container 1 O To stop the osmosis P must be equal to osmotic pressure To carry out osmosis P must be lesser than P2 If P2 is greater than P then reverse osmosis will occur

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsIdentify the incorrect statement s in volume of solution On adding HCI to NaOH aqueous solution the boiling point of the solution decreases initially and then gradually increases On adding NaOH to Ca OH 2 aqueous solution the freezing point increases initially On adding HCI to NaOH aqueous solution the relative lowering in vapour pressure increases initially then decreases On adding water to a solution containing 0 1 M NaOH and 0 1 M HCI boiling point of

Physical Chemistry
Solutions2 Which of the following solutions cannot act as a buffer system 1 KH PO H PO 2 NaCIO HCIO A buff 3 C H N CH NH 4 Na CO NaHCO
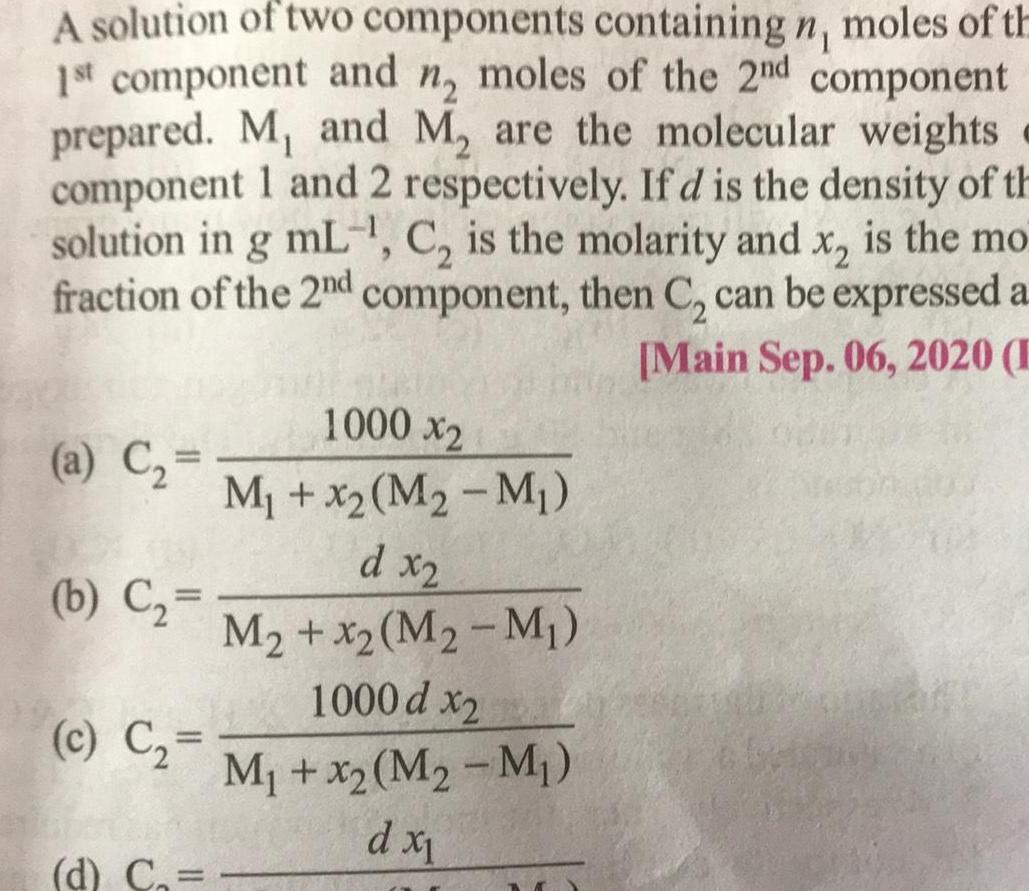
Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA solution of two components containing n moles of th 1st component and n moles of the 2nd component prepared M and M are the molecular weights component 1 and 2 respectively If d is the density of th solution in g mL C is the molarity and x is the mo fraction of the 2nd component then C can be expressed a Main Sep 06 2020 E a C b C c C 1000 x2 M x M M d x2 M x2 M M 1000 d x2 M x2 M2 M d x d C

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsb A piece of wood that measures 3 2 cm by 5 7 cm by 7 3 cm has a mass of 100 g What is the density of the wood Would it float on water 7 Known Values 1 Formula s and Equation s 5 Final Statement 1

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsa 9 5 b 1 c 10 5 d 17 36 Given the two concentration of HCN K 10 are 0 1 M and 0 001 M respectively Wh will be the ratio of degree of dissociation a 1 9 0 1 c 0 003 d 0 01

Physical Chemistry
Solutions32 One litre of a solution contains 15 12 g of HNO3 RITAN and one litre of another solution contains 3 2 g of NaOH In what volume ratio must these solutions be mixed to obtain a neutral solution 1 3 Im 010 L 2 4 2 N 3 3744

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsh Kw KxK 14 10 10 x 10 10 14 x 10 10 10 102 BEGINNER S BOX 2 When sodium acetate CH COONa is added to aqueous solution of acetic acid CH COOH the 1 the pH value becomes zero 2 pH value remains unchanged

Physical Chemistry
Solutions22 Calcium hydroxide is a strong base Compute Ca 2 and OH for a solution that is prepare by dissolving 0 60 g of Ca OH in enough water to make a 1500 ml of solution Atomic mass Ca 40 0 16 H 1 a 5 4 x 10 3 9 1 x 10 13 3 c 5 4 x 10 5 4 x 10 3 3 b 5 4 x 10 3 1 08 10 2 d 8 1x10 3 8 1x 10 3

Physical Chemistry
Solutions26 A 25 0 mL sample of 0 10 M HCl is titrated with 0 10 M NaOH What is the pH of the solution at the points where 24 9 and 25 1 mL of NaOH have been added a 3 70 10 70 b 3 30 10 30 c 3 70 10 30 d 3 0 11 0 What is the all of anlution in which 250 ml of 0 1 M NaOH is added to 25 mL of 0 08 MHC 377 37

Physical Chemistry
Solutions9 Which of the following expressions correctly represents the equivalent conductance at infinite dilution of Al SO4 3 Given that 1 and SO are the equivalent conductances at infinite dilution of the respective ions So a 2 3850 b SO c A1 0 6 SO4 1 2 SO 1 d 2 A1 Mains 2010

Physical Chemistry
Solutions68 KBr is 80 dissociated in aqueous solution 68 0 5milar ca faca KBr 80 fa refer K 1 86 K kg mol of 0 5m concentration Given K for water 1 86 K kg mol The solution freezes at 1 271 326 K 3 270 5 K 2 272 K 4 268 5 K fer 1 271 326 K 3 270 5 K 2 272 K 4 268 5 KM

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA 25 mL 0 05 M HCl solution was mixed with 75 00 mL 0 01 M KOH solution 20 mL of the resulting solution was titrated for neutralization using a standard Ba OH solution and its 25 mL was required The molarity of Ba OH solution is a 0 004 M b 0 002 M c 0 001 M d 0 02 M

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhich of the given observations are correct when a solution containing a non volatile solid solute is allowed to freeze i The vapor pressure of the solution is less than that of pure solvent ii The vapor pressure of the solution is greater than that of pure solvent iii Only solute molecules solidify at the freezing point iv Only solvent molecules solidify at the freezing point i iii i iv ii iii ii iv

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsIdentify and define the process Applied Pressure Salt Water O Contaminants Semi Permeable Membrane Water Flow Pure Water Fresh Water O State the condition under which process takes place and give one application of the process

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsTwo liquids A and B form an ideal solution At 300 K the 52 A BIGHT facer 300 K B 3 550 mm Hg 2 vapour pressure of a solution containing 1 mole of A and 3 moles of B is 550 mm of Hg At the same temperature if one mole of B is added to this solution the vapour pressure of the solution increases by 10 mm of Hg Determine the apour pressure of A and B in their pure states 0 1 P PA PB 0 400 400 P 600 0 2 PA 200 0 p 600 PB SE Spartan Batch Atomic Structure Chemical Arithmetics Solution Thermodynamics Atn 0 PA 400 P 500 O None of these motic pressure of 30 solution of al 1 PB 600 Book A PO BF G facer an 10 mm Hg 123 850 mm of my PA Yo TUR 0 1 PA 400 PB 600 2 PA 200 p 600 500 0 3 PA 400 P 4 o

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA certain substance X condenses at a temperature of 141 2 C But if a 300 g sample of X is prepared with 17 g of urea sample is found to have a condensation point of 143 3 C instead Calculate the molal boiling point elevation constant K of X Round your answer to 2 significant digits 1 C mol kg NH 2CO dissolved in it tl x10

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA very small amount of a non volatile solute that does no dissociate is dissolved in 56 8 cm of benzene density 0 89 g cm At room temperature vapour pressure of this solution is 98 88 mm Hg while that of benzene is 100 mm Hg If the freezing temperature of this solution is 0 73 degree lower than that of benzene what is the value of molal freezing depression constant of benzene in nearest integer

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAmong the following CORRECT statement is are A De Broglie s wave nature of fast moving electrons used in making an electron microscope B Tyndal effect used to set up ultra microscope C Ultra microscope does render the actual colloidal particles visible and it provide information about the size and shape of colloidal particles

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsIn the saturated aqueous solution of PbC1 the freezing point of water decreases by DC 100 then D is Given k of PbCl 4 x 106 Kwater 2 K kg mole assume molality molarity A roversible evelie process involves 6 etong In eten 1 and 2 motom absorb 500 Land 800 I of

Physical Chemistry
Solutions58 59 1 17 g of NaCl in one litre water If density of 2 molal sucrose solution is 1 4 g mL at 25 C find osmotic pressure 1 4 06 atm 2 2 atm 3 40 6 atm 4 3 4 atm How many unit cells of KBr are present in Imm 66 in nu 1 3 Flu U

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsRATION 8 6 Based on solute solvent interactions arrange owing in order of increasing solubility in n octane and its reason ohexane KC1 CH OH CH3CN We know that like dissolves like n octane is a ar medium hence non polar compounds will be more in it KCI CH OH CH3CN Cyclohexane Increasing solubility Conditions of Henry s Law a The pressure should not be very high b The temperature should not be too low BILITY OF GASES c Solubility of the gas in the solvent should not be very high d The gas should not chemically combine with the solvent or dissociate in the solvent A ability of a gas in any solvent is increased as the pres as over solvent increases By contrast the pressure has ble effect on the solutions of solids and liquids The ive aspect of solubility of a gas with pressure has been erms of Henry s Law s Law unt of gas dissolved w per unit volume of solvent is proportional to its pressure PA i e PA Inference It is obvious from Eq mp or m kup that higher the value of K at a given pressure the lower is the solubility of the gas in the liquid It can be seen from the table that the K value for both N and O increase with temperature indicating that the solubility of gases decreases with increase of tem perature It is due to this reason that aquatic species are more comfortable in cold water rather than in warm water Slope k atm Application of Henry s Law a In the production of carbonated beverages Why cold drink water bottles are sealed under high pressure According to Henry s law solubility of gas increases with increase in pressure of the solution that is why cold drink bottles are sealed under high pressure so that more CO can be dissolved in it b In the deep sea diving For those people who do deep sea diving nitrogen and oxygen get dissolved in their blood under the effect of pressure of water This dissolved oxygen gets utilized in the metabolic activities but nitrogen remains as such When a person comes out of the sea this nitrogen which was dissolved in blood comes out in the form of

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsCalculate the normality of a solution containing 10 5 g of NaHCO3 in 500ml water Molecular weight of NaHCO3 is 84g Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction between copper sulphate and potassium iodide

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhat is the molarity of a NaOH solution if 15 5 mL of a 0 220 M H SO4 solution is required to neutralize a 25 0 mL sample of NaOH solution Select one a 0 710 b 0 355 c 0 273 d 42 6 e 0 136 X

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe change in boiling point of a solution containing 1 40 mol of KCN in a kg of water is AT On additio of 1 80 mol of Hg CN 2 all KCN reacts to form Hg CN 42 and change in boiling point is observed as AT 2 Calculate the ratio of AT AT

Physical Chemistry
Solutions45 The variation of solubility of four different gases G1 G2 etc in a given solvent with pressure at a constant temperature is shown in the plot Solubility G4 G3 G2 Pressure G1 The gas with the highest value of Henry s law constant is a G4 c G3 b G2 d G1

Physical Chemistry
Solutions2 moles of benzoic acid and 5 moles of benzene are mixed together to form a solution Which is the solute and which is the solvent O solute benzene benzoic acid solvent water impossible to determine solute benzene solvent benzoic acid Osolute benzoic acid solvent benzene

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAn aqueous solution of sucrose C12H22O11 having a concentration of 34 2 g l has an osmotic pressure of 2 38 atm at 17 C What should be the concentration of an aqueous solution of glucose C6H12O6 to be isotonic with this solution

Physical Chemistry
Solutions52 If pressure is applied to the following equilibrium Liquid Vapour the boiling point of the liquid 1 Will increase 2 Will decrease 3 Will not change 4 Can not be predicted 3 Consider the following equilibrium Class XI Marcel Batc Chemical lonic Equilibe 52 G for all alle 1 za ich farg 1 2 3 M 4 53 A far

Physical Chemistry
Solutions63 A decimolar solution of potassium ferrocyanide is 50 dissociated at 300 K Calculate the osmotic pressure of the solution 1 7 389 atm 2 73 89 atm 3 6 157 atm 4 2 463 atm

Physical Chemistry
Solutionswater shows depressions in freezing point in the ratio of 4 1 Assuming KCl to be completely ionised the compound X in solution must 1 dissociate to the extent of 50 2 hydrolyse to the extent of 80 3 dimerize to the extent of 50 4 trimerize to the extent of 75

Physical Chemistry
Solutions1 Which of the following mixture will lead to the formatio of negatively charged colloid AgI I 1 50 ml of 0 1 M AgNO3 50 ml of 0 1 M KI 2 50 ml of 0 1 M AgNO3 50 ml of 0 2 M KI 3 50 ml of 0 2 M AgNO3 50 ml of 0 1 M KI 4 50 ml of 0 2 M AgNO3 50 ml of 0 2 M KI

Physical Chemistry
Solutions5 If degree of dissociation of Al2 SO4 3 is 25 in a solvent then NCERT Pg 58 1 Normal boiling point experimental boiling point 2 Normal osmotic pressure 2 experimental osmotic pressure 3 Normal molecular weight 2 experimental molecular weight 4 Normal freezing point freezing point 1 4 x experimental