Matrices & Determinants Questions and Answers
![Determine whether the eigenvalues of each matrix are distinct real, repeated real, or complex.
[7/-20 +4/-11]
[3/3 -4/1]
[26/-60 +12/-28]
[-1/-4 +/1-5]](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/81046264-1659812414.1980286.jpeg?w=256)
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsDetermine whether the eigenvalues of each matrix are distinct real, repeated real, or complex.
[7/-20 +4/-11]
[3/3 -4/1]
[26/-60 +12/-28]
[-1/-4 +/1-5]
![Suppose matrix A is a 4 x 4 matrix such that A.
[-18/24/36/-24]=[-3/4/6/-4]
Find an eigenvalue of A.](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/81022414-1659812288.671723.jpeg?w=256)
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsSuppose matrix A is a 4 x 4 matrix such that A.
[-18/24/36/-24]=[-3/4/6/-4]
Find an eigenvalue of A.

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsThe corresponding linear combination would be: is a linear combination of the set S containing the vectors

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsLet T: R³→ R³ be a linear transformation defined by T(v) = Av,
1 0 0
A = 1 0 -1 Find T(3,1,-1)
2 1 -2

Algebra
Matrices & Determinants4 1 2
A = 0-3 3
0 0 2
Describe the set of all solutions to the homogeneous system Ax = 0.
Find A⁻¹, if it exists.
a) Describe the set of all solutions to the homogenous system Ax = 0
b) Find A⁻¹, if it exists.

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsGiven v₁ and v₂ in a vector space V, let H= Span {v₁, v₂}. Show that H is a subspace of V.
Algebra
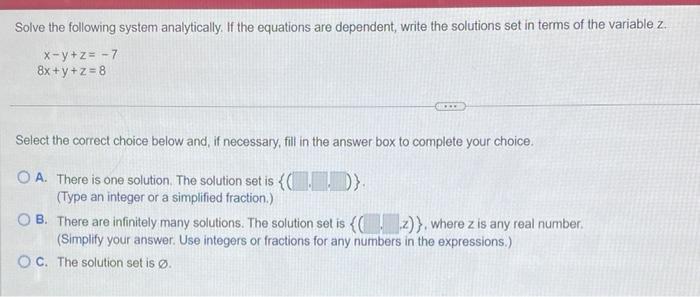
Matrices & DeterminantsSolve the following system analytically. If the equations are dependent, write the solutions set in terms of the variable z.
x-y+z= -7
8x+y+z=8
Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice.
A. There is one solution. The solution set is {}. (Type an integer or a simplified fraction.)
B. There are infinitely many solutions. The solution set is {(z)}, where z is any real number. (Simplify your answer. Use integers or fractions for any numbers in the expressions.)
C. The solution set is Ø.

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsWrite the system of linear equations in the form Ax= b and solve this matrix equation for x.
-2x₁-3x₂ = -11
6x₁+ X₂=-39

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsSuppose that ѵ₁ = (2,1,0,3), ѵ₂ = (3,-1,5,2), and v₃= (-1,0,2,1). Find the vector spanned by vectors ѵ₁, ѵ₂ and ѵ₃

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsThe probability of event A is 0.43, and the probability of event B is 0.55. What is the probability of both occurring if A and B are independent events?

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsDetermine the domain and range of the function f(x) = ln (-x+5).
Select the correct answer below:
a) Domain: (-∞, -5); Range: (-∞,∞)
b) Domain: (5,∞); Range: (-∞,3)
c) Domain: (-∞, 5); Range: (-∞,∞)
d) Domain: (-∞, ∞); Range: (-∞, ∞)
![Consider the set X= (2,3) U (8,10)
1. show that this set is open.
2. show that this set is not convex.
3. consider set Y=[3,8]. Is Y an open set? is X U Y open? Why/ Why not?
4. Is X and Y connected? WHY/WHY NOT?](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/81032550-1659803461.3465083.jpeg?w=256)
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsConsider the set X= (2,3) U (8,10)
1. show that this set is open.
2. show that this set is not convex.
3. consider set Y=[3,8]. Is Y an open set? is X U Y open? Why/ Why not?
4. Is X and Y connected? WHY/WHY NOT?

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsFor given equations
10x₁ + 2x₂-x₃ = 27
- 3x₁ - 5x₂ + 2x₃ = -61.5
x₁ + x₂ + 6x₃ = -21.5
(a) Solve by naive Gauss elimination.
(b) Solve by LU factorization.
(c) Solve by iterative method.

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsIf u and v are vectors in R³, then ||u – v|| = ||u|| - ||v||.
(a) True
(b) False

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsFind the vector equation of line of intersection of the planes 2x+2y+2z=4 and 2x-y+3z=1.
Algebra
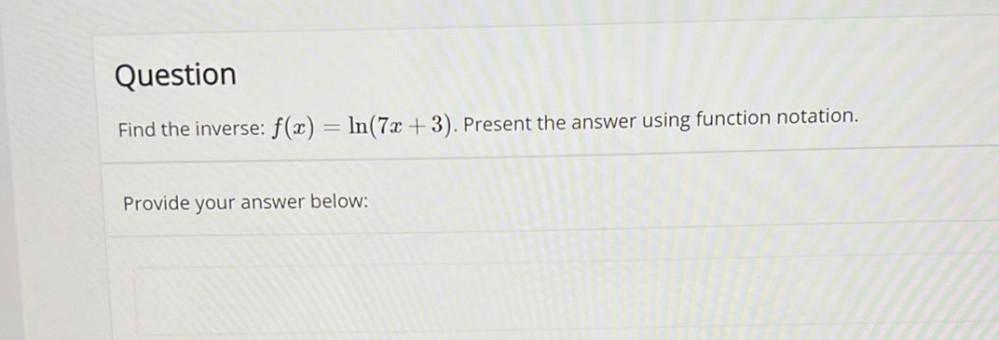
Matrices & DeterminantsFind the inverse: f(x) = ln(7x + 3). Present the answer using function notation.

Algebra
Matrices & Determinantscos θ=(2/3), tan θ <0 Find the exact value of sin θ
A. - √5
B. -√5/2
C. -√ 5/3
D. -3/2

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsLet f be: R²→R given by f(x,y) = (y - x²) (y – 2x²)
Show that f has no local minimum at (0,0), but that every restriction flg for every line G⊂R² through the origin, has a local minimum at (0,0).
Algebra
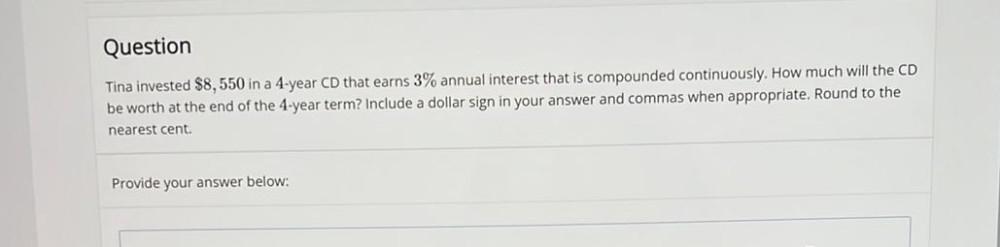
Matrices & DeterminantsTina invested $8, 550 in a 4-year CD that earns 3% annual interest that is compounded continuously. How much will the CD be worth at the end of the 4-year term? Include a dollar sign in your answer and commas when appropriate. Round to the nearest cent. Provide your answer below:
![Let v = [2, 0, -1] and w = [0, 2, 3]. Write w as the sum of a vector u₁ parallel to v and a vector u₂ orthogonal to v.](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/81512161-1659793586.7432566.jpeg?w=256)
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsLet v = [2, 0, -1] and w = [0, 2, 3]. Write w as the sum of a vector u₁ parallel to v and a vector u₂ orthogonal to v.

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsKindly help with the Answer to the question mentioned below. Thank you. If G is a group of order 208 then show that there exists a normal subgroup of order 27 or 9

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsLet W be the subspace of R4 generated by the vectors (1, -2, 5, -3), (2, 3, 1, -4), and (3, 8, -3, -5). Find a basis and the dimension of W.

Algebra
Matrices & Determinants(T/F) A matrix A is invertible if and only if 0 is an eigenvalue of A.

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsIs the subset below independent? Support your answer.
{(1, 1, 1, 1), (2, 0, 1, 0), (0, 2, 1, 2)} in R4
Algebra
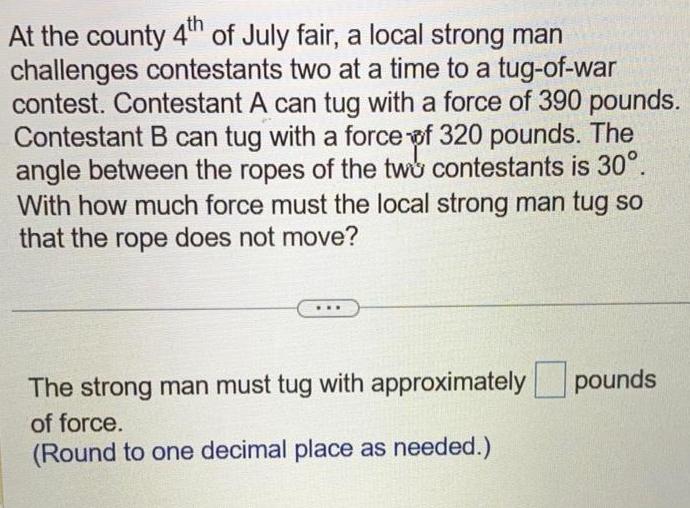
Matrices & DeterminantsAt the county 4th of July fair, a local strong man challenges contestants two at a time to a tug-of-war contest. Contestant A can tug with a force of 390 pounds. Contestant B can tug with a force of 320 pounds. The angle between the ropes of the two contestants is 30°. With how much force must the local strong man tug so that the rope does not move?
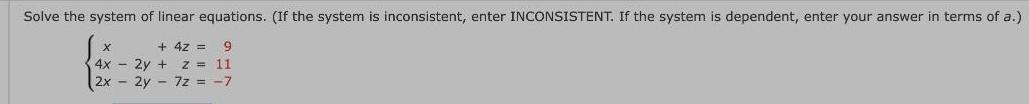
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsSolve the system of linear equations. (If the system is inconsistent, enter INCONSISTENT. If the system is dependent, enter your answer in terms of a.)
x+4z = 9
4x - 2y + z = 11
2x - 2y - 7z = -7

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsWhich of the following describes H = Span{v₁, v2, v3), where
v1 =1 v2= -2 v3= 1
1 -1 4
-3 7 0
A. H is a plane through the origin.
B. H = R³.
C. H is a line through the origin.
D. H is a line not through the origin.
E. H is a plane not through the origin.

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsLet f: R² → R² be the rotation transformation about the origin by 60° counterclockwise.
Let g: R² → R²³ be defined by g(x, y) = ( −x/2+my,mx+y/2)
1. Find m ER so that fo g is the reflection in the y-
m=
2. With this m, find the image of the point A(-4, 5) through go f.
3. Find the dimension of ker(go fogof).
Answer:

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsFind the equation of the hyperbola centered at (-1,4), vertices at (-1,-3) and (-1,11) and foci at (-1-5) and (-1, 13)

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsWrite a matrix for rotation of the plane R² clockwise by 60°. Show that the matrix is orthogonal.

Algebra
Matrices & Determinants5. Consider the following system of linear equations:
x₁ - x₃ - 2x₄ - 8x₅ = -3
-2x₁ + x₃ + 2x₄ + 9x₅ = 5
3x₁ -2x₃ -3x₄ -15x₅ = -9
a) Write the system in the matrix-vector form by finding the coefficient matrix A, variable vector x, and the right-hand-side vector b. Also form the augmented matrix for the system.

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsConsider the matrix equation Ax = b where,
a b
A= 1 1
where a, b>0.
(a) When is A strictly diagonally dominant and what does this tell us about the Gauss-Seidel method for Ax = b.
(b) Find the iteration matrix for the Gauss-Seidel method applied to Ax = b.

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsCompute the determinant of the n x n matrix A = (aj) such that, for all i, j, aij = 3 if i j and aij = 2 if i ≠ j.

Algebra
Matrices & Determinantsx+y+z= 14
For the system x -z = 5, what is the corresponding augmented matrix
2x - y = 3
before solving?
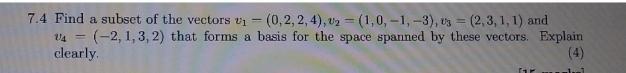
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsFind a subset of the vectors v₁ = (0,2,2,4), v₂ = (1, 0,-1,-3), v₃ = (2,3, 1, 1) and v₄ = (-2, 1, 3, 2) that forms a basis for the space spanned by these vectors. Explain clearly.

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsConsider the following matrix: A =
4 0 1
-1 1 0
-2 0 1
a) Find the eigenvalues of A
b) Using the eigenvalues of A, find the corresponding eigenvectors
![Let v₁= [2 v₂= [10 v₃= [-6 , and y= [-4
-1 -4 1 3
-1] -7/2] 0] h/2]
For what value(s) of h is y e span {v₁,v₂,v₃}?](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/81573201-1659554923.228775.jpeg?w=256)
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsLet v₁= [2 v₂= [10 v₃= [-6 , and y= [-4
-1 -4 1 3
-1] -7/2] 0] h/2]
For what value(s) of h is y e span {v₁,v₂,v₃}?
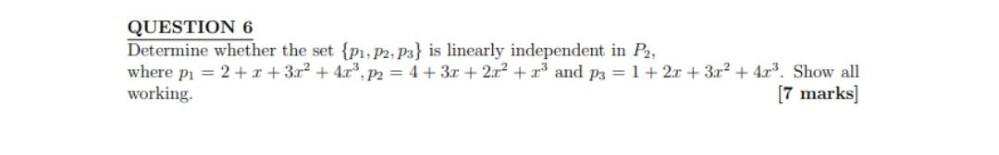
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsDetermine whether the set {Pᵢ, P₂, P₃} is linearly independent in P₂, where p₁ = 2+x+3x² + 4x³, p₂ = 4 + 3x + 2x² + x³ and p₃ = 1 + 2x + 3x² + 4x³. Show all working.
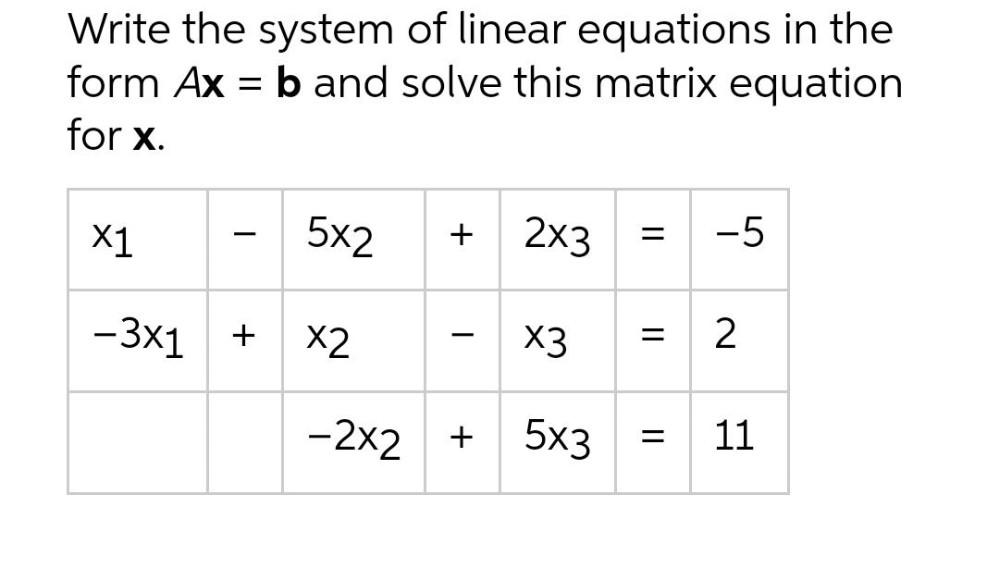
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsWrite the system of linear equations in the form Ax=b and solve this matrix equation for x.
x₁-5x₂+2x₃=-5
-3x₁+x₂-x₃=2
-2x₂+5x₃=11
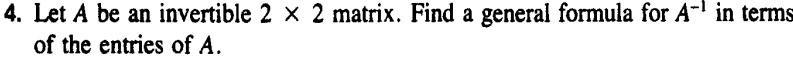
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsLet A be an invertible 2 x 2 matrix. Find a general formula for A-¹ in terms of the entries of A.
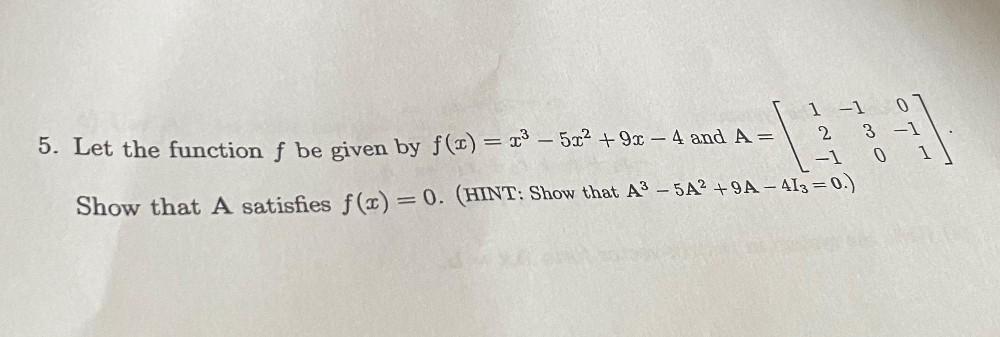
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsLet the function f be given by f(x) = x³ − 5x² + 9x − 4 and
A = 1 -1 0
2 3 -1
-1 0 1
Show that A satisfies f(x) = 0. (HINT: Show that A³ -5A² +9A-4I₃=0.)
![2) Shou that the Projection onto the vector v = [1, -2,1] is a linear transformation
T: R³ R3
b) Find the Standard matrix [T] for this transformation
C) Find the nullity ([T]) and rank ([T])](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/84831866-1659550287.5987208.jpeg?w=256)
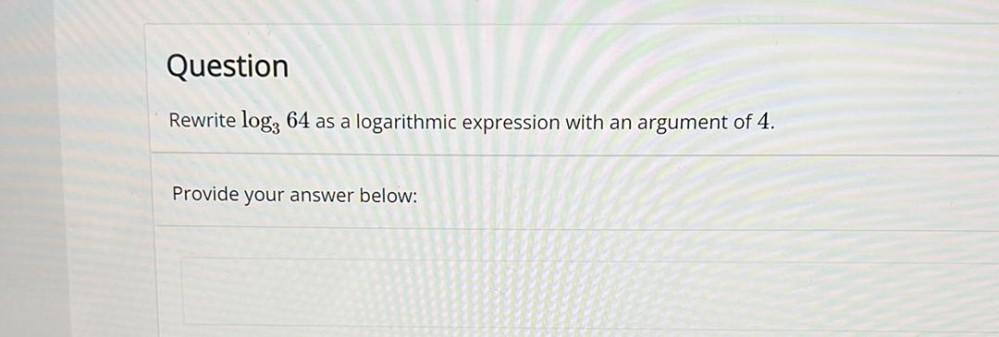
Algebra
Matrices & Determinants2) Shou that the Projection onto the vector v = [1, -2,1] is a linear transformation
T: R³ R3
b) Find the Standard matrix [T] for this transformation
C) Find the nullity ([T]) and rank ([T])
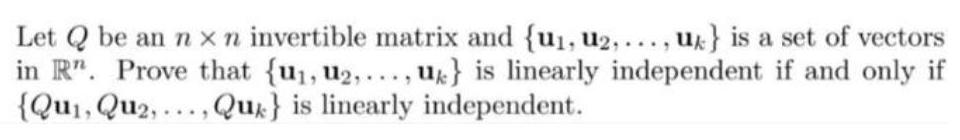
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsLet Q be an nxn invertible matrix and {u₁, U2,..., uk} is a set of vectors in R. Prove that {u₁, 12,..., uk} is linearly independent if and only if {Qui, Qu₂,..., Que} is linearly independent.

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsFind a formula in terms of k for the entries of Ak, where A is the diagonalizable matrix below.
A= -3 -4
2 3
A^k=

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsFind all unit vectors u E R³ that are orthogonal to both v₁ = (2,7,9) and V₂ = (-7,8,1).

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsConsider a scalar valued function
g(W) = 4w₁₁ +6w₁₂+6w₂₁+9w₂₂ of the 2×2 matrix W = {wij}.
(1) Express the matrix form of g (W).
(2) Find the matrix gradient of g (W) with respect to W.
![Suppose the augmented coefficient matrix of a certain linear system is:
[1 1 3 Ⅰ -3]
[1 2 -2 Ⅰ 1]
[3 9 k Ⅰ 16]
for some k∈ R.
For what value(s) of k will the system have no solution?
k =?
For what value(s) of k will the system have infinitely many solutions?
k= =?
Enter your answers as comma-separated lists. If there are no values of k satisfying the given condition, enter NONE.](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/81709518-1659521287.417267.jpeg?w=256)
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsSuppose the augmented coefficient matrix of a certain linear system is:
[1 1 3 Ⅰ -3]
[1 2 -2 Ⅰ 1]
[3 9 k Ⅰ 16]
for some k∈ R.
For what value(s) of k will the system have no solution?
k =?
For what value(s) of k will the system have infinitely many solutions?
k= =?
Enter your answers as comma-separated lists. If there are no values of k satisfying the given condition, enter NONE.

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsRewrite log 3 √10 as a a logarithmic expression with an argument of 10.
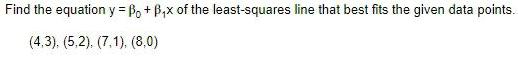
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsFind the equation y = Bo + B₁x of the least-squares line that best fits the given data points.
(4.3). (5,2). (7.1), (8,0)