In the field of geometry, a quadrilateral is a polygon with four sides, four vertices (corners), and four angles. The term “quadrilateral” is derived from the Latin words “quadri,” meaning “four,” and “latus,” meaning “side.” Quadrilaterals are two-dimensional shapes that exist in a plane.
A quadrilateral is formed by connecting four non-collinear points. The four sides of a quadrilateral are designated as AB, BC, CD, and DA, while the four vertices are represented by the points A, B, C, and D. The interior angles of a quadrilateral are denoted as ∠ABC, ∠BCD, ∠CDA, and ∠DAB.
One of the key properties of a quadrilateral is that the sum of all its interior angles is always equal to 360 degrees. This property holds true for all types of quadrilaterals.
What is a Quadrilateral?
A quadrilateral is a two-dimensional geometric figure with four straight sides that close to form a single enclosed shape. The sum of the interior angles of any quadrilateral is always 360°. The sides of a quadrilateral can be of varying lengths and the shape itself can take on many forms, depending on the lengths of the sides and the angles between them.
Quadrilateral Formulas
Area of Quadrilateral
The area of a quadrilateral is the space occupied by the shape in a two-dimensional plane. Different types of quadrilaterals have different formulas for calculating the area based on their properties.
| Area of a Parallelogram | Base x Height |
| Area of a Rectangle | Length x Width |
| Area of a Square | Side x Side |
| Area of a Rhombus | (1/2) x Diagonal 1 x Diagonal 2 |
| Area of a Kite | 1/2 x Diagonal 1 x Diagonal 2 |
Perimeter of Quadrilateral
The perimeter of a quadrilateral is the total length of its boundaries. It is calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides of the quadrilateral.
| Quadrilateral Name | Perimeter |
| Square | 4 x Side |
| Rectangle | 2(Length + Breadth) |
| Parallelogram | 2(Base + Side) |
| Rhombus | 4 x Side |
| Kite | 2 (a + b), a and b are adjacent pairs |
Sides and Angles of Quadrilateral
| Sides and Angles | Square | Rectangle | Rhombus | Parallelogram | Trapezium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All sides are equal | Yes | No | Yes | No | No |
| Opposite sides are parallel | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Opposite sides are equal | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| All the angles are of the same measure | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| Opposite angles are of equal measure | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Diagonals bisect each other | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Two adjacent angles are supplementary | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
Properties of a Quadrilateral
Quadrilaterals have some unique properties, which distinguish them from other polygons:
- They have four sides.
- They are two-dimensional shapes.
- They have four vertices.
- They have two diagonals.
- The sum of all the interior angles of a quadrilateral is always 360°.
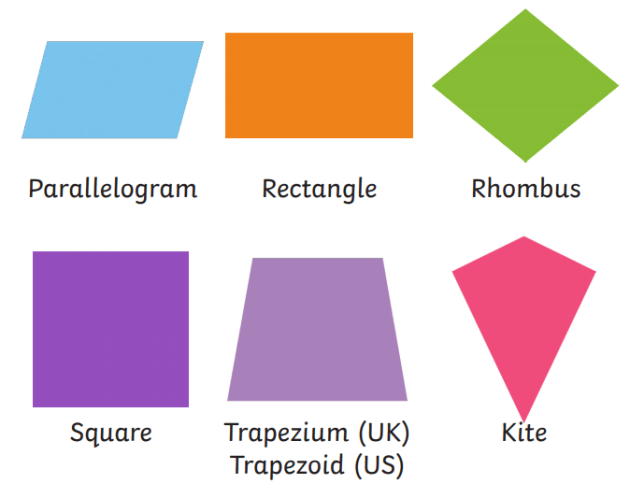
Types of Quadrilaterals
Quadrilaterals can be classified into six major types: Parallelogram, Trapezium, Rhombus, Rectangle, Square, and Kite.
| Type of Quadrilateral | Definition |
|---|---|
| Parallelogram | A quadrilateral with opposite sides parallel and equal |
| Trapezium | A quadrilateral with one pair of opposite sides parallel |
| Rhombus | A quadrilateral with all sides of equal length |
| Rectangle | A quadrilateral with all angles measuring 90° and opposite sides equal |
| Square | A quadrilateral with all sides and angles equal |
| Kite | A quadrilateral with two pairs of adjacent sides of equal length |
Concave Quadrilaterals
A concave quadrilateral is a type of quadrilateral where at least one of its interior angles measures more than 180°. In such a quadrilateral, one of the diagonals lies outside the quadrilateral. An example of a concave quadrilateral is a dart or arrowhead.
Convex Quadrilaterals
A convex quadrilateral is a quadrilateral where all its interior angles measure less than 180°. In such a quadrilateral, both diagonals lie inside the quadrilateral. Examples of convex quadrilaterals include a square, rectangle, rhombus, and trapezium.
Trapezium
A trapezium is a quadrilateral where only one pair of opposite sides is parallel. The sides that are parallel to each other are known as the bases of the trapezium, and the sides that are not parallel are called the legs.
Square
A square is a quadrilateral where all sides are of equal length, and each interior angle measures 90°. It is also a regular quadrilateral, meaning it is both equiangular and equilateral.
Kite
A kite is a quadrilateral where two pairs of adjacent sides are equal in length. The diagonals of a kite intersect at a right angle, and the longer diagonal bisects the shorter one.
Parallelogram
A parallelogram is a quadrilateral where opposite sides are equal in length and are parallel to each other. The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other, and opposite angles are equal.
Rectangle
A rectangle is a quadrilateral where all angles measure 90°, and opposite sides are equal in length. The diagonals of a rectangle are equal in length and bisect each other.
Rhombus
A rhombus is a quadrilateral where all sides are equal in length, and opposite sides are parallel. The diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at right angles.

Simple Quadrilaterals
A simple quadrilateral is a quadrilateral that does not intersect itself. It can be either convex or concave in shape. Examples of simple quadrilaterals include a square, rectangle, and dart.
Complex Quadrilaterals
A complex quadrilateral, also known as a crossed quadrilateral or a butterfly quadrilateral, is a quadrilateral where the sides intersect each other. Examples of complex quadrilaterals include a crossed trapezoid, crossed-square, and crossed-rectangle.
Intersecting Quadrilaterals
Intersecting quadrilaterals are quadrilaterals where non-adjacent sides intersect each other. These are also known as self-intersecting or crossed quadrilaterals.
Parts of a Quadrilateral
A quadrilateral is composed of several parts, including sides, vertices, and diagonals. The sides of a quadrilateral are the lines that form the shape, and the vertices are the points where the sides meet. The diagonals are lines that connect opposite vertices. Each quadrilateral has four sides, four vertices, and two diagonals.
Frequently Asked Questions on Quadrilateral
How many sides does a quadrilateral have?
A quadrilateral, by definition, has four sides.
How to draw a quadrilateral?
To draw a quadrilateral, you need to draw four straight lines that connect to form a closed shape. The points where the lines meet are the vertices of the quadrilateral.
What is the sum of the internal angles of a quadrilateral?
The sum of the internal angles of any quadrilateral is always 360 degrees.
Are all Sides of a Quadrilateral Equal?
No, not all sides of a quadrilateral are equal. However, in specific types of quadrilaterals like a square or a rhombus, all sides are equal.
How many vertices does a quadrilateral have?
A quadrilateral has four vertices or corners.
Can all the angles of a quadrilateral be acute?
No, not all angles of a quadrilateral can be acute. The sum of all the angles in a quadrilateral is 360 degrees, so it cannot have all acute angles.
What is a cyclic quadrilateral?
A cyclic quadrilateral is a quadrilateral whose vertices all lie on a single circle. This means that you can draw a circle that passes through all four vertices of the quadrilateral.
What is the Golden quadrilateral?
The term “Golden Quadrilateral” is often used to refer to a highway network in India that connects four of the country’s major cities: Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, and Kolkata.
What does a quadrilateral look like?
A quadrilateral looks like a four-sided polygon. The exact shape can vary greatly depending on the lengths of the sides and the sizes of the angles.
Solved Examples on Quadrilateral
Let’s take a look at some solved examples to better understand the concepts related to quadrilaterals:
Example 1: Find the perimeter of a quadrilateral whose sides measure 6 cm, 7 cm, 8 cm, and 13 cm.
Solution: The perimeter of a quadrilateral is the sum of the lengths of all four sides. So, the perimeter of this quadrilateral = 6 cm + 7 cm + 8 cm + 13 cm = 34 cm.
Example 2: What is the area of a kite with diagonals measuring 22 cm and 6 cm?
Solution: The area of a kite can be found using the formula 1/2 × Diagonal 1 × Diagonal 2. So, the area of this kite = 1/2 × 22 cm × 6 cm = 66 square cm.
Example 3: What is the perimeter of a parallelogram with opposite sides measuring 13 cm and 6 cm?
Solution: The perimeter of a parallelogram is the sum of the lengths of all four sides. Since opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal, the perimeter = 2(13 cm + 6 cm) = 38 cm.
Example 4: Find the base of a rectangle if its area is 72 square units and its height is 8 units.
Solution: The area of a rectangle is given by the formula Base × Height. So, if the area is 72 square units and the height is 8 units, then the base = Area ÷ Height = 72 ÷ 8 = 9 units.
How Can Kunduz Help You Learn Quadrilateral?
Kunduz is an online learning platform that provides comprehensive learning materials and resources for various subjects, including geometry. With Kunduz, you can access well-detailed and compelling SEO-friendly learning materials, including blog posts and articles, to help you understand quadrilateral and its various types, properties, formulas, and solved examples. As a top-notch online learning platform, Kunduz is committed to providing high-quality, easy-to-understand, and well-structured learning materials to help students excel in their academics and achieve their educational goals.
For readers exploring the properties of quadrilateral and interested in a broader understanding of polygons, we offer various other polygon pages. These resources delve into the formulas, characteristics, and classifications of polygons, providing a comprehensive exploration of geometric shapes beyond the quadrilateral:
Pentagon: Definition, Shape, Properties, Types, Formula & Example
What is a Heptagon: Definition, Properties, Types, Formula, Solved Example
Octagon Shape: Definition, Properties, Formula, Examples, Sides & Angles
