Ethane is an important chemical compound that plays a significant role in various industries. It is a colorless and odorless gas that is commonly found in natural gas and petroleum. Ethane is the second simplest alkane, with a chemical formula of C2H6. It is a saturated hydrocarbon, meaning it contains only single covalent bonds between carbon and hydrogen atoms.
Ethane is widely used in the production of ethylene, which is a key component in the manufacture of plastics. It is also used in the production of ethanol, acetic acid, and other organic compounds. In addition, ethane is used as a fuel in certain types of engines.
In this article, we will explore the formula, properties, chemical structure, and various uses of ethane.
What is Ethane?
Ethane, with a chemical formula of C2H6, is a hydrocarbon compound that consists of two carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms. It is the second simplest alkane, after methane. Ethane is a colorless and odorless gas at room temperature and pressure. It is slightly heavier than air and is highly flammable.
Ethane is an important component of natural gas, and it can be separated from natural gas through various processes. It is also produced industrially through the steam cracking of ethane, ethylene, or gasoline fractions from petroleum refining.
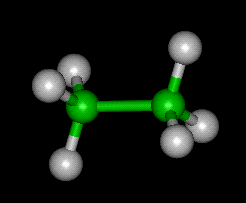
History of Ethane
The discovery of ethane is associated with the chemist Dmitri Mendeleev, who worked in the 1830s. It was first observed in 1859 by Mendeleev, and its melting point was measured in 1862. The name “ethane” was first reported by Charles-Marie de La Hire, a French chemist, who isolated the gas from coal and natural gas.
Synthesis of Ethane – C2H6
Ethane can be synthesized through various methods. One common method is the reduction of ethyl iodide using zinc and copper couple in alcohol. The chemical equation for this reaction is:
CH3CH2I + 2[H] → C2H6 + HI
Another method is the Wurtz reaction, where methyl bromide or methyl iodide and sodium are heated in the presence of dry ether to form ethane:
CH3I + 2Na + CH3I → CH3–CH3 + 2NaI
Ethane Structure – C2H6
The structure of ethane consists of two carbon atoms bonded together by a single bond, with three hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. It is a straight-chain molecule, with a tetrahedral geometry shape and sp3 hybridization of carbon atoms.

Molecular Structure
The molecular structure of ethane is a straight chain with a single carbon-carbon bond. Each carbon atom is bonded to three hydrogen atoms, resulting in a tetrahedral geometry. The carbon-carbon bond in ethane is a sigma bond, which is formed by the overlap of sp3 hybrid orbitals.

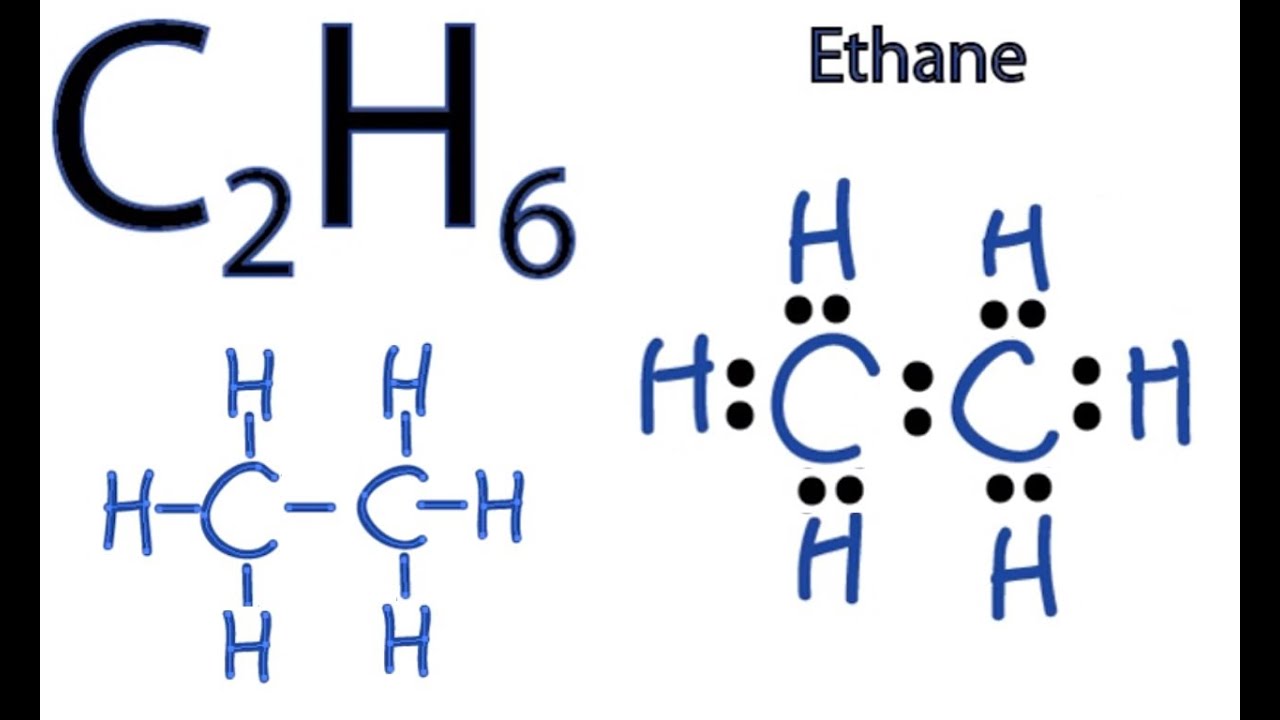
C2H6 Lewis Structure
The Lewis structure of ethane shows the arrangement of atoms and the distribution of valence electrons. In the Lewis structure, each carbon atom is surrounded by four electrons, while each hydrogen atom has two electrons. The Lewis structure of ethane can be represented as:
H H | | C-C | | H H
Steps for drawing the C2H6 Lewis structure
- Determine the total number of valence electrons. In ethane, carbon has 4 valence electrons, and each hydrogen atom has 1 valence electron. So the total number of valence electrons is 2(4) + 6(1) = 16.
- Place the carbon atoms in the center and connect them with a single bond.
- Distribute the remaining valence electrons around the hydrogen atoms to satisfy the octet rule. Each hydrogen atom should have 2 electrons, and carbon should have 8 electrons.
- Check if all atoms have a complete octet. In the case of ethane, each carbon atom has 8 electrons, and each hydrogen atom has 2 electrons.
- If there are any remaining valence electrons, place them on the central atom to complete the octet.
C2H6 Hybridization
The carbon atoms in ethane undergo sp3 hybridization. In sp3 hybridization, the s orbital and three p orbitals of the carbon atom combine to form four sp3 hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals are arranged in a tetrahedral geometry, with bond angles of approximately 109.5 degrees.
C2H6 Molecular Geometry
The molecular geometry of ethane is tetrahedral. The carbon atoms in ethane are surrounded by four other atoms (three hydrogen atoms and one carbon atom), resulting in a tetrahedral arrangement. The bond angles between the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms are approximately 109.5 degrees.
Molar Mass of Ethane
The molar mass of ethane can be calculated by adding up the atomic masses of all the atoms in the molecule. The atomic mass of carbon is 12.01 g/mol, and the atomic mass of hydrogen is 1.0079 g/mol. Therefore, the molar mass of ethane (C2H6) is:
2(12.01 g/mol) + 6(1.0079 g/mol) = 30.07 g/mol
Physical Properties of Ethane – C2H6
Ethane is a colorless and odorless gas at room temperature and pressure. It has a boiling point of -89 °C and a melting point of -182.8 °C. Ethane is slightly soluble in water and is lighter than air. It is highly flammable and can form explosive mixtures with air.
Chemical Properties of Ethane – C2H6
Ethane is a hydrocarbon compound that is relatively unreactive under normal conditions. However, it can undergo various chemical reactions under specific conditions. For example, ethane can react with oxygen or nitric acid to form ethylene oxide. It can also undergo cracking reactions to produce smaller hydrocarbons.
Uses of Ethane – C2H6
Ethane has a wide range of uses in various industries. It is primarily used as a feedstock for the production of ethylene, which is a key component in the manufacture of plastics, synthetic fibers, and other materials. Ethane is also used in the production of ethanol, acetic acid, and other organic compounds.
Additionally, ethane is used as a fuel in certain types of engines. It is also used as a refrigerant and a propellant in aerosol products. Ethane is an important component of natural gas and is used for heating and cooking purposes.
Preparation of Methylene Blue
Methylene blue is a synthetic organic compound with a blue color. It is used as a medication, a dye, and as a biological stain. Methylene blue can be prepared through various methods, including the Beyer route and the Hantzsch-Widman route.
The Beyer route involves the reaction of aniline and formaldehyde to form 4-amino-N,N-dimethylaniline. This compound is then reacted with phenol to produce methylene blue. The Hantzsch-Widman route starts with 3,5-diaminobenzoic acid, which is then reacted with formaldehyde and acetophenone to form 4-amino-3,5-dihydroxyphenylacetone. This compound is then reacted with hydrochloric acid to produce methylene blue.
Isomerism
Isomerism is a phenomenon where molecules with the same chemical formula but different structures are called isomers. Ethane does not exhibit isomerism, as it consists of a straight chain with a single carbon-carbon bond.
Frequently Asked Questions on Ethane
What is Ethane?
Ethane is a colorless, odorless gas that is a member of the alkane family of hydrocarbons. It is the second simplest alkane after methane and is a significant component of natural gas.
Is ethane poisonous
Ethane is not considered toxic or harmful if inhaled in small quantities. However, in large concentrations, it may displace oxygen and lead to asphyxiation.
What is ethane used for?
Ethane is primarily used as a raw material in the production of ethylene, which is further used in the production of a variety of products, including plastics, detergents, and ripening fruits.
What is ethane made from?
Ethane can be extracted from natural gas and petroleum. It can also be artificially synthesized in laboratories using various methods, such as the reduction of ethyl iodide or the Wurtz reaction.
Can ethane be classified as a hydrocarbon?
As ethane is composed of only carbon and hydrogen atoms, it is classified as a hydrocarbon. It is specifically an alkane, which is a type of saturated hydrocarbon.
Is ethane a good fuel?
Ethane is a major component of natural gas and is widely used as a fuel. It has a high heat of combustion and burns with a clean, smokeless flame, making it an efficient source of energy.
What is the boiling point for Ethane?
The boiling point of ethane is around 89 °C.
How is ethane produced?
Ethane can be produced by distilling and purifying crude ethane. It can also be synthesized by converting ethane to ethylene and hydrogen by the reaction with hydrogenation and carbon monoxide over an iron catalyst.
Is Ethane Polar or Nonpolar?
Ethane is a nonpolar molecule. While the C-H bonds do have a difference in electronegativity, the molecule itself is symmetric, and the individual bond polarities cancel each other out, making the overall molecule nonpolar.
Solved Examples on Ethane
Example 1: What is the molar mass of ethane (C2H6)?
Solution: The molar mass of carbon (C) is 12.01 g/mol, and the molar mass of hydrogen (H) is 1.0079 g/mol. To calculate the molar mass of ethane, we multiply the molar mass of each atom by the number of atoms in the molecule:
2(12.01 g/mol) + 6(1.0079 g/mol) = 30.07 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of ethane is 30.07 g/mol.
Example 2: Draw the Lewis structure for ethane (C2H6).
Solution: To draw the Lewis structure for ethane, we follow these steps:
- Determine the total number of valence electrons: Carbon has 4 valence electrons, and hydrogen has 1 valence electron. So the total number of valence electrons is 2(4) + 6(1) = 16.
- Place the carbon atoms in the center and connect them with a single bond.
- Distribute the remaining valence electrons around the hydrogen atoms to satisfy the octet rule. Each hydrogen atom should have 2 electrons, and carbon should have 8 electrons.
- Check if all atoms have a complete octet. In the case of ethane, each carbon atom has 8 electrons, and each hydrogen atom has 2 electrons.
- If there are any remaining valence electrons, place them on the central atom to complete the octet.
The Lewis structure for ethane can be represented as: H H | | C-C | | H H
How Kunduz Can Help You Learn Ethane?
Kunduz is a comprehensive online learning platform that offers a wide range of resources to help you learn about ethane and other chemistry topics. Whether you are a student or a professional, Kunduz provides interactive lessons, practice problems, and in-depth explanations to enhance your understanding of ethane.
With Kunduz, you can access high-quality educational content at your own pace and convenience. The platform offers step-by-step tutorials, video lectures, and interactive quizzes to reinforce your learning. You can also connect with expert tutors and fellow learners through the online community to ask questions and discuss concepts.
Start your journey to mastering ethane and chemistry with Kunduz today!
