In today’s digital age, the need for fast and efficient communication has become paramount. Optical fiber has emerged as a revolutionary technology that enables high-speed data transmission over long distances with minimal loss. It has transformed the way we communicate, providing faster internet, phone, and TV services. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of optical fiber, exploring its definition, design, working principle, types, and the advantages it offers over traditional wires. So, let’s embark on this enlightening journey into the fascinating realm of optical fiber.
What is Optical Fiber?
Optical fiber is a technology that involves the transmission of data using light pulses along a long, flexible fiber made of plastic or glass. The core of the optical fiber is specifically designed to facilitate the propagation of light based on the power and distance requirements of the transmission. It offers numerous advantages over traditional metal wires, such as lower power consumption, non-flammability, and immunity to electromagnetic interference. Optical fibers are classified based on the refractive index, materials used, and mode of propagation of light.
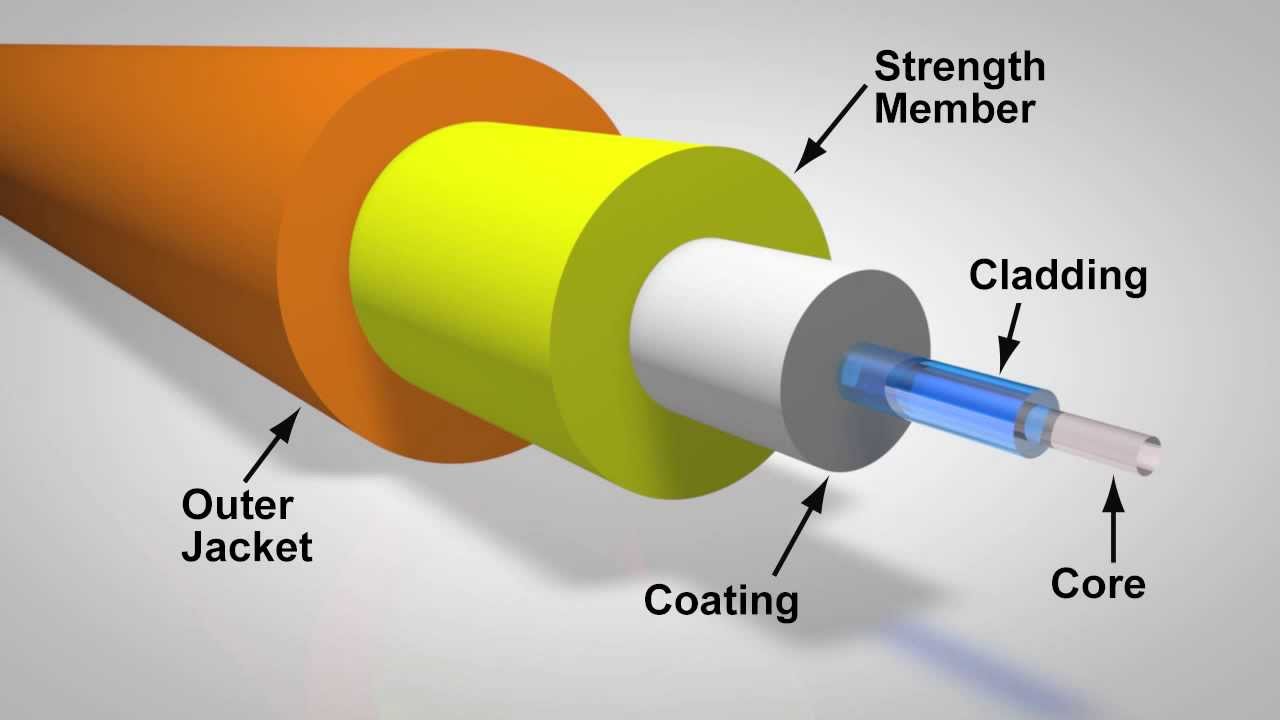
Design of an Optical Fiber
The design of an optical fiber consists of several components that work together to enable efficient data transmission. These components include the core, cladding, coating, strengthening fibers, and cable jacket. The core serves as the medium for transmitting light, surrounded by the cladding, which ensures total internal reflection. The coating provides protection and flexibility to the fiber, while the strengthening fibers prevent damage from crushing or excessive tension. Finally, the cable jacket acts as an external shield, safeguarding the fiber from environmental factors.
How Does an Optical Fiber Work?
The working principle of an optical fiber is based on total internal reflection. When light rays enter the core of the fiber at an angle greater than the critical angle, they undergo continuous reflection, bouncing off the fiber walls and transmitting data from end to end. This allows for the efficient transmission of light signals over long distances with minimal loss. Optical fiber systems typically consist of a transmitter that encodes light signals, the optical fiber itself, a receiver that decodes the transmitted signals, and an optical regenerator for long-distance data transmission.
Types of Optical Fibers
Optical fibers can be classified based on various criteria such as refractive index, materials used, and mode of propagation of light.
Step Index Fibres
These fibers consist of a core surrounded by cladding, each having a single uniform index of refraction.
Graded Index Fibres
In these fibers, the refractive index of the optical fiber decreases as the radial distance from the fiber axis increases.
Plastic Optical Fibres
These fibers use polymethylmethacrylate as a core material for the transmission of light.
Glass Fibres
These fibers consist of extremely fine glass fibers that serve as the core.
Single-Mode Fibres
These fibers are used for the long-distance transmission of signals.
Multimode Fibres
These fibers are used for the short-distance transmission of signals.
Advantages of Optical Fiber Communication
Optical fiber communication offers numerous advantages over traditional wire-based communication systems. Some of the key advantages include:
- Economical and cost-effective: Optical fiber systems are more cost-effective in the long run, requiring less maintenance and offering higher bandwidth capabilities.
- Thin and non-flammable: Optical fibers are thin, lightweight, and non-flammable, making them easy to install and safer to use.
- Less power consumption: Optical fiber systems consume less power compared to traditional wire-based systems, resulting in energy savings.
- Less signal degradation: Optical fibers experience minimal signal degradation over long distances, ensuring reliable and high-quality data transmission.
- Flexible and lightweight: Optical fibers are highly flexible and lightweight, making them ideal for installations in various environments and applications.
Construction of Optical Fibers
Optical fibers are constructed using five primary layers: the core, cladding, coating, strengthening fibers, and cable jacket. The core serves as the medium for light transmission, surrounded by the cladding, which provides continuous reflection. The coating acts as a protective layer, absorbing shocks and preventing bending damage. Strengthening fibers protect the layers from crushing forces and excessive tension. Finally, the cable jacket provides external protection against environmental factors.

Principle of Operation of Optical Fibers
The principle of operation of optical fibers is based on total internal reflection. When light rays enter the fiber core at an angle greater than the critical angle, they undergo total internal reflection, bouncing off the fiber walls and propagating through the fiber. This principle allows for the efficient transmission of light signals without significant loss.
Components of Optical Fiber
An optical fiber system consists of several components that work together to enable data transmission. These components include the transmitter, optical fiber, optical receiver, and optical regenerator. The transmitter produces light signals and encodes them for transmission. The optical fiber serves as the medium for transmitting the light pulse. The optical receiver receives the transmitted light pulse and decodes it for use. In long-distance data transmission, an optical regenerator is necessary to maintain the integrity of the transmitted data.
Key Terms Used In Optical Fiber
Understanding optical fiber involves key terms such as critical angle, acceptance angle, numerical aperture, and fiber attenuation. These terms are essential in grasping the operation and functionality of optical fibers.
Critical Angle (θc)
This term refers to the angle at which light undergoes total internal reflection within the fiber.
Acceptance Angle (θa)
This term refers to the maximum angle of incidence with the axis of the fiber for which all the incident light is totally reflected.
Numerical Aperture
This term defines the light-gathering capability of an optical fiber, equivalent to the sine of its acceptance angle.
Fibre Attenuation
This term refers to the reduction in light energy or signal power as it travels through the fiber.
Uses of Optical Fibers
Optical fibers find applications in various fields, including communication, medicine, sensing, and lighting. In the communication sector, optical fibers serve as the backbone of global telecommunications networks, providing high-speed data transmission over long distances. In medicine, they are used in devices such as endoscopes and microscopes for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Optical fibers also find applications in sensing physical parameters like temperature and pressure. Additionally, they are used in lighting systems for hard-to-reach places and decorative lighting.
What is Fiber Network?
A fiber network is a network infrastructure that utilizes optical fibers to transmit information using light pulses. It provides high-speed and reliable connectivity for voice, data, and video transmission. Fiber networks are capable of transmitting signals over long distances without significant loss or degradation. They offer numerous benefits, including high data security, cost-effectiveness, and immunity to electromagnetic interference. Fiber networks are widely used in telecommunications, providing internet, phone, and TV services to homes, businesses, and other institutions.
How Kunduz Can Help You Learn Optical Fiber?
At Kunduz, we are dedicated to providing comprehensive and accessible learning materials for students. Our expert tutors are well-versed in the intricacies of optical fiber technology and can guide you through the concepts and applications with ease. Whether you need help understanding the design of optical fibers, the principle of operation, or the types and uses of optical fibers, Kunduz is here to assist you every step of the way. With our in-depth tutorials and step-by-step explanations, you can master the world of optical fiber and excel in your studies.
Related Topics: