Matrices & Determinants Questions and Answers
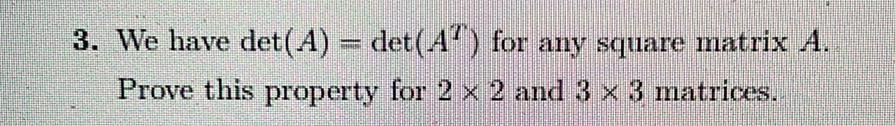
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsWe have det (A) = det(A^T) for any square matrix A. Prove this property for 2 x 2 and 3 × 3 matrices.
Algebra
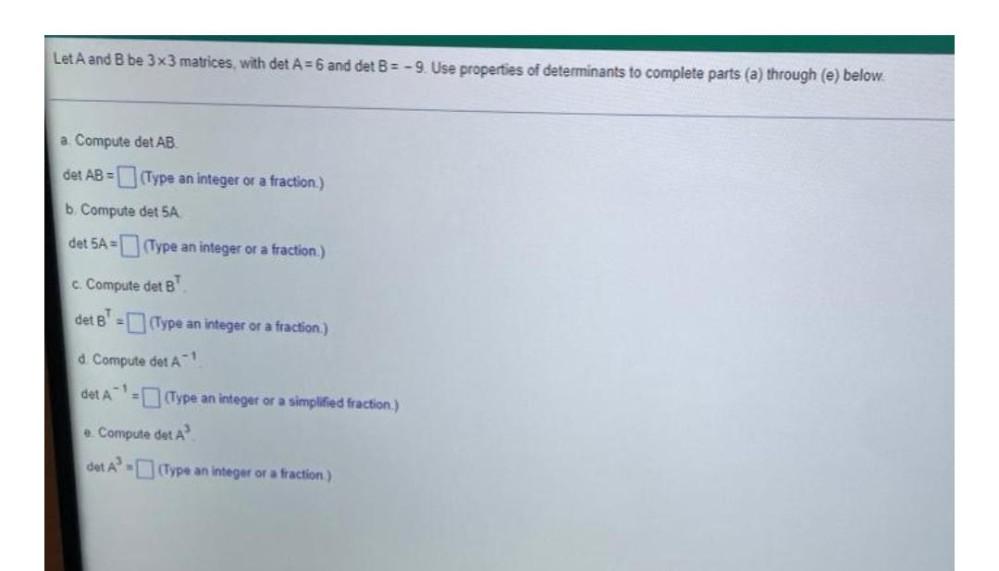
Matrices & DeterminantsLet A and B be 3x3 matrices, with det A=6 and det B=-9. Use properties of determinants to complete parts (a) through (e) below.
a) Compute det AB.
det AB = __________ (Type an integer or a fraction.)
b) Compute det 5A
det 5A= ____________ (Type an integer or a fraction.)
c) Compute det B
det B= ________________ (Type an integer or a fraction.)
d) Compute det A^(-1)
det A^(-1) = ___________ (Type an integer or a simplified fraction.)
e) Compute det A³
det A³ = ___________ (Type an integer or a fraction.)

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsThe simple row-echelon form matrix:
1 2 0 0
0 0 1 0
0 0 0 4,
shows that the system is.... of linear equations
(1) an inconsistent system
(2) a consistent system
(3) non linear system
(4) non of the above

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsPick the correct statements for the given set.
-1 -7
7 0
-6 2
Not a basis of R³.
Does not span R³.
Linearly independent.
All of the above.

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsConsider the following system of equations.
2x + y=2
y-z= 4
-2x + y + 2 = −4
Find the LU-factorization of the coefficient matrix.

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsSolve the system of equations graphically. Then
classify the system as consistent or inconsistent and
the equations as dependent or independent.
4u+v=1
4u=v+7

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsSolve the following system of equations by elimination
x + y = 8
4x + y = 23


Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsFind the standard matrix for the linear transformation T on R2 that first projects the resulting vector on y-axis then rotates the resulting vector with an angle, and then finally reflects a vector about the y-axis.
![Let B=(b₁ b₂} and C= (C₁.C₂} be bases for a vector space V, and suppose b₁ = -2c₁ +6c₂ and b₂ = 8c₁ - 3c₂
a. Find the change-of-coordinates matrix from B to C.
b. Find [x]c for x = 6b₁-5b₂. Use part (a).
a. P =
C←B](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/82382541-1659200339.5093608.jpeg?w=256)
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsLet B=(b₁ b₂} and C= (C₁.C₂} be bases for a vector space V, and suppose b₁ = -2c₁ +6c₂ and b₂ = 8c₁ - 3c₂
a. Find the change-of-coordinates matrix from B to C.
b. Find [x]c for x = 6b₁-5b₂. Use part (a).
a. P =
C←B

Algebra
Matrices & Determinants1. A matrix model is given by the following system of linear equations.
A(t+1)=2At + Ct
B(t+1)=3At + 5Bt
C(t+1)=4A +6Bt
(a) Write the corresponding matrix equation.
(b) Write the corresponding matrix diagram.
![Find the product of the two matrices below. Is each the inverse of the other?
7 4 3 4
-5 3 -5 -7
Find the inverse of matrix A by using row operations to get [1] A-¹]
A = 4 3
3 2](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/82391861-1659197129.3406668.jpeg?w=256)
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsFind the product of the two matrices below. Is each the inverse of the other?
7 4 3 4
-5 3 -5 -7
Find the inverse of matrix A by using row operations to get [1] A-¹]
A = 4 3
3 2
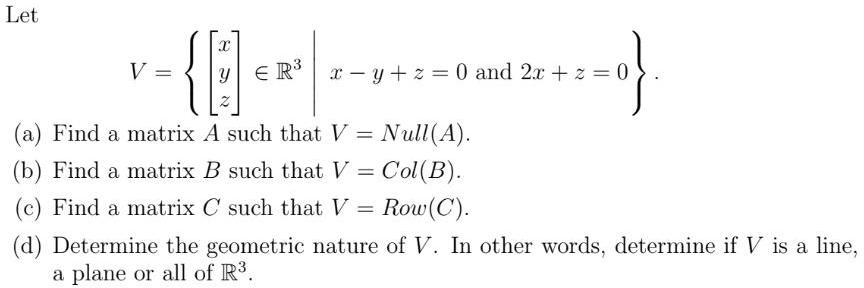
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsLet
V =x x-y+z= 0 and 2x + z = 0
y ER³
z
(a) Find a matrix A such that V = Null(A).
(b) Find a matrix B such that V = Col(B).
(c) Find a matrix C such that V = Row (C).
(d) Determine the geometric nature of V. In other words, determine if V is a line,
a plane or all of R³.

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsUse the Gram-Schmidt Orthonormalization Process to transform the basis B = {(1, 0, 1), (1, 2, 0), (2, 1, 1)} into an orthonormal basis for R³.

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsA 3x3 matrix has eigenvalues (3, 2, 1) and (1, 1, 1). Is the matrix diagonalizable?
Explain.

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsFind a basis of the subspace of R³ defined by the equation - 8x1 - 3x2 + 6x3 = 0.
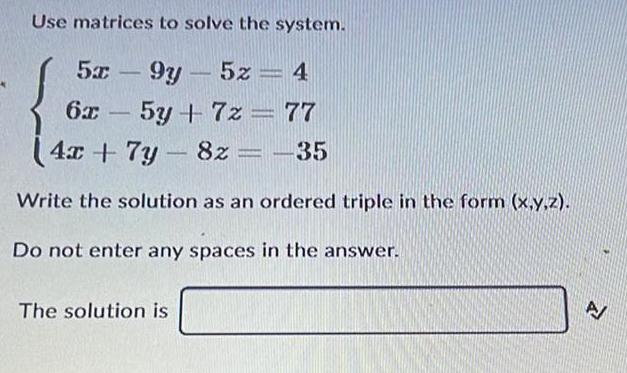
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsUse matrices to solve the system.
5x-9y-5z = 4
6x-5y + 7z = 77
4x + 7y-8z = -35
Write the solution as an ordered triple in the form (x,y,z).
Do not enter any spaces in the answer.
The solution is__
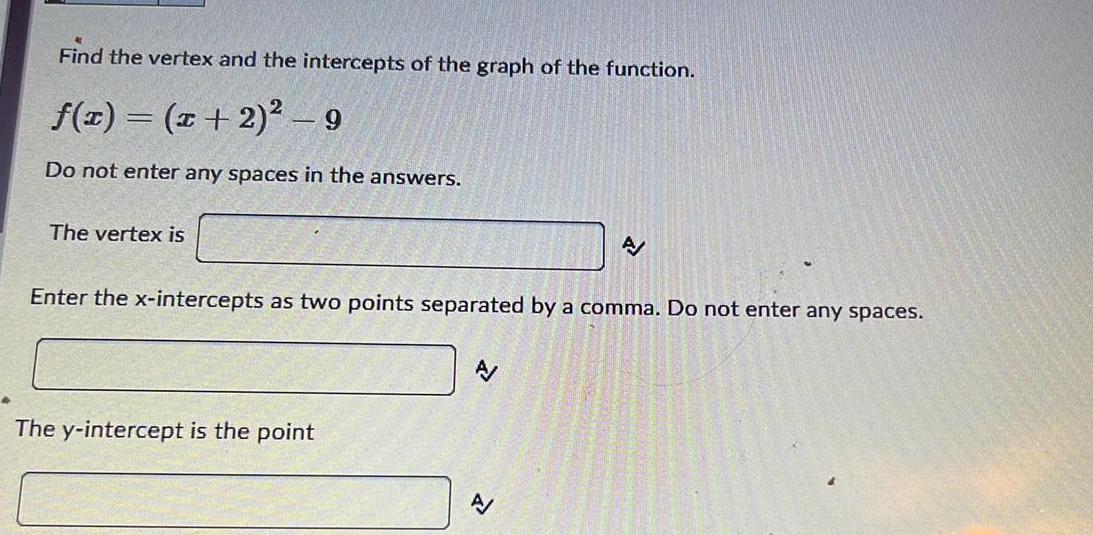
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsFind the vertex and the intercepts of the graph of the function.
f(x) = (x + 2)² - 9
Do not enter any spaces in the answers.
The vertex is
Enter the x-intercepts as two points separated by a comma. Do not enter any spaces.
The y-intercept is the point

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsLet A and B be invertible nxn matrices.
Find a formula A-1 in terms of B if:
(3ATB − I)-¹ = (A-¹B)T
Your formula for A-1 should be simplified
and should not depend on A.

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsInterpret the slope in terms of this application.
The annual cost at the community college increased by 366 dollars per year since 2005.
The annual cost at the community college increased by 3 dollars per year since 2005
The annual cost at the community college increased by 1098 dollars per year since 2005.
The annual cost at the community college decreased by 366 dollars per year since 2005.
The annual cost at the community college increased by 1 dollar per 366 years since 2005.


Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsBill is playing a board game that has a spinner divided into equal sections numbered 1 to 20. The probability of the spinner landing on an even number or a multiple of 5 is?
Select one:
a. 1/5
b. 7/15
c. 12/20
d. 3/5
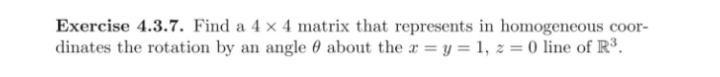
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsFind a 4 x 4 matrix that represents in homogeneous coordinates the rotation by an angle θ about the x = y = 1, z = 0 line of R^3.

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsSolve the equation. Then determine whether the equation is an identity, a conditional equation, or an inconsistent equation.
9x+6=7x+6
What is the solution?
A. The equation has a single solution. The solution set is .
B. The solution set is {x|x is a real number}.
C. The solution set is Ø.
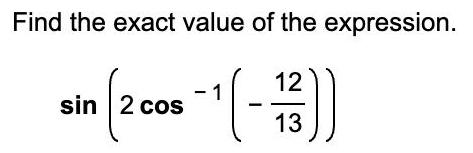
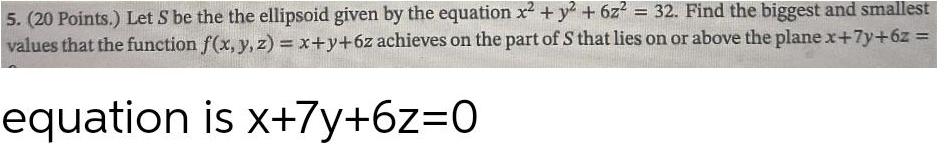
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsLet S be the the ellipsoid given by the equation x² + y² + 6z² = 32. Find the biggest and smallest values that the function f(x, y, z) = x+y+6z achieves on the part of S that lies on or above the plane x+7y+6z =
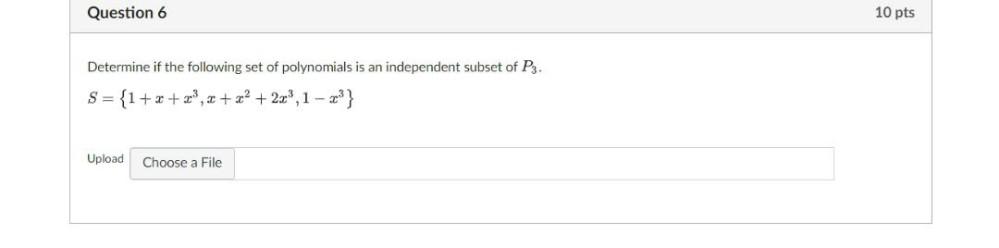
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsDetermine if the following set of polynomials is an independent subset of P₃.
S = {1+x+x³,x+x²+2x³,1-x³}

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsFind both the standard and parametric equations of the plane containing the points (-1,2,3), (0, 1,-1), and (1,0,2).
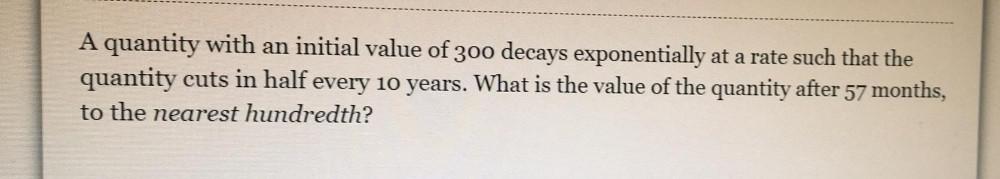
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsA quantity with an initial value of 300 decays exponentially at a rate such that the quantity cuts in half every 10 years. What is the value of the quantity after 57 months, to the nearest hundredth?
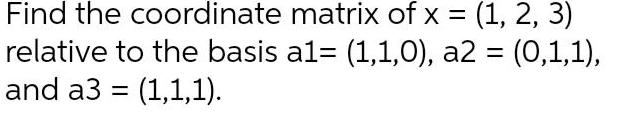
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsFind the coordinate matrix of x = (1, 2, 3) relative to the basis a1= (1,1,0), a2 = (0,1,1), and a3 = (1,1,1).
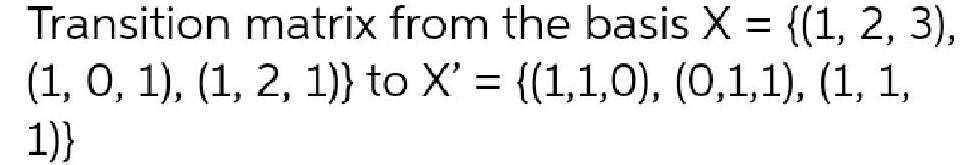
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsTransition matrix from the basis X = {(1, 2, 3), (1, 0, 1), (1, 2, 1)} to X' = {(1,1,0), (0,1,1), (1, 1,1)}
![Define the linear transformation T: Rn⇒Rm by T(v) = Av. Find the dimensions of Rn and Rm.
A [-1 0 -1 0]
dimension of Rn
dimension of Rm](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/84714222-1659004271.4125783.jpeg?w=256)
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsDefine the linear transformation T: Rn⇒Rm by T(v) = Av. Find the dimensions of Rn and Rm.
A [-1 0 -1 0]
dimension of Rn
dimension of Rm

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsDetermine the solution of the simultaneous nonlinear equations
y = -x² + x +0.5
y + 5xy = x²
Use the Newton-Raphson method and employ initial guesses
of x = y = 1.2.

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsConsider the linear subspace U of R4 generated by {(2,-1,3,-2), (-4,2, -6,4)}. The dimension of U is
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3.
d) 4

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsAnswer each of the following as True or False justifying your
answers:
c) The inverse of a non-singular matrix A is unique

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsLet k ε R and consider the linear system in the unknowns x, y, z:
kx + 2y+z=0
y+z=0
3z = 0
Find all values of k for which this system has
(a) a unique solution,
(b) infinitely many solutions,
(c) no solutions.

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsFind the basis and rank of the vector system. Express non basis vectors with basis vectors: a1=(-2;3;4;11), a2=(7;-2;3;4), a3=(1;-3;-5;-13), a4=(3;2;7;16)
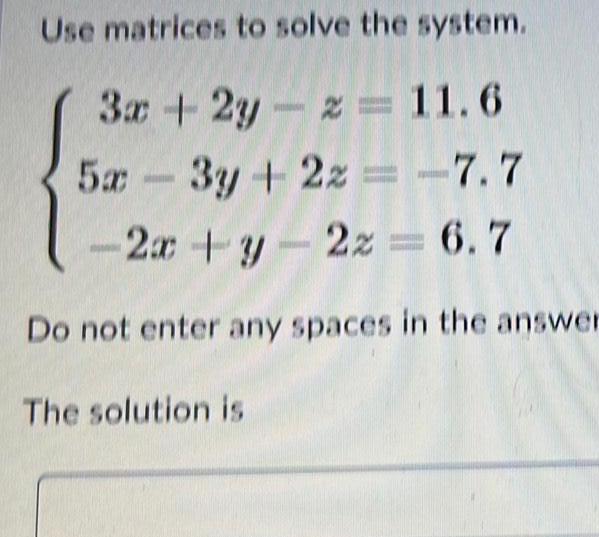
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsUse matrices to solve the system.
3x +2y-z = 11.6
5x -3y + 2z = -7.7
-2x + y - 2z = 6.7

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsUse matrices to solve the system.
2w + 2x +2y+z=-2
3w+ 4x + y2z = -10
4w + 3x - 2y + 2z = 22
w - 2x+3x = 7

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsFind a unit vector that has the same direction as the given vector.
v=-5,6
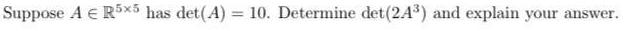
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsSuppose A € R5x5 has det(A) = 10. Determine det (2A³) and explain your answer.

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsGiven the matrix A 1357. What is the inverse of A?
A. -187-3-51
B. 187-3-51
C. -167-3-51
O. 167-3-51

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsSuppose Amanda, Claudia and Delaney go to a donut shop.
Amanda buys 6 apple crumb, 6 brown butter pecan and 2 chocolate frosted donuts and ends up spending $19.56.
Claudia gets 5 of the apple crumb, 4 brown butter pecan and 2 chocolate frosted donuts for a total cost of $15.94.
Lastly, Delaney spends $19.69 on 5 apple crumb, 8 brown butter pecan, and 3 chocolate frosted donuts.
Write this scenario as a system of equations, then solve that system using an augmented matrix
and RREF on your calculator before answering the question below.
How much does a single chocolate frosted donut cost? Round your answer to 2 decimal places.
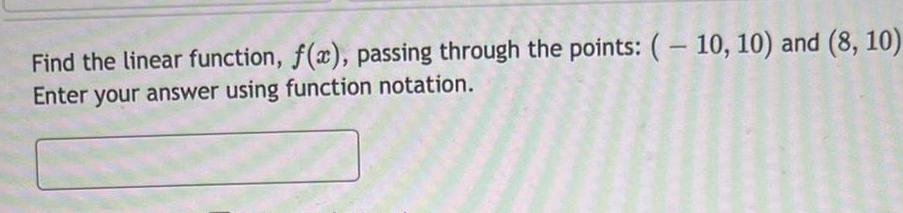
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsFind the linear function, f(x), passing through the points: (-10, 10) and (8, 10)
Enter your answer using function notation.
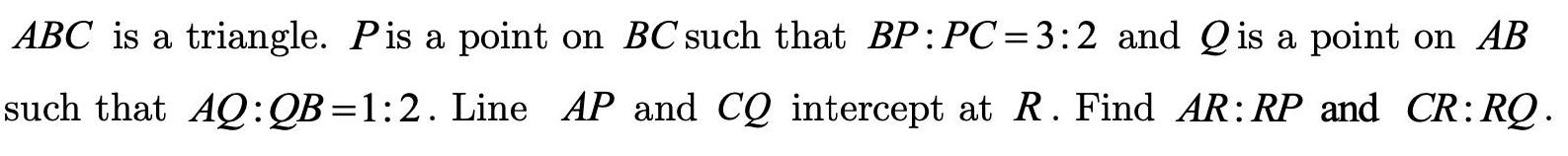
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsABC is a triangle. Pis a point on BC such that BP: PC=3:2 and Qis a point on AB such that AQ: QB=1:2. Line AP and CQ intercept at R. Find AR: RP and CR: RQ.

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsLet A, B be 4 x 4 matrices with |A| = -2 and |B| = 5.
Calculate
|- 2A¯¹ B² AT |.
![Let A = [110] b = [3] Find A^-1 and use it to solve the system Ax = b.](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/84639420-1658664306.6099732.jpeg?w=256)
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsLet A = [110] b = [3] Find A^-1 and use it to solve the system Ax = b.
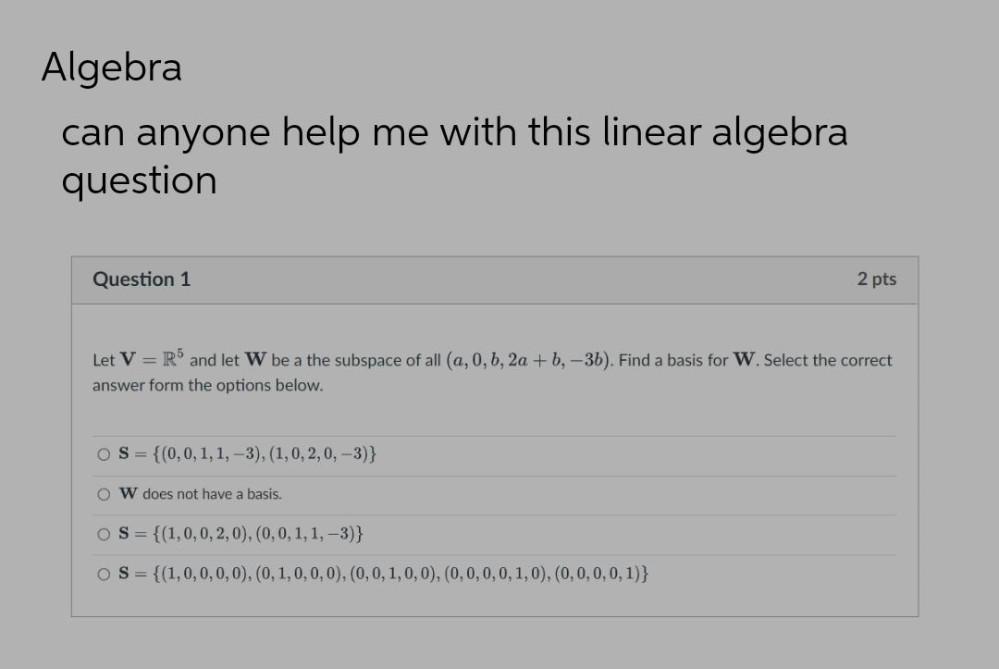
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsLet V = R⁵ and let W be a the subspace of all (a, 0, b, 2a +b, -3b). Find a basis for W. Select the correct answer form the options below.
O S= {(0, 0, 1, 1, -3), (1, 0, 2, 0, -3)}
O W does not have a basis.
O S = {(1,0,0,2, 0), (0, 0, 1, 1, -3)}
O S = {(1,0,0,0,0), (0, 1, 0, 0, 0), (0, 0, 1, 0, 0), (0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0), (0, 0, 0, 0, 1)}
![Consider the following 3 x 3 matrix:
[ζ 1 7
ζ 3 2
4 -1 1]
Find the values of for which the matrix is:
1. positive definite
2. positive semidefinite
3. negative definite
4. negative semidefinite
5. indefinite](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/82704795-1658659746.8788128.jpeg?w=256)
Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsConsider the following 3 x 3 matrix:
[ζ 1 7
ζ 3 2
4 -1 1]
Find the values of for which the matrix is:
1. positive definite
2. positive semidefinite
3. negative definite
4. negative semidefinite
5. indefinite