Geometry Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.

Geometry
Coordinate systemGiven quadrilateral A 2 1 B 1 3 C 6 5 D 7 1 you want to prove that it is a parallelogram by showing opposite sides are parallel What formula would you use Show that AB is parallel to CD Show all work

Geometry
2D GeometryJohnny is wanting to prove that parallelogram ABCD is a rectangle He shows that opposite sides are congruent and opposite sides are parallel Can he conclude ABCD is a rectangle Why or why not Explain your reasoning in complete sentences
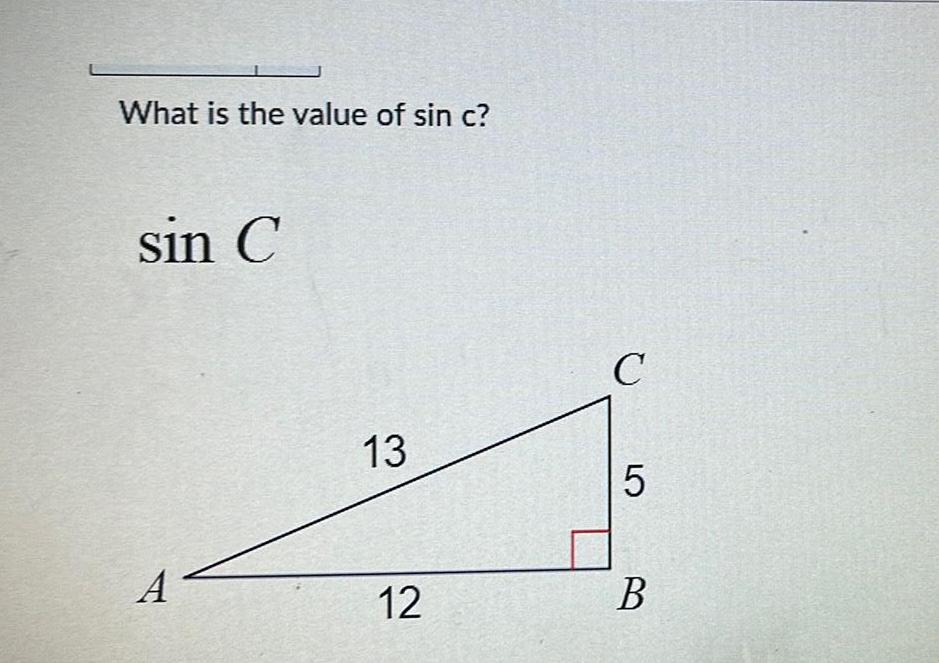
Geometry
Solution of trianglesWhat is the reason for 5 Given Line I is an auxiliary line parallel to m Prove m2 m24 m2 5 180 D 3 4 2 m 1 m2 4 Statements 1 Line I is an auxiliary line parallel to m 4 DBC m2 3 180 5 m 1 B 1 m 2 DBC 2 3 1 5 3 E C Reasons 1 Given 2 Alternate Interior Angle Theorem 3 Alternate Interior Angle Theorem 4 Linear Pair Postulate 5

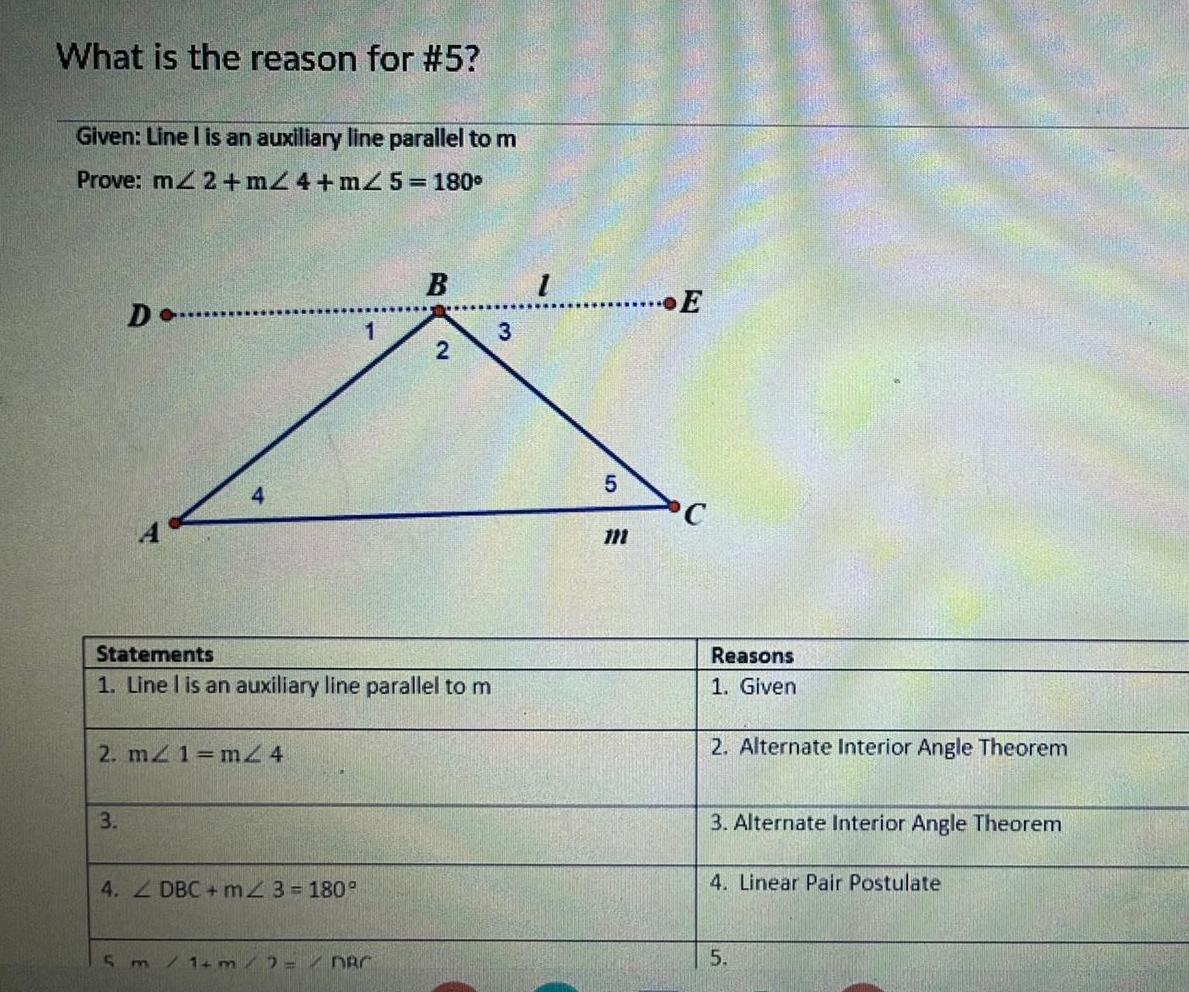
Geometry
2D GeometryParallelogram ABCD is shown below D C B Which pair of triangles can be established to be congruent to prove that ZDAB ZBCD A DAB and A BCD A AED and A BEC A ADC and A BCD A DEC and A BEA
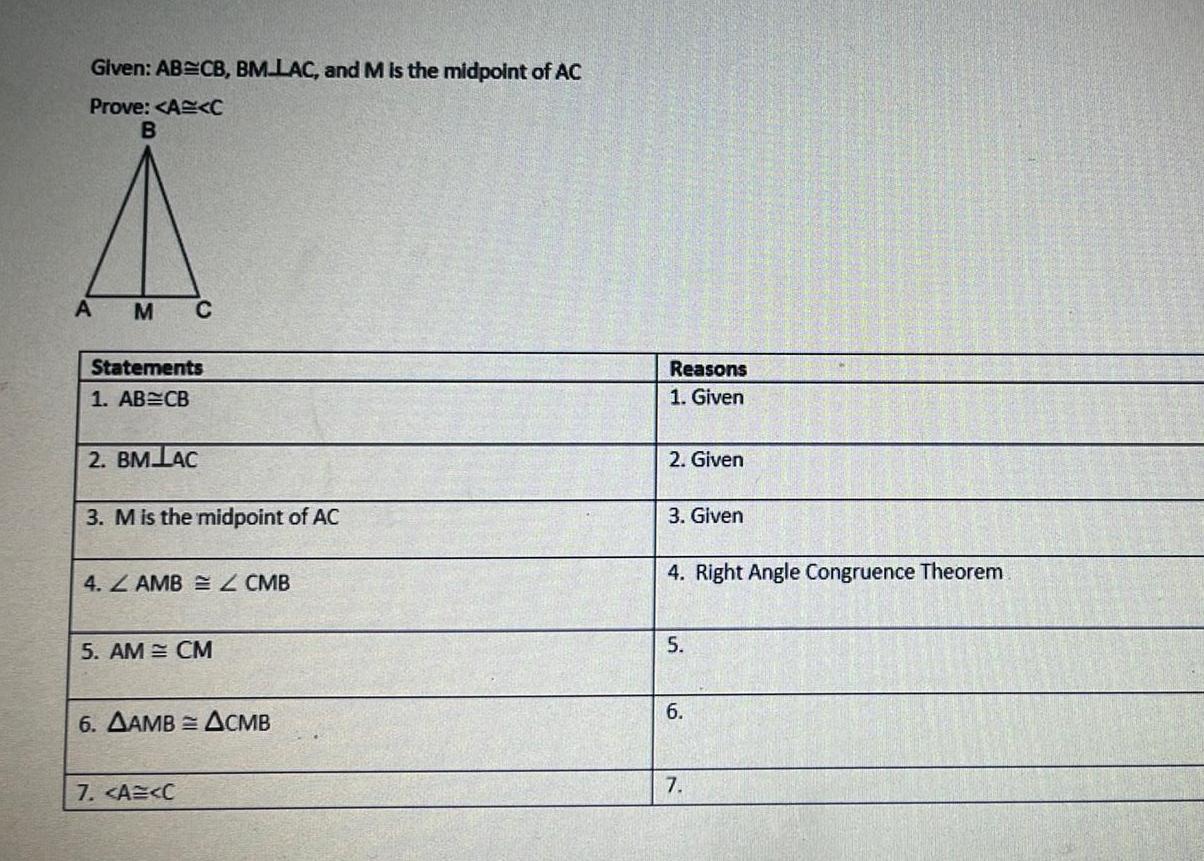
Geometry
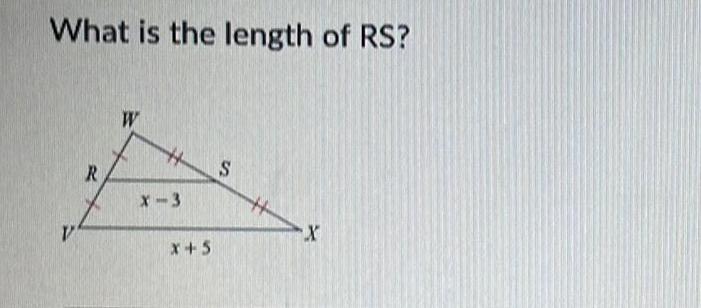
Coordinate systemGiven AB CB BM LAC and M is the midpoint of AC Prove A C B A M C Statements 1 AB CB 2 BM LAC 3 M is the midpoint of AC 4 AMB Z CMB 5 AM CM 6 AAMB ACMB 7 A C Reasons 1 Given 2 Given 3 Given 4 Right Angle Congruence Theorem 5 6 7

Geometry
2D GeometryGiven the quadrilateral is a parallelogram solve for x L K 10x 10 I Ox 20 Ox 4 Ox 7 x 10 N

Geometry
2D GeometryWhat could be shown about the diagonals of parallelogram PQRS to complete the proof that diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other P r t BI R s 0 S 0 0 r s t PR is a perpendicular bisector of SQ Angles formed by the intersection of PR and SQ each measure 90 PR and SQ have the same midpoint RR and So have the same length
Geometry
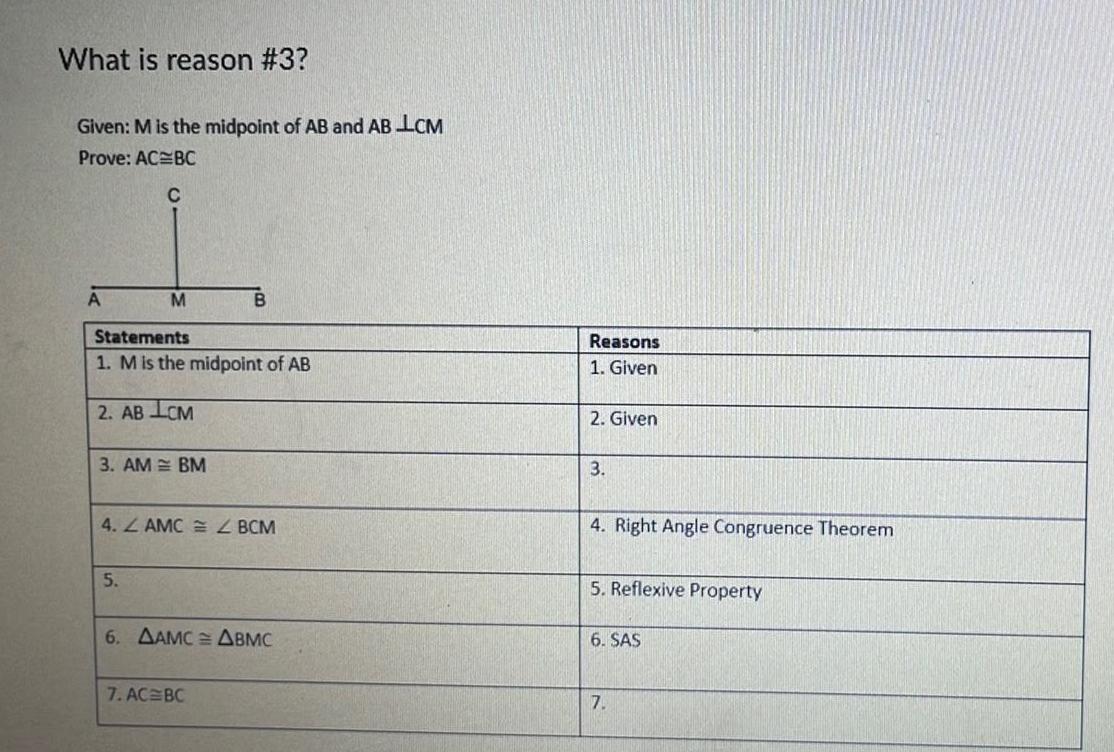
Solution of trianglesWhat is reason 3 Given M is the midpoint of AB and AB LCM Prove AC BC C A M Statements 1 M is the midpoint of AB 2 AB LCM 3 AM BM 5 B 4 ZAMCZ BCM 6 AAMC ABMC 7 AC BC Reasons 1 Given 2 Given 3 4 Right Angle Congruence Theorem 5 Reflexive Property 6 SAS 7

Geometry
Solution of trianglesSarah said that the reason for 2 is Vertical Angles which is incorrect Why can t they be vertical angles What is the correct answer Complete the proof that mZVUW m2PRS 180 1 2 3 S P R Statement QS TV ZVUW ZSRU U m2PRS m2SRU 180 W CYLIN m PRS 180 T Reason Given Angles forming a linear pair sum to 180

Geometry
Solution of trianglesWhat is the reason for 3 Complete the proof that ZTWV ZUTW 1 2 3 4 Y Statement W 1 SU VX ZTWV ZRTS ZRTS ZUTW ZTWV ZUTW T X R Reason Given


Geometry
Coordinate systemWhat is the reason for 4 Proof of the Pythagorean Theorem Given Triangle ABC is a right Triangle and CD is an altitude Prove a b c Statement 1 Triangle ABC is a right Triangle and 1 CD is an altitude 2 m BDC 90 mzADC 90 3 m A m A 4 m B m B 5 m ACB m CDB m ADC 6 AACB ACDB AADC 7 b 1 a b c 10 C e Reason a 2 3 4 5 6 7 B
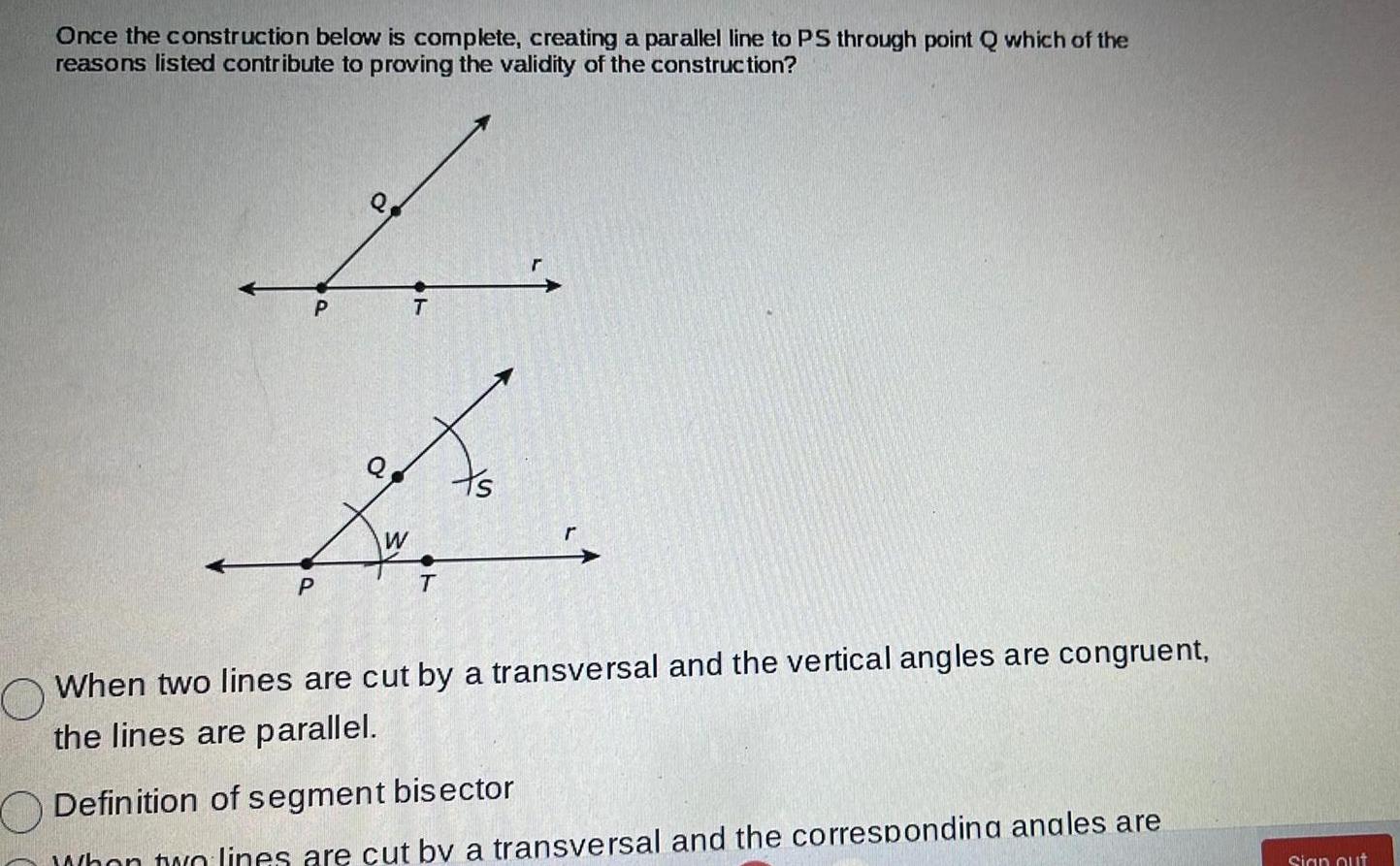
Geometry
2D GeometryOnce the construction below is complete creating a parallel line to PS through point Q which of the reasons listed contribute to proving the validity of the construction P P Q W T To T O When two lines are cut by a transversal and the vertical angles are congruent the lines are parallel Definition of segment bisector When two lines are cut by a transversal and the correspondina anales are Sign out
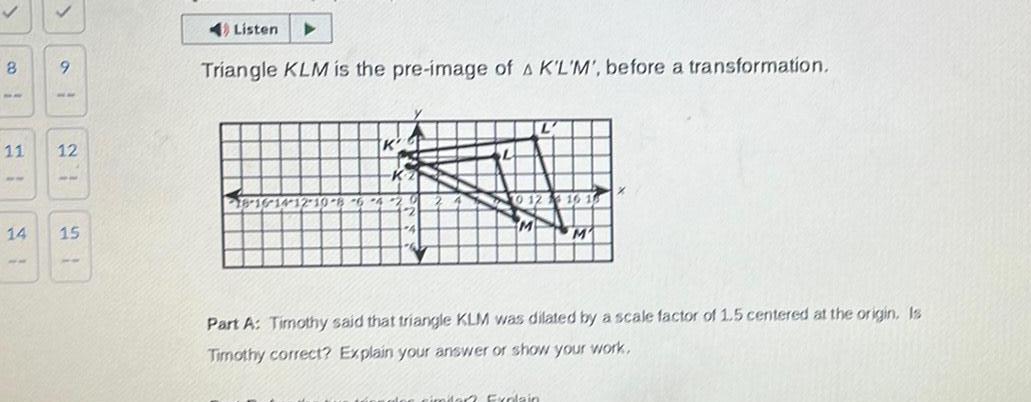
Geometry
Solution of triangles8 8 11 14 9 12 15 4 Listen Triangle KLM is the pre image of A K L M before a transformation 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 K Part A Timothy said that triangle KLM was dilated by a scale factor of 1 5 centered at the origin Is Timothy correct Explain your answer or show your work nimdar Explain

Geometry
2D GeometryGiven A ABC with points A 1 2 B 4 3 and C 0 0 dilated about a center at the origin by a scale factor of 3 an c
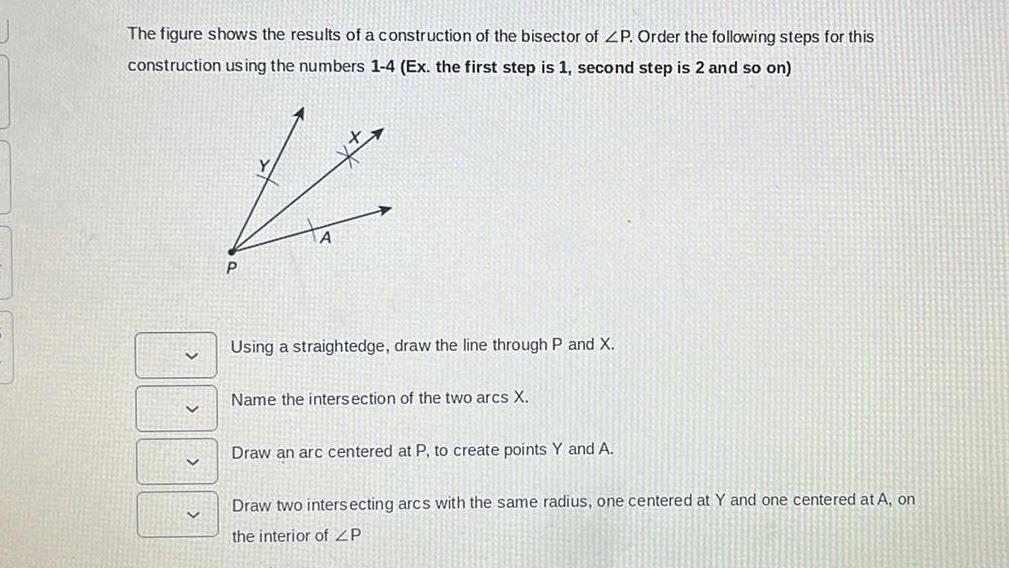
Geometry
2D GeometryThe figure shows the results of a construction of the bisector of ZP Order the following steps for this construction using the numbers 1 4 Ex the first step is 1 second step is 2 and so on V Using a straightedge draw the line through P and X Name the intersection of the two arcs X Draw an arc centered at P to create points Y and A Draw two intersecting arcs with the same radius one centered at Y and one centered at A on the interior of ZP

Geometry
Solution of trianglesSolve for DG Show all work using the equation editor 24 F 3044 32 E 40 D G
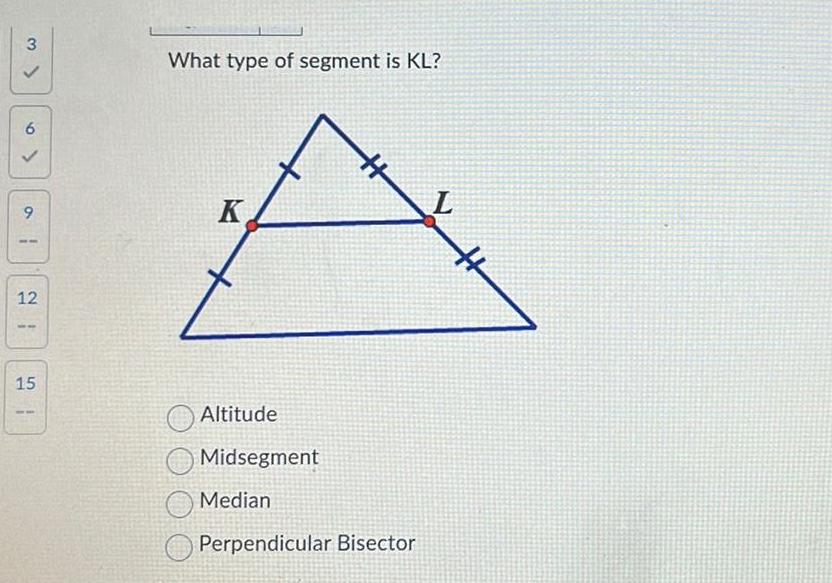
Geometry
Solution of triangles3 a 6 9 1 12 15 1 What type of segment is KL K Altitude Midsegment Median Perpendicular Bisector L
Geometry
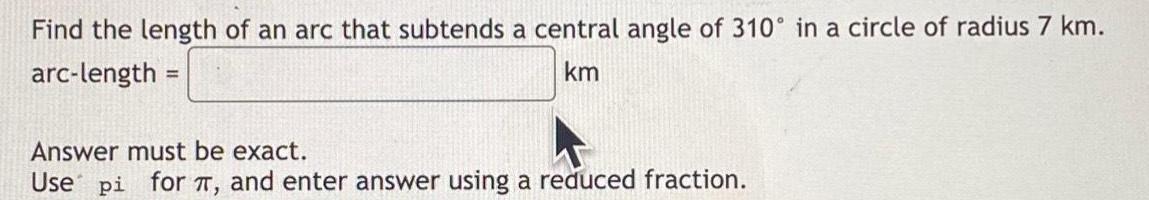
2D GeometryFind the length of an arc that subtends a central angle of 310 in a circle of radius 7 km arc length km Answer must be exact Use pi for and enter answer using a reduced fraction

Geometry
2D GeometryOne way to show that two triangles are similar is to show that two angles of one are congruent to two angles of the other an angle of one is congruent to an angle of the other a side of one is congruent to a side of the other two sides of one are proportional to two sides of the other

Geometry
Heights & DistancesA tree with a height of 22 ft casts a shadow 5 ft long on the ground How high is another tree that casts a shadow which is 2 ft long 11 4 ft 8 8 ft 2 5 ft 6 3 ft

Geometry
2D GeometryWrite a similarity statement for the following triangles Be sure to match up the correct corresponding proportional sides M 6 N O
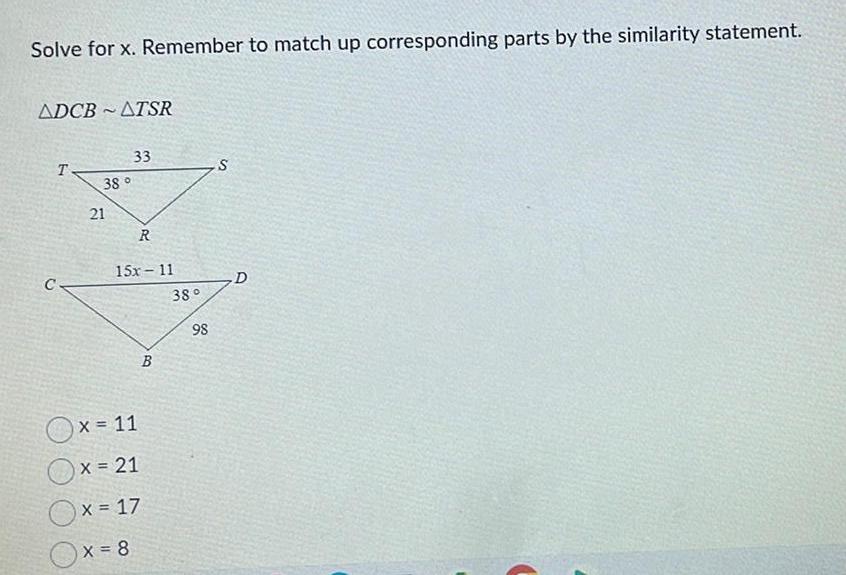
Geometry
2D GeometrySolve for x Remember to match up corresponding parts by the similarity statement ADCBATSR C T 38 21 33 R 15x 11 Ox 11 x 21 x 17 x 8 B 38 98 S D
Geometry
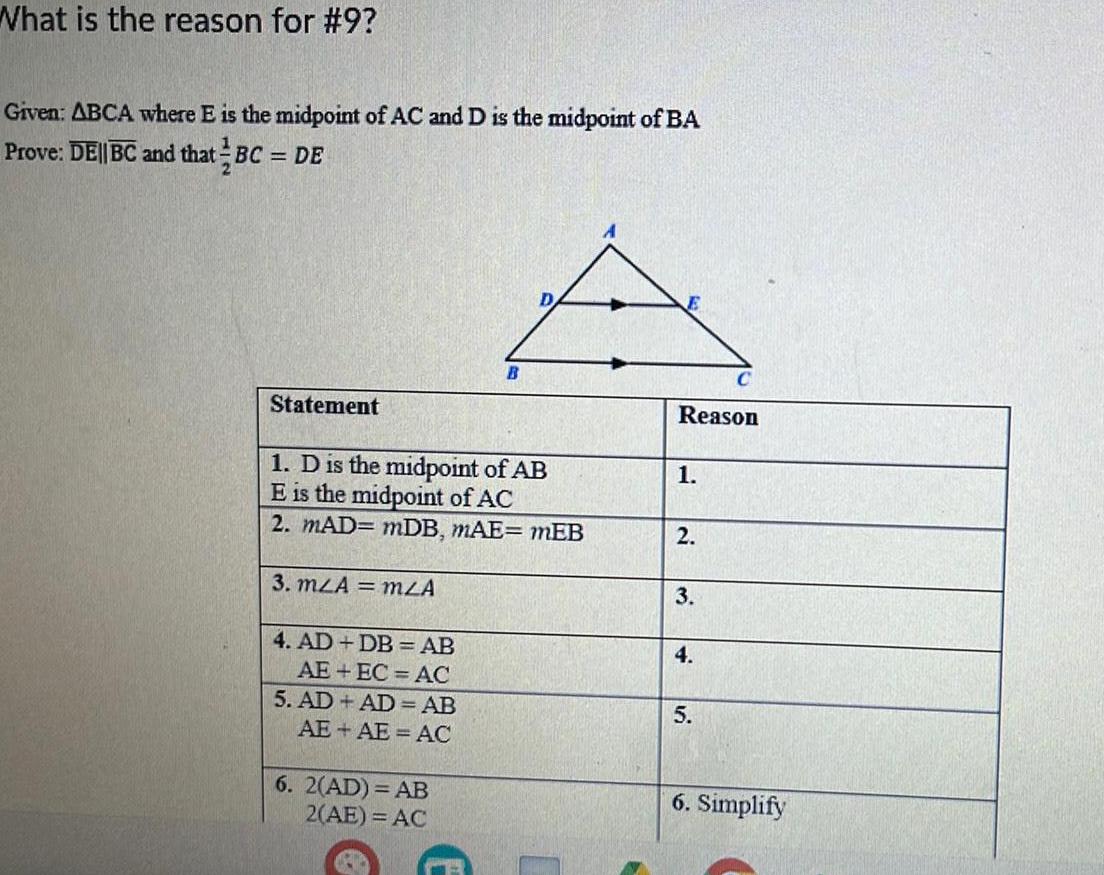
Coordinate systemWhat is the reason for 9 Given ABCA where E is the midpoint of AC and D is the midpoint of BA Prove DE BC and that BC DE Statement 1 D is the midpoint of AB E is the midpoint of AC 2 MAD mDB MAE mEB 3 mzA mZA 4 AD DB AB AE EC AC 5 AD AD AB AE AE AC B 6 2 AD AB 2 AE AC Reason 1 2 3 4 C 5 6 Simplify

Geometry
2D GeometryWhat is the reason for 4 Given DE BC Prove AD AB DB EC Statement 1 DE BC 2 mzA mZA 3 m AED m ACB 4 AACB AAED AD 5 AB AE EC 6 AD DB AB AF FC AG B Reason 1 2 3 4 5 6
Geometry
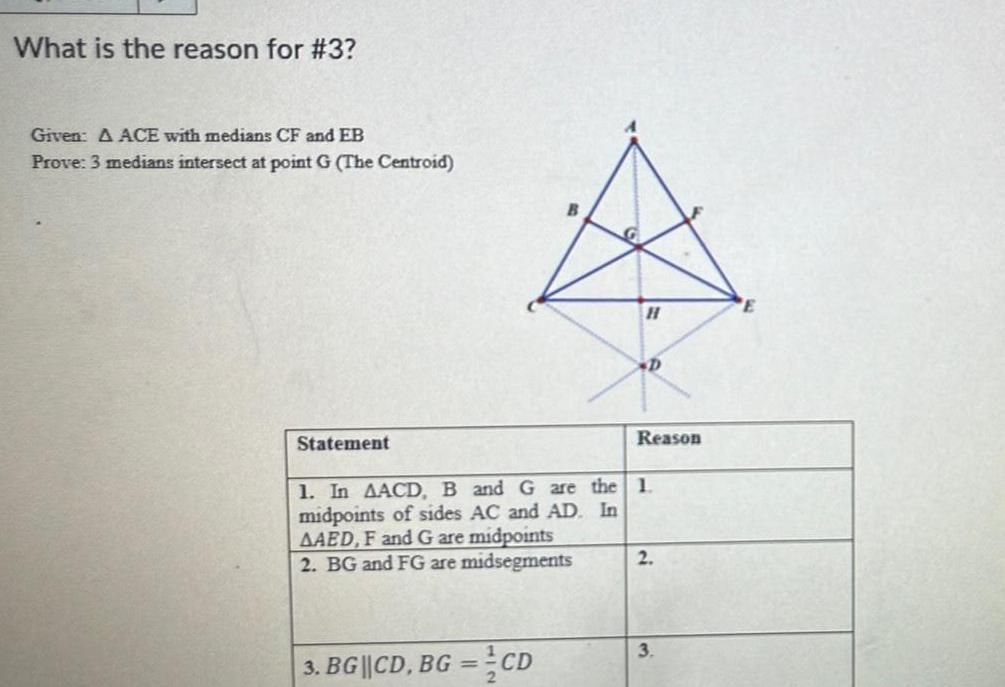
Solution of trianglesWhat is the reason for 3 Given A ACE with medians CF and EB Prove 3 medians intersect at point G The Centroid Statement H 3 BG CD BG CD D Reason 1 In AACD B and G are the 1 midpoints of sides AC and AD In AAED F and G are midpoints 2 BG and FG are midsegments 2 3
Geometry
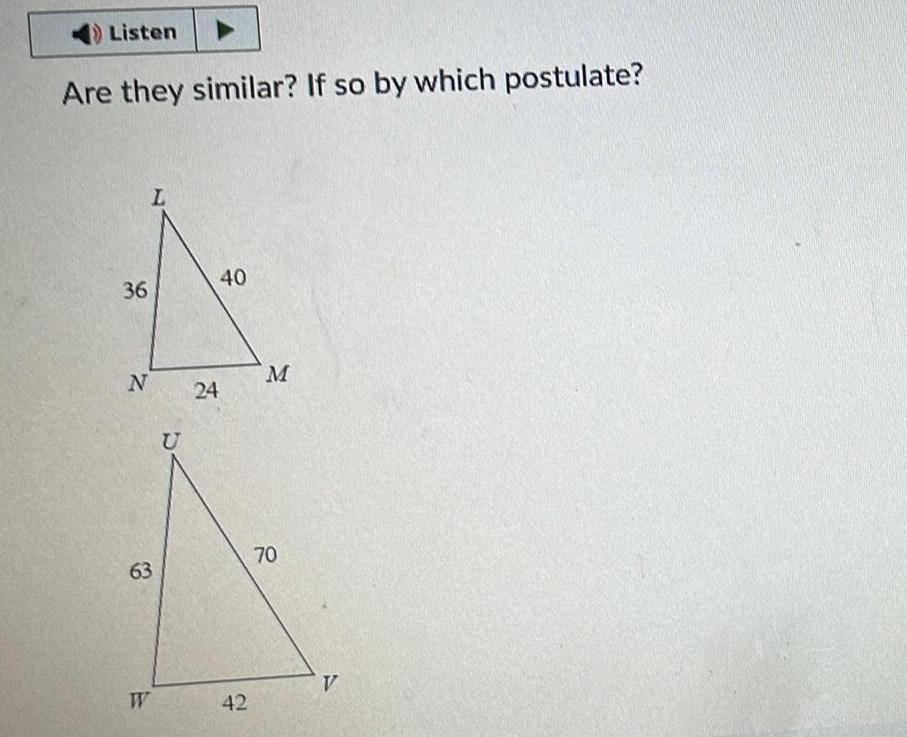
Solution of trianglesListen Are they similar If so by which postulate 36 N L 63 W U 24 40 42 M 70 A

Geometry
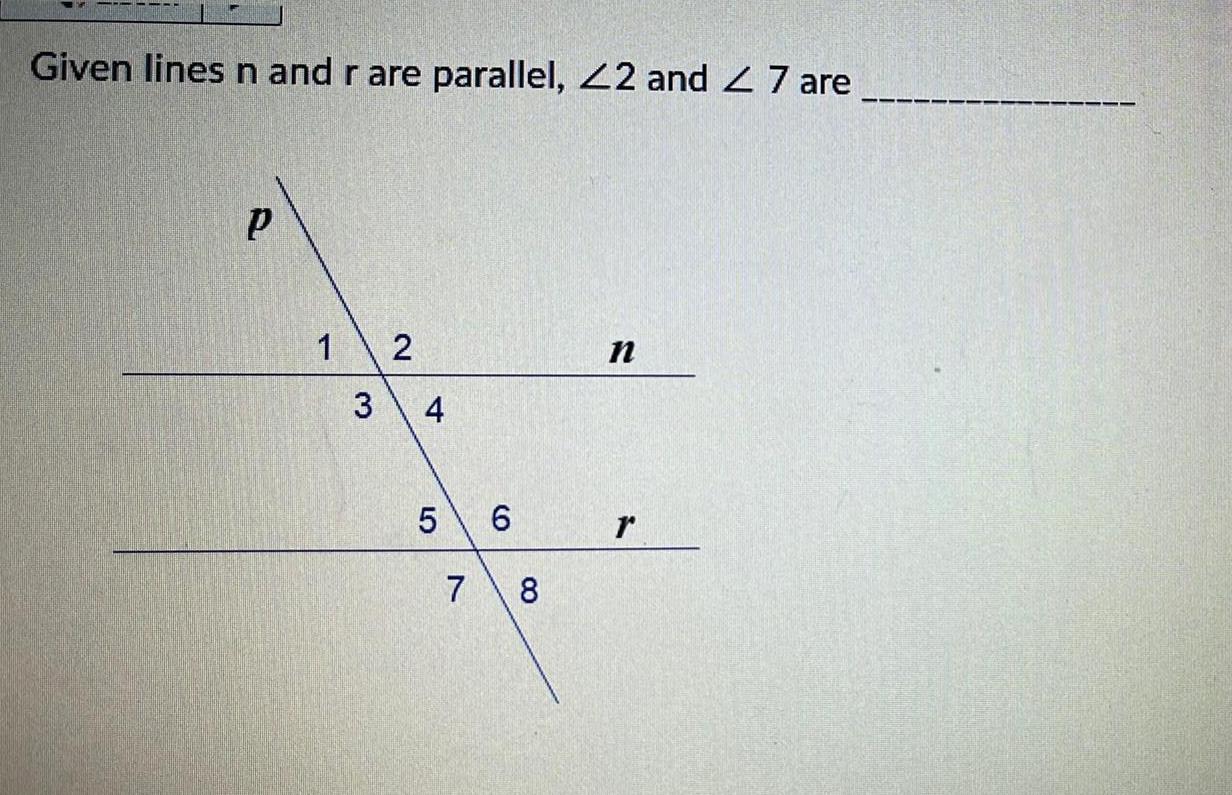
2D GeometryListen What is the reason for 4 Prove Corresponding Angles 7 5 3 8 1 6 2 m n Given 23 and 27 are corresponding angles Prove 43 27 Statements 1 23 and 27 are corresponding angles 2 3 26 27 4 3 27 Reasons 1 2 3 Vertical Angles Congruency Theorem 4
Geometry
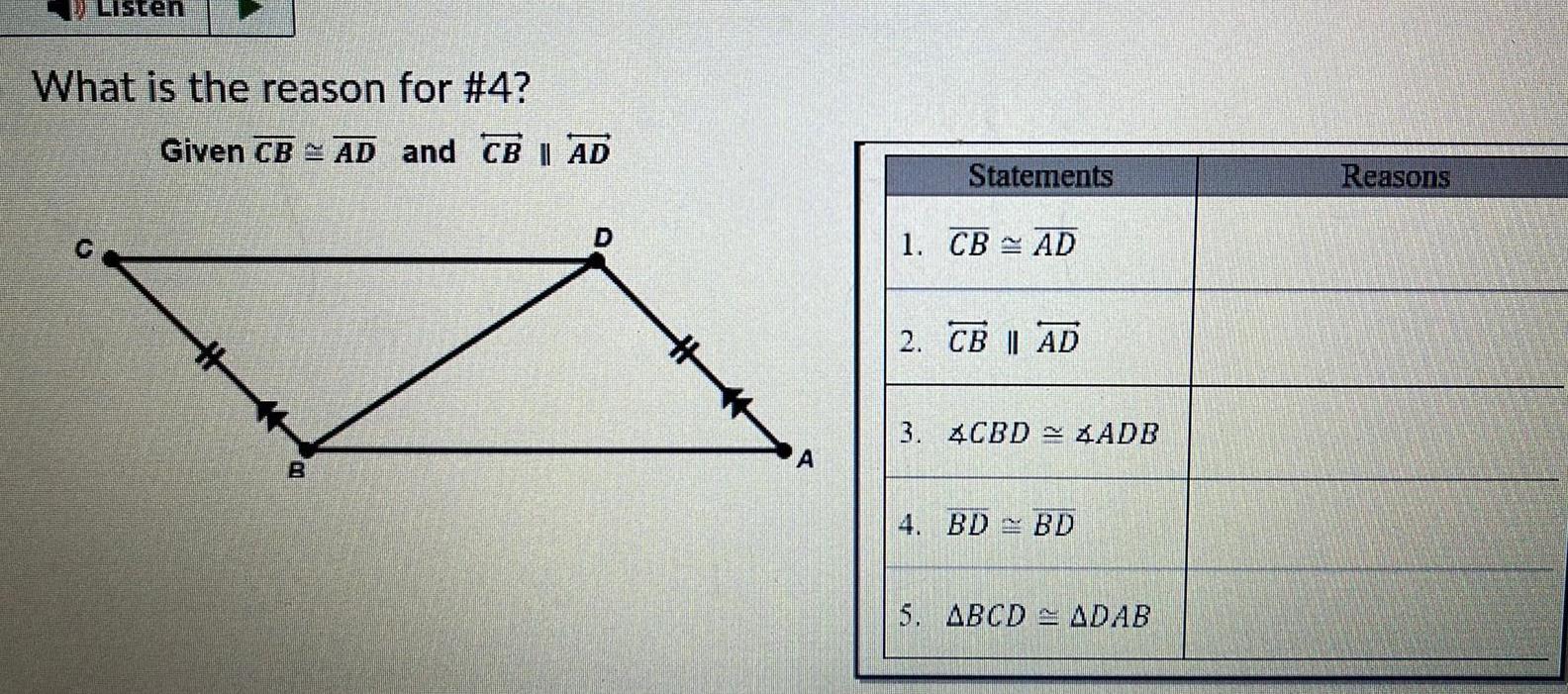
Coordinate systemListen What is the reason for 4 Given CB AD and CBI AD H B A Statements 1 CB AD 2 CB AD 3 4CBD ADB 4 BD BD 5 ABCD ADAB Reasons

Geometry
2D GeometryIf statement 3 is ZPORZEOV what would be the reason Given VO RO and PR VE R E 1 2 3 4 Statements 5 APRO AEVO Given Given Reasons
Geometry
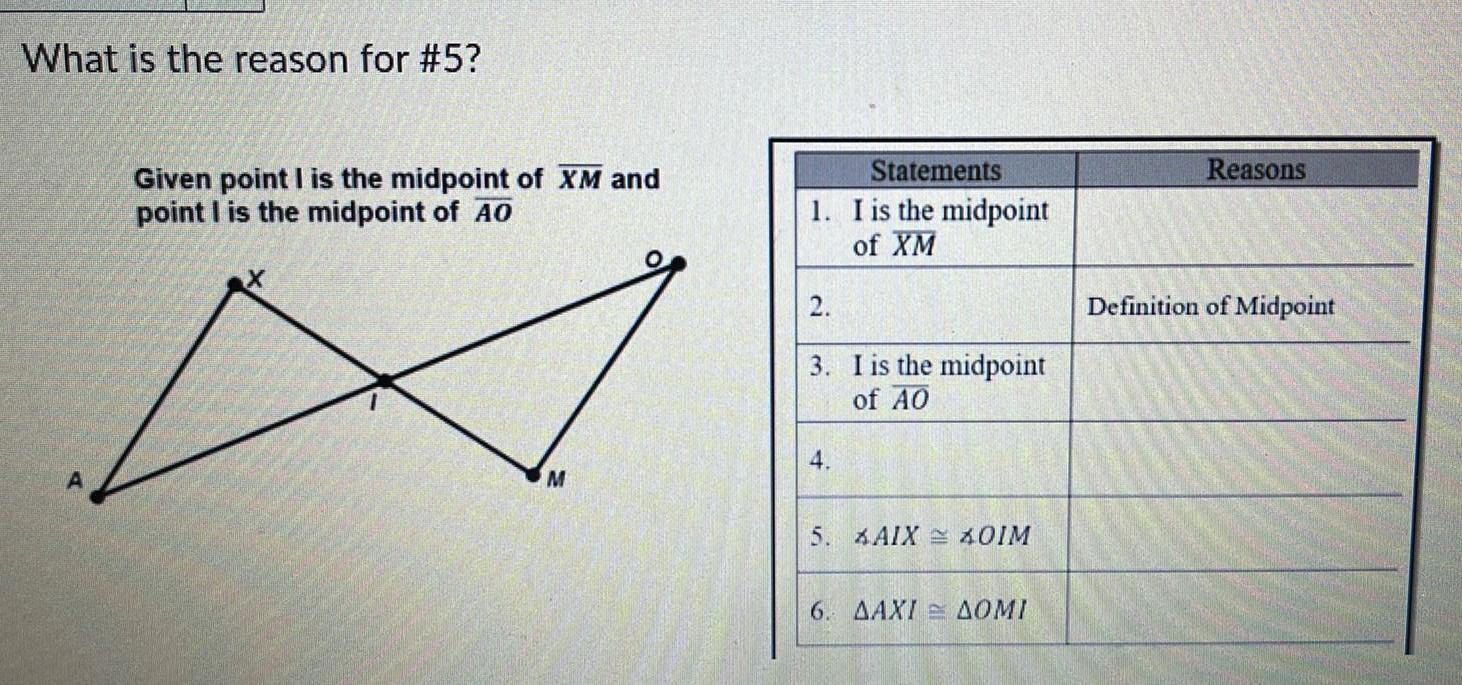
Coordinate systemWhat is the reason for 5 A Given point I is the midpoint of XM and point I is the midpoint of AO M Statements 1 I is the midpoint of XM 2 3 I is the midpoint of AO 4 5 AIXOIM 6 AAXIAOMI Reasons Definition of Midpoint

Geometry
Coordinate systemChoose all quadrilaterals in which the property applies Both pairs of opposite sides are parallel Square Rhombus 000 Parallelogram Kite Rectangle Trapezoid

Geometry
2D GeometryChoose all quadrilaterals in which the property applies All angles are congruent Parallelogram Rectangle Rhombus Square Trapezoid Kite

Geometry
Coordinate systemChoose all quadrilaterals in which the property applies Diagonals are Perpendicular Rectangle Parallelogram Trapezoid Square Rhombus Kite

Geometry
AreaGiven the proof below and that Statement 4 is 1 23 23 22 by the reason substitution What is reason 5 Prove Vertical Angles 3 2 Given 21 and 22 are vertical angles Prove 41 42 Statements 1 41 and 42 are 2 3 4 vertical angles 5 41 22 Reasons 2 Definition of Linear Pair 3 4 5
Geometry
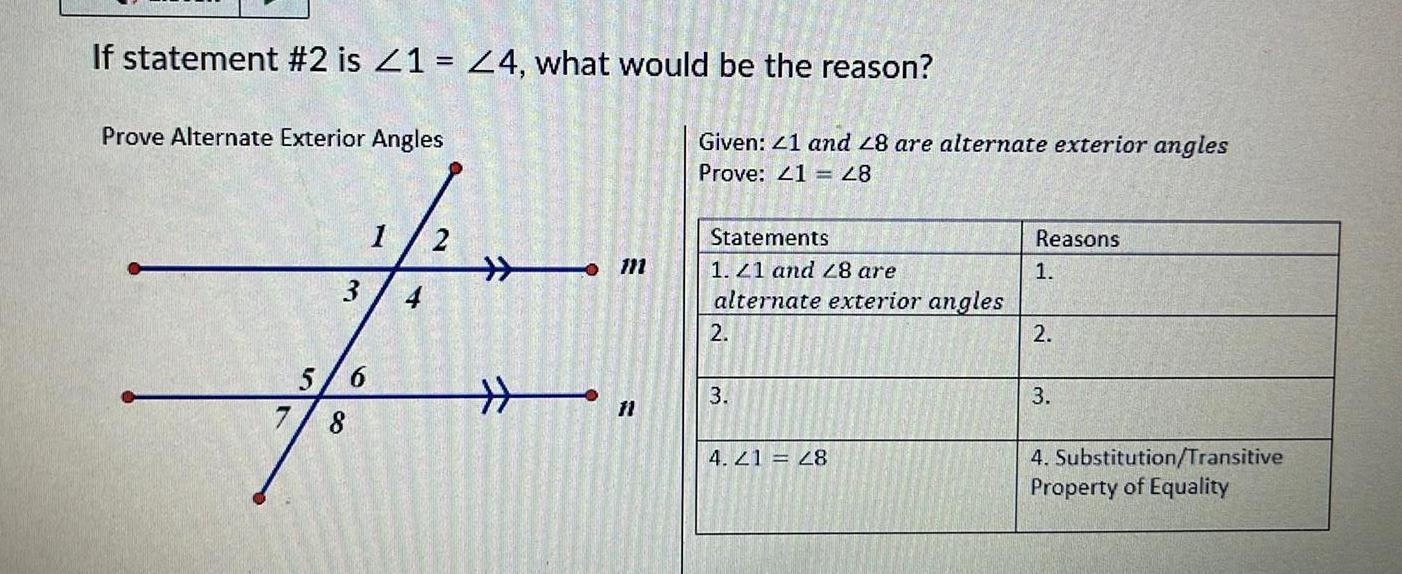
2D GeometryIf statement 2 is 21 24 what would be the reason Prove Alternate Exterior Angles 3 5 6 7 8 1 2 4 m t Given 41 and 48 are alternate exterior angles Prove 41 28 Statements 1 41 and 28 are alternate exterior angles 2 3 4 21 28 Reasons 1 2 3 4 Substitution Transitive Property of Equality

Geometry
3D GeometryLet f be a differentiable function such that f 8 2 and f 8 5 If g is the function defined by g x f x 3 x what is the value of g 8 59 24 NOT 2 61 24 60

Geometry
AreaWhat is the most specific name for the figure 14 10 9 110 110 70 70 74 Parallelogram Isosceles Trapezoid Trapezoid Rhombus
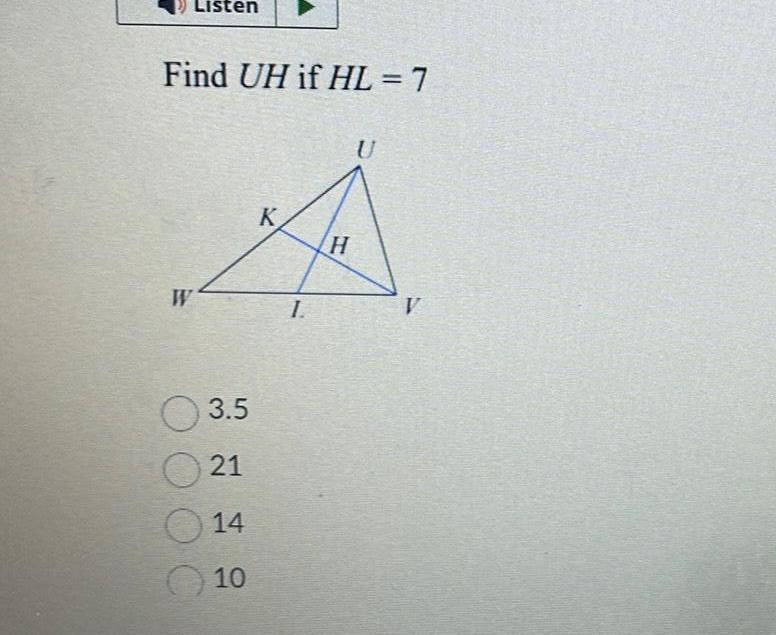
Geometry
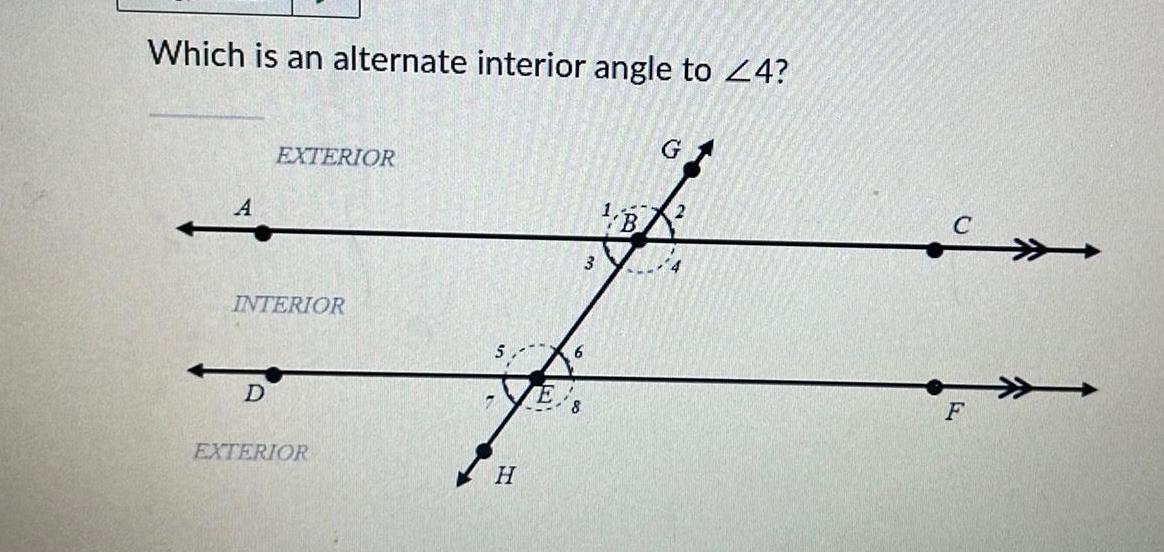
AreaWhich is an alternate interior angle to 24 A EXTERIOR INTERIOR D EXTERIOR H E 6 3 1 B G 2 4 F
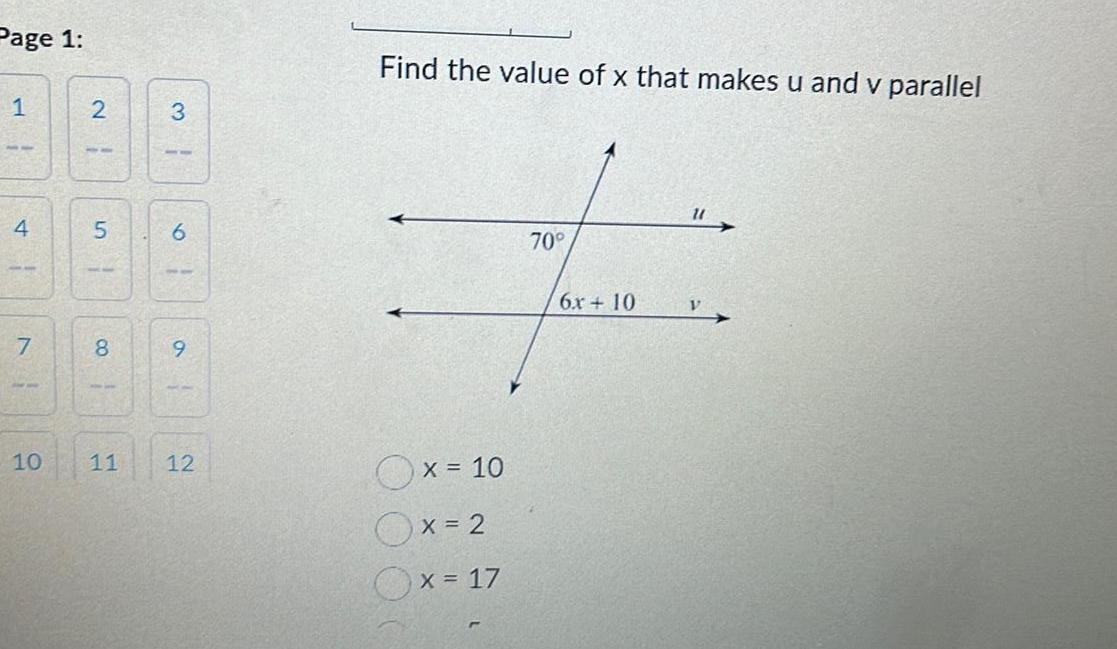
Geometry
Coordinate systemPage 1 1 1 4 7 1 10 2 1 5 00 8 1 3 1 6 9 11 12 Find the value of x that makes u and v parallel Ox 10 Ox 2 x 17 70 6x 10 11 V
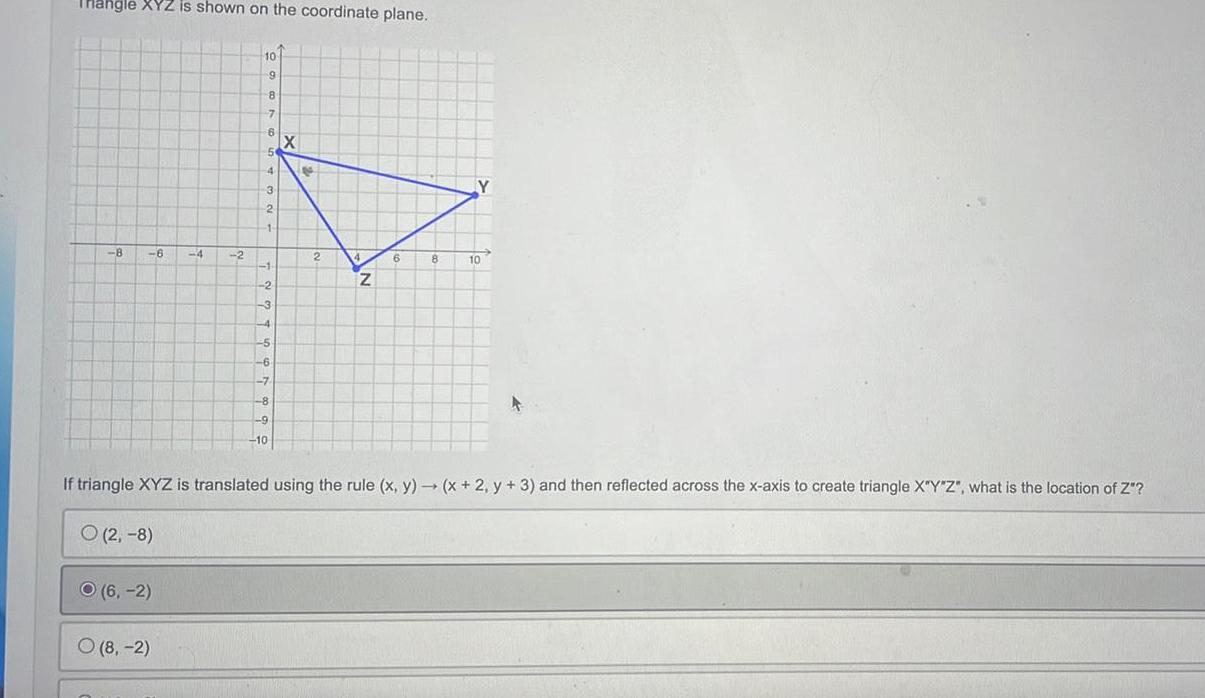
Geometry
Solution of trianglesThangle XYZ is shown on the coordinate plane 8 6 O 6 2 4 O 8 2 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 X po 2 4 Z 6 8 Y If triangle XYZ is translated using the rule x y x 2 y 3 and then reflected across the x axis to create triangle X Y Z what is the location of Z O 2 8 10
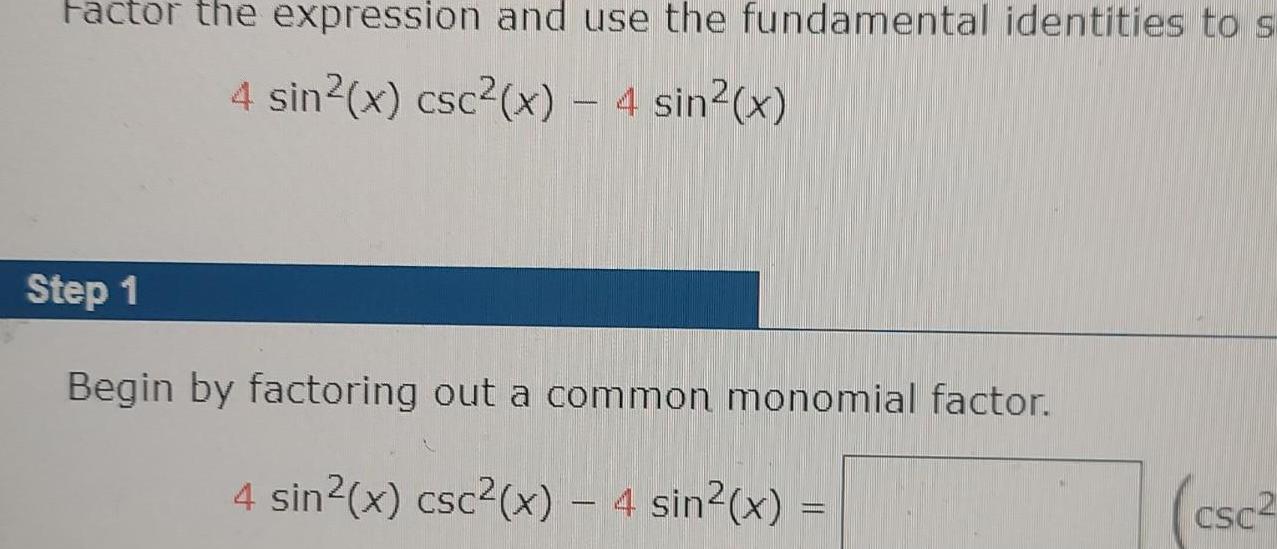
Geometry
Coordinate systemFactor the expression and use the fundamental identities to s 4 sin x csc x 4 sin x Step 1 Begin by factoring out a common monomial factor 4 sin x csc x 4 sin x CSC2
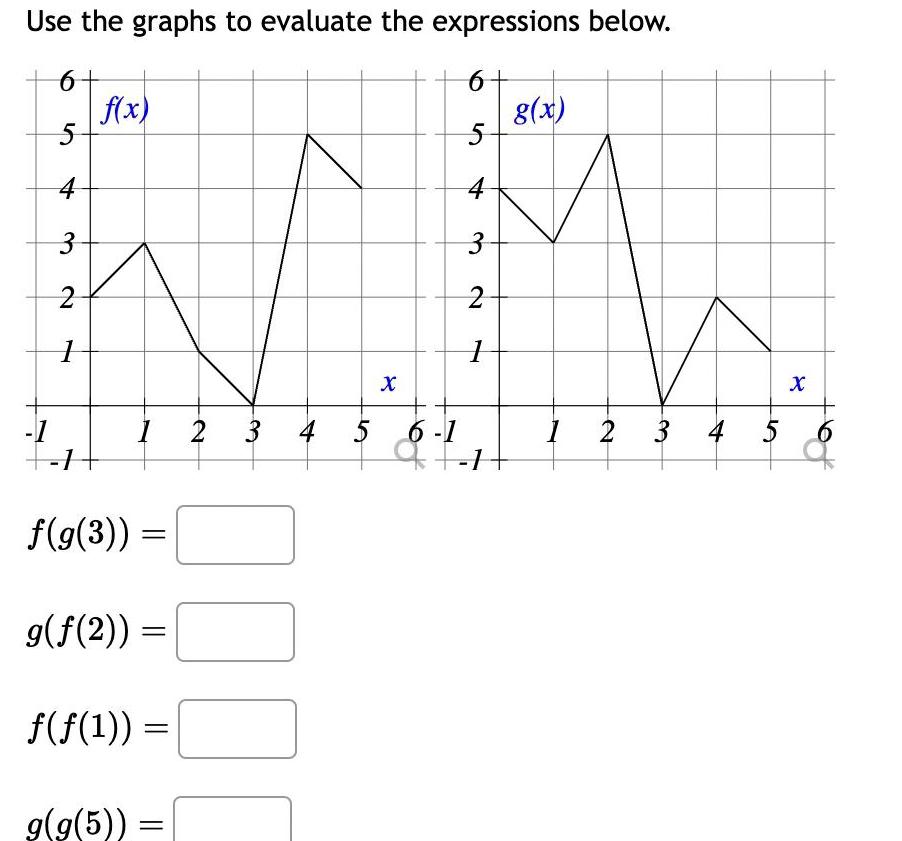
Geometry
2D GeometryUse the graphs to evaluate the expressions below 6 5 4 3 2 1 1 1 f x 1 f g 3 g f 2 f f 1 g g 5 2 3 4 00 X 6 5 4 3 2 1 5 6 1 9 F 1 g x 1 2 3 4 5 X 6