Geometry Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.
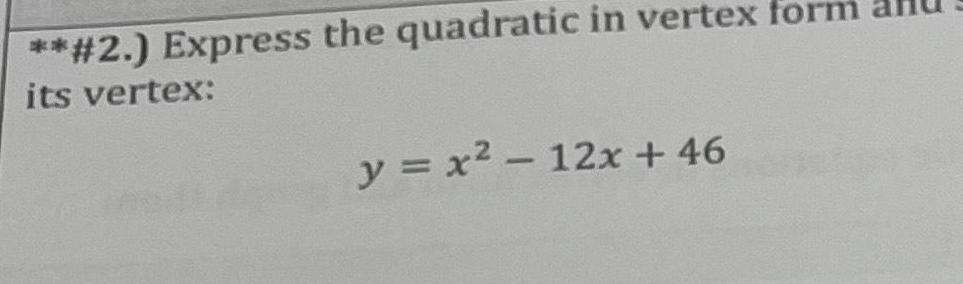


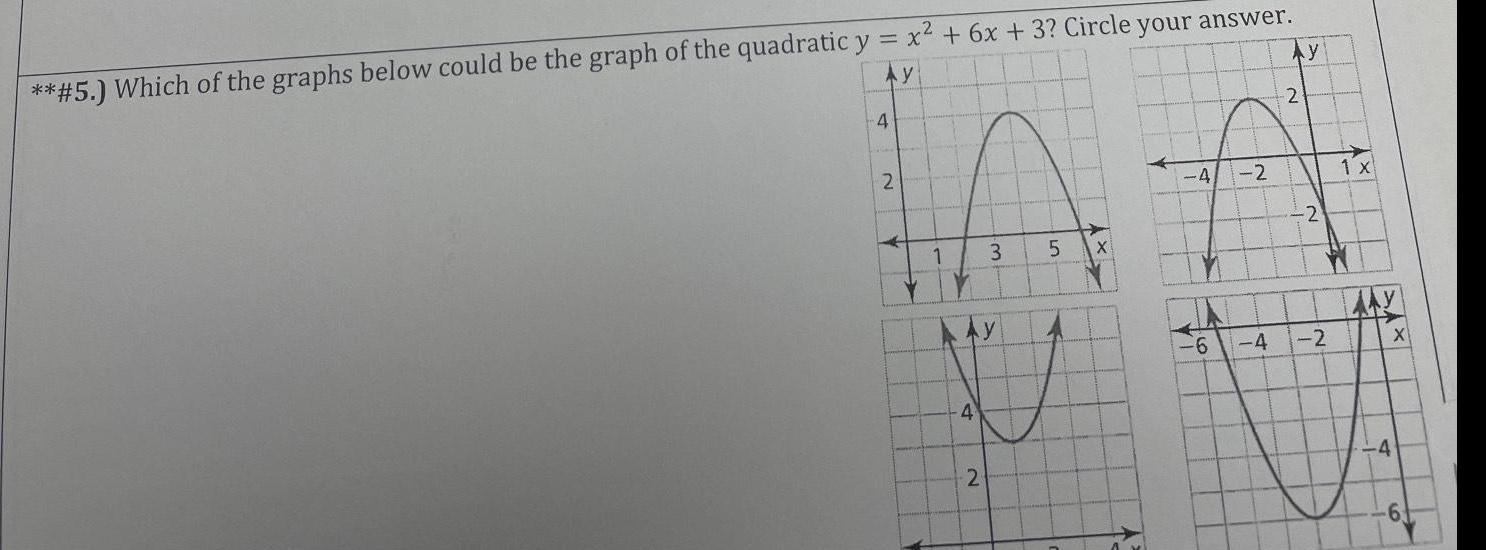
Geometry
2D Geometry5 Which of the graphs below could be the graph of the quadratic y x 6x 3 Circle your answer Ay 4 2 Ay 4 3 2 5 XY 4 IA 6 3 2 Ay 4 2 2 2 1 x X YA Ex 4 6

Geometry
3D GeometryFind the volume of each of the following Round your tenth if necessary 3 a square prism with base length 7 m and height 15 m 4 a cylinder with radius 9 in and height 10 in 5 a triangular prism with height 14 ft and a right triangle base with legs measuring 9 ft and 12 ft 6 a cylinder with diameter 24 cm and height 5 cm
Geometry
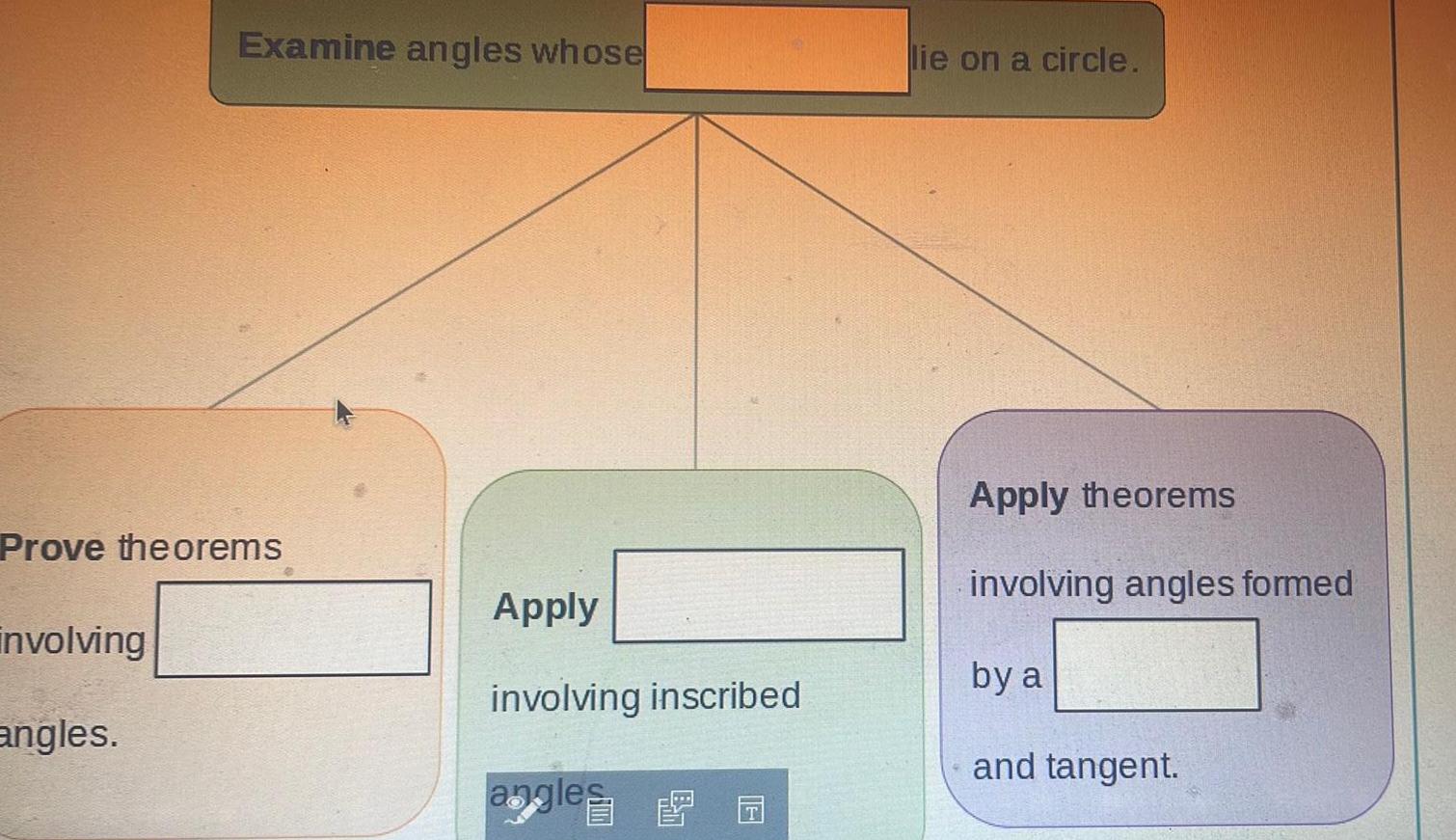
2D GeometryExamine angles whose Prove theorems involving angles Apply involving inscribed angles G lie on a circle Apply theorems involving angles formed by a and tangent
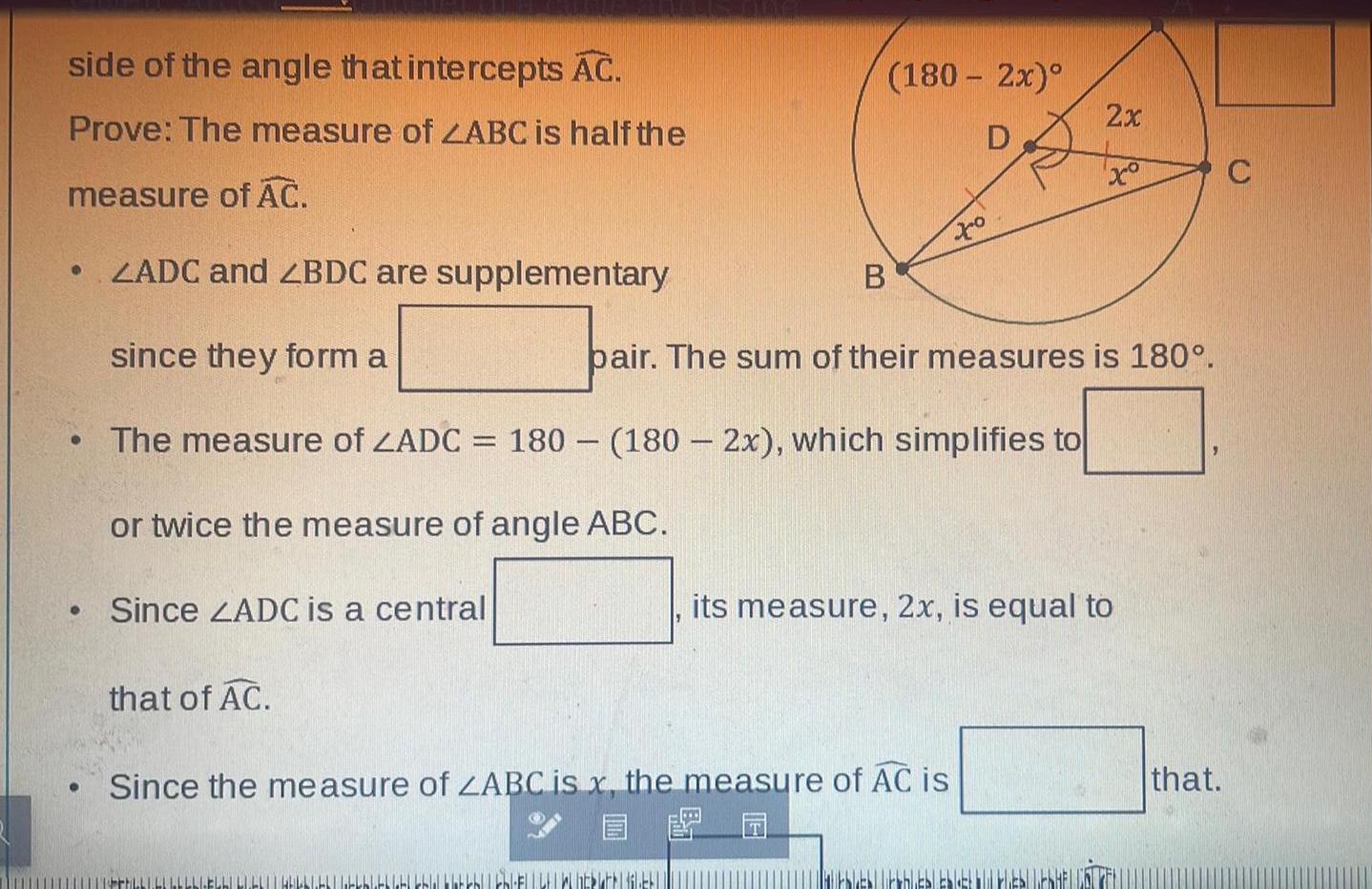
Geometry
2D Geometryside of the angle that intercepts AC Prove The measure of ZABC is half the measure of AC ZADC and ZBDC are supplementary since they form a The measure of ZADC 180 180 2x which simplifies to or twice the measure of angle ABC Since ZADC is a central that of AC FLL LLL LLLL 180 2x D B thlebblebi bla bla kbEWERBLETT Since the measure of ZABC is x the measure of AC is 2x pair The sum of their measures is 180 xo its measure 2x is equal to that C

Geometry
Solution of trianglesReview Key Concepts The measure of an inscribed angle is half the measure of its intercepted arc Two inscribed angles that interceptthe are congruent An angle inscribed in a semicircle is a angle The opposite sides of a quadrilateral inscribed in acirde are supplementary If a tangent and chord intersect on a cirde the measure of each angle they form is the measure of its intercepted arc
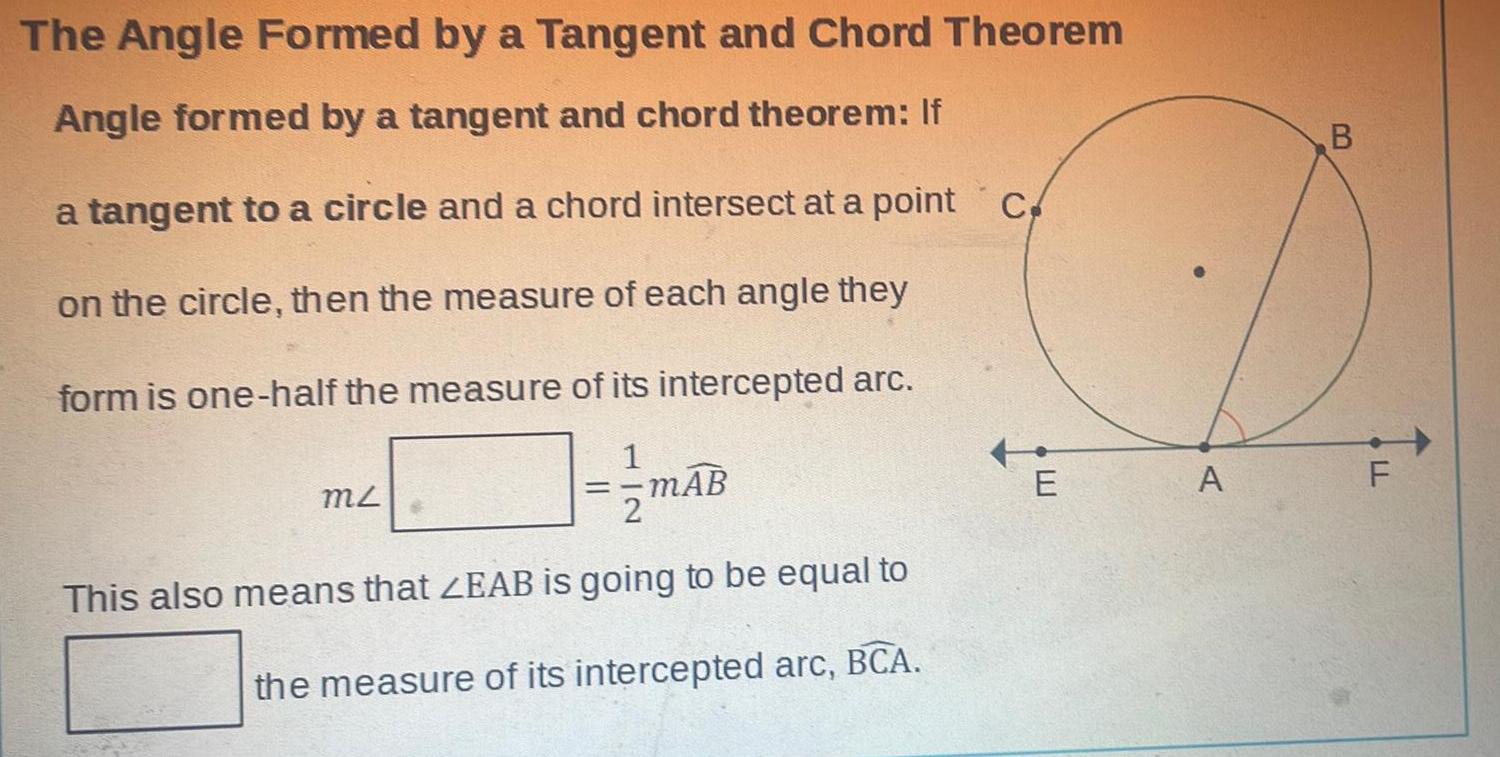
Geometry
2D GeometryThe Angle Formed by a Tangent and Chord Theorem Angle formed by a tangent and chord theorem If a tangent to a circle and a chord intersect at a point c on the circle then the measure of each angle they form is one half the measure of its intercepted arc MZ mAB This also means that ZEAB is going to be equal to the measure of its intercepted arc BCA E A B LL F
Geometry
2D GeometryThe trinket store is open for 14 hours per day They sell an average of 5 trinkets per hour The back storeroom currently has 560 trinkets in it 1 Write an equation that estimates the number of trinkets T that will be in the storeroom after H hours 2 How many days will it take to run out of trinkets

Geometry
2D GeometryFind the volume of each object 1 the rectangular prism part of the milk container 2 the cylinder part of the measuring cup 6 3 cm 7 cm 10 cm 7 cm 7 cm
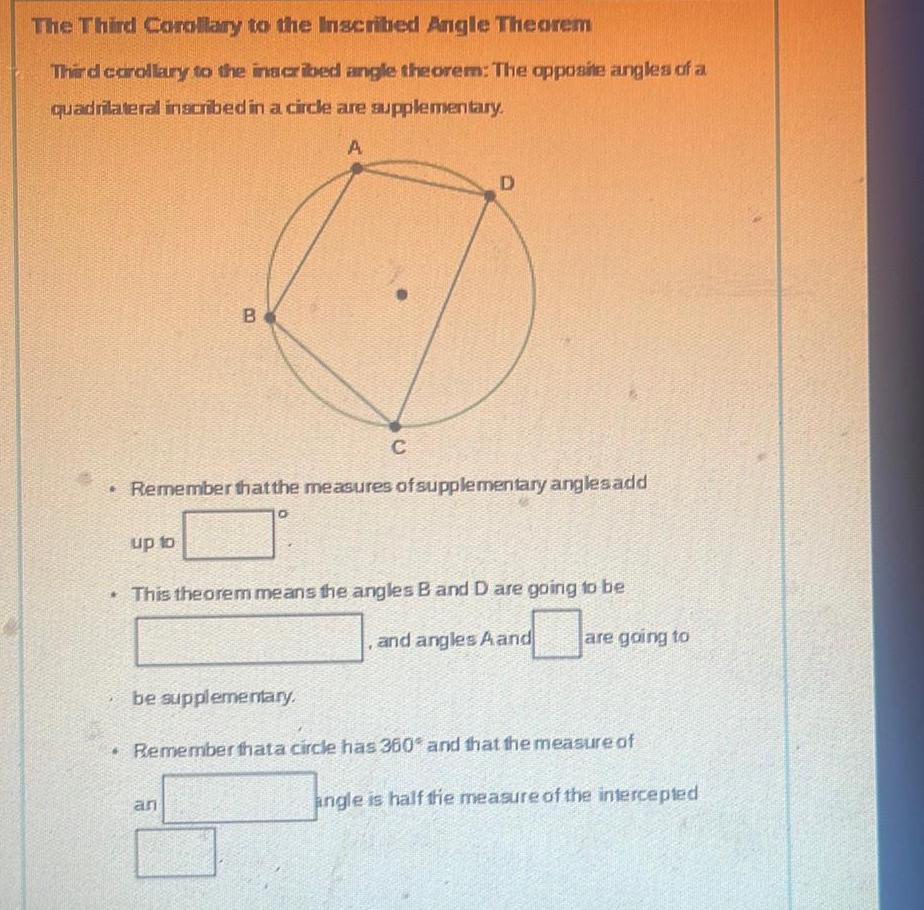
Geometry
2D GeometryThe Third Corollary to the Inscribed Angle Theorem Third corollary to the inscribed angle theorem The opposite angles of a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle are supplementary A B up to C Remember that the measures of supplementary anglesadd O D This theorem means the angles B and D are going to be and angles A and be supplementary are going to Remember thata circle has 360 and that the measure of angle is half the measure of the intercepted
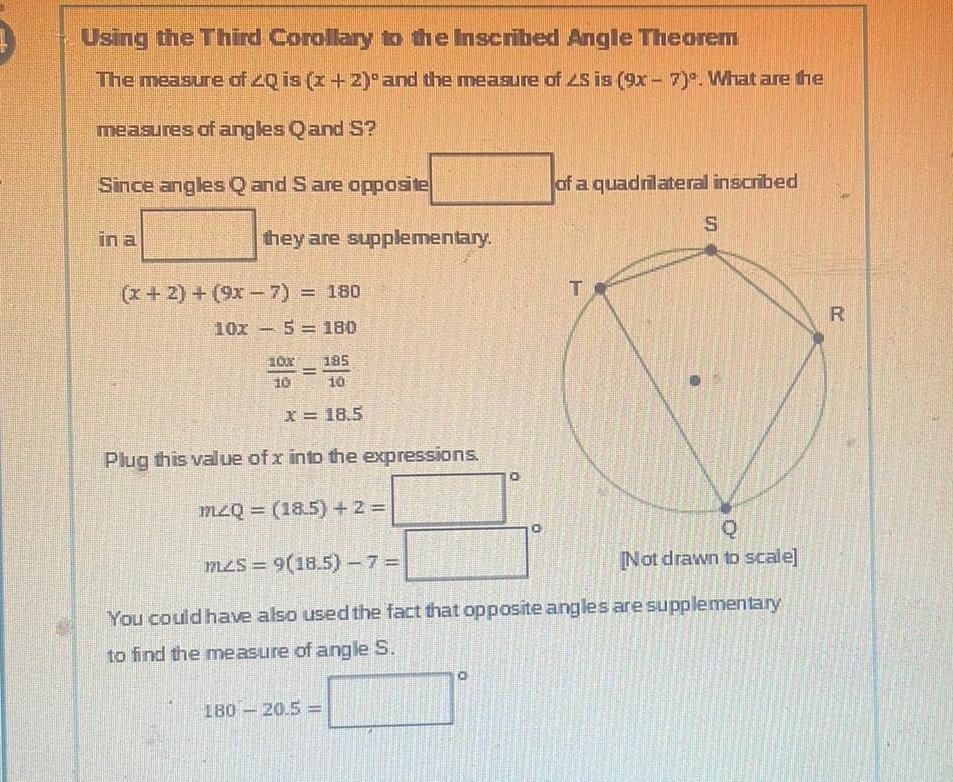
Geometry
2D GeometryUsing the Third Corollary to the Inscribed Angle Theorem The measure of 20 is x 2 and the measure of 2S is 9x 7 What are the measures of angles Q and S Since angles Q and S are opposite in a they are supplementary x 2 9x 7 180 10x5 180 Our 185 10 10 x 18 5 Plug this value of x into the expressions m20 18 5 2 180 20 5 0 0 of a quadrilateral inscribed T S m s 9 18 5 7 You could have also used the fact that opposite angles are supplementary to find the measure of angle S Q Not drawn to scale R

Geometry
AreaInscribed angle theorem The measure of an inscribed angle is measure of its intercepted arc The Case 1 is one side of the angle Case 2 The center of the circle lies the angle The Case 3 the the circle lies within the angle of
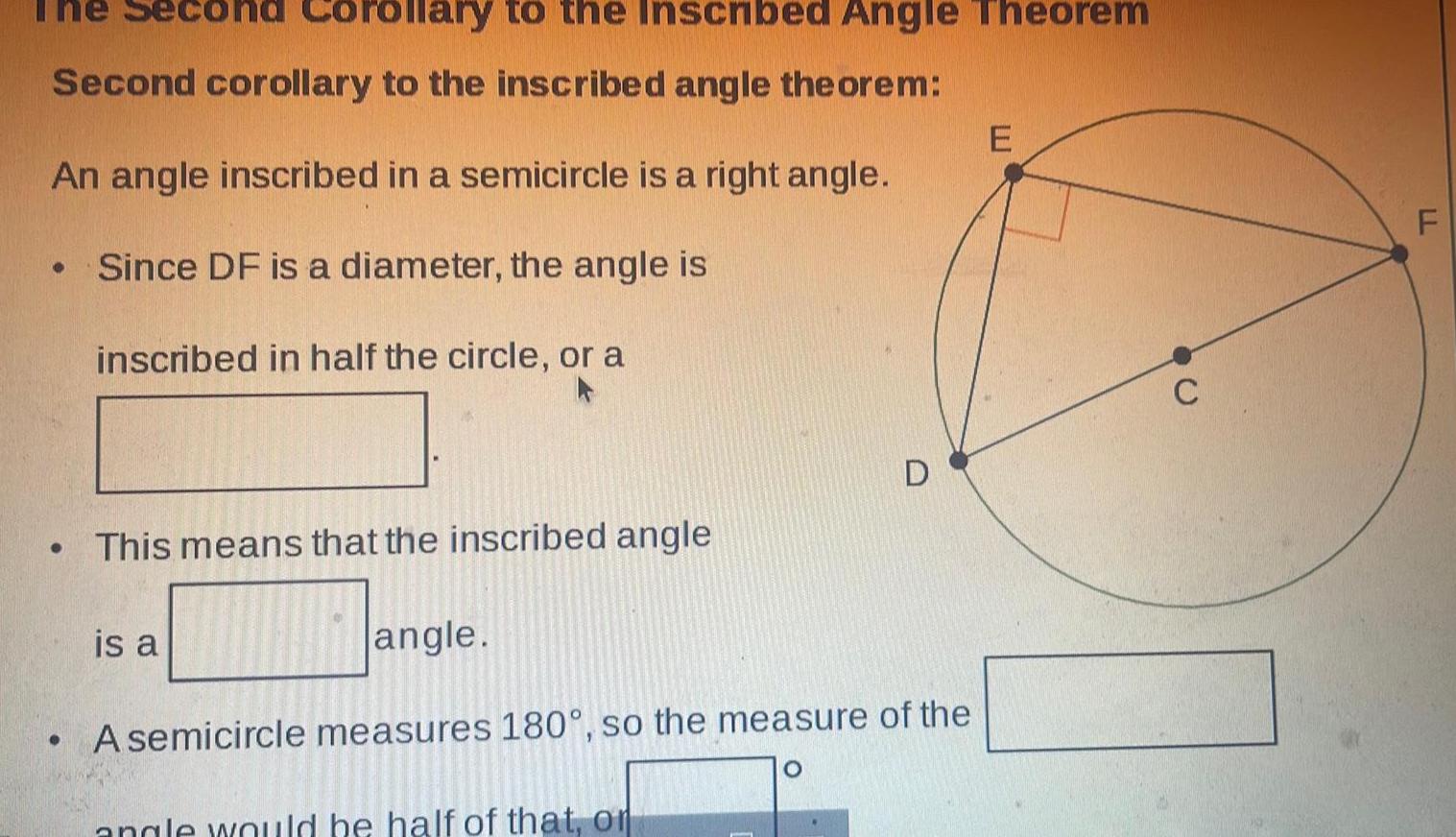
Geometry
2D GeometrySecond corollary to the inscribed angle theorem An angle inscribed in a semicircle is a right angle Since DF is a diameter the angle is inscribed in half the circle or a Coroll ry to the Inscribed Angle Theorem This means that the inscribed angle is a angle A semicircle measures 180 so the measure of the angle would be half of that or E C LL

Geometry
Solution of trianglesThe First Corollary to the Inscribed Angle Theorem First corollary to the inscribed angle theorem Two inscribed angles that intercept the same arc are congruent ZKJL and ZKML are their angles intercept the same arc KL same A JM because We can also say that JKM and congruent because their angles also intersect the are J K M
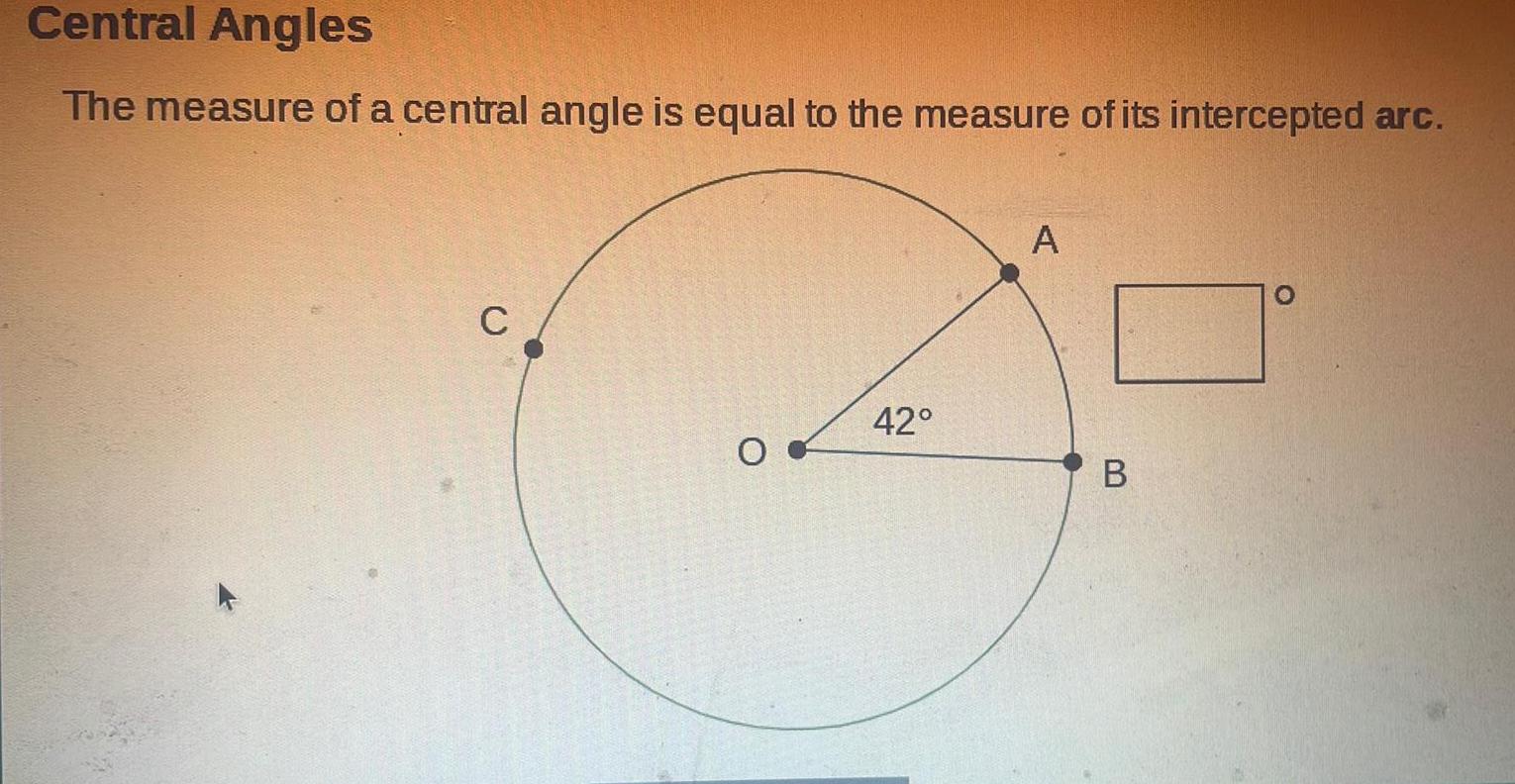
Geometry
2D GeometryCentral Angles The measure of a central angle is equal to the measure of its intercepted arc C 42 A B
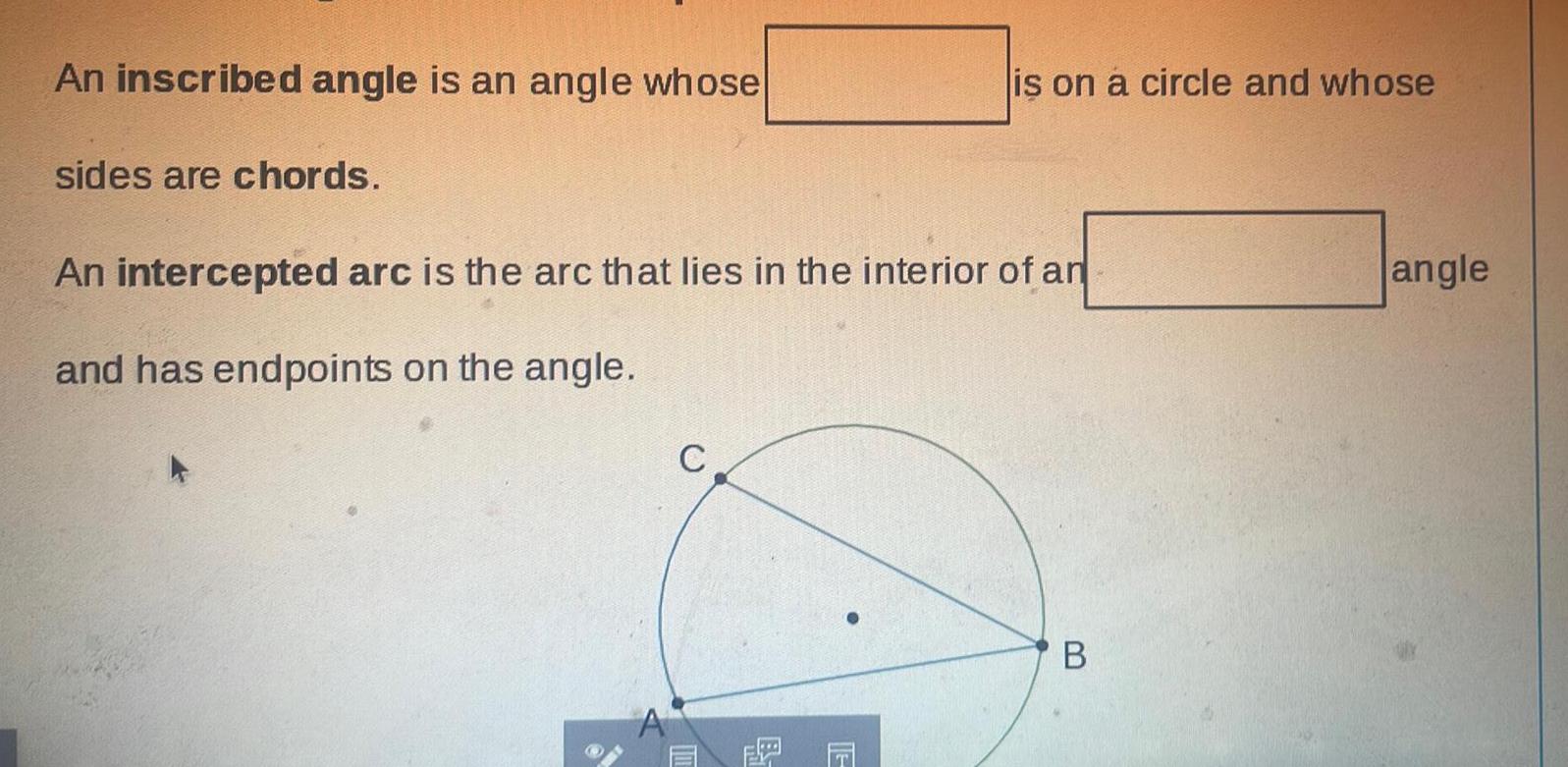
Geometry
2D GeometryAn inscribed angle is an angle whose sides are chords is on a circle and whose An intercepted arc is the arc that lies in the interior of an and has endpoints on the angle C B angle
Geometry
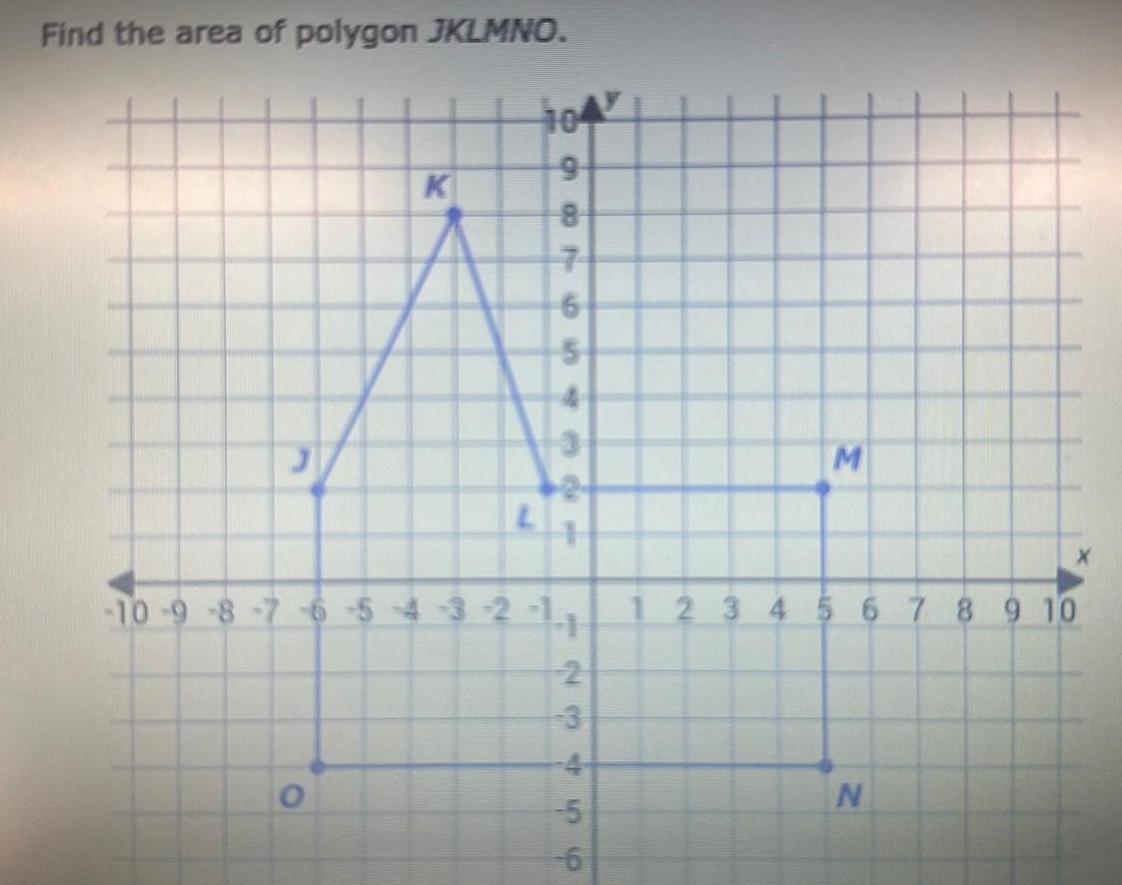
2D GeometryFind the area of polygon JKLMNO K 104 886 9 7 bl 2 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 11 123 2 456 M 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 N

Geometry
Coordinate systemAngle ABD measures 4x 10 Angle ACD measures 5x 2 A D E C B What is the measure of arc AD O 12 O 58 O 96 O 116

Geometry
Solution of trianglesAngle BAC measures 56 D B O What is the measure of angle BDC O 28 O 34 O 56 O 112
Geometry
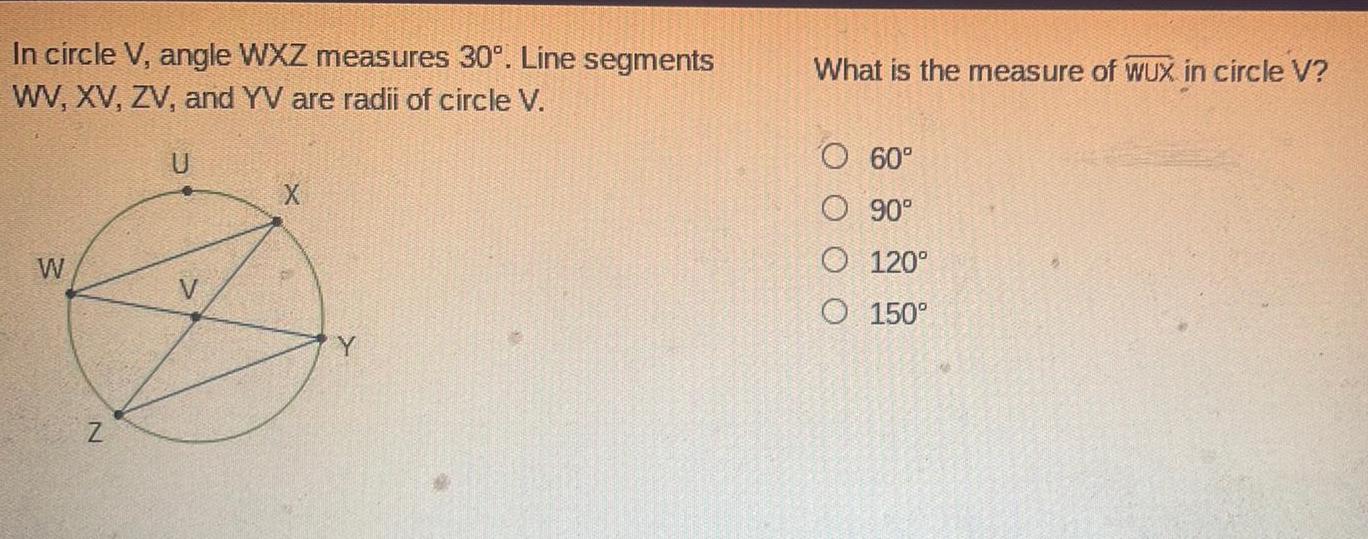
2D GeometryIn circle V angle WXZ measures 30 Line segments WV XV ZV and YV are radii of circle V W U X Y What is the measure of WUX in circle V O 60 O 90 O 120 O 150

Geometry
Coordinate system104 D 79 G LL F What is the measure of arc ECF in circle G O 52 O 98 O 158 O 177

Geometry
2D GeometryLine segment GJ is a diameter of circle L Angle K measures 4x 6 H K What is the value of x O 21 24 O 32 044

Geometry
2D GeometryLine segment XY is tangent to circle Z at point U X T U W Y 12 If the measure of UV is 84 what is the measure of ZYUV A O O O O 42 84 96 168

Geometry
2D GeometryIn circle D angle ADC measures 7x 2 Arc AC measures 8x 8 A B C What is the measure of ZABE O 36 O 43 O 72 O 144

Geometry
Heights & Distances10 Scott set up a volleyball net in his backyard One of the poles which forms a right angle with the ground is 7 feet high To secure the pole he attached two ropes from the top of the pole to a stake 4 feet from the bottom of the pole Find the total length of the two ropes A 160 ft B 8 5 ft C 4 ft D 8 3 ft 10
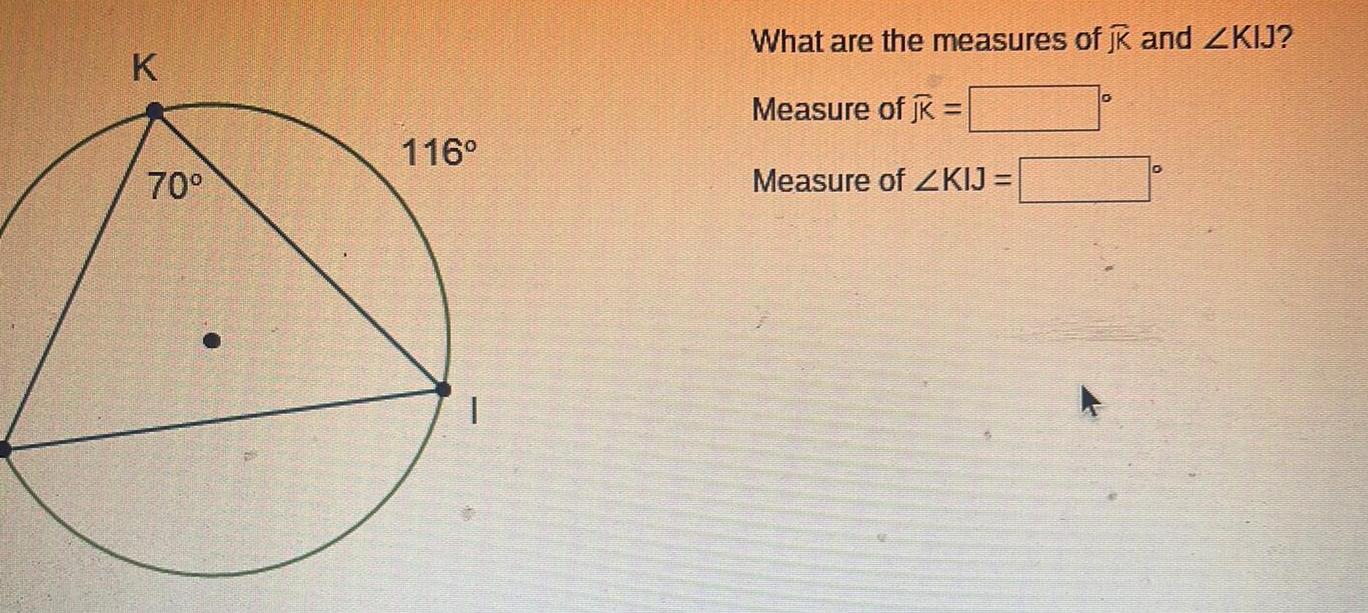
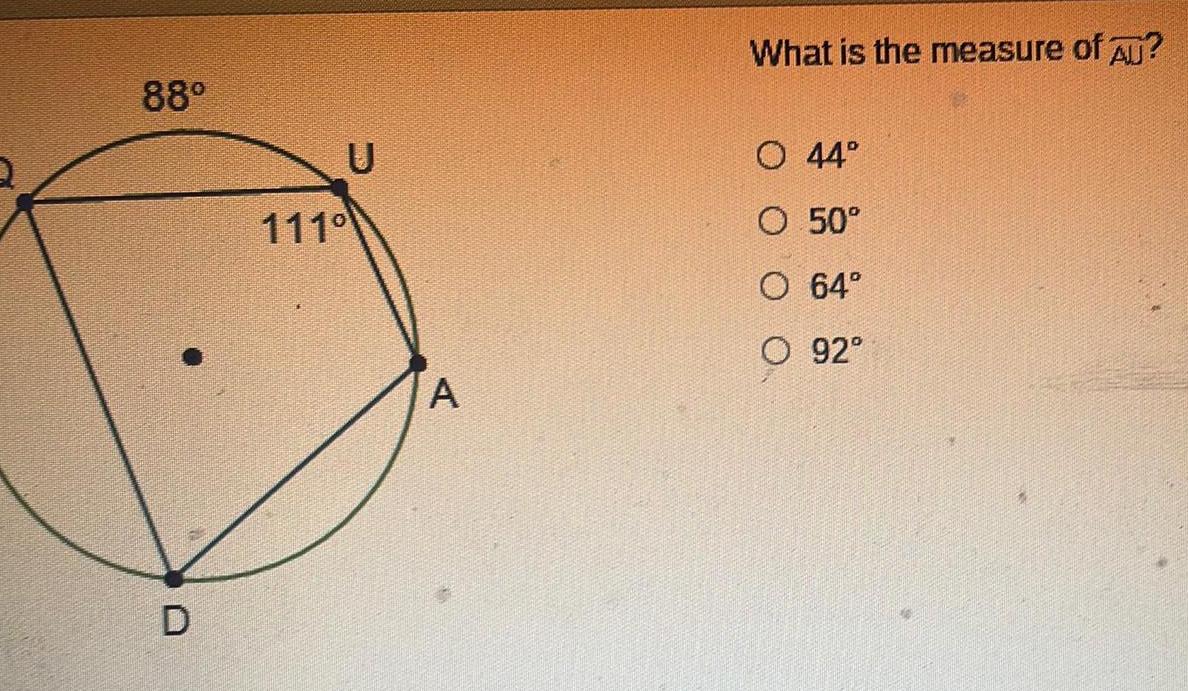
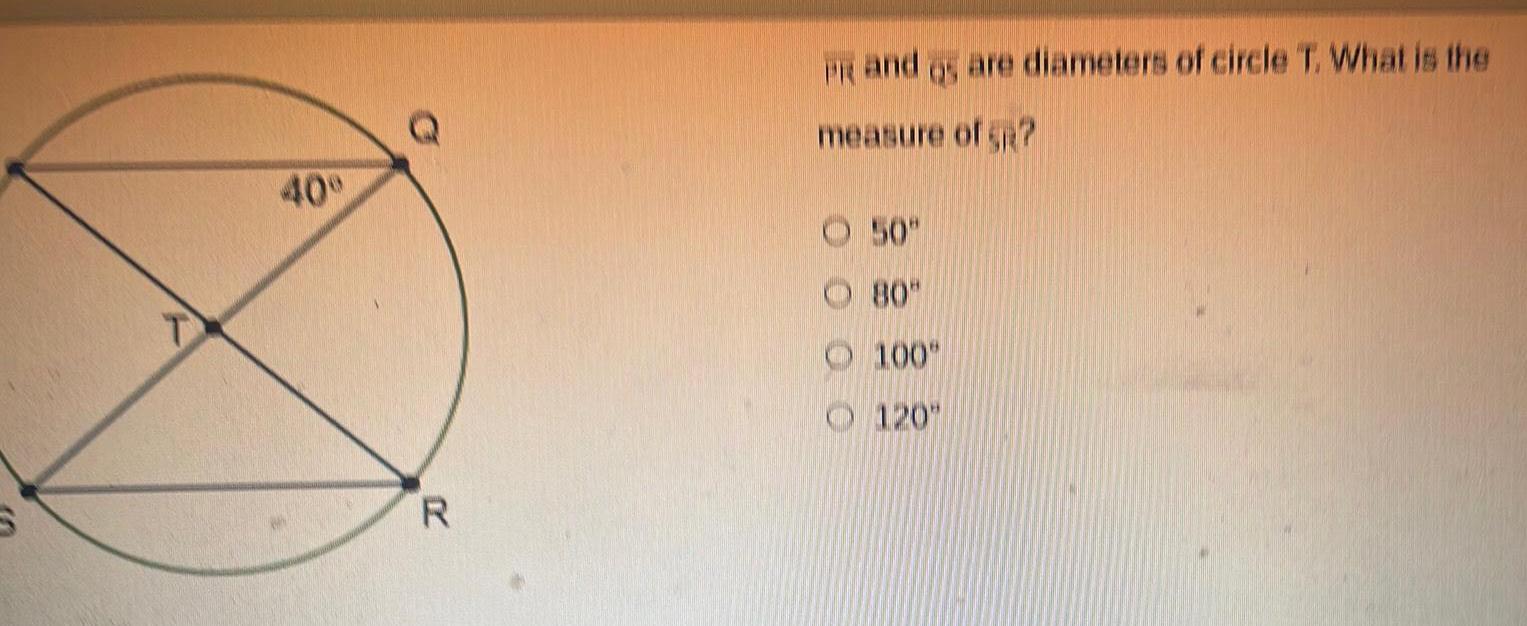
Geometry
2D Geometry40 Q R PR and gs are diameters of circle T What is the measure of SR 50 80 100 120

Geometry
Solution of trianglesJustifying the Second Corollary to the Inscribed Angle Theore Explain how you can use the inscribed angle theorem to justify its second corollary that an angle inscribed in a semicircle is a right angle
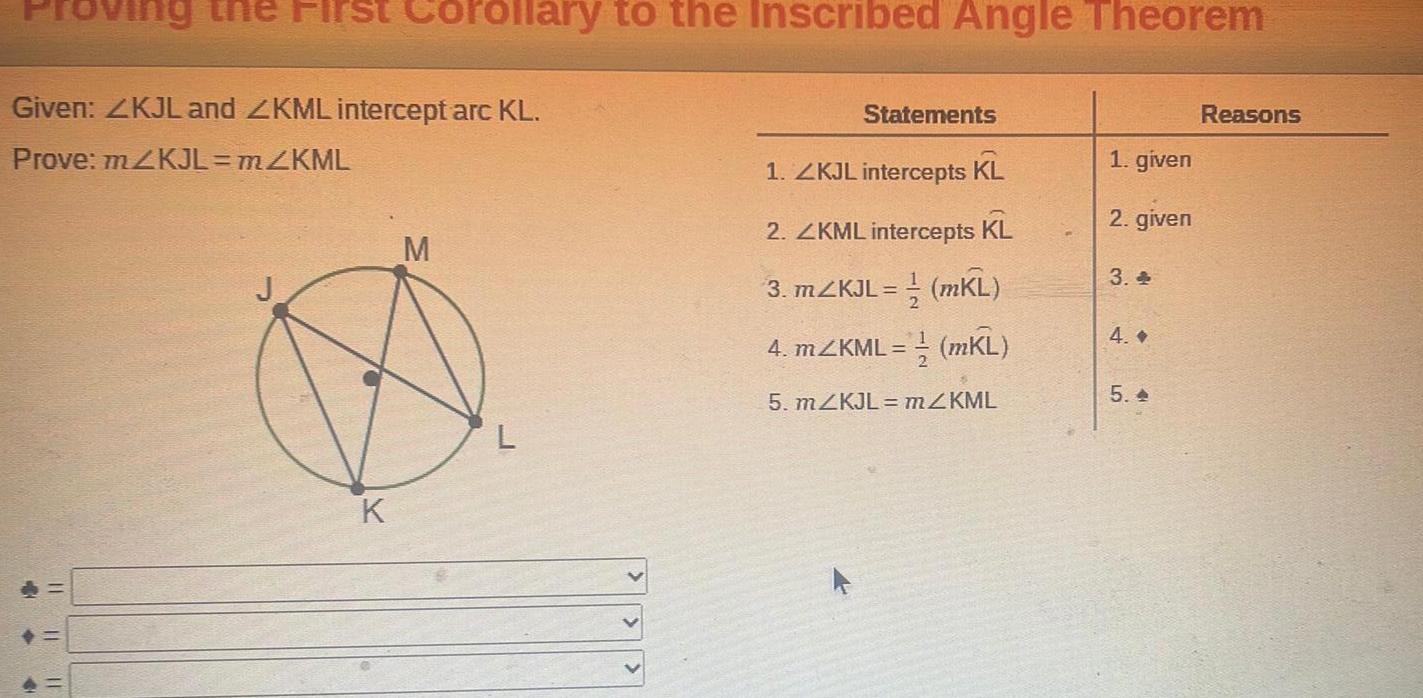
Geometry
2D Geometry4 11 Given ZKJL and ZKML intercept arc KL Prove m2KJL mZKML 19 11 rst Co 11 orollary to the Inscribed Angle Theorem K M L Statements 1 ZKJL intercepts KL 2 ZKML intercepts KL 3 mZKJL mKL 4 mZKML mKL 5 mZKJL m KML 1 given 2 given 3 4 5 Reasons

Geometry
2D GeometryA C B The measure of ZB is 3x 4 and the measure of ZD is 2x 6 What are the measures of angles B and D m2B mZD

Geometry
Heights & DistancesCalculate the angle A in the following right angled triangle where a 53 2 m and b 5

Geometry
3D GeometryB C E D F ZFAE measures 72 What other angle must measure 72 OZBFD OZDEA O ZEDF OZFBE

Geometry
2D GeometryR T S The measure of arc QS is 4x 18 What is the value of x O 40 5 O 49 5 O 94 5 O 180


Geometry
2D GeometryAdd Work Question 16 Prove the following identity 1 cos 2y sin 2y degrees 1 cos 2y sin 2y tan y 1


Geometry
2D Geometry58 3 4 2 106 Is the measure of 21 equal to the measure of 22 Why O yes because they intercept the same arc O no because the sides of 22 are longer O no because they intercept the circle at different points

Geometry
2D GeometryGround anchor 2 is exactly 58 feet from the base of the tower dashed line in diagram The bottom ground support cable from level 6 to ground anchor 2 is attached to the tower at a height of 142 feet The top ground support cable from level 6 to ground anchor 2 is attached to the tower at a height of 150 feet How long is each support cable to level 6 The bottom cable is SCIEN feet long Round to the nearest hundredth Lesel Lami Support cables Grou aschin


Geometry
2D Geometrye is a central angle that cuts off an arc of length s Find the radius of the circle if 8 155 s 5 km O 2 25 km O 1 95 km O 1 85 km 2 15 km O 2 05 km


Geometry
Coordinate system10 9 8 7 16 1 5 A 3 2 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 11 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 IC 2 1 3 14 15 6 1 7 8 A X 9 Write the standard equation for the hyperbola graphed above

Geometry
2D Geometryharuca a 270 Which of the following shows the correct rotation of parallelogram ABCD OA GOO OB GTS O C

Geometry
2D GeometryWatch help video In circle F with m EFG 70 and EF Round to the nearest hundredth E F 19 units find the length of arc EG G 4

Geometry
Solution of trianglesFor triangle ABC we are given that mZC 89 1 AC 12 3 ft and BC 23 3 ft We can use the Law of Cosines Law of Sines and other properties of triangles to determine all of the missing information Note that the diagram may not be drawn to scale a AB B Determine all of the missing information about this triangle d m B 23 3 ft feet Preview b Draw the triangle and add the length of AB to your diagram c m A degrees Preview degrees Preview 89 10 A 12 3 ft

Geometry
Heights & Distancessin u v x 1 Points DETAILS Use the figure to find the exact value of the trigonometric function sin