Geometry Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.

Geometry
2D GeometryComplete the statement W Z Y If ZXYZZZXY then 211 Select the theorem used to find the answer O Converse of the Base Angles Theorem O Third Angles Theorem O Base Angles Theorem Trianglo S www XV D VX
Geometry
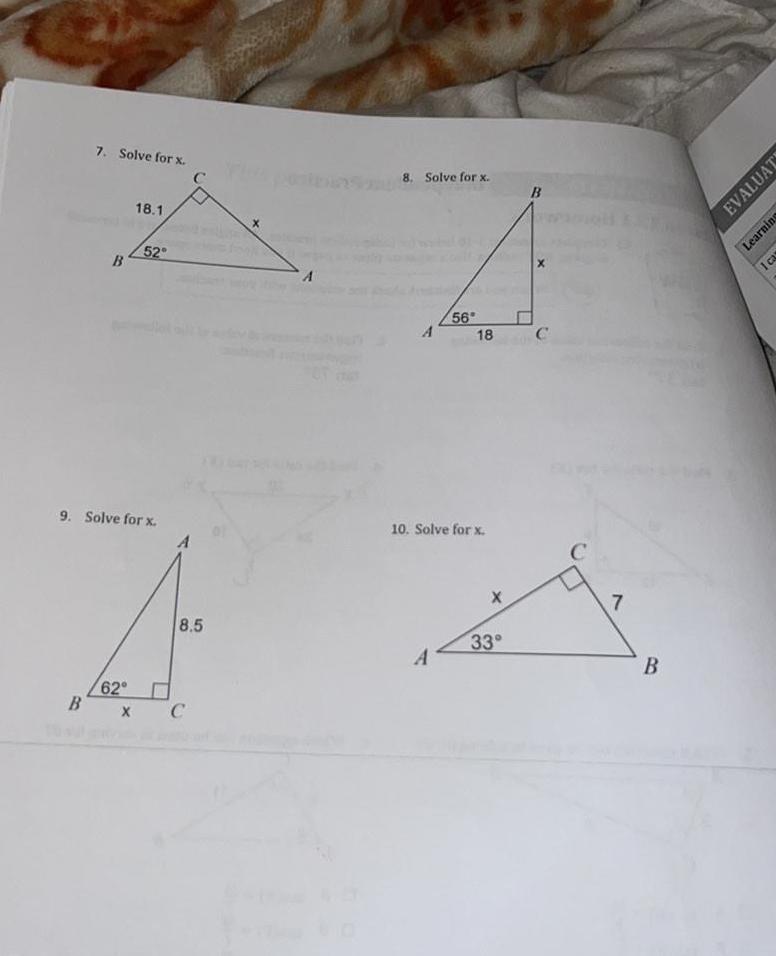
Solution of triangles7 Solve for x B 18 1 62 B X 52 9 Solve for x C 8 5 C A 8 Solve for x A 56 A 18 10 Solve for x 33 C C 7 B EVALUAT Learning I ca

Geometry
Area7 Throughout this question leave all answers as exact expressions in terms of it and 2n square roots for example 2 n 3 or etc In the diagram below the circle centred at O has radius 3cm The curved line AOC is part of a circle also of radius 3cm centred at D OD is perpendicular to AC a Calculate the length AB DIAGRAM 1 b Calculate the area of triangle AOC A B D c Calculate the area of sector OADC in diagram 1 indicated for refere 2 below DIAGRAM 2 B A d Calculate the shaded area indicated in diagram 1 D 1

Geometry
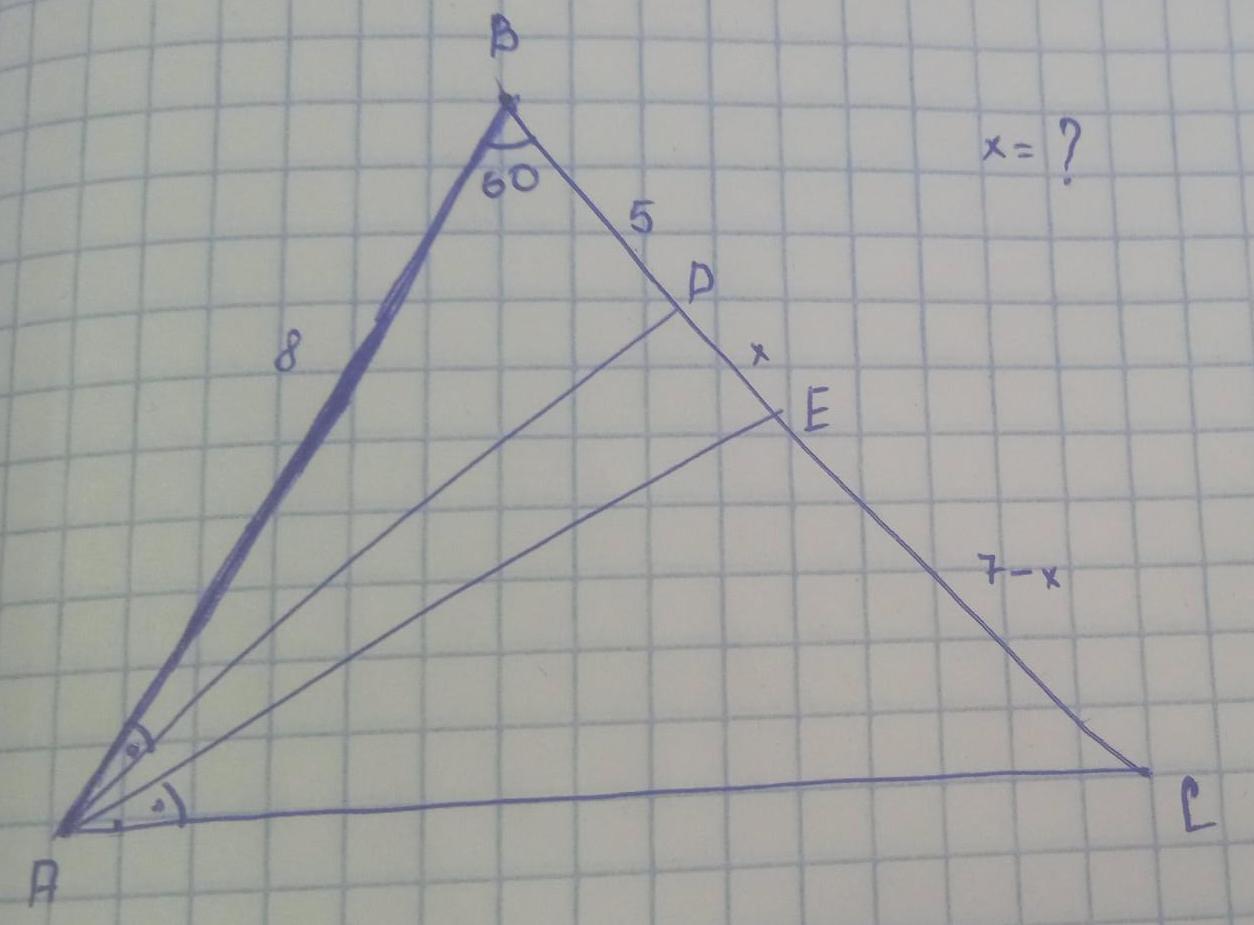
Vectors4 Let 0 A B and C be the vertices of a tetrahedron and 2 1 2 is the centroid of OABC by ratio 3 1 Vertex O is the origin If G is a centroid of AABC for the tetrahedron evaluate the value of 1OG 1

Geometry
2D GeometryD S cian ka t r E 3 D r 11 K eleri A 2 3 B 6 6 ve C 4 0 olan ABC ge ninin BC na ait kenarortay iziliyor Buna g re kenarortay do rusunun y eksenini kesti i noktan n ordinat ka t r A 2 B 1 C O B D 1 E 3

Geometry
Area12 x ka t r What is x A 13 y D 16 X 12 ekilde verilen 5x5 lik kareye 1 den 25 e kadar say lar birer kez kullan larak yerle tirildi inde her sat r ve s tu nun top The total of every row and column is equal when the numbers to 25 from 1 are placed into 5x5 square in the figure given by used once N B 14 E 17 C 15

Geometry
2D GeometryAD Rhombus Statement ABCD is a rhombus DF bisects BC ZDEC FEB ZCZEBF DC AB BE CE BF AD BF DC ADECAFEB DC AD Reorder steps to make Given it logical Vertical angles are congruent Parallel lines cut by a transversal fo Opposite sides of a rhombus are par A segment bisector divides a segmer Transitive Property Corresponding Parts of Congruent T ASA All sides of a rhombus are congruen D E C


Geometry
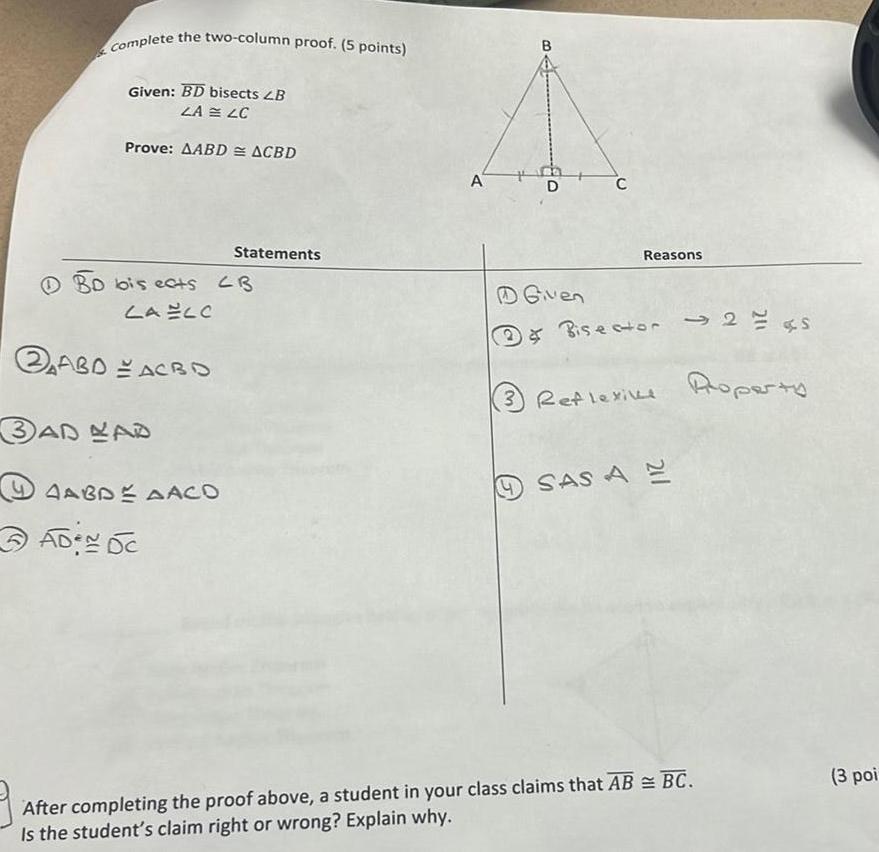
Solution of trianglesComplete the two column proof 5 points Given BD bisects LB ZA LC Prove AABD ACBD BD bis ects CB LA ELO ABD ACBO 3AD LAD AAGDE AACO Statements ADEN DC A D D Given C Reasons Bisector 2 s 3 Reflexive Roperty SAS AE After completing the proof above a student in your class claims that AB BC Is the student s claim right or wrong Explain why 3 poi


Geometry
2D Geometry11 AABC Azx B Z 3 AUVW AYLS C by AAS Y by SSS aining 2 co tam 12 ANRM ANG P by ASS M A R 14 APQR ARMQ by SAS P

Geometry
2D GeometryDetermine whether each set of triangles is congruent 2 points each If they are complete the congruency statement and name the triangle congruency theorem that applies and mark any implied relationships Your markings MUST match your theorem If they are not congruent cross off the figure completely 9 AEGHA GEF E H by SSS F visloxo 61 G 10 AABDARD by HL B mt no b5263 neo mengert A BA C M1 15 101

Geometry
Coordinate systemIf AB DE and AC DF which statement does NOT allow you to conclude that AABC ADEF A BC EF B LA LD C ZA and ZD are right angles D LB LE yriw nislaxs of beau 9d 60 me10ert w woladelgmsmit no bez B F menosdT asignA 9268 A C E 643

Geometry
2D Geometry5 You are given ARST and AEFD such that m R 60 m2S 80 m2F 60 m2D 40 RS 4 and EF 4 Are the two triangles congruent If so which segment is congruent to RT nomic ross A Yes the triangles are congruent FD B Yes the triangles are congruent EDNA gnitbelter norw woled engil silf no bezsa C Yes the triangles are congruent FE D No the triangles are not congruent ZVGWIA A 29mizemcz

Geometry
2D GeometryLength of a circular arc Length of AB 2ar A Find the length of AB Round your answer to the nearest ten 8 in 100 B Select one a 50 3 in d Ob 55 9 in OC 20 9 in 14 0 in

Geometry
Heights & DistancesS 4 Consider a rectangular box with one of the vertics at the origin and point A 2 3 5 as shown Determine the angle between BC and BA Round to the nearest degree ZA B A 2 3 5 C

Geometry
2D Geometry10 Determine the value s of k such that the area of the parallelogram formed by the vectors k 1 1 2 and b k 3 0 is 41

Geometry
Vectors8 Using vectors explain how to determine the volume of the following parallelepiped Determine its volume B 6 3 5 A 4 0 0 x O C 2 3 5 D 6 5 3

Geometry
Vectors1 Consider the vectors a 2i k b 4i j 3k and c i 4j 3k determine the following fully simplified b 3b 2c a a b c c 1 e exb 2 g Vector projection of bonto c 2 d x 1 f b c

Geometry
Coordinate system11 The scalar projection of a onto b is 8 If the length of a is 11 then what is the angle to the nearest degree between a and b

Geometry
Vectors9 Explain why it is not possible to determine a vector that is mutually perpendicular to vectors 2 1 and b 2 2

Geometry
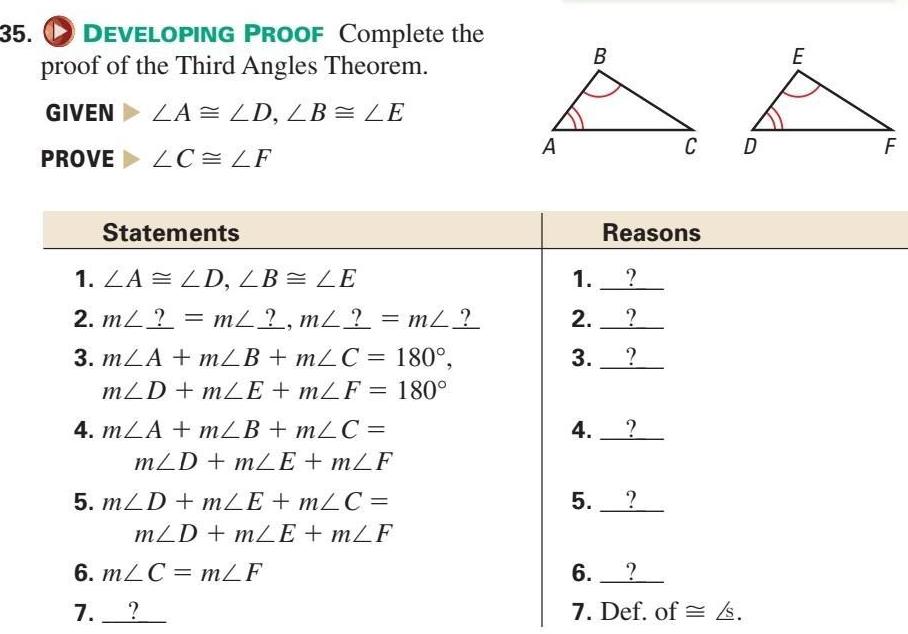
Solution of triangles35 DEVELOPING PROOF Complete the proof of the Third Angles Theorem GIVEN LA LD LB LE PROVELC LF Statements 1 LA LD LB LE 2 m m m m 3 mLA mLB mLC 180 mLD mLE mLF 180 4 mLA m B m C mLD mLE mLF 5 m D m E m C mLD mLE mLF 6 m C m F 7 A B 1 2 3 Reasons 4 5 C D 6 7 Def of s E F

Geometry
2D Geometry7 Suppose DE a DG and LEDF 2GDF Are there congruent triangles in the diagram Where do you find the corresponding congruent parts to satisfy either SSS SAS or ASA G CO B 7 A F Analyze the triangles shown G CO B 7 AY 86 810 6 A RAKAN ENABLEDES

Geometry
Coordinate systemcoordinates 10 8 6 4 2 R S S R 104 8 6 9 4 2 2 4 6 8 10 2 4 ection over the x axis T 6 U 8 X 10


Geometry
Heights & DistancesNate heard stories about the massive Sierra redwoods in California and looked forward to seeing one of these trees for himself On his first actual encounter with one of the trees Nate wants to know just how tall the tree is He places a mirror on the ground and experiments several times until he determines the correct distance from the base of the tree as well as the correct angle of incidence that allows him to see the top of the tree 1 9 m

Geometry
3D GeometryFind the volume blank 1 and total surface area blank 2 of this solid shown below 3 cm 4 cm Blank 1 Blank 2 5 cm 7 cm A A
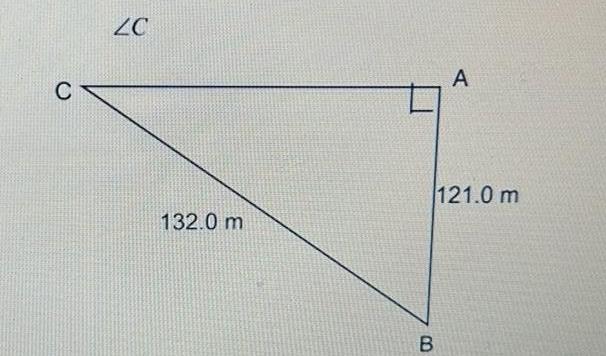

Geometry
2D GeometryCalculate perimeter blank 1 and area blank 2 of the following shape 1 5 cm 2 5 cm Blank 1 Blank 2 9 2 cm A

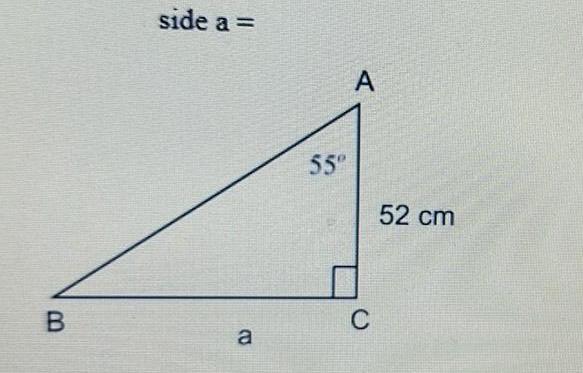

Geometry
2D GeometryCalculate the volume of the cone below look at formulas sheet or formulas above 4 2 m J 3 6 m




Geometry
2D GeometryBased on the following diagram and assuming that the wall and floor meet at a right angle how far up the wall does the ladder reach Top 5 feet 13 feet

Geometry
2D Geometrythe following problems using Pythagorean Theorem Round to the nearest tenth where necessary Always include units in your answer For example if you answer is 100 feet write 100ft Question 6 2 points Listen If a rectangular soccer field has length of 240 meters and width of 70 meters How long is its diagonal D 70 m 240 m

Geometry
Heights & DistancesIn an isosceles triangle ABC with AB AC the bisector of angle C meets side AB at D if BC AC AD then A ZA B C T 3 3 8 C length of angle bisector CD 4 2 2 AB cos D length of angle bisector CD 4 2 2 AB cos RO ROO 8 TC 8 N REDMI 7 CAMERA



Geometry
Coordinate system1 Follow the steps below to help you prove or disprove that the point 1 15 lies on the circle that is centered at the origin and contains the poin 0 4 To earn full credit you must show your work Step 1 Plot a point at the origin and at 0 4 Use these to help you draw the circle centered at the origin that contains 0 4 Step 2 Determine the radius Step 3 Use the radius and the coordinates of the center to write the equation of the circle Step 4 Substitute the x and y coordinates of the point 1 15 in the equation of the circle to check whether they satisfy the equation

Geometry
Heights & DistancesA hot air balloon is floating above a straight road To calculate their height above the ground the balloonists simultaneously measure the angle of depression to two consecutive mileposts on the road on the same side of the balloon The angles of depression are found to be 16 and 19 How high in feet is the ballon Hint




Geometry
2D GeometryUse the figure at the right If JK 7x 16 and NO 15 what is the value of x N HE L M K

Geometry
2D GeometryIn ADEF the midpoint of the side opposite vertex D is M and the centroid is C If DM is 21 what are DC and CM DC 14 units CM 7 units