Geometry Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.

Geometry
Coordinate systemUse the given below to answer items 4 and 5 Given 4 distinct points W X Y Z on a line o To prove that there exists a projectivity which camies W X Y Z into X W 2 consider the outline of the prof given below Proof Project the points W X Y Z from point A not on a Section by b distinct from a and AY on Y and obtain the points W X Y Z so that that Y Y Join W and X meeting A2 rat 2 4 Draw the figure with the conditions in the given and in the outline of the proof stated above 5 Supply the missing basis of each pencil and center of perspectivity that are established below W X Y Z 2 AZZ X W Z Y WXY 2

Geometry
2D GeometryEXPLAIN 1 Using Vertical Angles Read Explain 1 and complete Your Turn 1 3 adapted from Lesson 4 1 Show all your work You can use the Vertical Angles Theorem to find missing angle measures Example A Find the angle measures 1 What is the measure of ZDEB Find the value of x mzAEC m2DEB 101 4x 3 104 4x Vertical angles are congruent 26 x So the value of x is 26 and m DEB 101 mLAED mLDEB 180 x 101 180 x 79 mLAED 79 mLAED m2CEB mLCEB 79 Substitute angle measures Add 3 on both sides Your Turn 1 Find the value of x 2 What is the measure of LAED What is the measure of ZCEB LAED and LDEB form a linear pair so they are supplementary Divide by 4 on both sides Definition of supplementary angles Substitute angle measures Subtract 101 on both sides Substitute x for its angle measure Vertical angles are congruent Transitive Property S D 2 The measure of two verticle angles are 58 and 3x 4 Find the value of x 101 4x 3 5x 11 P T 4 x 6 B R

Geometry
Solution of trianglesGiven the BJT data and circuit diagram shown in Figure 1 calculate the total power losses in the BJT when used to switch an inductive load across a 400 V dc supply at I 0 kHz Assume that the inductance of the load is large so that the load current is constant with a value of 10 A and the transistor is in the on state and off state for the same length of duration Neglect the on state voltage drop of the diode and the effects of trn and Toff on the static losses 8 YCC SURNAME FIRST NAME MI STUDENT NUMBER 20XX XXXXX XX X BJT DC ANALYSIS Input Input 9 11k RC 4 7k 2 01 MAT 02 RE Output

Geometry
Coordinate systemIdentify each pair of angles as complementary supplementary linear vertical or adjacent Use the Angle Pair Definitions to help you Keep in mind that there may be more than one answer for each exercise 3 5 123 57 4

Geometry
3D GeometryYour Turn 1 Determine the measure of the unknown angles A 68 b 3 Find the measure of ZAEC and LBED E 60 I D B 2 40 X 25 Z y

Geometry
3D GeometryUsing what you know about angles and translations find all of the angle measures in the image below 21 135 22 23 24 25 26 Explain how you found the measure of 28 27 28 5 6 7 8 3

Geometry
Heights & Distances3 The measure of two vertical angles are given by the expressions x 3 and 2x 7 Find the value of x What is the measure of each angle

Geometry
Coordinate systemFrom the previous page use the Paragraph Proof of the Vertical Angles Theorem to write a two column proof of the Vertical Angles Theorem Refer to the reason bank below C Given 21 and 23 are vertical angles Prove 41 23 Two Column Proof of the Vertical Angles Theorem Statements 1 21 and 23 are vertical angles 2 21 and 22 are a linear pair and 22 and 23 are a linear pair 3 21 and 22 are supplementary and 22 and 23 are supplementary 4 m21 m2 180 and m22 m23 180 5 mz1 m2 mc2 m23 6 m21 m23 7 21 23 Reason Bank Subtraction Property of Equality Reasons Definition of Linear Pair 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Definition of Congruence Linear Pair Theorem Definition of Supplementary Angles 4 3 Transitive Property of Equality Given

Geometry
Coordinate systemUnderstanding how weighted averages work will be a very important topic for you in this course since your grades are determined in this way In this project you will create an Excel spreadsheet that can calculate a MATH 123 student s final grade You will then write a reflection paper answering several questions regarding your project In this project you are required to do the following 1 Create a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet file that will be capable of cakulating a student s final grade in this course Keep in mind that weighting by percentages is used in determining the final grade o Open a new Excel spreadsheet file Create 4 additional sheets in Excel 5 sheets total How to create a new sheet in an Excel file Click on the plus sign at the bottom of the page Copy and paste the original spreadsheet into the new sheet before making changes Rename the new sheets appropriatelybyright clicking on the sheet name and selecting Rename Use the

Geometry
Coordinate systemI has a payload of 50000 lbs The haul road is 5000 feet long with a rolling resistance estimated to be 100 pounds per ton and a coefficient of traction of 0 5 The haul road has an uphill of 3 when traveling from the load site to the dump site 65 of the loaded weight is carried by the rear driving wheels and 42 of the empty truck weight is carried by the driving whes Estimate the Rimpull available in the loaded truck and empty trucks Also estimate the speed of the truck with load using the performance curve and travel time of truck with load

Geometry
Coordinate systemunterclockwise rotation of 270 about the origin 1 point 11 4 2 2 0 2 y 1 and T 2 1 Draw and label the image after a 2 Transformation Rule Preimage Coordinates x y Image

Geometry
Heights & Distancesglacier is a mass of ice on land that flows under its own weight due to gravity Which way does a glacier flow Downhill Uphill Depends on the temperature The glacier shown in Cross Section 1 is flowing downhill due to gravity A spike was put in the glacie at the arrow On Cross Section 1 draw an arrow showing the direction that the glacier is moving Imagine the glacier in Cross Section 1 shown is now shrinking due to warming temperatures Which diagram in Cross Section 2 A or B shows where the spike will be found in several years Explain your choice Two students are discussing which way glacier ice moves when a glacier is shrinking Student 1 Glacier ice always flows downhill because of gravity and A shows the ice flowing downhill The glacier shrinks because it melts faster than the glacier is flowing Student 2 I think the ice would flow backwards and carry the spike with it as shown in B Because the glacier is shrinking the ice would flow uphill I With which student do you agree Why rt 2 Glacier budget When a glacier is getting smaller it is often said that it is retreating Explain why this term may cause confusion in understanding how a glacier moves The amount of ice in a glacier is a balance between additions e g snowfall and subtractions e g melting a On Cross Section 3 circle where most material leaves the glacier due to melting b On Cross Section 3 circle where most material is added to the glacier due to snowfall that does not melt in summer

Geometry
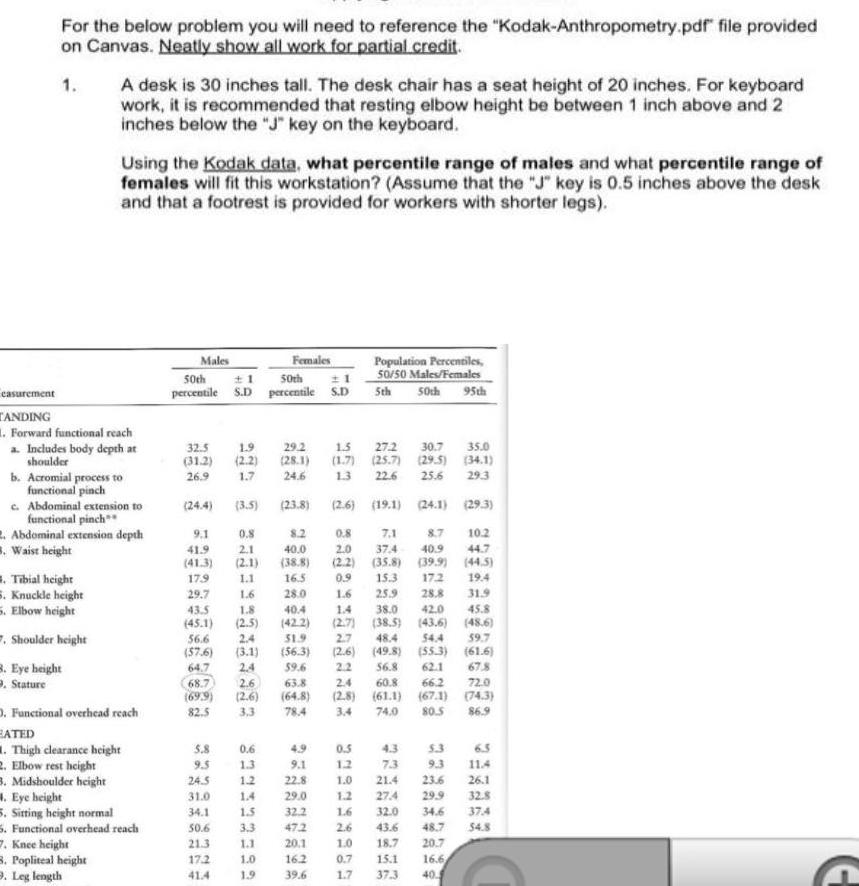
Heights & DistancesFor the below problem you will need to reference the Kodak Anthropometry pdf file provided on Canvas Neatly show all work for partial credit 1 A desk is 30 inches tall The desk chair has a seat height of 20 inches For keyboard work it is recommended that resting elbow height be between 1 inch above and 2 inches below the J key on the keyboard Using the Kodak data what percentile range of males and what percentile range of females will fit this workstation Assume that the J key is 0 5 inches above the desk and that a footrest is provided for workers with shorter legs easurement TANDING 1 Forward functional reach a Includes body depth at shoulder b Acromial process to functional pinch c Abdominal extension to functional pinch Abdominal extension depth B Waist height 3 Popliteal height 9 Leg length Tibial height 5 Knuckle height 5 Elbow height Shoulder height B Eye height Stature D Functional overhead reach ATED 1 Thigh clearance height 2 Elbow rest height 3 Midshoulder height 4 Eye height 5 Sitting height normal 5 Functional overhead reach 7 Knee height Males Females 50th 1 1 50th percentile S D percentile S D 32 5 31 2 26 9 24 4 9 1 41 9 41 3 17 9 29 7 43 5 45 1 5 8 9 5 1 9 29 2 2 2 28 1 1 7 24 6 24 5 31 0 34 1 50 6 21 3 17 2 41 4 3 5 0 8 2 1 2 1 1 1 1 6 1 8 2 5 56 6 57 6 64 7 68 7 12 6 69 9 2 6 82 5 3 3 2 4 3 1 24 0 6 1 3 1 2 1 4 15 3 3 1 1 1 0 1 9 23 8 8 2 40 0 38 8 16 5 28 0 40 4 42 2 51 9 56 3 39 6 63 8 64 8 78 4 4 9 9 1 22 8 29 0 32 2 47 2 20 1 16 2 39 6 1 5 27 2 30 7 35 0 1 7 25 7 29 5 34 1 13 22 6 25 6 29 3 2 6 19 1 24 1 29 3 0 8 7 1 8 7 2 0 37 4 40 9 2 2 35 8 39 9 0 9 15 3 17 2 Population Percentiles 50 50 Males Females 5th 50th 95th 1 6 1 4 2 7 38 5 25 9 28 8 38 0 42 0 43 6 54 4 59 7 49 8 55 3 61 6 56 8 62 1 67 8 60 8 66 2 72 0 61 1 67 1 74 3 3 4 74 0 80 5 86 9 2 7 48 4 2 6 2 2 2 4 2 8 0 5 1 2 4 3 7 3 1 0 21 4 1 2 27 4 5 3 9 3 23 6 29 9 10 2 44 7 44 5 19 4 31 9 45 8 48 6 1 6 32 0 34 6 2 6 43 6 48 7 1 0 18 7 20 7 0 7 15 1 16 6 1 7 37 3 40 6 5 11 4 26 1 32 8 37 4 54 8

Geometry
Solution of trianglesmodelling is the Integrate and Fire model Here a neuron is reduced to its most basic function fire action potentials or not Most of the physiological and mathematical richness of the Hodgkin Huxley model and the FHN model as per Question 1 to some extent is removed for the benefit of computational efficiency This becomes important as the number of neurons in a simulation increases to match what is seen in neural tissue about 105 per mm3 In its most basic form the Integrate and Fire nouron above the following DE

Geometry
Heights & DistancesFor the below problem you will need to reference the Kodak Anthropometry pdf file provided on Canvas Neatly show all work for partial credit 1 A desk is 30 inches tall The desk chair has a seat height of 20 inches For keyboard work it is recommended that resting elbow height be between 1 inch above and 2 inches below the J key on the keyboard Using the Kodak data what percentile range of males and what percentile range of females will fit this workstation Assume that the J key is 0 5 inches above the desk and that a footrest is provided for workers with shorter legs easurement TANDING 1 Forward functional reach a Includes body depth at shoulder b Acromial process to functional pinch c Abdominal extension to functional pinch Abdominal extension depth B Waist height 3 Popliteal height 9 Leg length Tibial height 5 Knuckle height 5 Elbow height Shoulder height B Eye height Stature D Functional overhead reach ATED 1 Thigh clearance height 2 Elbow rest height 3 Midshoulder height 4 Eye height 5 Sitting height normal 5 Functional overhead reach 7 Knee height Males Females 50th 1 1 50th percentile S D percentile S D 32 5 31 2 26 9 24 4 9 1 41 9 41 3 17 9 29 7 43 5 45 1 5 8 9 5 1 9 29 2 2 2 28 1 1 7 24 6 24 5 31 0 34 1 50 6 21 3 17 2 41 4 3 5 0 8 2 1 2 1 1 1 1 6 1 8 2 5 56 6 57 6 64 7 68 7 12 6 69 9 2 6 82 5 3 3 2 4 3 1 24 0 6 1 3 1 2 1 4 15 3 3 1 1 1 0 1 9 23 8 8 2 40 0 38 8 16 5 28 0 40 4 42 2 51 9 56 3 39 6 63 8 64 8 78 4 4 9 9 1 22 8 29 0 32 2 47 2 20 1 16 2 39 6 1 5 27 2 30 7 35 0 1 7 25 7 29 5 34 1 13 22 6 25 6 29 3 2 6 19 1 24 1 29 3 0 8 7 1 8 7 2 0 37 4 40 9 2 2 35 8 39 9 0 9 15 3 17 2 Population Percentiles 50 50 Males Females 5th 50th 95th 1 6 1 4 2 7 38 5 25 9 28 8 38 0 42 0 43 6 54 4 59 7 49 8 55 3 61 6 56 8 62 1 67 8 60 8 66 2 72 0 61 1 67 1 74 3 3 4 74 0 80 5 86 9 2 7 48 4 2 6 2 2 2 4 2 8 0 5 1 2 4 3 7 3 1 0 21 4 1 2 27 4 5 3 9 3 23 6 29 9 10 2 44 7 44 5 19 4 31 9 45 8 48 6 1 6 32 0 34 6 2 6 43 6 48 7 1 0 18 7 20 7 0 7 15 1 16 6 1 7 37 3 40 6 5 11 4 26 1 32 8 37 4 54 8

Geometry
Coordinate systemFor the below problem you will need to reference the Kodak Anthropometry pdf file provided on Canvas Neatly show all work for partial credit 1 A desk is 30 inches tall The desk chair has a seat height of 20 inches For keyboard work it is recommended that resting elbow height be between 1 inch above and 2 inches below the J key on the keyboard Using the Kodak data what percentile range of males and what percentile range of females will fit this workstation Assume that the J key is 0 5 inches above the desk and that a footrest is provided for workers with shorter legs easurement TANDING 1 Forward functional reach a Includes body depth at shoulder b Acromial process to functional pinch c Abdominal extension to functional pinch Abdominal extension depth B Waist height 3 Popliteal height 9 Leg length Tibial height 5 Knuckle height 5 Elbow height Shoulder height B Eye height Stature D Functional overhead reach ATED 1 Thigh clearance height 2 Elbow rest height 3 Midshoulder height 4 Eye height 5 Sitting height normal 5 Functional overhead reach 7 Knee height Males Females 50th 1 1 50th percentile S D percentile S D 32 5 31 2 26 9 24 4 9 1 41 9 41 3 17 9 29 7 43 5 45 1 5 8 9 5 1 9 29 2 2 2 28 1 1 7 24 6 24 5 31 0 34 1 50 6 21 3 17 2 41 4 3 5 0 8 2 1 2 1 1 1 1 6 1 8 2 5 56 6 57 6 64 7 68 7 12 6 69 9 2 6 82 5 3 3 2 4 3 1 24 0 6 1 3 1 2 1 4 15 3 3 1 1 1 0 1 9 23 8 8 2 40 0 38 8 16 5 28 0 40 4 42 2 51 9 56 3 39 6 63 8 64 8 78 4 4 9 9 1 22 8 29 0 32 2 47 2 20 1 16 2 39 6 1 5 27 2 30 7 35 0 1 7 25 7 29 5 34 1 13 22 6 25 6 29 3 2 6 19 1 24 1 29 3 0 8 7 1 8 7 2 0 37 4 40 9 2 2 35 8 39 9 0 9 15 3 17 2 Population Percentiles 50 50 Males Females 5th 50th 95th 1 6 1 4 2 7 38 5 25 9 28 8 38 0 42 0 43 6 54 4 59 7 49 8 55 3 61 6 56 8 62 1 67 8 60 8 66 2 72 0 61 1 67 1 74 3 3 4 74 0 80 5 86 9 2 7 48 4 2 6 2 2 2 4 2 8 0 5 1 2 4 3 7 3 1 0 21 4 1 2 27 4 5 3 9 3 23 6 29 9 10 2 44 7 44 5 19 4 31 9 45 8 48 6 1 6 32 0 34 6 2 6 43 6 48 7 1 0 18 7 20 7 0 7 15 1 16 6 1 7 37 3 40 6 5 11 4 26 1 32 8 37 4 54 8

Geometry
Heights & DistancesFor the below problem you will need to reference the Kodak Anthropometry pdf file provided on Canvas Neatly show all work for partial credit 1 A desk is 30 inches tall The desk chair has a seat height of 20 inches For keyboard work it is recommended that resting elbow height be between 1 inch above and 2 inches below the J key on the keyboard Using the Kodak data what percentile range of males and what percentile range of females will fit this workstation Assume that the J key is 0 5 inches above the desk and that a footrest is provided for workers with shorter legs easurement TANDING 1 Forward functional reach a Includes body depth at shoulder b Acromial process to functional pinch c Abdominal extension to functional pinch Abdominal extension depth B Waist height 3 Popliteal height 9 Leg length Tibial height 5 Knuckle height 5 Elbow height Shoulder height B Eye height Stature D Functional overhead reach ATED 1 Thigh clearance height 2 Elbow rest height 3 Midshoulder height 4 Eye height 5 Sitting height normal 5 Functional overhead reach 7 Knee height Males Females 50th 1 1 50th percentile S D percentile S D 32 5 31 2 26 9 24 4 9 1 41 9 41 3 17 9 29 7 43 5 45 1 5 8 9 5 1 9 29 2 2 2 28 1 1 7 24 6 24 5 31 0 34 1 50 6 21 3 17 2 41 4 3 5 0 8 2 1 2 1 1 1 1 6 1 8 2 5 56 6 57 6 64 7 68 7 12 6 69 9 2 6 82 5 3 3 2 4 3 1 24 0 6 1 3 1 2 1 4 15 3 3 1 1 1 0 1 9 23 8 8 2 40 0 38 8 16 5 28 0 40 4 42 2 51 9 56 3 39 6 63 8 64 8 78 4 4 9 9 1 22 8 29 0 32 2 47 2 20 1 16 2 39 6 1 5 27 2 30 7 35 0 1 7 25 7 29 5 34 1 13 22 6 25 6 29 3 2 6 19 1 24 1 29 3 0 8 7 1 8 7 2 0 37 4 40 9 2 2 35 8 39 9 0 9 15 3 17 2 Population Percentiles 50 50 Males Females 5th 50th 95th 1 6 1 4 2 7 38 5 25 9 28 8 38 0 42 0 43 6 54 4 59 7 49 8 55 3 61 6 56 8 62 1 67 8 60 8 66 2 72 0 61 1 67 1 74 3 3 4 74 0 80 5 86 9 2 7 48 4 2 6 2 2 2 4 2 8 0 5 1 2 4 3 7 3 1 0 21 4 1 2 27 4 5 3 9 3 23 6 29 9 10 2 44 7 44 5 19 4 31 9 45 8 48 6 1 6 32 0 34 6 2 6 43 6 48 7 1 0 18 7 20 7 0 7 15 1 16 6 1 7 37 3 40 6 5 11 4 26 1 32 8 37 4 54 8

Geometry
AreaA engine pumps up 100 kg of water through a hight of 10 m in 5s If the efficiency of theengine is 60 what is the power of the engine 1 33 kw 2 3 3 kw 3 0 33 kw
Geometry
Coordinate systemFor the below problem you will need to reference the Kodak Anthropometry pdf file provided on Canvas Neatly show all work for partial credit 1 A desk is 30 inches tall The desk chair has a seat height of 20 inches For keyboard work it is recommended that resting elbow height be between 1 inch above and 2 inches below the J key on the keyboard Using the Kodak data what percentile range of males and what percentile range of females will fit this workstation Assume that the J key is 0 5 inches above the desk and that a footrest is provided for workers with shorter legs easurement TANDING 1 Forward functional reach a Includes body depth at shoulder b Acromial process to functional pinch c Abdominal extension to functional pinch Abdominal extension depth B Waist height 3 Popliteal height 9 Leg length Tibial height 5 Knuckle height 5 Elbow height Shoulder height B Eye height Stature D Functional overhead reach ATED 1 Thigh clearance height 2 Elbow rest height 3 Midshoulder height 4 Eye height 5 Sitting height normal 5 Functional overhead reach 7 Knee height Males Females 50th 1 1 50th percentile S D percentile S D 32 5 31 2 26 9 24 4 9 1 41 9 41 3 17 9 29 7 43 5 45 1 5 8 9 5 1 9 29 2 2 2 28 1 1 7 24 6 24 5 31 0 34 1 50 6 21 3 17 2 41 4 3 5 0 8 2 1 2 1 1 1 1 6 1 8 2 5 56 6 57 6 64 7 68 7 12 6 69 9 2 6 82 5 3 3 2 4 3 1 24 0 6 1 3 1 2 1 4 15 3 3 1 1 1 0 1 9 23 8 8 2 40 0 38 8 16 5 28 0 40 4 42 2 51 9 56 3 39 6 63 8 64 8 78 4 4 9 9 1 22 8 29 0 32 2 47 2 20 1 16 2 39 6 1 5 27 2 30 7 35 0 1 7 25 7 29 5 34 1 13 22 6 25 6 29 3 2 6 19 1 24 1 29 3 0 8 7 1 8 7 2 0 37 4 40 9 2 2 35 8 39 9 0 9 15 3 17 2 Population Percentiles 50 50 Males Females 5th 50th 95th 1 6 1 4 2 7 38 5 25 9 28 8 38 0 42 0 43 6 54 4 59 7 49 8 55 3 61 6 56 8 62 1 67 8 60 8 66 2 72 0 61 1 67 1 74 3 3 4 74 0 80 5 86 9 2 7 48 4 2 6 2 2 2 4 2 8 0 5 1 2 4 3 7 3 1 0 21 4 1 2 27 4 5 3 9 3 23 6 29 9 10 2 44 7 44 5 19 4 31 9 45 8 48 6 1 6 32 0 34 6 2 6 43 6 48 7 1 0 18 7 20 7 0 7 15 1 16 6 1 7 37 3 40 6 5 11 4 26 1 32 8 37 4 54 8

Geometry
Coordinate systemCOMPANY table Write a query to print the IDs of the companies that have more than 10000 employees in ascending order of ID Input Format Name ID NAME EMPLOYEES Type Integer String Integer COMPANY Description A company ID in the inclusive range 1 1000 This is the primary key A company name This field contains between 1 and 100 characters inclusive The total number of employees in the company Output Format The result should contain the IDs of all the companies that have more than 10000 employees in

Geometry
Heights & Distanceses iable Costs ntribution Margin ed Cost Ome Loss HENNA COMPANY Contribution Margin Income Statement Carvings Units 30 000 17 30 30 000 10 38 Mementos Per Unit Total Per Unit 519 000 17 30 311 400 1 73 207 600 194 240 13 360 Total Total 519 000 1 038 000 51 900 363 300 467 100 674 700 600 790 795 030 133 690 120 330

Geometry
Heights & Distances19 Part 3 of 3 3 points Variable costs Contribution margin Fixed costs Income Sales Variable cost Contribution margin Fixed costs 3 Assume that the company expects sales of each product to increase to 61 000 units next year with no change in unit selling price Prepare a contribution margin income statement for the next year as shown above with columns for each of the two products Note Round per unit answers to 2 decimal places Ingame logo 487 860 81 310 325 240 731 790 194 240 600 790 131 000 131 000 Units HENNA COMPANY Contribution Margin Income Statement Carvings Per unit 17 30 X Answer is not complete 61 000 61 000 61 000 Total 1 055 300 0 17 30 1 055 300 194 240 861 060 Mementos Per unit IS 17 03 X 17 03 17 30 Total 1 038 830 1 038 830 1 055 300 600 790 454 510 IS Total 2 094 130 1 038 830 2 110 600 795 030 Return to question 1 315 570

Geometry
Heights & DistancesSlitherlink is a puzzle presented as a dotted grid surrounding some numbers Groups of four adjacent dots act as corners of a square called a cell Some cells of the grid are filled with numbers To fill in the puzzle you create one continuous non intersecting loop drawn from one dot to an adjacent dot horizontally or vertically Connecting one dot to the next draws a side or border of the cell The goal of the puzzle is for your loop to provide the indicated number of sides borders to numbered cells each cell that has a number in it has that many borders from the loop surrounding its cell For example here is a completed puzzle 1 1 3 2 1 2 2 1 12 2 1 1 131 121 3 3 3 21 1 Now let s try putting these strategies to use in some puzzles Here is a Slitherlink puzzle Solve the puzzle but also describe HOW you solve it ww NHO 2 1 0 1 3
Geometry
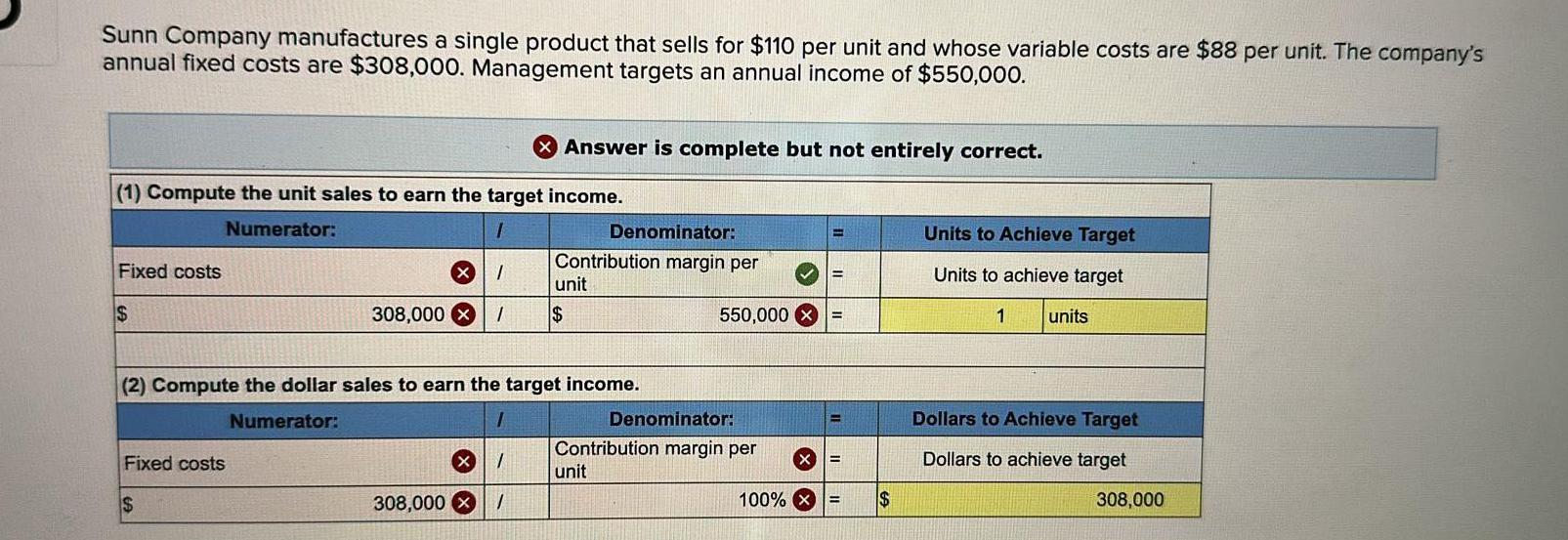
Coordinate systemSunn Company manufactures a single product that sells for 110 per unit and whose variable costs are 88 per unit The company s annual fixed costs are 308 000 Management targets an annual income of 550 000 1 Compute the unit sales to earn the target income Numerator 1 X 1 308 000 x 1 Fixed costs Answer is complete but not entirely correct Fixed costs Denominator Contribution margin per unit 2 Compute the dollar sales to earn the target income Numerator I X 1 308 000x 1 Denominator Contribution margin per unit E 550 000 X 100 X X B E Units to Achieve Target Units to achieve target 1 units Dollars to Achieve Target Dollars to achieve target 308 000


Geometry
Heights & DistancesThe hungry warrior was all bones Her jaw hung open in a perpetual shout I knew them I loved them I realized instantly that I would be a part of them My love I asked Who are these sisters of mine They wronged me he said How have they wronged you He did not answer but tried to take me from behind I would not oblige I clawed at his face He roared I fought I ended He ripped me from the inside out Indeed he had evolved in his passion He was born anew When I watched him sob over my body it was a confirmation He had not cried over the others To atone for such betrayal he said As if my body was the betrayal Let me say this Do not dare mistake my passion my love for forgiveness it is I who

Geometry
Coordinate systemGiven the BJT data and circuit diagram shown in Figure 1 calculate the total power losses in the BJT when used to switch an inductive load across a 400 V dc supply at I 0 kHz Assume that the inductance of the load is large so that the load current is constant with a value of 10 A and the transistor is in the on state and off state for the same length of duration Neglect the on state voltage drop of the diode and the effects of trn and Toff on the static losses SURNAME FIRST NAME MI STUDENT NUMBER 20XX XXXXX XX X DIT DO ANA OTO

Geometry
3D Geometryx t 8 10 cos 27 100 7 20cos 2 250 a Using Euler s relation the signal x t defined above can be expressed as a sum of complex exponential signals using the finite Fourier synthesis summation 3 37 Determine values for fo N and all the complex amplitudes a It is not necessary to evaluate any integrals to obtain a b Is the signal x t periodic If so what is the fundamental period c Plot the spectrum of this signal versus f in Hz P 3 20 A real signal x t has the two sided spectrum shown in Fig P 3 20 The frequency axis has its of rads 90 0 4 90 Figure P 3 20

Geometry
2D GeometryTWO 0 10 C so P T L A 44 y Show Transcribed Text Calculate the angle delta theta CA 23 98

Geometry
Solution of triangles4 List all possible samples of size three without replacement from the small population 2 4 6 8 10 Q 4 6 8 4 6 10 4 8 10 6 8 10 O 2 4 6 2 4 8 2 4 10 2 6 8 2 6 10 2 8 10 O 2 4 6 2 4 8 2 4 10 4 6 8 4 6 10 6 8 10 O 2 4 6 2 4 8 2 4 10 2 6 8 2 6 10 2 8 10 4 6 8 4 6 10 4 8 10 6 8 10 Continue Reset answer

Geometry
Heights & Distancesa 3 Draw the preimage of a triangle with coordinates 7 2 1 U 0 1 and V 3 3 Then use the following coordinate plane to complete the following 1 point each T U V Draw a reflection of the triangle across y x Label the new triangle as AT U V Mark the coordinates below 2 4 2 0 4 2 4 Parallelogram QRST has vertices Q 4 2 R 2 4 S 0 1 and T 2 1 Draw and label the image after a counterclockwise rotation of 270 about the origin 1 point 2 4 2 0 2 4 b Rotate AT U V 90 clockwise Label the new figure as AT U V Mark the coordinates below T U V Transformation Rule Preimage Coordinates x y Image

Geometry
2D GeometryQuestion 3 of 5 3 A particular vehicle gets an average of 35 mpg on the highway Is 35 mpg a parameter or statistic Q Parameter Statistic Continue Reset answer

Geometry
2D GeometryHW When you are finished check the solutions with your teacher Convert the following vector into coordinate notation rule 3 1 2 Convert the following vector into coordinate notation rule 4 7

Geometry
3D GeometryThe diagram shows a triangular prism CD 7 cm AD 10 cm Angle FDC 30 A E 10 cm B Calculate the size of angle AFC Give your answer correct to 1 decimal place D 30 7 cm C

Geometry
2D GeometryFind the Reference Number t bar and the Terminal Point for each value of t To receive full credit you must clearly show how you got these numbers by drawing Unit Circle and showing what it is 5 d t 5


Geometry
Coordinate system1 Parallel Line Construction For this part of the assignment you will construct a parallel line through a given line and point First draw a segment AB and point C on your paper Next construct a line through point C that is parallel to AB Label all points and lines used in the construction 2 Perpendicular Line Construction For this part of the assignment you will construct a perpendicular line to a given segment that passes through a given point First draw a segment AB on your paper Draw a point C above that line Construct a perpendicular line through segment AB and point C Label all points and lines used in the construction

Geometry
2D GeometryA 16 ft ladder leans against the side of a house The bottom of the ladder is 6 ft away from the side of the house Find x the angle of elevation of the ladder Round your answer to the nearest tenth of a degree 16 XA X 68 0 X

Geometry
Coordinate systemFind the absolute maximum and minimum if either exists for the function on the indicated interval f x x 2 x 6 2 A 0 4 B 1 7 C 4 8 A Find the absolute maximum Select the correct choice below and if necessary fill in the answer boxes to complete your choic OA The absolute maximum is at x Use a comma to separate answers as needed OB There is no absolute maximum

Geometry
3D GeometryQ4 a Find the ratio of areas and volumes of the two spheres O 2a 2 marks D b Two similar cones have heights in the ratio 3 5 If the total surface area of the larger cone is 75 cm find the total surface area of the smaller one 3 marks

Geometry
2D Geometryrag each equation to the correct location on the table Not all equations will be used etermine which equations represent lines that are parallel or perpendicular to the linear equation provided on the graph y y 4 5 y 8 y 2x 2 8 6 4 2 Parallel Line x 3 8 6 4 S 2 2 4 6 0 to 2 A 4 y 6 8 2x 1 Perpendicular Line


Geometry
3D GeometryHint Since AB is perpendicular to BC the slope of AB x the slope of BC 1 O A p q 7 B p q 7 O O C g p 7 O D 9 p 7 B 90 O

Geometry
3D GeometryJsing the information provided on the graph draw the line the line that is perpendicular to line segment AB and passes through point P Drawing Tools Select Point Line Click on a tool to begin drawing Reset 10 8 6 4 B 2 A 10 6 2 4 6 8 Delete 2 4 Undo 6 8 a 10 A

Geometry
Coordinate systemWhich line is perpendicular to AB line 1 6 4 2 8 6 4 2 O 2 line 2 B line 3 8 line 4

Geometry
2D Geometry8 AS A M is the result of rotating ASAM by 50 about Point C If the length of S C is 6 then the lengths of SC is 6 What is the measure of LA CA What is the measure of ZMCM

Geometry
Coordinate systemS AS A M is the result of reflecting ASAM over BC If the slope of AA is then the slope of BC is If the slope of AA is then the slope of MM is If AA intersects BC at Point X what is the measure of ZBXA

Geometry
Heights & Distances6 M AS A M is the result of translating ASAM If the slope of SS is the the slope of MM is If the length of AA is 6 then the lengths of MM is If the length of AM is 5 then the length of A M is


Geometry
2D GeometryT 8 The circle at right has its center at 1 2 instead of 0 0 The radius is still 5 Move the purple point to a point on the circle whose x value is 4 What is the horizontal distance between these points VE Submit