Area Questions and Answers

Geometry
Area1 1 Find the terminal points P x y on the unit circle determined by the given value t 11x 6 a t b t c t 4x 3 5T 4

Geometry
Area1 How many surfaces must the Smiths apply concrete to so that the pool is properly sealed Length Rectangular Prisin Surfaces need concrete Height of the pool has a length of 65 feet across a width of 20 feet and a depth of 15 feet what is the Total Surface Area in ft that needs to be concreted Width Total Surface Area 3 It cost 5 00 a square foot for concrete what is the total cost to seal the entire pool with concrete

Geometry
AreaFind the eccentricity of the conic section shown in the graph 2 y 5 10 8 6 T N 7246 8 10 NIL 2 6 8 10 O A e OB e 1 O C e 29 2 OD e 29 LO 21 5

Geometry
AreaA rectangle has dimensions of 6 in by 3 in Find the exact volume of the solid of revolution formed when the rectangle is rotated about its 6 in side
Geometry
Area6 If the area of the circle is 360 in what is the area of the sector if its central angle measures 90

Geometry
Area7 Find the exact lengths of the radius and the diameter of a cir cle whose area is a 257 in 2 b 2 257 cm 1


Geometry
Area13 Find the area of a square with apothem a 3 2 cm and perimeter P 25 6 cm 11 Find the area of aquilotoral triangle with anothom
Geometry
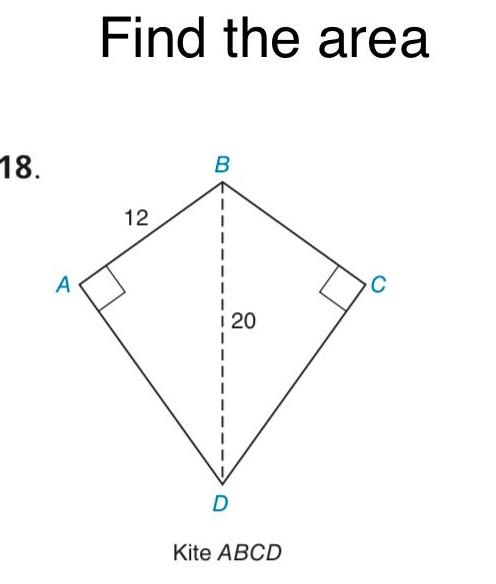
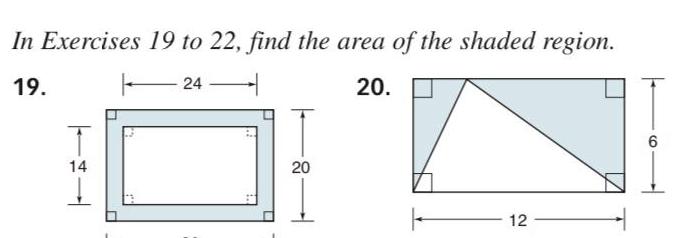
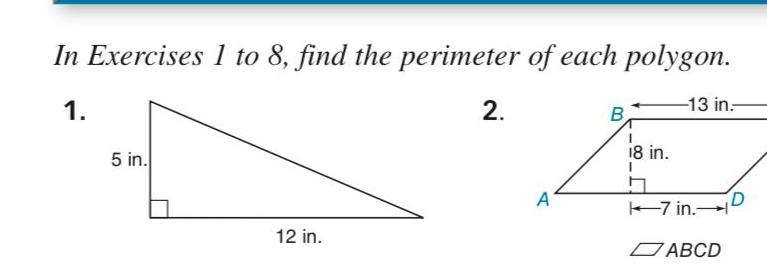
AreaIn Exercises 1 to 8 find the perimeter of each polygon 13 in 1 5 in 12 in 2 A B 18 in 7 in ABCD D
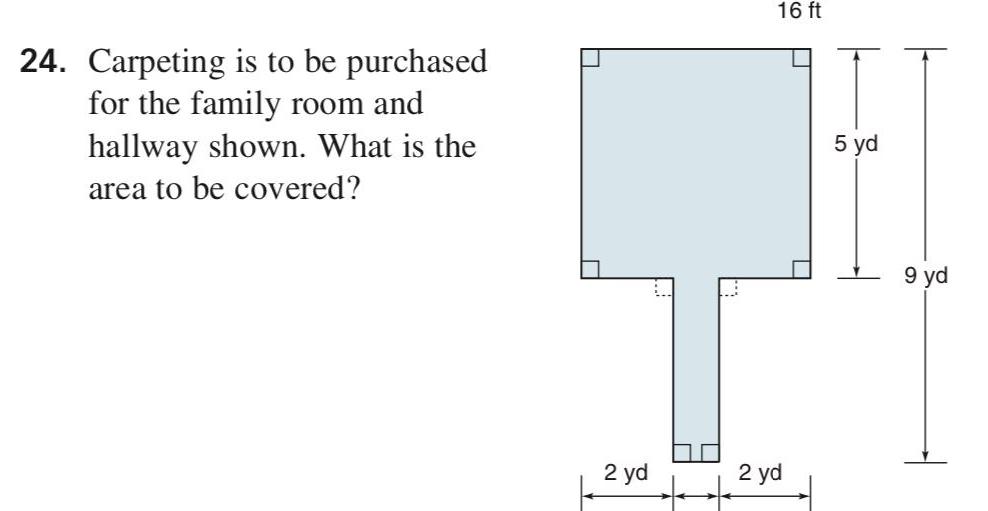
Geometry
Area24 Carpeting is to be purchased for the family room and hallway shown What is the area to be covered 2 yd 16 ft 2 yd 5 yd 9 yd

Geometry
Area5 O 10 What is the measure of the radius of the SMALL circle T Small Circle What is the area of the SMALL circle Asmall Circle ft ft What is the measure of the radius of the LARGE circle Large Circle ft What is the area of the LARGE circle ALarge Circle What is the EXACT area of the shaded region Am f42

Geometry
Area4 Find the area of the quadrilateral ABCD AB 15 AD 9 BC 5 CD 13 2 points B 50 C 15 13 A 9

Geometry
Area3 Given kite ABCD with diagonal AC 10 cm m ABD 30 m ADB 45 Find the area of the kite 3 points B 30 E A C 45 D

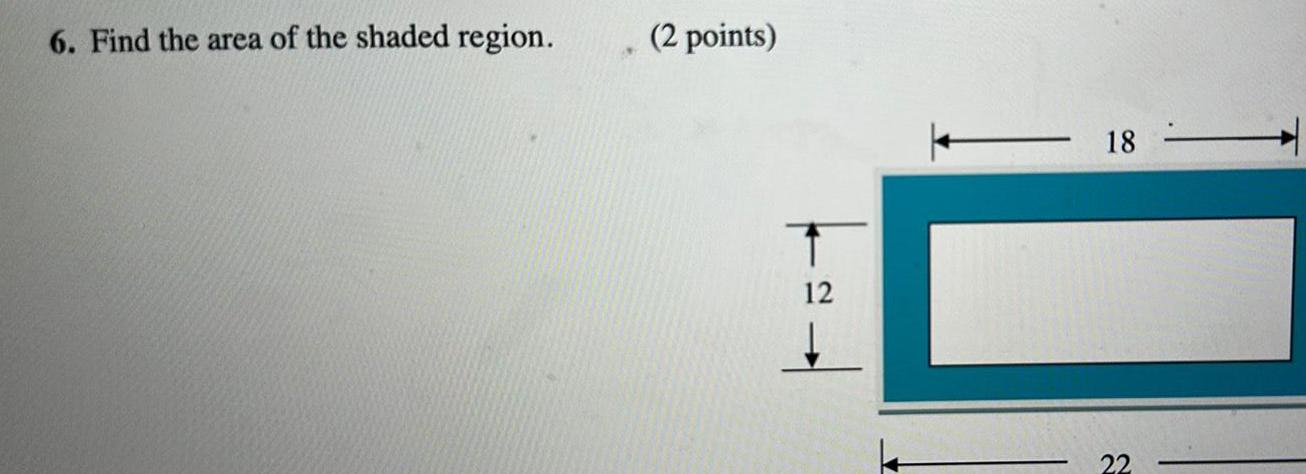

Geometry
Area8 Find the area of the regular hexagon whose sides have length s 8cm and apothem a 4 3 cm 2 points s 8cm

Geometry
AreaFor an object in an elliptical orbit around the moon the points in the orbit that are closest to and farthest from the center of the moon are called perilune and apolune respectively These are the vertices of the orbit The center of the moon is at one focus of the orbit A spacecraft was placed in a lunar orbit with perilune at a 89 mi and apolune at b 258 mi above the surface of the moon Assuming that the moon is a sphere of radius 1075 mi find an equation for the orbit of this spacecraft Place the coordinate axes so that the origin is at the center of the orbit and the foci are located on the x axis Round each answer to the nearest whole number x X apolune y2 b X 1 moon perilune
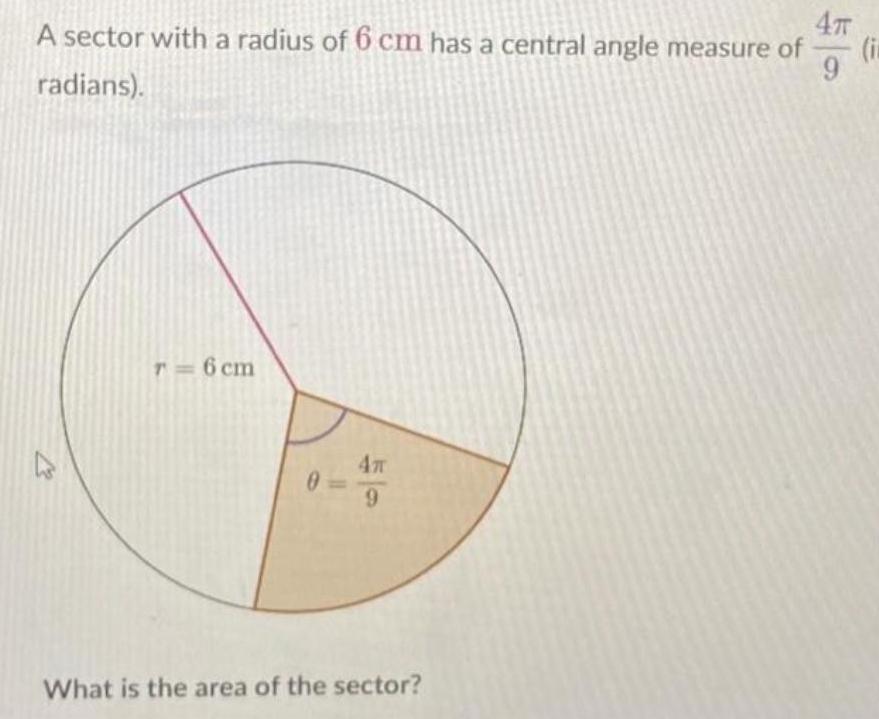
Geometry
Area4T A sector with a radius of 6 cm has a central angle measure of i 9 radians r 6 cm 0 4T 9 What is the area of the sector

Geometry
Area1 What are the similarities and differences between finding the areas of Parallelograms Rectangles and Square BU Font Family AA A E


Geometry
Area9 This shape is BEST described as being a n X 30 10 Find the measures of x y and z y N Z degrees degrees degrees


Geometry
AreaDivide Check your answer If there is a remainder write the remainder over the divisor 2x 3 2x 2 6 x 2

Geometry
AreaQuestion 8 Points 2 Find the slant height of a regular pentagonal pyramid whose length of an edge is 6 cm and lateral surface area is 160 cm O 10 67 cm O 12 85 cm 9 45 cm 18 65 cm

Geometry
AreaFind the volume of the rectangular pyramid whose base is 3 m 6 m and whose height is 5 m 30 m 60 m O 90 m O 10 m

Geometry
Areaesson Posttest Question 1 Points 2 The height of a cylinder is five times its radius Find the surface area of the cylinder if the radius is 5 units O 1007 sq units 2007 sq units O 300 sq units O 4007 sq units


Geometry
AreaOnline Soap20 Tell me what you want to 10 1 Points 1 ormula to find the volume of a cone is O 4 3 r h cubic units O h cubic units 3 r h cubic units O 3 r cubic units

Geometry
AreaPoints 2 3 Cavaliers Part II 1021 1 Ims graderesults com Tell me what you want to do Q dimensions of the cylindrical tank are given in the f Calculate the volume of the cylindrical tank Use 3 14 21 m 1838 84 m 79 56 m

Geometry
AreaGeometric figures in the same plane can be said to relate to each other in several different ways Match the following terms regarding these relationships to their best description Rigid transformations that preserve lengths angle measures parallel lines and distances between points The operation that maps or moves the original figure onto the new figure Uses a line that acts like a mirror between the pre image and the image The operation that uses a fixed point on which to spin the pre image in order to create the new image The relation between two figures that follows this type of notation x a y b Choose Rotation Isometry Translation Transformation Reflection Choose Choose Choose

Geometry
Area15 Find the area of the figure below when the apothem is 8 feet the base is 5 feet and the radius of the circle is 4 feet Answer Apothem Base

Geometry
AreaMatch each figure with a description Descriptions may NOT be used more than once A D R N B E C


Geometry
Area57 find the area of each triangle ABC A 30 50 6 13 00 cm C 112 60 Area of triangle bh formula bn bh 2

Geometry
AreaThe indirect proof is unlike the proofs taught during the beginning chapters of geometry Before you can begin an indirect proof it is important to determine the steps that you will follow Please put the steps of the indirect proof in the correct order from beginning to end 2 3 4 5 Choose Reason logically until you reach a contradiction of a known fact Identify the statement that you want to prove is true Obtain statements that logically follow from your assumption Assume temporarily that the statement is false assume the opposite is true Point out that your assumption must be false and the statement must then be true Choose Choose Choose

Geometry
AreaWhich of the following terms is used to describe the organization s defined goal Mission

Geometry
AreaWhen organizations fail to successfully respond to the needs or concerns of the employees a sub culture will develop which may evolve into a counter culture True False

Geometry
AreaDetermine the measure of ZDAC Claim m DAC 18 degrees Reason Angle DAC is an interior angle formed by two tangents AD and AC so the interior angle has a measure equal to half the difference of the arcs AD and AC intercepts 70 40 18 O Claim m DAC 15 degrees Reason Angle DAC is an interior angle formed by two tangents AD and AC so the interior angle has a measure equal to half the difference of the arcs AD and AC intercepts 70 40 Claim m DAC 18 degrees Reason Angle DAC is an exterior angle formed by two secants AD and AC so the exterior angle has a measure equal to half the difference of the arcs AD and AC intercepts 70 40 18 Claim m DAC 15 degrees Reason Angle DAC is an exterior angle formed by two secants AD and AC so the exterior angle has a measure equal to half the difference of the arcs AD and AC intercepts 70 40 15

Geometry
AreaQuestion 5 Points 3 Which ordered pair indicates the location of Linda s house TY 10 School Linda house O 10 6 O 6 10 O 10 6 O 5 5 10 Mall Beach 10 5 0 5 4

Geometry
Area6 Explain the mathematical process that you would go through to determine the diameter of Phillip e tire A What formula did you use 8 How did you solve to formula to arrive at the answer i U Font Family AAAF E V

Geometry
AreaFind the area of a sector of a circle whose radius is 3 4 cm and whose central angle is 344 degrees 344 O 3 47 sq cm O 34 sq cm 34 7 sq cm

Geometry
AreaFind the area of a sector whose radius is 5 inches and whose central angle is 28 Use 3 14 O4 square inches O 6 10 square inches 3 square inches O 11 square inches

Geometry
AreaQuestion 8 Find the equation of a circle whose center is at 1 2 and radius is 2 units Points 2 O x y 4x 2y 3 0 O x y 2x 4y 2 0 O x y 2x 4y 3 0 O x y 4x 2y 2 0

Geometry
AreaThe grade of a road is its slope written as a percent Find the grade of the road shown 22 feet Find the slope of the line 3 feet OA The slope of the line is m GCLER Select the correct choice below and if necessary fill in the answer box to complete your choice Simplify your answer Type an integer or fraction The grade is Round to one decimal place as neede Ay

Geometry
AreaA College is trying to determine if there is a significant difference in the mean GMAT score of students from different undergraduate backgrounds who apply to the MBA program The accompanying GMAT Sc data comes from a sample of students What conclusion can be reached using ANOVA Click the icon to view the GMAT Scores data Determine the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis Ho H H H3 H at least one mean is different from the others Find the F test statistic F 15 26 Type an integer or decimal rounded to two decimal places as needed Find the p value p Type an integer or decimal rounded to three decimal places as needed GMAT Scores Data GMAT Scores by Undergraduate Major Business Liberal Arts 578 Sciences 593 583 585 583 592 568 567 599 603 593 572 589 562 576 583 570 562 575 571 607 606 582 593 608 592 595 593 604 582 616 588 595 616 585 609 C X

Geometry
Area4 10pts Find the perimeter and the area of the outlined region on the followin geoboard if the unit of measurements is 1 cm Label units accurately P

Geometry
AreaT ARST Exercises 1 6 3 Use Lemma 5 4 3 to form a proportion in which RS is a geometric mean HINT ARVS S

Geometry
Area15 A guy wire 25 ft long supports an antenna at a point that is 20 ft above the base of the antenna How far from the base of the antenna is the guy wire secured 20 ft