Classification of Elements and Periodicity Questions and Answers

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityWhat is the concentration of chloride ions in a solution obtained by mixing 210. mL of 0.500 M potassium chloride (aq) with 260. mL of 0.440 M barium chloride(aq).
![What is the ground-state electron configuration of a neutral atom of titanium?
What is the ground-state electron configuration of the chloride ion CI?
Which element has the following configuration: [Xe]6s²4f75d¹?
Enter the chemical symbol for the element.](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/58975353-1659770536.1293256.jpeg?w=256)
Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityWhat is the ground-state electron configuration of a neutral atom of titanium?
What is the ground-state electron configuration of the chloride ion CI?
Which element has the following configuration: [Xe]6s²4f75d¹?
Enter the chemical symbol for the element.

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityIf exactly 18 moles of propanol (C3H8O) is combusted in the presence of excess oxygen (O₂) for form
carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O), how many moles of water will be produced?
Enter the integer number of moles of H₂O, do not enter the unit.
Hint: Since this problem and two problems below rely on this reaction, make sure you balance this
reaction very carefully on paper as your first step before doing any calculations. The reaction to be
balanced is reaction between C3H8O(l) and O₂(g) to produce CO2(g) and H₂O(l).

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityRank the following items in order of decreasing radius: Na, Na+, and Na

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and Periodicitythe first ionization energy of nitrogen
N(g) + 2e → N² (g)
N(g) + e→N¯(g)
N(g) →N+(g) + e¯
N(g) → N²+(g) + 2e-
N+ (g) → N2²+ (g) + e¯

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityThe concentration of iron in a solution is 0.0400 mg/mL. A new solution is prepared from this solution by diluting 5.00 mL of the original solution to a final volume of 50.00 mL. What is the concentration of iron in the diluted solution?
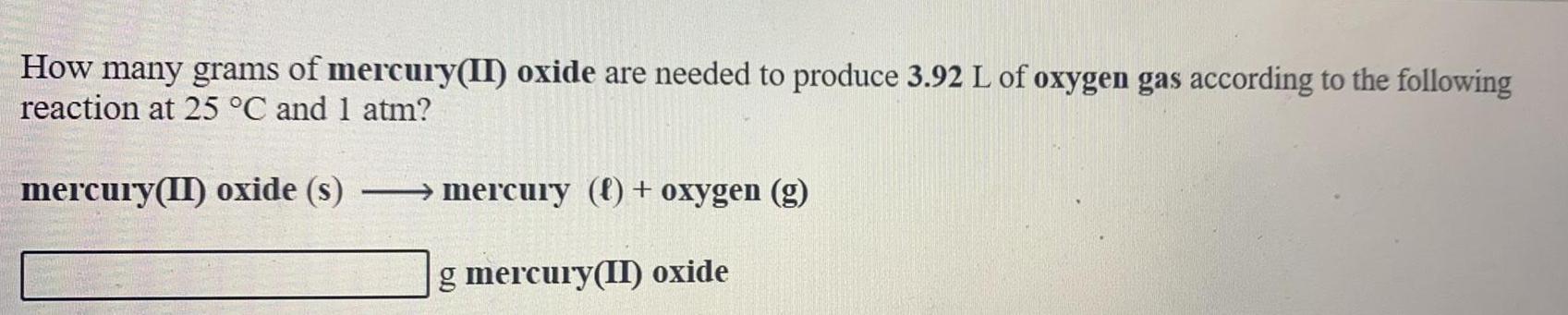
Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityHow many grams of mercury(II) oxide are needed to produce 3.92 L of oxygen gas according to the following reaction at 25 °C and 1 atm?
mercury(II) oxide (s) → mercury (f) + oxygen (g)

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityWhich of the following aqueous solutions contains the lowest amount of ions or molecules dissolved in water?
1.5 L of 0.5 M Na3PO4
500. mL of 0.75 M Nal
500 mL of 2.25 M CH3OH
2.0 L of 2.25 M CuCl₂
1.75 L of 1.25 M HBrO3

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityStrontium-90 is radioactive and has a half life of 28.8 years. Calculate the activity of a 4.9 mg sample of strontium-90. Give your answer in becquerels and in curies

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityPotassium hydrogen phthalate (abbreviated as KHP) has the molecular formula KHC8H4O4 and a molar mass of 204.22 g/mol. KHP has one acidic hydrogen. A solid sample of KHP is dissolved in 50 mL of water and titrated to the equivalence point with 22.90 mL of a 0.5010 M NaOH solution. How many grams of KHP were used in the titration?

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityWhich statement below accurately describes the elements in Group 16 of the Periodic Table as considered from top to bottom?
The atomic radii decrease and the ionization energies increase.
The atomic radii increase and the ionization energies increase.
The atomic radii decrease and the ionization energies decrease.
The atomic radii increase and the ionization energies decrease.

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityA chemist adds 330.0 mL of a 0.319 mol/L sodium nitrate (NaNO3) solution to a reaction flask. Calculate the millimoles of sodium nitrate the chemist has added to the flask. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityA chemist must dilute 52.8 mL of 62.1 µM aqueous mercury(II) iodide (HgI₂) solution until the concentration falls to 14.0 μM. He'll do this by adding distilled water to the solution until it reaches a certain final volume.
Calculate this final volume, in liters. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityConsidering your property drawn Lewis dot structure and what you know about polarity and "like dissolves like", select all of the compounds that are miscible with hexanes, C6H14.
A. N2
B. HF
C. C6H6
D. CH3OH (methanol)
E. CH4
F. SO2
G. CO₂
H. CH₂O
I. NH3
J. Al2O3

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityA student prepared 0.250 mole of what he claimed to be a stable form of CrBr4. Assuming that this compound is stable and soluble, how many equivalents of the cation did the student prepare?
0.500 equivalent
1.00 equivalent
0.125 equivalent
0.750 equivalent
0.250 equivalent

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityUse the standard reaction enthalpies given below to determine ΔH°rxn for the following reaction:
2 NO(g) + O2(g) → 2 NO2(g) ΔH°rxn = ?
Given:
N2(g) + O2(g) → 2 NO(g) ΔH rxn = +183 kJ
1/2 N2(g) + O2(g) → NO2(g) ΔH°rxn = +33 kJ
A) -150. kJ
B) -117 kJ
C) -333 kJ
D) +115 kJ
E) +238 kJ
![Give the ground-state electron configuration for silicon (Si) using noble-gas shorthand.
Express your answer in condensed form as a series of orbitals. For example, [Ar]4s²3d³ would be entered as [Ar] 4s^23d^8.](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/58389943-1659730178.4533637.jpeg?w=256)
Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityGive the ground-state electron configuration for silicon (Si) using noble-gas shorthand.
Express your answer in condensed form as a series of orbitals. For example, [Ar]4s²3d³ would be entered as [Ar] 4s^23d^8.

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityTwo of the types of infrared light, IR-C and IR-A, are both components of sunlight. Their wavelengths range from 3000 to 1,000,000 nm for IR-C and from 700 to 1400 nm for IR-A. Compare the energy of microwaves, IR-C, and IR-A.
Rank from greatest to least energy per photon. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them.

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityThe solubility of calcium hydroxide in water is 0.930 grams per liter. If a calcium hydroxide solution had a concentration of 5.94x10-3 grams per liter, it would be said to be relatively
concentrated
dilute

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityReduction is indicated when there is the
loss of oxygen atoms or gain of hydrogen atoms
gain of oxygen and hydrogen atoms
gain of oxygen atoms or loss of hydrogen atoms
loss of oxygen and hydrogen atoms
I DON'T KNOW YET

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityFill in the blanks.
The forces that connect two hydrogen atoms to an oxygen atom in a water molecule are________, but the forces that hold water molecules close together in an ice cube are _________.
intramolecular, intramolecular
intermolecular, intramolecular
intermolecular, intermolecular
intramolecular, intermolecular

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityIf 0.00858 mol neon gas at a particular temperature and pressure occupies a volume of 168 mL, what volume would 0.00637 mol neon gas occupy under the same conditions?

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityIf the volume of a sample of oxygen gas is 130.1 mL at 749.4 torr and 33.4 °C, what is the volume (in mL) at standard temperature and pressure (STP)?
Do NOT include units in your answer. If you round during your calculation, be sure to keep at least
three (3) decimal places. Report your answer to one (1) decimal place.

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityAqueous hydrobromic acid (HBr) reacts with solid sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to produce aqueous sodium bromide (NaBr) and liquid water (H₂O). If 36.6 g of sodium bromide is produced from the reaction of 72.0 g of hydrobromic acid and 63.0 g of sodium hydroxide, calculate the percent yield of sodium bromide.
Round your answer to 3 significant figures.

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityThe Bohr model explains that the color of the flame is a reflection of the size of electronic
transition that occurs in The cations. Based on your observation, in which metal cation did the
smallest electronic transition occur? Provide a reason for your answer.

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityAccording to the following reaction, how much energy is evolved/released during
the reaction of 32.5 g B2H6 and 72.5 g Cl2? The molar mass of B2H6 is 27.67
g/mol.
B2H6(g) + 6 Cl2(g) --> 2 BCl3(g) + 6 HCl(g) ΔH rxn=-1396 kJ
A) 1640 kJ
B) 238 kJ
C) 1430 kJ
D) 3070 kJ
E) 429 kJ

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityInstructions:
You may use your notes, textbook or other reference sources to complete the assignment.
In order to receive full credit for a question, your answer must be clear, coherent and correct.
The completed assignment is due by 5:00 PM on Thursday, November 4th. See the Chem 115
Blackboard course site for submission details.
1. For the polyatomic anion, NO₂™:
a. Draw the best Lewis structure. Clearly show all bonds, lone pairs, and formal charges.
b. Draw the structure in its proper three-dimensional arrangement. Clearly show all bonds,
lone pairs, and formal charges.
c. Identify the electron geometry of the central atom.

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityHow many milliliters of 6.46 M hydrochloric acid solution should be used to prepare 4.50 L of 0.700 M HCI?
mL

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityA 12.8 g sample of an aqueous solution of nitric acid contains an unknown amount of the acid.
If 20.0 mL of 0.299 M sodium hydroxide are required to neutralize the nitric acid, what is the percent by mass of nitric acid in the mixture?

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityFor the following reaction, 56.3 grams of barium hydroxide are allowed to react with 30.3 grams of sulfuric acid.
barium hydroxide (aq) + sulfuric acid(aq) --> barium sulfate(s) + water(l)
What is the maximum amount of barium sulfate that can be formed?
What is the FORMULA for the limiting reagent?
What amount of the excess reagent remains after the reaction is complete?

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityWhich of the following are conclusions from Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment?
Select all that apply.
Most of the atom's volume is occupied by nearly zero-mass particles.
The nucleus is negatively charged.
The atom's mass is uniformly distributed throughout its volume.
Essentially all of the mass is concentrated in a tiny spot.
Neutral (no charge) particles are found throughout the atom's volume.

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityIsotopes differ in the number of _ inside the nucleus and therefore they differ in _.
Select the choice that correctly fills in the blanks
protons, charge
protons, mass
electrons, charge
electrons, mass
neutrons, mass

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityCalculate ΔE, if a system releases 66.4 kJ of heat to its surroundings while the surroundings do 41.0 kJ of work on the system.
Express your answer in kilojoules using two significant figures.

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityIdentify whether each process is endothermic or exothermic:
1. the process from Part A: q = 0.768 kJ and w = -890 J ;
2. the process from Part B: a system releases 66.4 kJ of heat to its surroundings while the surroundings do 41.0 kJ of work on the system.
Both the processes from Parts A and B are endothermic.
The process from Part A is endothermic and the process from Part B is exothermic.
Both the processes from Parts A and B are exothermic.
The process from Part A is exothermic and the process from Part B is endothermic.
![Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction:
using enthalpies of formation:
2 H₂O₂(l)→ 2 H₂O(l) + O₂(g)
ΔH° ƒ [H₂O2] = −187.8 kJ/mol
ΔH° ƒ [H₂O] = -285.8 kJ/mol
-98.0 kJ
-196.0 kJ
+98.0 kJ
+196.0 kJ
more information needed](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/57555062-1659725045.8898091.jpeg?w=256)
Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityCalculate the enthalpy change for the reaction:
using enthalpies of formation:
2 H₂O₂(l)→ 2 H₂O(l) + O₂(g)
ΔH° ƒ [H₂O2] = −187.8 kJ/mol
ΔH° ƒ [H₂O] = -285.8 kJ/mol
-98.0 kJ
-196.0 kJ
+98.0 kJ
+196.0 kJ
more information needed

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and Periodicity(1) Identify each of the following half-reactions as either an oxidation half-reaction or a reduction half-reaction.
Cr³+ (aq) + 3e- ---> Cr(s)
Mn(s)→ Mn2+ (aq) + 2e-
(2) Write a balanced equation for the overall redox reaction. Use smallest possible integer coefficients.

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityWhen the following equation is balanced properly under basic conditions, what are the coefficients of the species shown?
F- + Br₂-> Br- + F2
Water appears in the balanced equation as a
Which element is reduced?
(reactant, product, neither) with a coefficient of
(Enter 0 for neither.)

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityA raindrop has a mass of 50. mg and the Pacific Ocean has a mass of 7.08 × 10^20 kg.
Use this information to answer the questions below. Be sure your answers have the correct number of significant digits.
What is the mass of 1 mole of raindrops?
Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
How many moles of raindrops are in the Pacific Ocean?
Round your answer to 2 significant digits.

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityHow much energy in kilocalories is lost when a sample 225 mL water cools from 75.0°C to
22.0°C? (Specific Heat Capacity of water is 1.00 cal/g °C or 4.184 J/g°C) Density 1.00 g/mL
(Show your calculations

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityWhat volume of a 0.170 M barium hydroxide solution is required to neutralize 27.3 mL of a 0.141 M perchloric acid solution?
mL barium hydroxide

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicitySolid iron and aqueous magnesium chloride are produced by the reaction of aqueous iron(III) chloride and solid magnesium. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and Periodicity0.29 g sodium iodide reacts with chlorine, producing 0.075 g sodium chloride and some amount of iodine. Find the percent yield of NaCl. Write and balance the equation first. Don't forget diatomics and how to write formulas.

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and Periodicity2.0 liters of ethanol (C₂H6O, density = 0.789 g/mL) combusts with 2.0 kilograms oxygen gas to produce carbon dioxide and water. What is the maximum mass of water than can form? Write the balance equation first.

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicitySilver ion reacts with chloride ion to form the precipitate silver chloride:
Ag+(aq)+C1-(aq) AgCl(s)
After the reaction reached equilibrium, the chemist filtered 99% of the solid silver chloride fromthe solution, hoping to shift the equilibrium to the right, to form more product. Critique the chemist's experiment.

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityNi(OH)₂ + HPbO₂- ---> NiO₂+ Pb+ H₂O+ OH-
In the above redox reaction, use oxidation numbers to identify the element oxidized, the element reduced, the oxidizing
agent and the reducing agent.
name of the element
oxidized:
formula of the oxidizing
agent:
name of the element
reduced:
formula of the reducing
agent:

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityThe oxidation number of H is +1 and of O is -2 in most compounds. Although this statement
applies to most compounds, a few important exceptions occur.
• When H forms a binary compound with a metal, the metal forms a positive ion and H
becomes a hydride ion, H. Thus, in CaH₂ the oxidation number of Ca is +2 (equal to the group
number) and that of H is -1.
Oxygen can have an oxidation number of -1 in a class of compounds called peroxides. For
example, in H₂O₂, hydrogen peroxide, H is assigned its usual oxidation number of +1, and so O
is -1.
The algebraic sum of the oxidation numbers for the atoms in a neutral compound must
be zero; in a polyatomic ion, the sum must be equal to the ion charge. For example, in HCIO,
the H atom is assigned +1 and the O atom is assigned -2. This means the Cl atom must be +7.
a. POCI3
Oxidation number =
b. C₂O42-
Oxidation number =
c. HSO4-
Oxidation number =

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityDetermine the oxidation number of each element in the following:
a. NH3
N:
H:
b. SO32-
S:
O:

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityWhat is the total number of valence electrons in the Lewis structure of SeF2O?
electrons
Draw a Lewis structure for SeF2O.
If the species contains oxygen, do not draw double bonds to oxygen unless they are needed in order for the central atom to obey the octet rule.

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityDetermine the oxidation number for each atom in H3ASO3.
As:
H:
O:

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityPlease complete the following reactions, and show the molecular equation, ionic equation and the net ionic equation for each equation:
6. K3PO4(aq) + Al(NO3)3(aq) →
7. Bel2 (aq) + Cu₂SO4(aq) →
8. Ni(NO3)3(aq) + KBr(aq) →
9. cobalt(III)bromide + potassium sulfide
10. barium nitrate + ammonium phosphate →
11. calcium hydroxide + iron(III) chloride →
12. rubidium fluoride + copper(II)sulfate