Preparation and Properties of Compounds Questions and Answers

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsDichlorobenzene, C6H4Cl2, exists in three forms (isomers), called ortho, meta, and para:
Which of these has a nonzero dipole moment?
Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins.

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsConsider the acid H3PO4. This acid will react with water by the following equation.
H₂PO4 + H₂<=> H₂PO4 + H₂O
What will be true of the resulting conjugate base H₂PO4?
Select the correct answer below:
H₂Pcan act as an acid.
H₂Pcan act as a base.
H₂PO4 can act as an acid or a base.
depends on the substance

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsBenzopyrene is a carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and
None of these responses is correct.
is an anti-carcinogen.
is a breakdown product of pesticides.
forms when certain foods are heated to a high temperature.
is by far the main pollutant produced by automobiles.
can act as a hormone.

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsUse formal charges to determine the best Lewis structure for ethene, C₂H4. Which of the following statements applies to the structure? Select all that apply.
The structure contains one or more double bonds.
Two or more resonance structures are possible.
The central element has an expanded octet.
One or more atoms does NOT follow the octet rule.
The formal charges of all atoms in the compound are all zero.

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsWhich of the following statements explains the correct reasoning for the use of molality (rather than molarity) in this equation?
a) As the temperature of a solution changes, its volume will also change, which will affect its molarity but not its molality.
b) In solutions, moles are not directly related to grams and the boiling point of a solution is dependent solely on the number of grams of solute.
c) The equation was originally published with m as a typo, rather than M, but the values are close enough that the equation is still valid.
d) Molality does not appear in many equations, so it is used here to distinguish this equation from other similar ones.

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsThe ability to see light scattering when passed through a colloidal suspension is known as ...
an emulsifying agent effect.
a particle size scattering effect.
the dispersing effect.
the Tyndall effect.
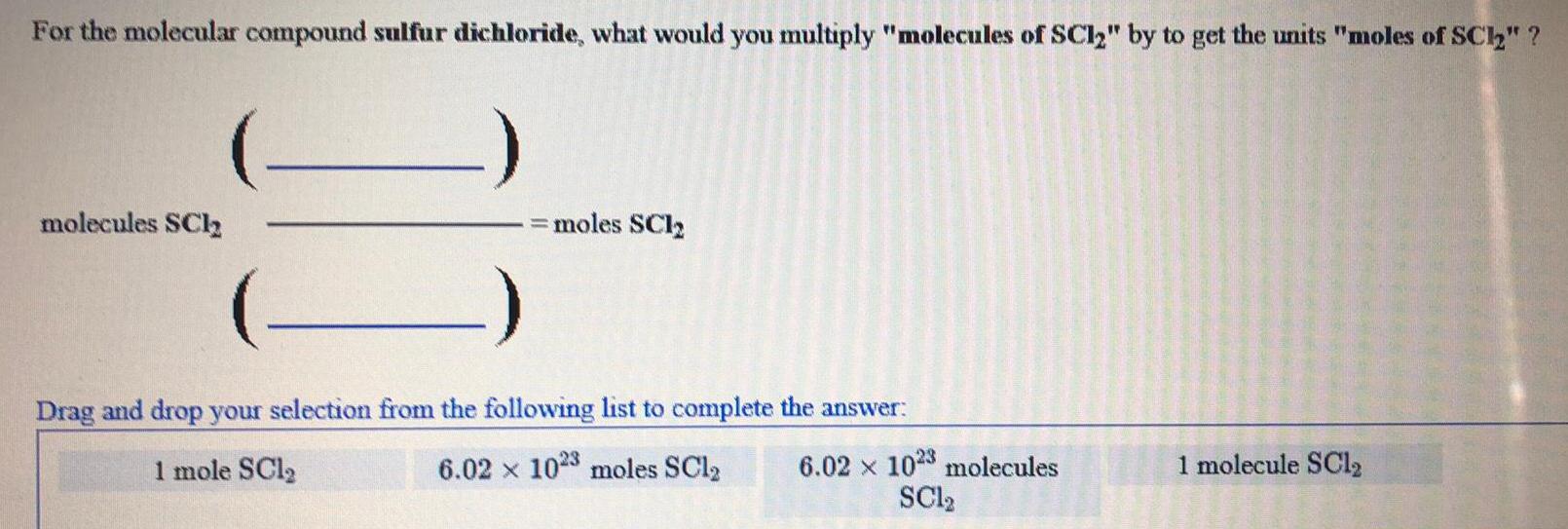
Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsFor the molecular compound sulfur dichloride, what would you multiply "molecules of SC12" by to get the units "moles of SC1₂" ?

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsThe citric acid in a lemon juice sample was neutralized by titration with a NaOH solution.
H3C6H5O7 + 3 NaOH Na3C6H507 + 3 H₂O
If 5.00 mL of lemon juice required 47.8 mL of 0.121 M NaOH for neutralization, what was the molarity of the citric acid in the lemon juice?

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsWhen aluminum, Al, metal is dipped in an aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid, HCl, hydrogen gas, H₂, is produced with the formation of an aluminum chloride, AICI3, solution Write the balanced chemical equation showing the phases of reactants and products

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsAcetylene gas, C₂H₂, used in welders' torches, releases 1300 kJ of heat when 1 mole of C₂H₂ undergoes combustion. Write a balanced equation for the reaction.

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsA chemistry student needs 55.0 mL of pentane for an experiment. By consulting the CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, the student discovers that the density of pentane is 0.626 g cm³. Calculate the mass of pentane the student should weigh out. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsSuppose a group of volunteers is planning to build a park near a local lake. The lake is known to contain low levels of arsenic (As). Therefore, prior to starting construction, the group decides to measure the current level of arsenic in the lake.
If a 14.9 cm³ sample of lake water is found to have 164.5 ng As, what is the concentration of arsenic in the sample in parts per billion (ppb), assuming that the density of the lake water is 1.00 g/cm³?

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsIron metal can be produced by reducing iron(III) oxide with hydrogen as follows:
Fe2O3(s) + 3 H₂(g) -> 2 Fe(s) + 3 H2O(g)
Answer the following questions if the AH = +98.8 kJ and AS° = +141.5 J/K for the above reaction.
(i) Is this reaction spontaneous under standard-state conditions (25 °C)? (Clue: Use the free energy expression,
(ii) At what temperature the reaction can get the equilibrium condition?

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsWhich of the following is NOT true?
The Bronsted-Lowry Model applies to a wider range of acid-base phenomena than does the Arrhenius Model.
The Arrhenius Model of acids and bases was developed before the Bronsted-Lowry Model.
The Bronsted-Lowry Model can apply to bases that do not contain hydroxide ions.
The Arrhenius Model of acids and bases applies toward substances that are nonaqueous.

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsDetermine the theoretical yield and the percent yield if 21.8 g of K₂CO3 is produced from reacting 27.9 g KO2 with 29.0 L of CO2 (at STP). The molar mass of KO2 = 71.10 g/mol and K₂CO3 = 138.21 g/mol.
4 KO2(s) + 2 CO2(g) → 2 K₂CO3(s) + 3 O2(g)
61.0 g. 35.7% yield
179 g. 12.2 % yield
91.7 g. 23.8 % yield
206 g. 10.6 % yield
27.1 g, 80.4 % yield

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsWhich statement about boiling point is FALSE?
The boiling point is higher for compounds with strong intermolecular forces.
The boiling point of a compound is higher for nonvolatile compounds.
The boiling point of a compound is an absolute constant.
The boiling point is higher for compounds with a high viscosity.

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsA coffee cup calorimeter is used to study a reaction. The temperature of the water/solution drops as the reaction takes place.
• Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic?
. Will qsoln be positive or negative?
• Will ΔHrxn be positive or negative?

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsHow many moles of nitrogen are formed when 58.6 g of KNO3 decomposes according to the following
reaction? The molar mass of KNO3 is 101.11 g/mol.
4 KNO3(s) → 2 K₂O(s) + 2 N₂(g) + 5O₂(g)
1.73 mol
0.580 mol
18.5 mol
0.290 mol
0.724 mol

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsWhich of the following statements about crystalline and amorphous solids is TRUE?
An example of an amorphous solid is table salt (NaCl).
An example of a crystalline solid is glass.
A crystalline solid is composed of atoms or molecules arranged with long-range repeating order.
An amorphous solid is composed of atoms or molecules with a majority of its volume empty.

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsIf the solubility of sodium acetate (Molar mass = 82 g/mol) is 76 grams per 100 grams of water, which of the following solutions would be considered supersaturated?
1.2 moles of sodium acetate dissolved in 200 mL of water
8.5 moles of sodium acetate dissolved in 1 L of water
5.5 moles of sodium acetate dissolved in 500 mL of water
1.8 moles of sodium acetate dissolved in 300 mL of water

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsExactly 17.0 mL of a H₂SO4 solution was required to neutralize 45.0 mL of 0.235 M NaOH. What was the concentration of the H₂SO4 solution?
Given: H₂SO4 (aq) + 2NaOH (aq) → 2H₂O(l) + Na₂SO4 (aq)
0.311 M
0.622 M
0.269 M
5.63 M
0.00529 M

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsFor the galvanic cell reaction, expressed below using shorthand notation, what half-
reaction occurs at the cathode?
Zn(s) | Zn2+ (aq) | Cu2+ (aq) | Cu(s)
Zn2+ (aq) + 2 e → Zn(s)
Zn(s) → Zn2+ (aq) + 2 e¯
Cu(s) → Cu2+ (aq) + 2 e¯
Cu2+ (aq) + 2e → Cu(s)

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsA solution contains 100.0 g water, 10.0 g NaCl, and 15.0 g methanol. What is the mass percent of methanol in the solution?
25%
8.00%
10.0%
12.0%
15.0%

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsIn the following reaction,
Mg (s) + Cu2+ (aq) → Mg2+(aq) + Cu (s):
A) Mg is the reducing agent and Cu is the oxidizing agent.
B) Mg2+ is the reducing agent and Cu is the oxidizing agent.
C) Cu is the reducing agent and Mg2+ is the oxidizing agent.
D) Cu2+ is the reducing agent and Mg is the oxidizing agent.
E) Mg is the reducing agent and Cu2+ is the oxidizing agent.
D
C
A
E
B

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsRadioactive isotopes with high atomic numbers often decay to form isotopes that are themselves
radioactive, and once formed, decay to form new isotopes. Sometimes a series of such decays occurs over many steps until a stable nucleus is formed. The following series of decays occurs: Polonium-218 decays with emission of an a particle to form X, which emits a ß particle to form Y, which emits an particle to form Z. Identify X, Y, and Z.
Give all nuclei in the form AZX.
X:
Y:
Z:

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsUse the standard half-cell potentials listed below to calculate the standard cell
potential for the following reaction occurring in an electrochemical cell at 25°C. (The
equation is balanced.)
3 Cl2(g) + 2 Fe(s) →6 CI (aq) + 2 Fe³+ (aq)
Cl2(g) + 2 e 2 E° = +1.36 V
Cl(aq)
Fe³+ (aq) + 3 e¯ → E° = -0.04 V
Fe(s)
+1.40 V
-1.32 V
-1.40 V
+4.16 V
+1.32 V

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsDraw the Lewis structure with the lowest formal charges for NO. Include any nonzero formal
charges and lone pair electrons in the structure.

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsClick in the answer box to activate the palette.
The half-life of thallium-201 is three days. What fraction of thallium-201 is still present in an
individual after twelve days? (Report your answer in fraction format.)

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsMatch the following scientists with their discover/belief.
-Earnest Rutherford
-Niels Bohr
-JJ Thomson
-Democritus
-Werner Heisenberg
-John Dalton
Used the quantum theory to predict that electrons orbit the nucleus of an atom
Proposed atoms are composed of positive and negative charges and believed
that electrons are evenly disbursed within the atom
Proposed different kinds of atoms called elements and stated that atoms cannot
be created or destroyed
Proposed all matter is composed of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms
Discovered the atom's positive charge was in the center (nucleus) of the atom
Believed the exact location of electrons at a given instance to be "uncertain"

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsYOU MUST SUBMIT WORK FOR THIS PROBLEM.
You are conducting Experiment 8: Molar Mass by Vapor Density as directed in the lab manual. You have determined the following. The volume of the flask is 255 mL. The boiling
water temperature is 98.9°C. The barometric pressure is 773.4 mm Hg
A) How will you determine the mass of your sample of gas?
B) If the mass is determined to be 0.630 g. what is the molar mass of the gas?
HELPFUL REFERENCE INFORMATION:
PV = nRT
atm L
R = 0.08206 atm L/mol K
1 atm = 760 mmHg
For the toolbar, press ALT+F10 (PC) or ALT+FN+F10 (Mac).

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsBe sure to answer all parts.
The acid in acid rain is generally sulfuric acid (H₂SO₂). When this rainwater falls on statues
composed of marble (CaCO3), the H₂SO4 slowly dissolves the CaCO3. Write a balanced equation for this acid-base reaction. (Include the phase of the substances.)

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsIf the outside of the flask is not dried after vaporizing the liquid, will the molar mass of
the compound be too high or too low? Explain.

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsWrite the full electron configurations for the following elements.
F
Mg2+
Si
N
P
S²-
K+
Ni
As
Kr

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsIn Experiment 4, you isolate iron(III) hydroxide from the following reaction:
Fe(NO3)3(aq) + 3 NaOH(aq) → Fe(OH)3(s) + 3 NaNO3(aq)
What method was used to isolate this product? Why was this method used?

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsDetermine the pH at the equivalence point of a titration between 50.0 mL of 0.173 M (CH3)2NH solution with 0.173 M HCIO4.

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsIs the calculated sodium hydroxide concentration higher, lower or the same as the actual sodium hydroxide concentration in the flask, if the oxalic acid that was weighed was not completely transferred to the volumetric flask? Explain your answer.

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsA student prepares a dilute solution of sodium hydroxide, NaOH(aq), starting with 6 M so- dium hydroxide. She then titrates a 1.372 g sample of KHP with the dilute sodium hydroxide solution, NaOH(aq), to a phenolphthalein end point. If the titration required 21.84 mL of sodium hydroxide, NaOH(aq), calculate the molar concentration of the sodium hydroxide solution, NaOH(aq). (Remember that KHP is potassium hydrogen phthalate, KHC,H,O, NOT potassium hydrogen phosphorus!)

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsWhich of the following statements is/are true for a compound AX4, where A has 6 valence electrons
and X has 7 valence electrons?
a) The Lewis structure cannot be drawn without violating the octet rule.
b) The central atom, A, has 4 bonding and 2 non-bonding electron pairs around it.
c) In order to create a valid Lewis structure, it must contain at least one double bond.

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsWhat is the total number of moles of products involved in the following reaction?
CaCO3 (s) + 2HCI (aq) → CaCl₂ (aq) + CO₂ (g) + H₂O(g)
6
2
3
5

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsA. What is the hybridization of the central atom in AlBr3?
Hybridization =
What are the approximate bond angles in this substance?
Bond angles =
B. What is the hybridization of the central atom in SiH4?
Hybridization =
What are the approximate bond angles in this substance?
Bond angles =

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsAn FM radio station broadcasts at 93.8 MHz. Calculate the wavelength of the corresponding radio waves.
Wavelength= m

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsJupiter's moon lo was discovered to have high concentrations of sulfur oxides in its atmosphere. This, in combination with research into sulfur oxides relating to pollution on Earth, has led to renewed interest in sulfur oxide compounds. One compound discovered on lo was the blue disulfur trioxide. Write the chemical formula for this compound Express your answer as a chemical formula.

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsHow many electrons can be contained in all of the orbitals with n = 4?
2
32
18
8
10

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsWhich of the following is an incorrect designation for an atomic orbital?
6s
3d
4f
1s
1p

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsA local FM radio station broadcasts at a frequency of 97.8 MHz.
Calculate the energy of the frequency at which it is broadcasting.
Energy = 5.8x10^14 kJ/photon
(1 MHz = 10 6 sec-¹)

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsCalculate the energy of an electron in the n = 7 level of a hydrogen atom.
Energy = J

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsHow many electrons in an atom can have the following designations?
1p:
5p
5 f:
5px
2p
n = 2:

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsThe absorption spectrum of sodium has a line at 589 nm. What is the energy of this line? (The speed of light in a vacuum is 3.00 x 10^8 m/s, and Planck's constant is 6.626 x 10^-34 J.s.)
A. 3.37 10^-19 J
B. 2.96 10^18 J
C. 8.89 x 10^26 J
D. 5.09 x 10^14 J

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsOrder the following species with respect to carbon-oxygen bond length (longest to shortest).
CO, CO₂, CO2^-2, CH3OH
What is the order from the weakest to the strongest carbon-oxygen bond? (CH3OH exists as H3 C - OH.)
(Express your answers as chemical formulas separated by a comma.)
From longest to shortest C- O bond:_____
From weakest to strongest C- O bond:_____

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsWhat is the wavelength of light with 5.53 x 10^-19 J of energy? (The speed of light in a vacuum is 3.00 x 10^8 m/s, and Planck's constant is 6.626 × 10^-34 J.s.)
A. 399 nm
B. 278 nm
C. 359 nm
D. 250 nm