Algebra Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.

Algebra
Quadratic equationsK Graph the function y 3 cos Choose the correct graph of the function O A Give the period and the amplitude 5 B 5 BICECHO OC 0 OD of

Algebra
Quadratic equationsy cos x Which of the following is the correct graph of the function y cos x OA 2 Give the amplitude 2 O B 2x Q G CO O C Ay O D 2 G

Algebra
Quadratic equationsGraph the following function over the interval 2x 2x Give the amplitude y 4sin x Which of the following is the correct graph of the function y 4sin x SOA OB Ay Q Q O C Ay O D

Algebra
Quadratic equationsGraph the following function over a two period interval Give the period and the amplitude 1 y cos x What is the period of the function y cos x HOLLA Simplify your answer Type an exact answer using as needed Use integers or fractions for any numbers in the express

Algebra
Quadratic equationsQuestion 1 4 1 1 Complete the sentence below The amplitude of the graphs of the sine and cosine functions is Type exact answers using as needed HW Score 0 0 of 14 points O Points 0 of 1 and the period of each is

Algebra
Complex numbersPoints 0 of 1 Complete the sentence below The domain of both the sine and cosine functions is and the range is Type your answers in interval notation Type exact answers using as needed

Algebra
Complex numbersDetermine the amplitude of the function y 4 cos x Also choose its graph The amplitude is
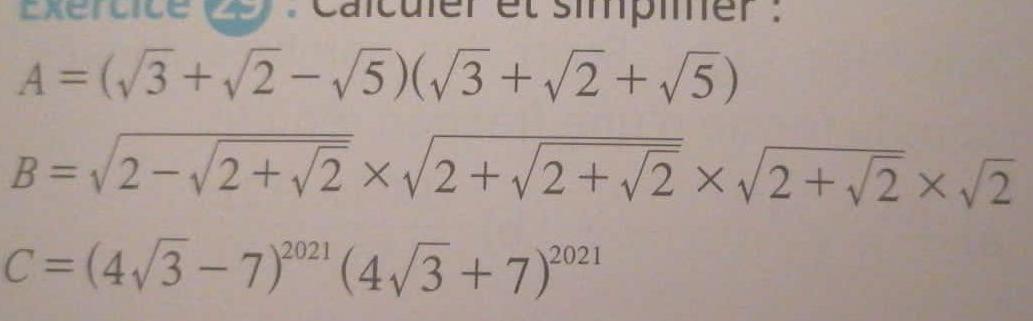

Algebra
Quadratic equationsLinear Inequalities Sketch the graph of each Bacar inequality 1 A 8 Z D here to search 2 27 C D


Algebra
Sequences & Series3 Write the equation of the line that passes through the point 4 3 and is PERPENDICULAR to the line y 2x 4



Algebra
Quadratic equations2 Write the equation of the line that passes through the point 3 1 and is PARALLEL to the line x 3y 9

Algebra
Quadratic equationsWrite the slope of the line that passes through the given points 4 y 3 x 5 A y x 7 1 B y 47 1747 7 4 y x D y x Write the slope intercept form of the equation of the line through the given points 5 through 5 4 and 2 2 A y 6x 2 C y 2x 6 B y 3x 2 D y 2x 3

Algebra
Quadratic equations1 2 EXTRA CREDIT for SUM 3 01 Determine the slope of the line represented by the equation 1 75 15y 12x Write the slope of the line that passes through the given points 2 through 3 2 and 0 5

Algebra
Complex numbersClearly A A a b 1 1 a b 1 H H G G A A H H H H Also 3ab 1 1 1 1 1 4 2006 H H 2a b and 2 1 3 b A A H H H H a b A A H H ab G G 1 3ab a b 3ab 2a a 1 2b a 2a b 2b a 2a b 9ab Let P n 25 1 24 n 5735 For n 1 P 1 625 24 5735 6336 24 x 11 which is divisible by 242 Hence P 1 Is true Let P K be the true where K 2 1 25 1 24 K 5735 24 2 where AEN For n k 1 P K 1 25 2 24 K 5735 25 25 1 24 K 5735 25 24 K 25 5735 5735 24 K 1 25 24 2 24 2K 5735 24 24 25 24 24 2 K 24 5736 25 24 24 K 24 239 24 25 K 230 which is divisible by 24 2 Hence by the method of mathematical Induction result is true vne N

Algebra
Matrices & Determinants1 2 3 n 1 division of vernier scale n division of main scale 5 one Vemier division n 1 main scale division 1 Least count 1 M S D 1 V D n 1M S D n 1M S adding i and ii Mg V For an object placed at infinity the image after first refraction will be formed at v 462 462 by R 1 The image after second refraction will be found at H3 H2 H3 H2 V V R HgR bbg jy R Therefore focal length will be s Hy 2 1 Rhc 7 2 hv 2 1 3RC SOLUTIONS Mg py R Z 42 Loss in K E of the gas where n number of moles If its temperature change by AT Then n RAT nm v mv AT 3R V v sincsti v cos cxtj n 1 AE nm f

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsTwo narrow cylindrical pipes A and B have the same length Pipe A is open at both ends and is filled with a monoatomic gas of molar mass M Pipe B is open at opne end and closed at the other end and is filled with a diatomic gas of molar mass M Both gases are at the same temperature a If the frequency of the second harmonic of the fundamental mode in Pipe Als equal to the frequency of the third harmonic of the fundamental mode in pipe B determine the value of M MB b Now the opeen end to pipe B is also closed so that the pipe is closed at both ends Find the ratio of the fundamental frequency in pipe A to that in pipe B 3 2 A cubical box of side 1 meter contains hellum gas atomic weight 4 at a pressure of 100N m During an observation time of 1 second an atom travelling with the root mean square speed parallel to one of the edges of the cube was found to make 500 hits with a particular wall wolthout any collision with other atoms Take R J mol K andk 1 38x10 J K a Evaluate the temperature of the gas b Evaluate the average kinetic energy per atom c Evaluate the total mass of helulm gas in the box A uniform solld cylinder of density 0 8 g cm floats in equilibrium in a combination of two non mixing liquids A and B with its axis vertical The densities of the liquids A and B are 0 7 g cm and 1 2 g cm respectively The height of liquid A is h 1 2 cm The length of the part of the cylinder Immersed in liquid B Ish 0 8 cm a Find the total force exerted by liquid A on the cylinder air A thin uniform wire AB of length 1m an unknown resistance X and a resistance of 1202 are connected by thick conducting strips as shown in A B 2 1 2 b Find h the length of the part of teh cylinder in air c The cylinder is depressed in such a way that is top surface is just below the upper surface of liquid A and is then released Find the acceleration of the cylinder immediately after it is released 1 2 2 ha 120

Algebra
Matrices & Determinants10 A proton and an alpha particle after being accelerated through same potential difference enter a uniform magnetic field the direction of which is perpendicular to their velocities Find the ratio of radii of the circular paths of the two particles 1 A solid sphere of radius R is floating in a liquid of density p with half of its volume submerged If the sphere is slightly pushed and released it starts performing simple harmonic motion Find the frequency of these oscillations 12 An object is approaching a thin convex lens of focal length 0 3 m with a speed of 0 01 m s Find the magnitudes of the rates of change of position and lateral magnification of image when the object is at a distance of 0 4 m from the lens 13 Draw the circuit for experimental verification of Ohm s using a source of variable D C voltage a main resistance of 10022 two galvanometers and two resistances of values 10 and 10 respectively Clearly show the positions of the voltmeter and the ammeter 14 A cube of coefficient of linear expansion a is floating in a bath containing a liquid of coefficient of volume expansiony When the temperature is raised by AT the depth upto which the cube is submerged in the liquid remains the same Find the relation between o and Y showing all the steps 15 One end of a rod of length L and cross sectional area A is kept in a fumace of temperature T The other end of the rod is kept at a temperature T The thermal conductivity of the material of the rod is K and emissivity of the rod is e It is given that T T AT where AT T T being the temperature of the surroundings If AT T T find the proportionality constant Consider that heat is lost only by radiation at the end where the temperature of the rod is T 16 Two blocks A and B of equal masses are released from an inclined plane of inclination 45 at t 0 Both the blocks are initially at rest The coefficient of kinetic friction between block A and the inclined plane is 02 while it is 19 In the circuit shown A and B are two cells of same emf E but different internal resistances r and r r r respectively Find the value of R such that the potential difference across the terminals of cell A is zero a long time after the key K is closed Pumace 0 3 for block B Initially the block A is 2m behind the block B When and where their front faces will come in a line Take g 10 m s 17 Wavelengths belonging to Balmer series lying in the range of 450 nm to 750 nm were used to eject photoelectrons from a metal surface whose work function is 2 0 eV Find in eV the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons Take hc 1242 eV nm 18 In a Young s double slit experiment two wavelengths of 500 nm and 700 nm were used What is the minimum distance from the central maximum where their maximas coincide again Take D d 10 Symbols have their usual meanings minumay 0 In a LR series circuit a sinusoidal voltage V V sin oot is applied VA It is given that L 35mH R 112 V V 220V 00 2m 50Hz and 1121 Mo anhyd 1 06 Lenina OPCHR
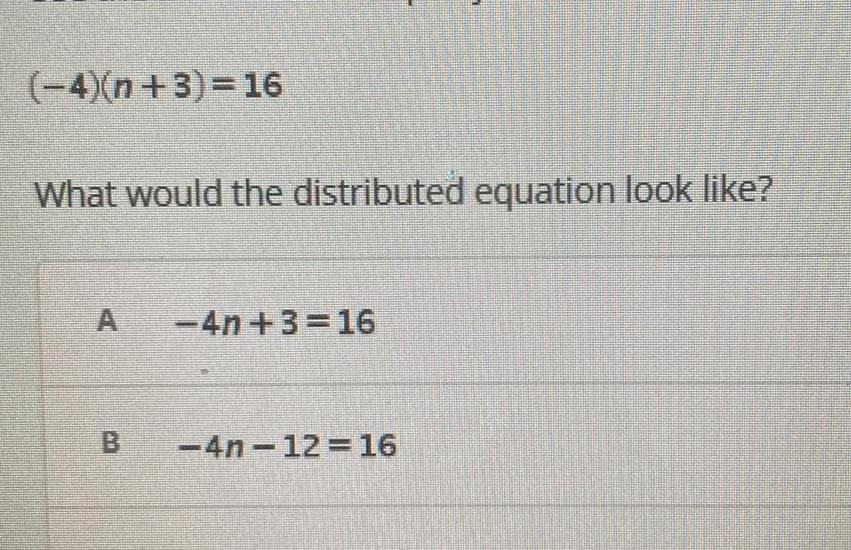
Algebra
Permutations and Combinations4 n 3 16 What would the distributed equation look like 4n 3 16 4n 12 16

Algebra
Sequences & Series7 4 points Determine whether the following are functions simply answer yes or no 1 2 2 2 3 2 a b

Algebra
Sequences & Series3 4 Across 4 A number that can be written a b where a and b are integers and b is not equal to numbers in decimal form are terminating or repeating zero 5 The numbers 3 2 1 0 1 2 3 consisting of the negative integers zero and positive integers are known as 6 Down 1 numbers start with the number zero ex 0 1 2 3 4 5 numbers are also known as natural numbers ex 1 2 3 4 5 2 all numbers on the number line 3 A number that cannot be written as the quotient of two integers The decimal form number neither terminates nor repeats of an

Algebra
Quadratic equationsFrom the data given it is clear that 1 Rate is independent of B because on doubling the initial concentration of B alone the initi rate remains unaffected while it is doubled when initial concentration of A is doubled ii Secondly data also suggest us that initial conc of A and initial rate have direct relationship The above findings can be checked as Let the order with respect to A and B are m and n then Rate K A B Now for A 0 05 k 0 11 0 1 0 1 K 0 2 0 1 CHEMISTRY Now comparing 1 and 2 we get Secondly for B 2 2 or m 1 0 05 k 0 1 0 1 0 05 k 0 1 0 2 Now comparing 1 and 2 we get 1 2 or Hence rate equation for the reaction is Rate k A BP Rate k A B 0 1 k 0 2 0 11 k 0 2 0 1 0 2 k hence AU q W For adiabatic process q 0 hence AU W and so Hence Now 0 5 sec n 0 W p AV P V V AU 100 99 100 100 1 AU 100 bar ml AH AU A PV Here AU already calculated above and APV P V PV So AH 100 100x99 1x100 9900 bar ml The shape of XeF is square planar or square pyramidal and structure is octahedral with sp d hybridisation The molecule looks like Structure and shape of OSF is irregular trigonal bipyramidal with less e o

Algebra
Permutations and CombinationsSolve each equation Describe the number of solutions one none or infinitely many 13 3x1 11 12 5x 4 8 5x 37443815X

Algebra
Matrices & Determinants2 1 ol On solving the lines we get S R points S 2 k k R k k Two lines intersect at Q 1 1 1 2 ol Solutions to IIT JEE 2005 Mains Paper Memory based Mathematics A line passes through the point P h k is parallel to the x axis It forms a triangle with the lines y x x y 2 of area 4h then find the locus of P 1 3 Area of the AQRS x2 k 1 QS QR SR 4h k 1 locus is the pair of straight lines A cricket player in his career plays n match and scores total no of If he scores k 2 runs in k match where 1 k n Find n Let S be the total scores in his career plays n matches S 241 SO n 20 1 n 1 8 But S 2 1 2 n as given 2 2 n 2 2 n 2 so n 7 Ans 4x y 1 Ans 22 4 2n 22 2n 4 n 1x2 n 2 4 runs 132 21 9 9 probability that he is reaching office late if he takes car scooter bus or train is probability that he has travelled by car if he reaches office in time Ramesh goes to office either by car scooter bus or train probability of which being and respectively and 2 40 and respectively Find the 2

Algebra
Matrices & Determinants1 MATHEMATICS Find the centre and radius of the circle formed by all the points represented by z x iy satisfyin k k 1 where a and are constant complex numbers given b the relation z BI a a B B iB 2 If 5 6 6 4 are four distinct vectors satisfying the conditions axb xd and ax bxd then prov that ab cd c bd 3 is an integer where n is a positive integer 4 If M is a 3x3 matrix where M M I and det M 1 then prove that det M 1 0 Using permutation or otherwise prove that 5 If y x 3 116 cosx cos 1 sin 8 that 0 de then find lin 7 If f 1 1 R and f 0 dy 5 T is a parallelopiped in which A B C and D are vertices of one face And the face just above has corresponding vertices A B C D T is now compressed to S with face ABCD remaining sam and A B C D shifted to A B C D in S The volume of parallelopiped S is reduced to 90 of T Prove that locus of A is a plane af and f 0 0 Find the value of 1 a 1 cos give n at x x EG If P x 51x 2323x45x 1035 using Rolle s theorem prove that atleast one root lie between 451 100 46 9 A plane is parallel to two lines whose direction ratios are 1 0 1 and 1 1 0 and it contain the point 1 1 1 If it cuts co ordinate axis at A B C Then find the volume of the tetrahedro OABC 10 If A and B are two independent events prove that P AUB P AB SP C where C is an ever defined that exactly one of A and B occurs x 1 y 3 11 A curve passes through 2 0 and the slope of tangent at point P x y equals the equation of the curve and area enclosed by the curve and the x axis in the fourth quadrant 12 A circle touches the line 2x 3y 1 0 at the point 1 1 and is orthogonal to the circle whic has the line segment having end points 0 1 and 2 3 as the diameter
Algebra
Sequences & Series1 litre water 1kg i e 1000 g water d 1000 kg m 1000 18 55 55 moles of water So molarity of water 55 55M Cir Ceme Cav CES PC BrFs H C 3RT M Ph 3RT M M 8RT 1 085 x C 1 085 400 434 ms Ziggler Natta catalyst RAI TICI Oxygen atom of diethyl ether by donation of its lone pair to vacant 3p orbitals of Al anhydrous AICI solvates it more compared to hydrous AICI sp d sp d 8RT M 3A Racemic mixture 1 085 X X COOH Trigonal bipyramid Square pyramidal HE Ph H C2 4 Ph H C The bonds attached to the chiral carbon in both the molecules are not broken during the esterification reaction Acid reacts with alcohol to give an ester while acid reacts with alcohol to give ester These two esters are diastereoisomers Ru is a constant and transition remaining the same

Algebra
Matrices & DeterminantsPhysics If n division of main scale coincides with n 1 divisions of vernier scale Given one main scale division is equal to a units Find the least count of the vernier Find the focal length of the lens shown in the figure The radii of curvature of both the surfaces are equal to R A particle of mass m moving in a circular path of radius R with a constant speed v is located at point 2R 0 at time t 0 and a man starts moving with a velocity v along the ve y axis from origin at time t 0 Calculate the linear momentum of the particle w r t the man as a function of time Hi H H Frequency of a photon emitted due to transition of electron of a certain element from L to K shell is found to be 4 2 x 10 Hz Using Moseley s law find the atomic number of the element given that the Rydberg s constant R 1 1 x 10 m R An insulated container containing mono atomic gas of molar mass m is moving with a velocity ve If the container is suddenly stopped find the change in temperature How a battery is to be connected so that the shown rheostat will behave like a potential divider Also indicate the points about which output can be taken Charges q and q are located at the corners of a cube of side a as shown in the figure Find the work done to separate the charges to infinite distance He H He A tuning fork of frequency 480 Hz resonates with a tube closed at one end of length 18 cm and diameter 5 cm in fundamental mode Calculate velocity of sound in air D ww R 44 A radioactive sample emits n 8 particles in 2 sec In next 2 sec it emits 0 75 n particle what is the mean life of the sample In a photoelectric experiment set up photons of energy 5 eV falls on the cathode having work function 3 eV a If the saturation current is i 4 A for intensity 10 W m then plot a graph between anode potential and current h Also draw a graph


Algebra
Complex numbers15 8 points Find BOTH f g x and g f x to verify the pair of given functions are inverses f x x 3 and g x x 3

Algebra
Quadratic equations2 8 points Solve for x 2x 13 1 x 3 6 points Solve for x Express your answer using interval notation 2 3 r 4 5r 9

Algebra
Quadratic equations3x 8216 5 6 points Find the domain and range of the function f x defined by the graph to the right Domain Range a Domain b 432A Range ATH 6 4 points Identify the domain and the range of the function defined by f 1 2 2 2 5 0 3 2 11 2 12345 7 4 points Determine whether the following are functions simply answer yes or no 1 2 2 2 3 2 X
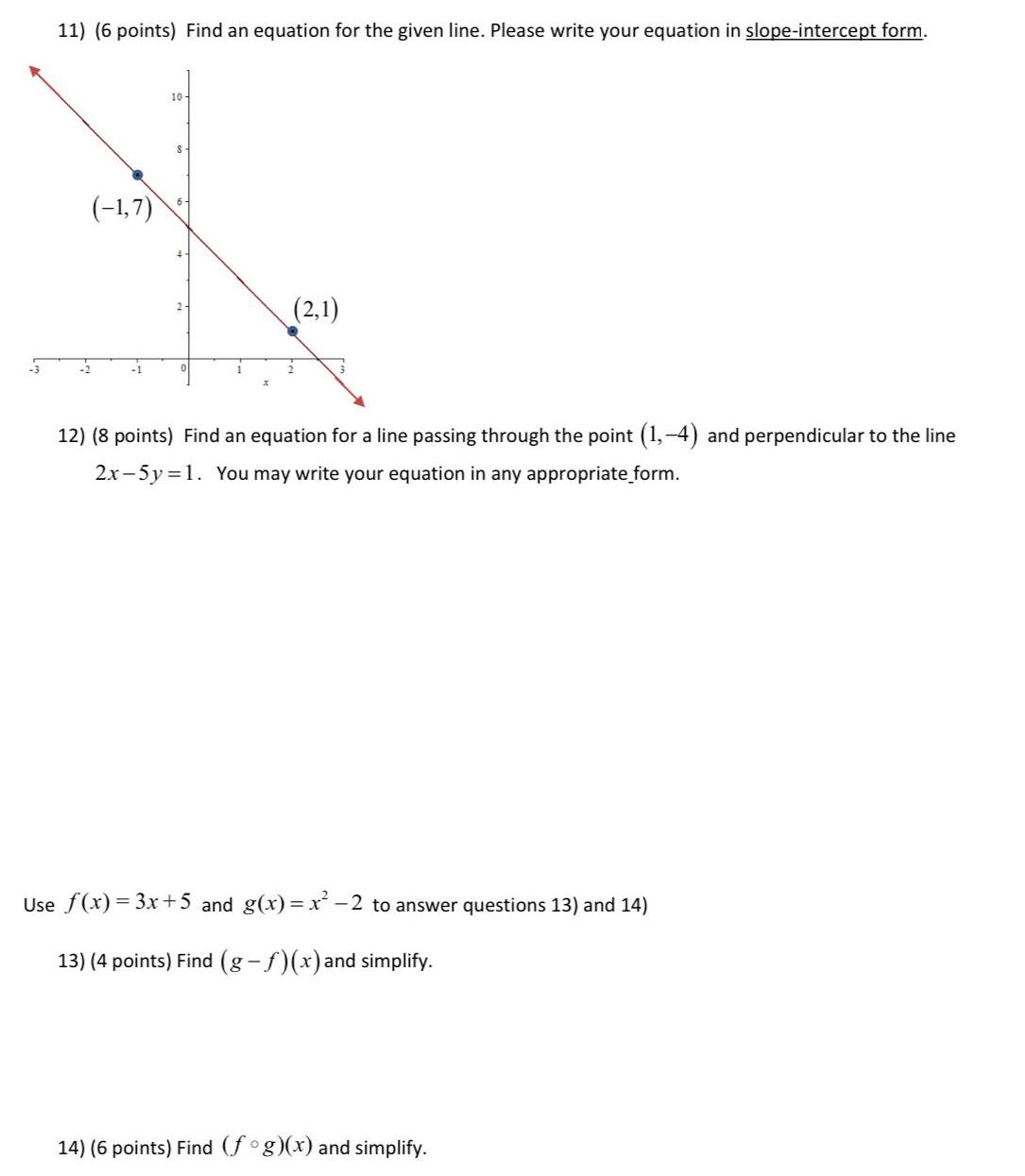
Algebra
Sequences & Series3 11 6 points Find an equation for the given line Please write your equation in slope intercept form 1 7 10 S 2 1 12 8 points Find an equation for a line passing through the point 1 4 and perpendicular to the line 2x 5y 1 You may write your equation in any appropriate form Use f x 3x 5 and g x x 2 to answer questions 13 and 14 13 4 points Find g f x and simplify 14 6 points Find fog x and simplify

Algebra
Quadratic equationsWhat is the domain of the function distance from post in feet 9 5 3 2 Nour answer 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 time in seconds


Algebra
Quadratic equations5 5 y2 8x 4 A B C D 6 14 22 6 4 6 44 2 y y y 2 4 0 x 2 4 x 6 7 6 y x 3 A B C D 6 6 16 1 A 21 44 2 AV y V 4 x x X

Algebra
Complex numbersDetermine if the vectors are linearly independent 6 12 Select the correct choice below and if necessary fill in the answer box to complete your choice A The vectors are linearly independent because the vector equation x v X V 0 has only the trivial so OB The vectors are not linearly independent because if c and C 1 both not zero then c v

Algebra
Quadratic equations1 ity Solutions Linear Inequalit Determine which point or points are solutions of each linear inequality gfiven 2 3x 5y 10 1 x y 3 6 54 3 2 1 3 y 2 5 615 4 3 2 1 Ay y 6 x X 2 4 6 5 4 3 2 1 4 5x 2y 10 6 4 3 2 1 4 V y 6 x 6 x

Algebra
Complex numbersEXTRA CREDIT for SUM 3 Q1 Determine the slope of the line represented by the equation 1 75 15y12x Write the slope of the line that passes through the given points 2 through 3 2 and 0 5 B Write the point slope form of the equation of the line that passes through the given points 3 through 3 1 and 1 1 A y 3 x 1 B y 3 x 1 2 C y 3 2 x 1 D y 1 1 x 3 Write the slope of the line that passes through the given points 4 y 3 x 5 4 7 A y x 7t 1 B y x 7 4 C y x 4 D y x All rights reserved 1 1 1 7 Write the slope intercept form of the equation of the line through the given points 5 through 5 4 and 2 2

Algebra
Quadratic equationsFind the difference quotient f x x 3x f x h f x x h 3 x h x 3x h 2xh h 3h h f x h f x h 2xh h 3 3h 7 3x h h 2x h 3 h 2x h 3 h f x x 2x 2

Algebra
Quadratic equationsame PopQuiz 3 Prof Rudy Meangru Use the definition of derivative f x lim f x h f x to find f x h 0 h f x x 2x
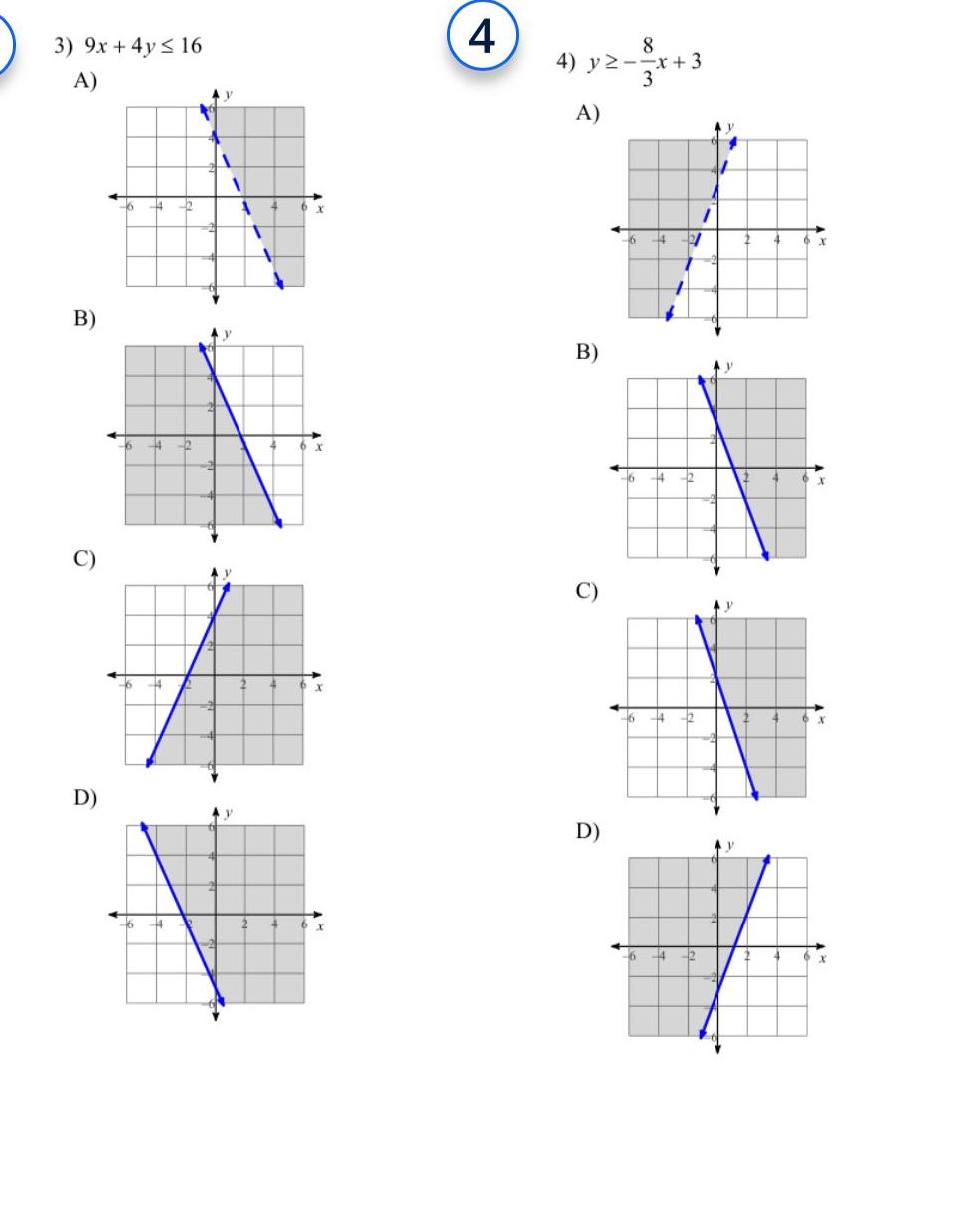
Algebra
Sequences & Series3 9x 4y 16 A B C D 16 H 2 6 4 16 44 4 22 y 1 y y T 4 4 x 4 8 4 y x 3 3 A B C D 6 4 2 6 6 6 2 2 2 4 12 1 y V y 2 4 4 X X

Algebra
Quadratic equations1 Given 4x 7 3x 7 28 find 2 Given 5 x 1 2 2x 3 17 find 6x 9 3 Given 2p 2 8p 8 5p find 3p 4 Solve the equation and justify each step 3 6x4 24 5 Write the steps to solve the following equation 2x 7 5
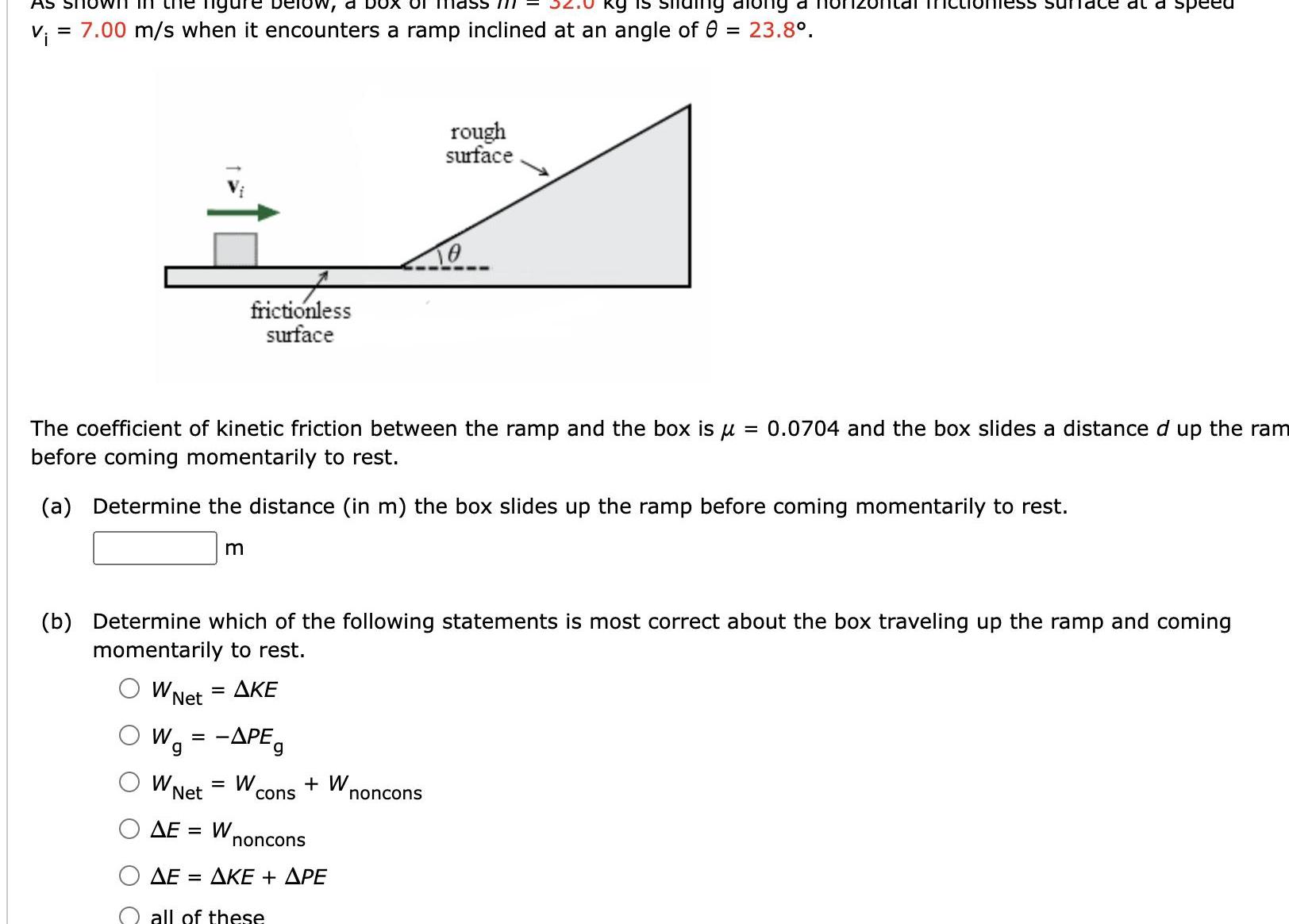
Algebra
Sequences & SeriesAS SI Tigure below a O 1112 kg is ng along a v 7 00 m s when it encounters a ramp inclined at an angle of 8 23 8 W Net Wa The coefficient of kinetic friction between the ramp and the box is 0 0704 and the box slides a distance d up the ram before coming momentarily to rest a Determine the distance in m the box slides up the ramp before coming momentarily to rest m W frictionless surface b Determine which of the following statements is most correct about the box traveling up the ramp and coming momentarily to rest AKE 1 APEg W Net AE W cons W noncons AKE APE AE all of these rough surface ess sun noncons ce at a speed

Algebra
Sequences & Seriesind the horizontal and vertical asymptotes of the curve You may want to use a graphing calculator or computer to heck your work by graphing the curve and estimating the asymptotes Enter your answers as comma separated list Fan answer does not exist enter DNE f x 6ex ex 5

Algebra
Quadratic equations9 Suppose a b means ab a b For example 3 5 3 5 3 5 17 Now if 4 x 36 then what number is x If you can find the answer show how you found it

Algebra
Sequences & Series1 point If a ball is thrown straight up into the air with an initial velocity of 95 ft s it height in feet after t second is given by y 95t 16t2 Find the average velocity for the time period begining when t 2 and lasting 1 0 1 seconds 29 4 ii 0 01 seconds 162 84 iii 0 001 seconds 125 984 Finally based on the above results guess what the instantaneous velocity of the ball is when t 2 125 984

Algebra
Complex numbersConsider the multivariate function f x y z 2x y z subject to x y z 1 and x2 2y 1 Find all the extreme values of f ii Find and classify all the critical points of f x y x3 y3 3x2 6y2 1
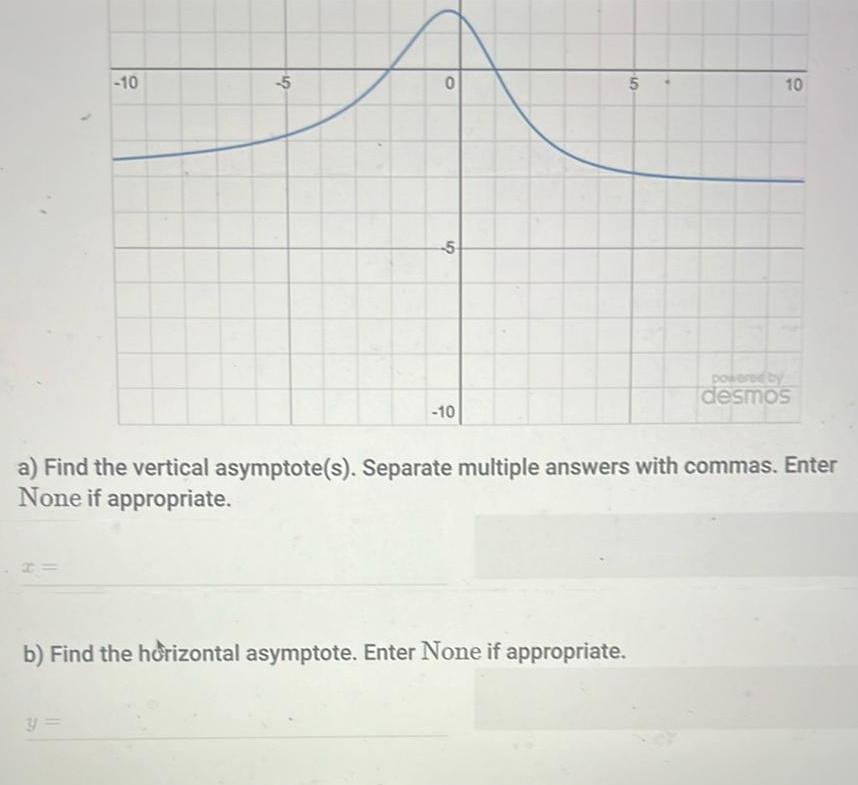
Algebra
Sequences & Series10 5 0 5 10 5 10 b Find the horizontal asymptote Enter None if appropriate powered by desmos a Find the vertical asymptote s Separate multiple answers with commas Enter None if appropriate