Inorganic Chemistry Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.
![What is the ground-state electron configuration of a neutral atom of titanium?
What is the ground-state electron configuration of the chloride ion CI?
Which element has the following configuration: [Xe]6s²4f75d¹?
Enter the chemical symbol for the element.](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/58975353-1659770536.1293256.jpeg?w=256)
Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityWhat is the ground-state electron configuration of a neutral atom of titanium?
What is the ground-state electron configuration of the chloride ion CI?
Which element has the following configuration: [Xe]6s²4f75d¹?
Enter the chemical symbol for the element.
![A neutral atom has the following electron configuration:
[Ne] 3s²3 p²
What is the chemical symbol for the atom?
How many electrons does the atom have?
How many 3p electrons are in the atom?](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/59052705-1659770513.049632.jpeg?w=256)
Inorganic Chemistry
P Block - Group 14A neutral atom has the following electron configuration:
[Ne] 3s²3 p²
What is the chemical symbol for the atom?
How many electrons does the atom have?
How many 3p electrons are in the atom?

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsA 0.7011-g mixture of sodium chloride and sodium nitrate is completely dissolved in water. When silver nitrate is added to the solution, 0.9805 g of solid precipitate. What is the percent by mass of chloride in the initial mixture?
34.59%
71.50%
65.41 %
28.50 %
13.99 %

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsNitrogen monoxide is a pollutant commonly found in smokestack emissions. One way to remove it is to react it with ammonia.
4NH3(g) + 6NO(g) → 5N₂(g) + 6H₂O(l)
How many liters of ammonia are required to change 49.6 L of nitrogen monoxide to nitrogen gas? Assume 100% yield and that all gases are measured at the same temperature and pressure.

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityIf exactly 18 moles of propanol (C3H8O) is combusted in the presence of excess oxygen (O₂) for form
carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O), how many moles of water will be produced?
Enter the integer number of moles of H₂O, do not enter the unit.
Hint: Since this problem and two problems below rely on this reaction, make sure you balance this
reaction very carefully on paper as your first step before doing any calculations. The reaction to be
balanced is reaction between C3H8O(l) and O₂(g) to produce CO2(g) and H₂O(l).

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsA compound has the empirical formula CHI. A 256-mL flask, at 373 K and 750. torr, contains 2.31 g of the gaseous compound. Give the molecular formula.

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityRank the following items in order of decreasing radius: Na, Na+, and Na

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and Periodicitythe first ionization energy of nitrogen
N(g) + 2e → N² (g)
N(g) + e→N¯(g)
N(g) →N+(g) + e¯
N(g) → N²+(g) + 2e-
N+ (g) → N2²+ (g) + e¯

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsA 1.25 mol sample of neon gas occupies a volume of _____L at STP.

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityThe concentration of iron in a solution is 0.0400 mg/mL. A new solution is prepared from this solution by diluting 5.00 mL of the original solution to a final volume of 50.00 mL. What is the concentration of iron in the diluted solution?

Inorganic Chemistry
P Block - Group 16Rank the following ions in order of decreasing radius: 02-S2,Se².Te², and Po2. Use the periodic table as necessary.
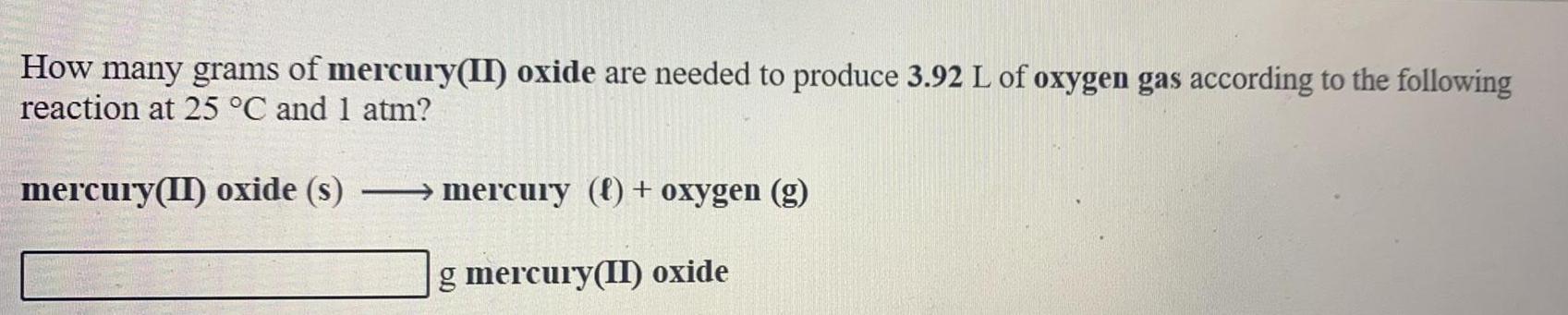
Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityHow many grams of mercury(II) oxide are needed to produce 3.92 L of oxygen gas according to the following reaction at 25 °C and 1 atm?
mercury(II) oxide (s) → mercury (f) + oxygen (g)

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityWhich of the following aqueous solutions contains the lowest amount of ions or molecules dissolved in water?
1.5 L of 0.5 M Na3PO4
500. mL of 0.75 M Nal
500 mL of 2.25 M CH3OH
2.0 L of 2.25 M CuCl₂
1.75 L of 1.25 M HBrO3

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityStrontium-90 is radioactive and has a half life of 28.8 years. Calculate the activity of a 4.9 mg sample of strontium-90. Give your answer in becquerels and in curies

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityPotassium hydrogen phthalate (abbreviated as KHP) has the molecular formula KHC8H4O4 and a molar mass of 204.22 g/mol. KHP has one acidic hydrogen. A solid sample of KHP is dissolved in 50 mL of water and titrated to the equivalence point with 22.90 mL of a 0.5010 M NaOH solution. How many grams of KHP were used in the titration?

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsEnter the electron configuration for the ion most likely formed by phosphorus.

Inorganic Chemistry
Qualitative analysisWhat mass of precipitate (in g) is formed when 20.5 mL of 0.800 M Co(NO3)2 reacts with 18.5 mL of 0.800 M NaOH in the following chemical reaction?
Co(NO3)2(aq) + 2 NaOH(aq) → Co(OH)₂(s) + 2 NaNO3(aq)

Inorganic Chemistry
P Block - Group 15From the plausible electronic configuration of yet undiscovered element number 165, predict which
of the elements from the second row in the periodic table has chemical properties similar to properties of this undiscovered element.
N
U
Be
C
O
F
Ne

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityWhich statement below accurately describes the elements in Group 16 of the Periodic Table as considered from top to bottom?
The atomic radii decrease and the ionization energies increase.
The atomic radii increase and the ionization energies increase.
The atomic radii decrease and the ionization energies decrease.
The atomic radii increase and the ionization energies decrease.

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityA chemist adds 330.0 mL of a 0.319 mol/L sodium nitrate (NaNO3) solution to a reaction flask. Calculate the millimoles of sodium nitrate the chemist has added to the flask. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsComplete the table below by deciding whether a precipitate forms when aqueous solutions A and B are mixed. If a precipitate will form, enter its empirical formula in the last column.

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsSucrose (C12H22011) is combusted in air according to the following reaction:
C12H22O11(s) + O₂(g) → CO₂(g) + H₂O(l)
How many moles of carbon dioxide would be produced by the complete combustion of 70.3 grams of sucrose in the presence of excess oxygen?

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityA chemist must dilute 52.8 mL of 62.1 µM aqueous mercury(II) iodide (HgI₂) solution until the concentration falls to 14.0 μM. He'll do this by adding distilled water to the solution until it reaches a certain final volume.
Calculate this final volume, in liters. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.

Inorganic Chemistry
P Block - Group 17For the molecule AX3, in which all the atoms are in Periodic Group VIIA or 17 (the Halogens):
1. Draw the correct Lewis Structure. If others are possible but less likely, draw them too and explain why the correct one is the selection.
2. What are the electron pair and molecular geometries?
a. Electron pair geometry:
b. Molecular geometry:
3. What is the predicted (ideal) bond angle about the central atom?
4. Is the molecule polar or nonpolar?
5. What is the orbital hybridization on the central atom?

Inorganic Chemistry
Qualitative analysisPhthalonitrile (C8H4N2) is produced by the ammoxidation of o-xylene (C8H10) according to the following reaction:
C8H10(l) + O2(g) + NH3(g) → C8H4N2(S) + H₂O(l)
How many grams of water would be produced by the complete ammoxidation of 20.8 moles of o-xylene?

Inorganic Chemistry
S Block - Group 1Copper(II) phthalocyanine (Cu(C32H16N3)) is produced by the cyclotetramerization of phthalonitrile (CsH4N2) according to the following reaction:
C8H4N2(l) + CuCl2(s)→ Cu(C32H16N8)(s) + Cl2(g)
How many grams of copper(II) phthalocyanine would be produced by the complete cyclotetramerization of 6.790 moles of phthalonitrile in the presence of excess copper(II) chloride?

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityConsidering your property drawn Lewis dot structure and what you know about polarity and "like dissolves like", select all of the compounds that are miscible with hexanes, C6H14.
A. N2
B. HF
C. C6H6
D. CH3OH (methanol)
E. CH4
F. SO2
G. CO₂
H. CH₂O
I. NH3
J. Al2O3

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsWhat does it mean to say that a solution is saturated with a solute?
It contains the maximum amount of solute possible at a particular temperature and is in equilibrium with undissolved solute.
It contains the minimum amount of solute possible at a particular temperature and is in equilibrium with undissolved solute.
It contains the maximum amount of solute possible at a particular temperature and is in equilibrium with dissolved solute.
It contains the minimum amount of solute possible at a particular temperature and is in equilibrium with dissolved solute.

Inorganic Chemistry
MetallurgyA 7.50 mL aliquot of a 0.33 M HCI solution is diluted to a final volume of 50.00 mL.
What is the molarity of this first dilution solution?
Then a second dilution was made by taking 4.00 mL of the first dilution and diluting it to 25.00 mL.
What is the molarity of this second dilution?
Select one:
1st Dilution = 0.0220 M; 2nd Dilution = 3.52 x 10-3 M
1st Dilution = 0.0660 M; 2nd Dilution = 1.06 x 10-2 M
1st Dilution = 0.0202 M; 2nd Dilution = 4.95 x 10-3 M
1st Dilution = 0.0495 M; 2nd Dilution = 7.92 x 10-3 M

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsHydrogen cyanide (HCN) is a poisonous gas that can be produced in the lab by reacting propane (C3H₂) with NH3 to produce HCN and H₂ (all in the gaseous state).
How many grams of ammonia are required to produce 14.4 g of HCN if the reaction runs to 65% completion?
Lets solve this question in a series of steps:
When properly balanced the coefficients for each species in the reaction are:
![Consider the exothermic equilibrium system below.
The [CuCl4]-2(aq) ion is light green while the [CuBr4]2 (aq) ion is dark brown. Originally the equilibrium below was a dark green.
[CuCl4]-2(aq) + 4 Br-(aq) = [CuBr4}-2(aq) + 4 Cl-(aq)
Predict the color of the solution after the system has re-established equilibrium.
Adding a few drops of colorless HCI to the solution.
Adding a few drops of Ag (aq) solution (Ag reacts with CI ions).](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/58600897-1659737955.0247545.jpeg?w=256)
Inorganic Chemistry
D Block elementsConsider the exothermic equilibrium system below.
The [CuCl4]-2(aq) ion is light green while the [CuBr4]2 (aq) ion is dark brown. Originally the equilibrium below was a dark green.
[CuCl4]-2(aq) + 4 Br-(aq) = [CuBr4}-2(aq) + 4 Cl-(aq)
Predict the color of the solution after the system has re-established equilibrium.
Adding a few drops of colorless HCI to the solution.
Adding a few drops of Ag (aq) solution (Ag reacts with CI ions).

Inorganic Chemistry
P Block - Group 15Which of the following neutral elements would be expected to have three unpaired electrons? (Hint: Draw the electron diagram for each)
boron (B)
lithium (Li)
nitrogen (N)
neon (Ne)
chlorine (CI)

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityA student prepared 0.250 mole of what he claimed to be a stable form of CrBr4. Assuming that this compound is stable and soluble, how many equivalents of the cation did the student prepare?
0.500 equivalent
1.00 equivalent
0.125 equivalent
0.750 equivalent
0.250 equivalent

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsCalculate the mass of oxygen in the copper oxide. The molar mass of copper is 63.55 g/mol and the molar mass of oxygen is 16.00 g/mol.

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsCalculate the pKa values for the acids shown below and then rank them in order of increasing acidity (weakest to strongest). (b) If the concentration of each acid is 0.10 M, which acid if any will produce the highest concentration of H3O*? Where applicable, show your work and report the pKa's to two decimal places. (5 pts)
Acid 1: Kal = 2.20 x10-7 Acid 2: Ka2 = 2.20 x10-8 Acid 3: Ka3 = 1.00 x10-7

Inorganic Chemistry
HydrogenNormally, the pH of the human body is fixed in a very narrow range between 7.35 and 7.45. A patient with an acidotic blood pH of 7.3 may be treated with an alkali such as sodium hydrogen carbonate. Why would this treatment raise the pH of the blood?

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityUse the standard reaction enthalpies given below to determine ΔH°rxn for the following reaction:
2 NO(g) + O2(g) → 2 NO2(g) ΔH°rxn = ?
Given:
N2(g) + O2(g) → 2 NO(g) ΔH rxn = +183 kJ
1/2 N2(g) + O2(g) → NO2(g) ΔH°rxn = +33 kJ
A) -150. kJ
B) -117 kJ
C) -333 kJ
D) +115 kJ
E) +238 kJ

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsCalculate the enthalpy of the reaction
4B (s) + 302 (g) -> 2B₂O3(s)
given the following pertinent information:
1. B2O3 (s) + 3H₂O(g)→302 (g) + B₂ H6 (g), ΔH = +2035 kJ
2. 2B(s) + 3H₂(g) →B₂ H6 (g), ΔH = +36 kJ
3. H₂(g) + O2(g) →H₂O(l), ΔH = -285 kJ
4. H₂O(1)→H₂O(g), ΔH = +44 kJ
Express your answer with the appropriate units.

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsYou may want to reference (Page) Section 12.2
while completing this problem. The following soluble salts are strong electrolytes. For each, enter a balanced equation for their dissociation in water.
Part B
NaNO3
Express your answer as a chemical equation. Identify all of the phases in your answer.
A chemical reaction does not occur for this question.
,

Inorganic Chemistry
Metallurgy0.20 mol A, 0.60 mol B, and 0.75 mol C are reacted according to the following reaction
A + 2B + 3C->2D + E
Identify the limiting reactant(s) in this scenario.
B and C only
C only
A only
B only
A, B, and C
![Give the ground-state electron configuration for silicon (Si) using noble-gas shorthand.
Express your answer in condensed form as a series of orbitals. For example, [Ar]4s²3d³ would be entered as [Ar] 4s^23d^8.](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/58389943-1659730178.4533637.jpeg?w=256)
Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityGive the ground-state electron configuration for silicon (Si) using noble-gas shorthand.
Express your answer in condensed form as a series of orbitals. For example, [Ar]4s²3d³ would be entered as [Ar] 4s^23d^8.

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsIdentify which sets of quantum numbers are valid for an electron. Each set is ordered (n, l, me, m.).
4,2,1,1/2
3,-2,-2,-1/2
3,2,-1,-1/2
1,2,0,-1/2
1,1,0,-1/2
3,-2,-1,0
3,2,0,1/2
3,0,0,1/2
2,1,0,1/2
1,3,0,1/2
4,3,4,-1/2
0,2,1,-1/2

Inorganic Chemistry
S Block - Group 2What is the only possible value of me for an electron in an s orbital?
Express your answer numerically.
Part B
What are the possible values of me for an electron in a d orbital?
Express your answer numerically with sequential values separated by commas.
Which of the following set of quantum numbers (ordered n, l, me, m.) are possible for an electron in an atom?
Check all that apply.
5, 3, -3, 1/2
2,1,0,-1
3, 2, 2, -1/2
2, 2, 2, 1/2
4,2,3, -1/2
3,1, -2, -1/2
-1,0,0,-1/2
5,3,0, 1/2
![Give the ground-state electron configuration for copper (Cu) using noble-gas shorthand.
Express your answer in condensed form as a series of orbitals. For example, [Ar]4s²3d³ would be entered as [Ar]4s^23d^8.](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/58389947-1659730076.4336758.jpeg?w=256)
Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsGive the ground-state electron configuration for copper (Cu) using noble-gas shorthand.
Express your answer in condensed form as a series of orbitals. For example, [Ar]4s²3d³ would be entered as [Ar]4s^23d^8.

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsFor which of the following reactions is AHxn equal to AH of the product(s)? You do not need to look up
any values to answer this question.
Check all that apply.
CO(g) + 1/2O2(g) →CO₂(g)
2Na(s) + F2 (g)→2NaF(s)
CaCO3(g)→CaO+CO2(g)
C(s, graphite) + O2(g) →CO₂(g)
Na(s) + F2(1)→NaF (s)
Na(s)+F2 (g) →NaF (s)

Inorganic Chemistry
MetallurgyElectron configurations are a shorthand form of an orbital diagram, describing which orbitals are occupied for a given element. For example, 1s²2s²2p¹ is the
electron configuration of boron.
Enter the complete electron configuration for arsenic (As).
Express your answer in complete form in the order of orbital filling as a string without blank space between orbitals. For example, 1s22s2 should be entered as 1s^22s^2.

Inorganic Chemistry
S Block - Group 1Which of the following set of quantum numbers (ordered n, l, me, m.) are possible for an electron in an atom?
Check all that apply.
5, 3, -3, 1/2
2, 1, 0, -1
3, 2, 2, -1/2
2, 2, 2, 1/2
4, 2, 3, -1/2
3, 1, -2, -1/2
-1, 0, 0, -1/2
5, 3, 0, 1/2

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsConsider the following three moving objects:
i. A golf ball with a mass of 45.9 g moving at a speed of 50.0 m/s.
ii. An electron moving at a speed of 3.5 × 105 m/s.
iii. A neutron moving at a speed of 2.3 x 10² m/s.
List the three objects in order from shortest to longest de Broglie wavelength.
iii<i<ii
i<ii<iii
iii<ii<i
ii<iii<i
i<iii<ii

Inorganic Chemistry
Preparation and Properties of CompoundsPart B
Green light has a frequency of about 6.00 x 10¹4 s-¹. What is the energy of a photon of green light?
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
Ephoton=

Inorganic Chemistry
Classification of Elements and PeriodicityTwo of the types of infrared light, IR-C and IR-A, are both components of sunlight. Their wavelengths range from 3000 to 1,000,000 nm for IR-C and from 700 to 1400 nm for IR-A. Compare the energy of microwaves, IR-C, and IR-A.
Rank from greatest to least energy per photon. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them.