Physical Chemistry Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.

Physical Chemistry
General10 M is a metal that forms an oxide M 0 MO M O AH 120 kcal When a sample of metal M reacts with one mole oxygen what will be the AH in that case 1 240 kcal 2 240 kcal 3 480 kcal 4 480 kcal TC012

Physical Chemistry
Energetics22 If C H O s 90 g 6CO g 6H O g AH 680 kCal The weight of CO g produced when 170 kCal of heat is evolved in the combustion of glucose is 1 265 g 3 11 g 2 66 g 4 64 g

Physical Chemistry
Solutions27 A 20 litre container at 400 K contains CO2 g at pressure 0 4 atm and an excess of SrO neglect the volume of solid SrO The volume of the container is now decreased by moving the movable piston fitted in the container The maximum volume of the container when pressure of CO2 attains its maximum value will be Given that SrCO3 s SrO s CO2 g a 5 litre c 4 litre b 10 litre d 2 litre Kp 1 6 atm NEET 2017

Physical Chemistry
Energetics7 The heat of combustion of CH4C and H at 25 C are 212 4 K Cal 94 0 K Cal and 68 4 K Cal respectively the heat of formation of CH will be a 1 54 4 K Cal 3 375 2 K Cal 2 18 4 K Cal 4 212 8 K Cal TC0120 1 3 114 T H ar

Physical Chemistry
Energetics5 The temperature at which the reaction Ag O s 2Ag s 1 0 g is at equilibrium is Given and 1 462 12 K 3 262 12 K AH 30 5 kJ mol AS 0 066 kJK mol 2 362 12 K 4 562 12 K TR007

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsPre Medical Chemistry 251 CH and 109 The standard heats of formation of NO g and The AH N O g are 8 0 and 2 0 kCal mol respectively the heat of dimerization of NO in kCal is

Physical Chemistry
Energeticsand ozone 97 Reaction H s L g 2HI AH 12 40 kCal 1 According to this heat of formation of HI will be nd oxygen TC0101 1 12 40 kCal 3 6 20 kCal 2 12 40 kCal 4 6 20 kCal TC0108

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kinetics66 98 Pre Medical Chemistry The energy of activation of a forward reaction is 50 kCal The energy of activation of its backward reaction is 1 Equal to 50 kcal 2 Greater than 50 kCal 3 Less than 50 kCal 4 Either greater or less than 50 kCal CK0108

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kinetics46 The rate constant of a first order reaction is 4 x 10 s At a reactant concentration of 0 02 M the rate of reaction would be 1 8 x 10 Ms 2 4 x 10 3 2 x 10 M s 4 4 x 10 Ms Ms CK

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsSolution which shows positive deviation from Raoults law is CHCl3 C6H6 HCI H O CH3COCH3 C H5OH ICH

Physical Chemistry
Energetics1 55 2 kCal 3 55 2 kCal 2 30 2 kCal 4 19 4 kCal TC0114 103 The standard molar heat of formation of ethane CO and water are respectively 21 1 94 1 and 68 3 kCal The standard molar heat of combustion of ethane will be 2 162 kcal 4 183 5 kCal 1 372 kCal 3 240 kCal TC0115 1 110 ME 2 Wh OXU 1 3

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsmin min 13 CK0067 or nth order this nature es when i posed 50 espectively 68 CK0074 The following data were obtained at a certain temperature for the decomposition of ammonia p mm 50 100 1 2 3 64 1 82 The order of the reaction is 2 1 1 O 3 2 4 3 200 0 91 CK0075

Physical Chemistry
General01 Given enthalpy of formation of CO g and Cao s are 94 0 kJ and 152 kJ respectively and the enthalpy of the reaction CaCO s CaO s CO g is 42 kJ The enthalpy of formation of CaCO s is 1 42 KJ 3 202 KJ 2 202 KJ 4 288KJ
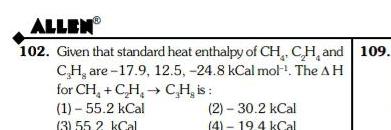
Physical Chemistry
GeneralALLEN 102 Given that standard heat enthalpy of CH CH and 109 CH are 17 9 12 5 24 8 kCal mol The AH for CH C H 1 55 2 kCal 3 55 2 kCal CH is 2 30 2 kCal 4 19 4 kCal

Physical Chemistry
GeneralH gas 2 Decrease in 50 mL 4 Decrease in 200 mL 4NO g 6H O 1 a and 1 mole of O are cion e consumed e produced roduced be consumed ntaining C H and N gave C 40 H 13 33 formula would be 2 CH N 4 C H N acid mol weight 200 00 ml of the aqueous C 1 7 gm N les gram 9 2 2 gm H 3 16 gm NO 4 16 gm O 41 In Haber process 30 litres of dihydrogen and 30 litres of dinitrogen were taken for reaction which yielded only 50 of the expected product What will be the composition of gaseous mixture under the aforesaid condition in the end 1 20 litres ammonia 20 litres nitrogen 20 litres hydrogen 2 10 litres ammonia 25 litres nitrogen 15 litres hydrogen 3 20 litres ammonia 10 litres nitrogen 30 litres hydrogen COL 4 20 litres ammonia 25 litres nitrogen 15 litres hydrogen 42 The maximum number of molecules is present in 1 15 L of water at STP 100x NA 18 OTD Naz Cac PE P

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhich of the following aqueous solutions has the least freezing point 0 2 m CaCl2 0 1 m AlCl3 1 m Glucose hr m 0 3 m Al2 SO4 3

Physical Chemistry
Energetics8 For hypothetical reversible reaction 1 A g B g AB g AH 20 kJ if standard entropies of A B and AB are 60 40 and 50 JK mole respectively The above reaction will be in equilibrium at 1 400K 3 250K 2 500K 4 200K

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsCK0075 A reaction is found to have the rate constant xs 1 by what factor the rate is increased if initial concentration of reactant is tripled 1 3 2 9 3 x 4 Remains same

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kinetics4 Unpredictable as rate constant is not given CK0065 61 The rate constant K for the reaction 2A B product was found to be 2 57 x 10 L mol s after 15 s 2 60 x 10 L mol s after 30 s and 2 55 x10 L mol s after 50 s The order of reaction is 1 2 2 3 3 Zero 4 1 CK0066

Physical Chemistry
Energetics104 The AH for CO CO and H O are 393 5 2 g 110 5 and 241 8 kJ mol respectively the standard enthalpy change in kJ for the reaction CO H CO H O is 2 1 524 1 2 41 2 3 262 5 4 41 2

Physical Chemistry
Energetics105 The enthalpies of combustion of carbon and carbon monoxide are 393 5 kJ and 283 kJ respectively the enthalpy of formation of carbon monoxide is 1 676 5 kJ 3 110 5 kJ 2 110 5 kJ 4 676 5 kJ

Physical Chemistry
GeneralA Reaction first order with respect to reactant A has a rate constant 6 0 x 10 2 min If we start with A 0 5 mol L when would A reach the value 0 05 mol L 1 48 4 min 3 38 4 min 2 28 9 min 4 18 6 min

Physical Chemistry
Energetics119 H TC0125 113 Given standard enthalpy of formation of CO 110 kJ mol and CO 394 kJ mol The heat of combustion when one mole of graphite burns is 1 110 kJ 3 394 kJ 2 284 kJ 4 504 kJ CO136

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kinetics1 3 2 1 3 2 4 0 CKOOE 59 The rate constant for a reaction is 10 8 x 105 mol L s The reaction obeys 2 Zero order 1 First order 3 Second order 4 All are wrong CKOOE

Physical Chemistry
Energeticsof these The rate constant of first order reaction becomes 6 times when the temperature is increased from 350 K to 410 K Energy of activation for the reactin is 1 35 63 KJ mol 3 25 20 KJ mol 2 45 63 KJ mol 1 4 23 62 KJ mol

Physical Chemistry
Energetics30 Which of the following reaction is expected never to be spontaneous 1 20 g 30 g AH Ve AS Ve 2 Mg s H g MgH AH Ve AS Ve 3 Br 1 Br g AH Ve AS Ve 4 2Ag s 3N g 2AgN AH Ve AS Ve 500

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kinetics55 From different sets of data of t 2 at different initial concentrations say a for a given reaction the txal is found to be constant The order of reaction is 1 0 2 1 3 2 4 3

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kinetics72 The expression which gives th life of 1st order reaction is 1 K 2 303 log 2 303 K log 4 3 4 2 4 2 303 K 2 303 K log 3 log 4 4 1413 79 TI ch 1 3

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kinetics1 Half life of a first order reaction is independer of initial concentration 2 Rate of reaction is constant for first order reactic 3 Unit of K for second order reaction mol 1 L s 1 4 Half life of zero order is proportional to initi

Physical Chemistry
Atomic StructureWhich one of the elements with the following outer orbital configurations may exhibit the largest number of oxidation states 1 3d 4s 2 3d5 4s 3 3d5 4s 4 3d 4s

Physical Chemistry
Generalme reaction CK0052 period of centration 4 Cannot be calculated CK0059 3 160 56 The reaction L M is started with 10 g L After 30 minute and 90 minute 5 g L and 1 25 g L are left respectively The order of reaction is 1 0 2 2 3 1 4 3 CK0061 TCHEWLENGR MODULE 12 CHEMICAL KINETICS

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsDetermine the entropy change for the below 2H g Og 2H O at 300 K If standard entropies of H a Oa and H O 0 are 126 6 201 20 and 68 0J K mol respectively 1 218 4 JK mol 2 318 4 JK mol 1 3 520 2 J K mol 1 128 6 JK mol 201

Physical Chemistry
Generalg is less is higher ower than 87 Which of the following values of heat of formation indicates that the product is least stable 1 94 kCal 2 231 6 kCal 3 21 4 kCal 4 64 8 kCal TC0096

Physical Chemistry
General5 H g 2NO g 2 NH3 g 2 H O g Express your answer using four significant figures VO AXO AG Submit Part D Request Answer AG will increase with increasing temperature SWED kJ

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid states3 0 85 litre 12 One litre of CO is passed through red hot coke The volume becomes 1 4 litres at same temperature and pressure The composition of products is co C 200 1 0 8 litre of CO and 0 6 litre of CO Pq no 2 0 7 litre of CO and 0 7 litre of CO 63 3 4 41 4 2 0 6 litre of CO and 0 8 litre of CO 0 4 litre of CO and 1 0 litre of CO 3

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsWhen enthalpy and entropy change for a chemical reaction are 2 5 x 103 cal and 7 4 cal deg respectively predict the reaction at 298 K is 1 Spontaneous 2 Nonspontaneous 3 At equilibrium 4 None of these If a gas at constant temperature and pressure

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsIf the limiting molar conductivities of KCI HCI and KAc are x y and z S cm mol respectively then the limiting molar conductivity of HAc is x y z x y z y z x x y z

Physical Chemistry
General13 The half life period and initial concentration for a reaction are as follows Initial concentration 1 order of reaction is 1 2 2 1 350 425 3 540 275 158 941 4 4

Physical Chemistry
GeneralThe accompanying figure depicts the change in concentration of species X and Y for the reaction X Y as a function of time the point of intersection of the two curves reperesents Concentration Y Time 1 2 4 3 4 Data are insufficient to predict

Physical Chemistry
Energetics53 The enthalpy of vaporisation of per mole of ethanol B pt 79 5 C and A S 109 8 JK mol is 1 27 35 kJ mol 2 32 19 kJ mol 4 42 37 kJ mol 3 38 70 kJ mol TD0058

Physical Chemistry
Equilibrium106 The standard heat of formation of CS will be given that the standard heat of combustion of carbon s sulphur s and CS are 393 3 293 72 and 1108 76 kJ mol respectively is 1 128 02 kJ mole 2 12 802 kJ mol 1 3 128 02 kJ mol 4 12 802 kJ mol TC0119 31 The 1 113 Giv CC hea is W

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumCalculate the magnitude of net work done in the following cycle for one mol of an ideal gas in Calorie Where in process BC PT constant R 2cal mol K A B 100 800 cal 200 cal 300 cal 300 T K C 900

Physical Chemistry
Generalthat of water TC0090 82 Which plot represents for an exothermic reaction R 1 H 3 H Progress in reaction R Progress in 2 H RP Progress in reaction 4 HR P Progress in

Physical Chemistry
General92 From the reaction P White P Red AH 18 4 kJ it follows that 1 Red P is readily formed from white P 2 White P is readily formed from red P 3 White P can not be converted to red p 4 White P can be converted into red P and red P is more stable

Physical Chemistry
Energetics250 Pre Medical Chemistry 90 Which of the following represents an exothermic reaction 1 N g O g 2NO g AH 180 5 kJ 2 H O g C s CO g H g AE 131 2kJ 3 2HqO s 180 4 KJ 2Hg O g

Physical Chemistry
Energetics2 One mole of a gas occupying 3dm expands against a constant external pressure of 1 atm to a volume of 13 lit Find work is 1 10 atm dm 3 3 39 atm dm 2 20 atm dm 4 48 atm dm

Physical Chemistry
Energeticsreaction at 373 K if Zero 375 kJ TC0105 100 The enthalpy of formation of ammonia is 46 0 kJ mol The enthalpy change for the reaction 2NH g N g 3H g is 1 46 0 kJ mol 2 92 0 kJ mol 3 23 0 kJ mol 4 92 0 kJ mol TC0112 15 THERMODYNAMICS02 EXP

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsA chemist fills a reaction vessel with 6 53 atm nitrogen N gas 7 33 atm hydrogen H gas and 0 962 atm ammonia NH3 gas at a temperature 25 0 C Under these conditions calculate the reaction free energy AG for the following chemical reaction N g 3H g 2NH g 2 Use the thermodynamic information in the ALEKS Data tab Round your answer to the nearest kilojoule kJ

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsCH C C H C AH 270 6 KJ mol AS 139 0 J K mol Find value of AG at T 300 K 1 328 9 KJ mol 3 129 8 KJ mol 1 2 228 9 KJ me 4 528 9 KJ mc

Physical Chemistry
Energetics1 2 6 1 Gibb s energy change for the dissolution of potassiumnitrate in water at 298 K is KNO S water K aq NO3 aq AH 34 KJ mol 45 0 116 KJ K mol 1 0 568 KJ mol 2 0 568 KJ mol 3 1 036 KJ mol