Physical Chemistry Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kinetics3 10 Consider a one dimensional harmonic oscillator with vibrational frequency 5x 10 3 sec and mass 1x 10 23 g These are typical values for a diatomic molecule Find the average lifetime of the v 1 vibrational state

Physical Chemistry
GeneralA 10 g mixture of K2CO3 MgCO3 on decomposition produces total 2 2 gm CO Mass of K2CO3 present in the mixture is Atomic mass C 12 O 16 Mg 24 K 39 A 42 B 5 8 C 58 D 22 A A

Physical Chemistry
Solid state0 93 1 0 If NaCl is dopped with 10 3 mol SrCl what is the numbers of cation vacancies per mole of NaC f NoC The edge length of unit cell of AgCl is found to

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistry71 Study the given figure and answer the question that follow t A OF i Give the names of the electrodes A and B a A Cathode B Anode b A Anode B Cathode c A Anode B Anode d A Cathode B Cathode ii Which electrode is the oxidising electrode a A b B c Both a and b

Physical Chemistry
GeneralF Na Mg 0 K Rb Cs 74 Be 7 Fr given below and answer the following questions PERIODIC TABLE OF THE ELEMENTS ww Ca Sc Sr Y Ba La Lu Hf 100 Ra Ac Lr Rf 41 LANTHAND ACTRONG V C Nb Mo Tc La Ce Pr 127 Db Sg Bh Hs Re Ac Th Pa Ru Rh R Ir AN 45 Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Pd Ag Cd Pt H Au Hg 1 What is this table called Who invented this table 2 Name the following a A metallic element 41 ww Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Np Pu Am Cm Bk b A non metallic element S Pb 3 Define atomic number of an element 4 What is the basis of arrangement of these elements in the table Ay Ds Rg Cn Uut FI Uup Lv Uus Uup Po 2 Br Kr c A noble gas At Rn CF Es Fm Md No Lr

Physical Chemistry
Solid stateAgCl has the same structure as that of NaCl The edge length of unit cell of AgCl is found to 555 pm and the density of AgCl is 5 561 g cm3 Find the percentage of sites that are unoccupied

Physical Chemistry
GeneralIf the radius of Mg2 ion Cs ion O2 ion S ion and Cl ion are 0 65 1 69 1 40 1 84 and 1 81 respectively Calculate the co ordination numbers of the cations in the crystals of MgS MgO and CsCl then of the hand

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe vapour pressure of a solvent decreased by 10 mm of mercury when a non volatile solute was added to the solvent The mole fraction of the solute in the solution is 0 2 What should be the mole fraction of the solvent if the decrease in the vapour pressure is to be 20 mm of mercury 1998 a 0 8 c 0 4 b d 0 6 0 2

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsIn a reaction between A and B the initial rate of reaction ro was measured for different initial concentrations of A and B as given below A mol L 1 0 20 B mol L 1 0 30 ro mol L s 5 07 x 10 5 What is the order of the reaction with respect to A and B 0 20 0 10 5 07 x 10 5 0 40 0 05 1 43 x 10 5

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kinetics25 The mechanism of esterification in presence of acid catalyst H SO4 is proposed as follows O H k H fast CH3 C 0 H H O C H5 CH3 C a c P E P E VI I II O III CH3COH 1 OC H5 ks III IV R C III k s H fast IV H fast k O C H5 V Which of the following potential energy Vs reaction co ordinate diagram is consistent with given mechanism H fast V VI V VI O H 9 CH CO H II CH3 C OH b P E C H5OH slow k d P E C H5OH fast k2 k4 H O slow K4 H O fast p II IV V VI R C N III IV I II III 15 V VI fast k H O H CH3 C OH k3 fast 0 C H5 IV

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsPressure cooker reduces cooking time for food because a boiling point of water involved in cooking is increased b heat is more evenly distributed in the cooking space c the higher pressure inside the cooker crushes the food material vi d cooking involves chemical changes helped by a rise in temperatura ix TX Mx X RHI

Physical Chemistry
Atomic Structuremax According to photoelectric equation K hv The photoelectric emission will not be possible if I K is negative II max III K is positive max a I and II c III and II Vo IV Vo V b d V I and IV III and IV

Physical Chemistry
General177 In the following colourless white sulphides is are CdS PbS HgS CuS FeS ZnS NiS Bi S 78 0 38 gm of a silver salt of a dibasic acid on ignition gave 0 27 gm of silver Molecular mass of acid is x x 10 gm then x value is 79 Find out number of alcohols that can give positive iodoform test CACHOU Ehi

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsA sample of air consisting of N and O was heated to 2500 K until the equilibrium N g O g 2NO g Was established with an equilibrium constant Kc 2 1 10 At equilibrium the mole of NO was 1 8 Estimate the initial composition of air in mole fraction of N2 and O2

Physical Chemistry
GeneralIn an Otto cycle air at 1bar and 290K is compressed isentropic ally until the pressure is 15bar The heat is added at constant volume until the pressure rises to 40bar Calculate the air standard efficiency and mean effective pressure for the cycle Take Cv 0 717 KJ Kg K and Runiv 8 314KJ Kg K

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsFor a reaction A B C product The rate of the reaction is given by Rate K A B C From the following data determine i The order with respect to A The order with respect to C Rate constant v a b C Initial concentrations mole dm B 0 005 0 005 0 010 0 005 A 0 010 0 010 0 010 0 020 C 0 010 0 015 0 010 0 010 ii iv The order with respect to B The over all order Initial rate mole dm s 5 0 10 5 5 0 10 5 2 5 10 14 x 10 5 Products ID B Products follow first order kinetic m

Physical Chemistry
Gaseous and liquid statesier in pressure cooke 200 a Boiling point increases with increasin because pressure b Boiling point decreases with increasi pressure c pressure cooker d Extra pressure of pressure cooker so the beans I energy is not lost while cookin

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kinetics1 For a unimolecular reaction AB has rate constant K and for another unimolecular reaction C D has rate constant K If half life of first reaction is half of half life of second reaction then find Ea Ea will be 1 RT n2 3 RT n2 2 RT n2 4 1 RT n2

Physical Chemistry
GeneralWhich reaction does not represent auto redox of disproportionation 45 A Cl OH CI CIO3 H O B C D 2H O2 2Cu H O O2 Cu Cu NH4 2Cr2O7 N2 Cr2O3 4H O

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsAt 27 C it was observed during a reaction of hydrogenation that the pressure of hydrogen gas decreases from 2 atmosphere to 1 1 atmosphere in 75 minutes Calculate the rate of disappearance in M sec

Physical Chemistry
General8 A solution containing 10 g dm 3 of urea molecular mass 60 g mol is isotonic with a 5 solution of a non volatile solute The molecular mass of this non volatile solute is 2006 a 300 g mol c 200 g mol b 350 g mol 1 d 250 g mol

Physical Chemistry
GeneralConsider the following reactions where metal gas reacts with iodine gas aluminum 2 Al 312 Al216 If 17 0 grams of aluminum metal reacts with 225 0 grams of iodine gas to produce 82 5 grams of Al216 what is the percent yield

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistry5 8 S cm mol During the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride the time required to produce 0 10 mol of chlorine gas us a current of 3 amperes is 1 220 minutes 44 110 minutes 2 330 minutes 3 55 minutes 900

Physical Chemistry
Equilibrium1 lit solution of Na3PO4 Na2HPO4 1 lit solution of Na3PO4 Na2HPO4 1 M each 1 M each Only water is electrolysed in both compartments 2 moles of electrons are transfer from anode to cathode pKaj pKa2 pKa3 values of H3PO4 are 4 6 8 respectivel Find pH of anode

Physical Chemistry
General3 4 4 1 66 0 5 g of an organic substance was kjeldahlised and the ammonia released was neutralised by 100 ml 0 1 M HCI Percentage of nitrogen in the compound is 1 14 3 28 2 42 4 72

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsSelect the true statement about this diagram Potential Energy Reaction Coordinate The activation energy is raised when a catalyst is used This reaction is endothermic It is not possible to tell if the activation energy changes or if the reaction is endothermic or e The catalyst lowers the activation energy and the reaction is exothermic
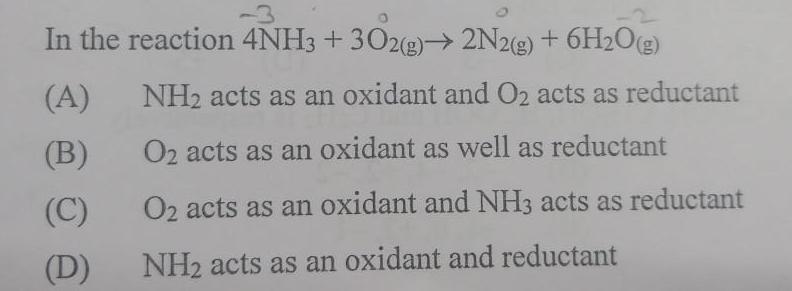
Physical Chemistry
GeneralIn the reaction 4NH3 302 g 2N2 g 6H O g A B C D NH acts as an oxidant and O2 acts as reductant O2 acts as an oxidant as well as reductant O2 acts as an oxidant and NH3 acts as reductant NH acts as an oxidant and reductant

Physical Chemistry
Equilibrium130 K for HCN is 5 x 100 at 25 C For maintaining a constant pH 9 the volume of 5 M KCN solution required to be added to 10 mL of 2 M HCN solution is a 4 mL b 2 5 mL c 2 mL d 6 4 mL AUMS

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsX Y 2XY is given below 2 1 X X X fast ii X Y XY Y slow iii X Y XY fast The overall order of the reaction will be NEET 2017 2 2 4 1 5 1 1 3 O

Physical Chemistry
GeneralOne sample of atmospheric air is found to have 0 03 of carbon dioxide and another sample 0 04 This is evidence that 1 The law of constant composition is not always true 2 The law of multiple proportions is true 3 Air is a compound 4 Air is a mixture Number of moles of water in 1 litre of water with density 1g cc are 1 55 56 3 56 55 2 45 56 4 56 45 One nanometre is equal to 1 10 cm 3 10 7 cm 2 10 cm 4 10 cm 0

Physical Chemistry
GeneralChlorine is prepared in the laboratory by treating manganese dioxide MnO with aqueous hydrochloric acid according to the reaction 4HCl aq MnO s 2H O MnCI aq Cl g How many gram of HCI react with 5 0 g of manganese dioxide At wt of Mn 55 1 2 12 g 2 44 24 g 3 8 4 g 4 3 65 g

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsnish the table below which is Table 1 in your procedure to find the concentration of Fe ndard in solutions A F after the dilutions Standard Blank A B C D E F Fe standard soln 0 00ml 0 00ml 0 50ml 1 00ml 2 00ml 5 00 ml 10 00ml Fe std 0 mg L

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kinetics54 When a biochemical reaction is carried out in laboratory outside the human body in absence of enzyme then rate of reaction obtained is 10 6 times the activation energy of reaction in the presence of enzyme is 1 6 RT 2 P is required 3 Different from E obtained in laboratory a

Physical Chemistry
General2 For the reaction N O5 g 2NO g 1 2 O g the value of rate of disappearance of N O is given as 6 25 10 3 mol L s 1 The rate of formation of 2 5 NO and O is given respectively as 2 AIPMT Prelims 2010 X 1 6 25 10 3 mol L s 1 6 25 x 10 3 mol L s 1 2 1 25 10 mol L s 1 3 125 10 mol L s 1 3 6 25 x 10 3 mol L s 1 3 125 x 10 3 mol L s 1 4 1 25 x 10 2 mol L s 1 6 25 10 mol L s 1 of activation is X

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsMaximum change in temperature is observed on mixing which of the following One litre each of 0 01 M HCI and 0 01 M KOH x 500 mL each of 0 02 M HCI and 0 02 M KOH One litre of 0 01 M HCI and 500 mL of 0 02 M KOH 100 mL of 0 1 M HCI and 50 mL of 0 2 M KOH Solution Answer 4 Enthalpy change is same in all but volume is minimum in

Physical Chemistry
Atomic Structureao IIT Academy What should be the ratio of the radii of the second orbit of Li 2 ion and the third orbit of Bet ion 0 B 16 27 C 4 9 D None of these A 3 1 The ratio of velocities of the electrons in the fifth orbit of Lit2 and He should be

Physical Chemistry
Chemical BondingChem Section A This section contains 20 SINGLE CORRECT TYPE questions Each question has 4 choices 1 2 3 Read More Consider the leaching of Ag and Au and the metal is obtained later by displacement reaction using Zn Find out the correct statement In case of Ag a complex of coordination number equal to 4 is obtained Au forms a complex of coordination number 4 during leaching Zn forms a complex of coordination number 2 during leaching NaCN can be used in aqueous medium for the leaching of Ag and Au

Physical Chemistry
GeneralThe chromate ion present in water sample is reduced to insoluble chromium hydroxide Cr OH 3 by dithionation in basic solution S 02 CrO2 2H O2SO3 Cr OH 3 OH 100 L of water requires 387 g of Na S O The molarity of CrO2 in waste water is 1 0 0448 3 0 0148 2 4 448 4 0 0224

Physical Chemistry
Equilibrium33 The pH of a solution obtained by mixing 100 ml of 0 2 M CH3COOH with 100 ml of 0 2 M NaOH will be PK for CH COOH 4 74 and log 2 0 301 1 4 74 3 9 10 2 8 87 4 8 57

Physical Chemistry
GeneralThe reaction between dinitrogen and dihydrogen is given as N2 3H2 2NH 3 What will be the mass of ammonia produced if 100 g of dinitrogen reacts with 500 g of dihydrogen 2833 a

Physical Chemistry
Atomic StructureThe electron in a hydrogen atom makes a transition from an excited state to the ground state Which of the following statements is correct Its kinetic energy increases and its potential and total energies decrease Its kinetic energy decreases potential energy increases and its total energy remain A B a D constant Its kinetic and total energies decrease and its potential energy increases Its kinetic potential and total energies decrease

Physical Chemistry
Solutions8 Fish generally needs O concentration in water at least 3 8 mg L for survival What partial pressure of O above the water is needed for the survival of fish Given the solubility of O in water at 0 C and 1 atm partial pressure is 2 2 x 10 mol L 0 054 atm

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistry28 At 25 C the standard reduction potential for the half cell reaction Zn s 2H aq Zn aq H g is 0 28 V What is the reduction potential of the half cell reaction in 10M H concentration assuming all other species to be at unit concentration Universal gas constant R 8 314 J K mol Faraday constant F 96500 C mol 0 339 V 0 870 V 0 398 V 0 290 V

Physical Chemistry
Equilibrium3 For the reaction A 3B 2C D initial mole of A is twice that of B If at equilibrium moles of B and are equal then percent of B reacted is 1 10 3 40 Refern des ga 2 20 4 60 4 uilibrium A g 4B g AB g is attained by mixing equal moles of A and B in a one litre vessel

Physical Chemistry
Atomic Structure3 A gas is found to contain 2 34 g of nitrogen and 5 34 g of oxygen Simplest formula of the compound is 1 N O 3 N O 2 NO 4 NO

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsThe rate constant of the production of 2B g by the reaction A g 2B g is 2 48 104 s 1 cemil 8st A 1 1 molar ratio of A to B in the reaction mixture is attained after 1 26 25 minute bns ito 2 27 25 minute 4 0 minute

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistry61 The molar conductivity of a 0 5 mol dm solution of AgNO with electrolytic conductivity of 5 76 x 10 Scm at 298 K is 1 0 086 S cm mol 44 11 52 S cm mol 2 28 8 S cm mol 3 2 88 S cm mol

Physical Chemistry
GeneralPay load is defined as the difference between the mass of displaced air and th mass of the balloon Calculate the pay load when a balloon of radius 10 m mas 100 kg is filled with helium at 1 66 bar at 27 C Density of air 1 2 kg m 3 an R 0 083 bar dm K 1 mol

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryWhich of the following is incorrect regarding batteries Primary batteries cannot be recharged and reused again Lead storage battery is an example of secondary battery In a H O fuel cell water is electrolysed to give H and 0 In a Ni Cd battery the specific gravity of the alkaline electrolyte remains same

Physical Chemistry
General4 Reduction of V O5 followed by addition of a strong base yields Na12V18042 24H O on crystallization if the addition of strong base causes no change in oxidation state of vanadium obtained after reduction the equivalent weight for reduction of V Os in this case will be if M denotes molecular weight of V 0s A M 2 B M S C M D Cannot determine