Electrochemistry Questions and Answers

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistryc 0 0133 M 11 0 04 N solution of a weak acid has conductivity 4 23x10 mho cm 1 If the degree of dissociation of acid at this dilution is 0 0612 then equivalent 2 conductivity at infinite dilution is mho cm eq b 180 a 172 8 c 190 d 160 onductance of H and CH3COO at

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistry4 0 001174 g 5 amp of current is passes for 193sec through on aqueous solution NaCl the total no of a equivalent of NaOH formed in the solution assuming 60 current efficiency for this process is 1 0 006 3 0 003 2 0 01 4 None

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryAt 291 K the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of NH4Cl NaOH NaCl are 129 8 217 4 108 9 ohm cm mol respectively If the molar conductivity of centinormal solution of NH4OH is 9 33 ohm cm mol 1 what is the percentage dissociation of NH4OH at th dilution A B 0 392 39 2 3 92

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryThe reduction potential for all other half reactions are measured relative to the half reaction 2H aq 2e H g Under standard conditions pH 0 000 PH2 1 atm this standard hydrogen electrode SHE is defined to have a reduction potential of 0 000 V 2nd attempt See Periodic Table See
Physical Chemistry
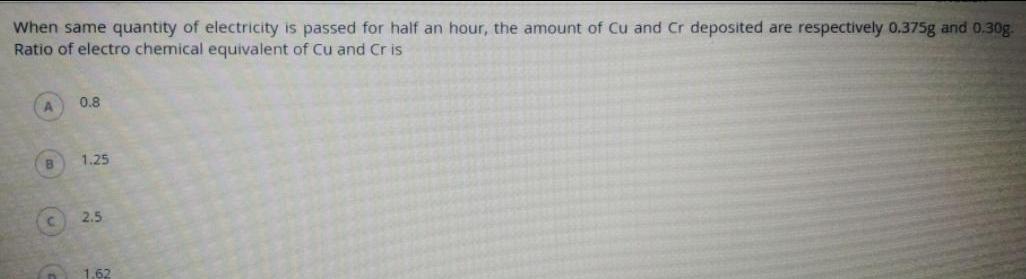
ElectrochemistryWhen same quantity of electricity is passed for half an hour the amount of Cu and Cr deposited are respectively 0 375g and 0 30g Ratio of electro chemical equivalent of Cu and Cris B n 0 8 1 25 2 5 1 62

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryIn an electrolysis experiment current was passed for 3 hour through two cells connected in series The first cell contains a solution of gold and second contains CuSO4 solution 5 2g of gold was deposited in the first cell If the oxidation number of gold is 3 the amount of Cu deposited on the cathode and the magnitude of the current in ampere are respectively 1F 96500 coulomb Au 197 A 4 76g 0 8 Ampere B 9 74g 1 Ampere C 5 5g 0 5 Ampere D 2 5g 0 7 Ampere

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistryd 3 14 mho cm 4 4 The resistance of 0 01 N solution of an electrolyte was found to be 210 ohm at 298 K using a conductivity cell of cell constant 0 66 cm The equivalent conductivity of solution is a 314 28 mhocm eq 1 b 3 14 mho cm eq 1 cm eq 1 c 314 28 mho cm eq d 3 14 mho 1 If the electrolyte used in problem 4 is Ba NO3 2 then

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryTwo half reactions of an electrochemical cell are given below MnO4 aq 8H aq 5e Mn2 aq 4H O 1 E 1 51 V Sn aq Sn4 aq 2e E 0 15 V Construct the redox reaction equation from the two half reactions and calculate the cell potential from the standard potentials and predict if the reaction is reactant or product favoured All India 2010

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistry20 Read the following and answer any four questions In the electrolytic refining of copper The electrolyte is a solution of acidified copper sulphate There are an anode and cathode Refining is carried out by passing an electric current Cathode 52 Cu a Anode i The anode is a pure strips b impure copper c refined copper d none of these ii Anode mud consists of a insoluble impurities b soluble impurities Acidified copper sulphate Impurities Ganode mudi c pure metal d impure metal iii Which of the following are refined electrolytically A Au B Cu C Zn D K a A and B b B and C c A B and C d B C and D iv On passing electric current Cu is deposited on a cathode b anode c bottom of cathode d bottom of anode v Which one of the following four metal would be displaced from the solutic

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistry33 a Calculate the maximum work and log Kc for the given reaction at 298 K Ni s 2Ag aq Ni aq 2Ag s Given E Ni2 Ni 0 25V EAg Ag 0 80 V 1F 96500 C mol 7 b On the basis of E values identify which amongst the following is the strongest oxidising agent and why Ch g 2 e 2CI E 1 36 V Mr out fot Mn 14 0 Co 1 51Y 3 2

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistry1 Calculate the concentration of Cu lon for an electrochemical cell consisting of different components of copper and Turkey in a CuSO4 solution Concentration and from an elevated electrode of silver dipped in an AgCl solution deepening of its height M 0 02 Note the output voltage of the search for a source 0 412 V and using our help In the following equations Ag aq e Ag s Eo 0 799 V Cu2 aq 2 e Cu s Eo 0 337 eV

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistrya 1 0 b 1 29 c 134 What is the molarity of Fions in a saturated solution of BaF Ksp 1 0 106 a 1 0 10 2 b 1 0 x 107 3 c 1 26 x 10 2 d 6 3 10 3 135 What is the molarity of F in a saturated solution of InF3 Ksp 7 9 10 0

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistryb of sodium benzoate hydrochloric acid sodium chloride are 82 4 426 2 26 53 Sm mol Calculate for benzoic acid A 482 07 Sm mo

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistryulate the current in mA required to deposit 0 195 g of platinum metal in 5 0 hours from a solution of PtCl2 Atomic weight Pt 195 PUC a 310 Duo b b 3100 5 HO d 5 36 HOW c 21 44

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistry3 In an electrolysis of acidulated water 4 48 L of hydrogen at STP was produced by passing a current of 2 14 A For how many hours was the current passed 1 4 3 6 2 3 4 5

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryAt 25 C molar conductance of 0 1 molar solution of ammonium hydroxide aqueous is 9 54 ohm cm mol and at infinite dilution its molar conductance is 238 ohm cm mol The degree of ionisation of ammonium hydroxide at the same concentration and temperature is a 4 008 b 40 800 c 2 080 d 20 800 NEET 2013

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistry4 The molecule of N O in planar Two different electrolytic cells filled with molten Cu NO and molten AI NO respectively are connected in series When electricity is passed 2 7 g Al is deposited on electrode Calculate the weight of Cu deposited on cathode Cu 63 5 Al 27 0 g mol 1 190 5 g 2 9 525 g 3 63 5 g 4 31 75 g

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryHgSO4 is 6 4 x 10 sp a 8 10 3 then d None of these b 6 4 x 10 5 c 8 x 10 6 130 The solubility of Ba 3 AsO 4 formula mass 690 is 6 9 x 10 2 g 100 mL What is the K 2 a 1 08 x 10 11 d 6 0 10 13 13 b 1 08 x 10 c 1 0 10 15 131 The solubility of AgBrO formula mass 236 is 0 0072 g in 1000 mL What is the K c 3 0 10 5 a 2 2 x 10 8 b 3 0 x 10 10 sp d 9 3 10 10

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistry4 Fi 43 Deduced from the following E values of half cells what combination of two half cells would result in a cell with the largest potential i A A e ii B2 e B iii C e C iv DD 2e 1 i and iii 3 ii and iv E 1 5 V E 2 1 V E 0 5 V E 1 5 V 2 i and ii 4 iii and iv

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistry6 THE DIAGRAM BELOW SHOWS ELECTROLYSIS OFACIDIFIED WATER 0 KIS di Nonieti fena cons ELECTROLYSIS OF WATER SOUTE 1 4N BATTHY HOFMANN VOLTAMETER HYDR A NAME THE APPARATUS USED FOR ELECTROLYSIS B NAME THE ELECTROLYTE USED

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryHydrogen gas is produced in laboratory by action of calcium on a dilute sulphuric acid solution If 90 L of wet H is collected over water at 27 C and a barometri pressure of 212 torr how many grams of Ca have been consumed The vapor pressure of water at this temperature is 22 torr Take R atm L mol K O 36 g O 40 17 g O 44 34 g O 32 g

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryThe gas phase reaction 2A g A g at 400 K has AG 25 2 kJ mol 1 The equilibrium constant Kc for this reaction is Integer Use R 8 3J mol 1 K 1 In 10 2 3 log10 2 0 30 1 atm 1 bar antilog 0 3 0 501 en x10 2 Round off to the Nearest

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryConsider the half cell reduction reaction Mn2 2e Mn E 1 18 V Mn e E 1 51 V 3 Mn2 The E for the reaction 3Mn Mn 2Mn and possibility of the forward reaction are respectively a 4 18 V and yes c 2 69 V and no b 0 33 V and yes d 2 69 V and no

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryFrom the available data predict at what tem perature will be the reaction given below be comes spontaneous N2 g O2 g 2NO g Given SN2 S02 204 9JK mol and SNO 210 5JK mol and AH 180 84JK mol 191 4JK mol

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryConsider the reaction ICI g Cl g ICl3 s The AG of the reaction is 17 09 kJ mol Calculate the AG in kJ mol for the reaction at 298 K if the partial pressure of ICI g is 0 0260 atm and the partial pressure of Cl g is 0 00100 atm

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryWhat is the potential of an electrode which originally contained 0 1 M NO and 0 4 MH and which has been treated by 60 of the cadmium necessary to reduce all the NO to NO g at 1 atm AAJ KA TOPPER Given NO 4H 3 NO 2H O E 0 95V and log2 0 3010 1 0 52 V 3 0 86 V 2 0 44 V What is the major product of the reaction 4 0 78 V

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryThe standard electrode potentials of Zn Zn Cu Cu and Ag are respectively 0 76 0 34 and 0 8 V The following cells were constructed 1 ZnZn Cu Cu II ZnZn Ag Ag III Cu Cu Ag Ag What is the correct order of E of these cells 1 2 II I III 3 III 4

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistry3 In which of the following cells EMF is greater than Eccell O A Pt H 8 H pH 5 H pH 3 H 8 Pr B Zn s Zn 0 2M Cu 0 1M Cu s C Cr s Cr 0 1 M Cu 0 2M Cu s 3 D Pt H g H pH 4 H pH 6 H g Pt

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryElectrochemical series helps us to calculate the standard EMF of any cell However if the con centrations of the electrolytes in the halfcells are not 1 M and temprature is not 298 K Nernst equation is used to know the exact EMf of the cell Further using the identical electrodes but with different concentrations of the elctrolyte in the two half cells a cell can be set up called concen tration cell For cell reactions in equilibrium Nernst equation can be applied to find the equilibrium constant of these reactions from the standard EMF of the cell 0 75 V E Fe Given Er Cr 3 will be A 0 2409V 3 0 45 V the EMF of the cell Cr Cr 0 1M Fe 0 01M Fe DY 0 2606 V B 0 3394 V C 0 30 V The Equlibrium constant of the cell reaction will be of the order of A 1010 B 1020 C 1030 D 1040 The iron electrodes are used in both the half cells but in one halfcell 0 1M FeSO4 solution is taken but in the other 0 01M FeSO solution is taken the EMF of the cell will be A 0 591 V B 0 0295 V C 0 0098 V D 0 0197 V 11

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistry25 What conclusion about the unknown substance can be inferred from the graph below Solubility of Unknown Substance in Water at 1 atm A The substance is a supersaturated sa salt B The substance is an unsaturated salt C The substance is a gas

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryThe EMF of a cell corresponding to the reaction Zn s 2H aq Zn 0 1M H g latm is 0 28 volt at 25 C The pH of the solution at the hydrogen electrode AAJ KA TOPPER E 0 76 volt E 0 1 2 30 2 7 8 3 9 2 Arrange the following in correct order of Lewis acidity BF BCL BBr 4 8 30

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistry2 Cu s Cut2 1 M Zn2 1 M Zn s Cist A cell represented above should have emf 1 Positive E 2 Negative 3 Zero 4 Cannot be predicted

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryWhich of the following is incorrect O Am NaCl Am NaBr Am KC1 Am KBr A H O A HCl NaOH Am NaCl 0 Am NaCl Am KCl AM NaBr Am KBr Am Nal Am NaBr Am NaBr Am KBr

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistryom the following equivalent conductances at infinite dilution A for Ba OH 288 8 ohm cm equivalent Ao for BaCl 120 3 ohm cm equivalent Ao for NH4C1 129 8 ohm cm equivalent culate Ao for NH OH Ans 238 3 ohm C

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistry4 trans Co en Cl 1 cis PI NH CI 2 trans PI NH CL1 3 cis Co en CLI How much chlorine will be liberated on passing one ampere current for 30 minutes throught NaCl solution 1 0 66 mole 2 0 33 mole 3 0 66 g 4 0 33 g The heat of dissociation of benzene in isolated gaseous atoms is 5335 kJ mol The bond enthalpies of C C C C and C H bonds are 347 3 615 and 416 2 kJ respectively Ma

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryConsidering entropy S as a thermodynamic parameter the criterion fo any reaction to be spontaneous is O ASsystem ASsurroundings 0 O AS system 0 O AS surroundings 0 O ASsystem AS surroundings V 0

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistry10 The conductivity of sodium chloride at 298 K has been determined at different concentrations and the results are given below Concentration M 10 x K S m 0 001 1 237 1 0 010 11 85 0 050 0 100 55 53 106 74 1 2 Calculate Am for all concentrations and draw a plot between Am and c 2 Find the value of A C 0 020 23 15
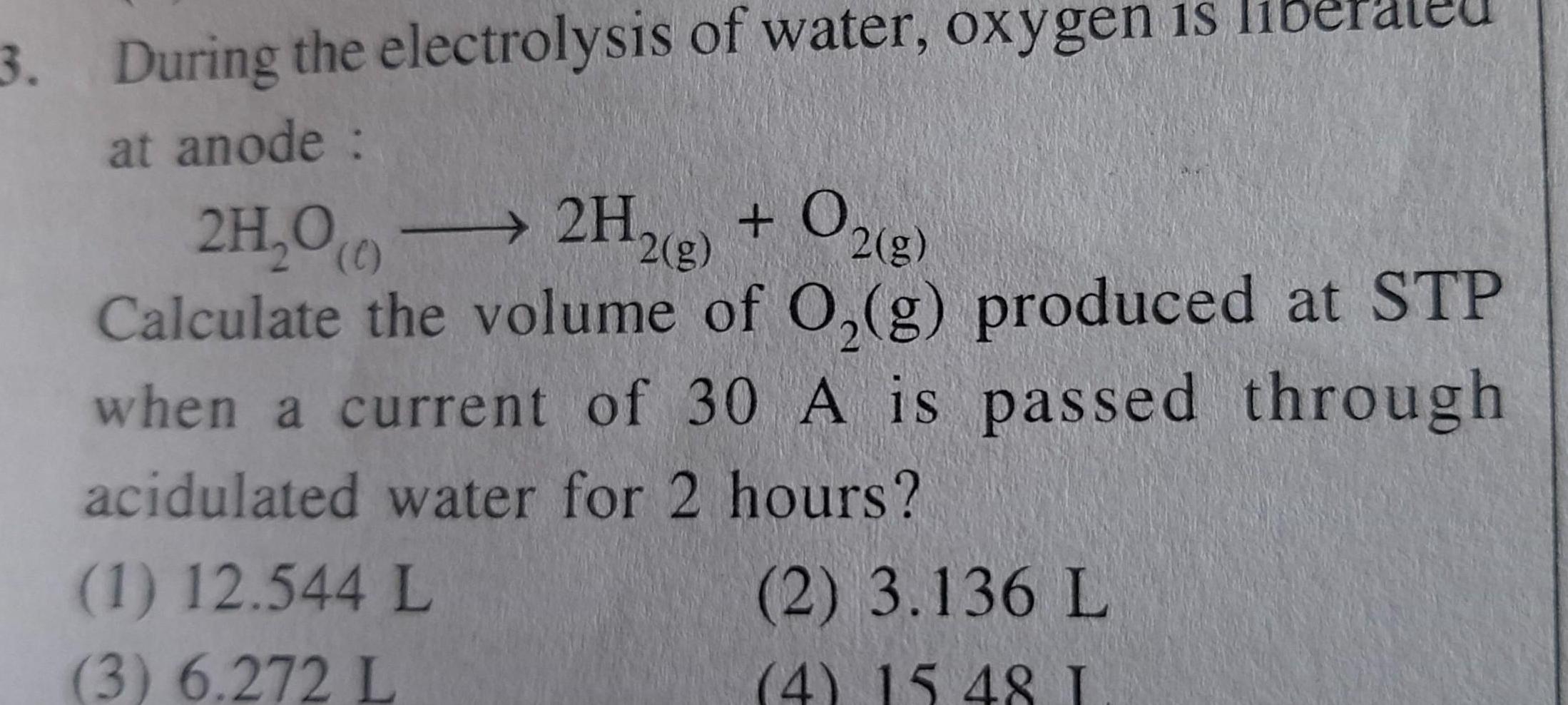
Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistry3 During the electrolysis of water oxygen is at anode 2H 00 2H2 g O2 g Calculate the volume of O g produced at STP when a current of 30 A is passed through acidulated water for 2 hours 1 12 544 L 3 6 272 L 2 3 136 L 4 15 48 I

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryHalf of a substance is consumed in 40 minutes When the quantity of the substance is decreased to half the half life of the change is 20 minute The order of the reaction is 1 zero 2 1

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryReduction potential of half cell AgI aq saturated Ag E 10 16 is V 0 328 c 0 328 Agt Ag 0 8 V Ksp of AgI is b 1 272 0 146 3 1 fo

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryFor the reaction Ni s Cu2 1M Ni29 1M Cu s E cell 0 57V AG of the reaction is a 110 kJ b 110 kJ c 55 kJ d 55 kJ

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryThe emf of the cell 1 1 10 PL H HAHCIH Pt 0 0IM IM 2 1 10 is 0 295V Dissociation constant of the acid HA is x 0 1 10 s 3 1 10 8 n 03 Pra

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryA drop of a solution volume 0 05 mL contains 6 x 10 7 mol of H If the rate of disappearance of H is 6 0 x 105 mol L 1 s 1 how long will it take for the H in the drop to disappear completely 1 8 0 x 10 8 S 3 6 0 x 10 6 S 2 2 0 x 10 8 s 4 2 0 x 10 2 S

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryTwo solutions concentrations conductivities have the ratio of their 0 4 and ratio of their 0 216 The ratio of their molar conductivities will be b 11 574 d 1 852 a 0 54 c 0 0864

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryStrong electrolytes are given NaOH KOH NaCl CH COONa BaC A B C D Molar conductivity of Ba OH 2 at infinite dilution can be determined with the help of molar conductivity at infinite dilution of O A B and D OA C and D O A C and E OB C and D E

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryBy diluting a weak electrolyte specific conductivity Kc and equivalent conductivity 2c change a A Both increase B Kc increases Ac decreases CKc decreases Ac increases D Both decrease

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryHow many coulombs of electricity are required for the oxidation of 1 mole of H O to O 1 9 65 x 104 C 2 4 825 x 105 C 4 1 93 x 104 C 3 1 93 x 105 C

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistry1 NH C During electrolysis of water cost of electricity for the production of X litre H at NTP at cathode is Rs X then cost of electricity for the production X litre O gas at NTP at anode will assume 1 mole of electrons as one unit of electricity 2x 2 4X 3 16X 4 32X

Physical Chemistry
ElectrochemistryAn aqueous solution of CuSO4 measuring 1 L was electrolysed till the pH of the solution was found to be 1 Then the amount of Cu deposited and the volume of gase evolved at STP are respectively Cu 63 5 g mol

Physical Chemistry
Electrochemistry22 An aqueous solution of Na SO4 in water is electrolysed using Pt electrodes The products at the cathode and anode are respectively a H2 SO 2 b O NaOH c H 02 enosups to d O2 SO2 da II a ot the cathode and O g a