Solutions Questions and Answers

Physical Chemistry
Solutions25 On addition of one ml solution of 10 Naci to 10 ml gold sol in the presence of 0 25 gm of starch the coagulation is just prevented Starch has the following gold number

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsx 2 A solution of ethanol in water is 10 by volume If the solution and pure ethanol have densities of 0 9866 g cc and 0 785 g cc respectively find the per cent by weight

Physical Chemistry
Solutions4 Two bottles of A and B contains 1M and 1m aqueous solution d 1gmL of sulphuric acid respectively 1 A is more concentrated than B 2 B is more concentrated than A 3 Concentration of A concentration of B

Physical Chemistry
Solutions137 What is the percentage hydrolysis of NaCN in N 80 solution when the dissoelation constant for HCN in 1 3 109 and Kw IC 1 0 10 14 1 2 48 3 8 2 2 5 26 4 9 6 1

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe mole fraction of a solute in a solution is 0 1 At 298 K molarity of this solution is the same as its molality Density of this solution at 298 K is 2 0 g cm The ratio of the molecular weights of the solute is JEE Advanced 2016 3 124 and solvent MWsolute MWsolvent

Physical Chemistry
Solutions1 A solution of sodium sulphate contains 92 g of Nations per kilogram of water The molality of Nations in that solution in mol kg is a 16 b 4 c 132 2019 Main 9 Jan I d 8

Physical Chemistry
Solutions0 5 molal aqueous solution of a weak acid HX is 20 ionised If K for water is 1 86 K kg mol the lowering in freezing point of the solution is 1 0 56 K 2 1 12 K 3 0 56 K 4 1 12 K

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsc 21 Which of the following statements about the composition of the vapour over an ideal 1 1 molar mixture of benzene and toluene is correct Assume that the temperature is constant at 25 C Given vapour pressure data at 25 C benzene 2016 12 8 kPa toluene 3 85 kPa a Not enough information is given to make a prediction b The vapour will contain a higher percentage of benzene c The vapour will contain a higher percentage of toluene d The vapour will contain equal amounts of benzene and toluene

Physical Chemistry
Solutions100 mL of 0 1N I oxidizes Na S O in 50 ml solution to Na S O The normality of this hypo soluti against KMnO which oxidizes it to Na SO would be A 0 1 B 0 2 C 1 0 D 16

Physical Chemistry
Solutions5 Calculate the pH of a buffer solution prepared by dissolving 30g of Na CO in 500 mL of an aqueous solution containing 150 mL of 1M HCl Ka for 3 133 109 150 HCO 5 63 x 10 11 log 1 8 197 3 10 197 0 05 2 9 197 4 11 197

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsOn adding 1mL solution of 10 NaCl to 10 mL 89 gold sol in presence of 0 25 g starch so that coagulation is just prevented what will be gold number of starch 1 0 25 2 2 5 3 250 4 0 025

Physical Chemistry
Solutions21 Calculate the mass percentage of benzene C6H and carbon tetrachloride CCL if 22 g of benzene is dissolved in 122 g of carbon tetrachloride 22 Calculate the mole fraction of benzene in solution containing 30 by mass in carbon tetrachloride 2 3 Calculate the molarity of each of the following solutions a 30 g of Co NO3 2 6H O in 4 3 L of solution b 30 mL of 0 5 M H SO4 diluted to 500 mL 2 4 Calculate the mass of urea NH CONH required in making 2 5 kg of 0 25 molal aqueous solution 2 5 Calculate a molality b molarity and c mole fraction of KI if the density of 20 mass mass aqueous KI is 1 202 g mL

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAn ideal solution was obtained by mixing methanol and ethanol If the partial vapour pressure of methanol and ethanol are 2 619 K Pa and 4 556 K Pa respectively the composition of vapour in terms of mole fraction will be 1 0 635 MeOH 0 365 EtOH 2 0 365 MeOH 0 635 EtOH 3 0 574 MeOH 0 326 EtOH 4 0 173 MeOH 0 827 EtOH

Physical Chemistry
Solutions8 How many g of dibasic acid mol wt 200 should be present in 100 ml of its aqueous solution to give 2003 decinormal strength a 1 g 10g b 2 g d 20 g

Physical Chemistry
Solutions20 Decomposition of a non volatile solute A into another non volatile solute B and C when dissolved in water follow first order kinetics as A 2B C When one mole of A is dissolved in 180 g of water and left for decomposition vapour pres sure after 12 hours was found to be 20 69 mm of Hg Determine V P of the solution after 30 hours Assume constant temperature through out to be 27 C and V P of pure water at 27 C is 24 mm of Hg

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsa total pressure of I atm The system N O4 2 NO maintained in a closed vessel at 60 C a pressure of 5 atm 2 average i e observed molecular weight of 69 calculate K At what pressure at the same temperature would the observed molecular weight be 230 3

Physical Chemistry
Solutions6 A detergent C12H25SO Na solution becomes a colloidal sol at a concentration of 10 3 M On an 100 average 1013 colloidal particles are present in 1 mm The average number of ions which are contained by one colloidal particle micelle is Given N 6 x 10 11

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe difference between elevated boiling point and depressed freezing point of an aqueous solution is 102 C The molality of the solution if it contains non volatile and non electrolyte solute will be 2 1 K Kb 3 K K 3 102 2 K K 3 4 K K

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsTwo bottles of A and B contains 1M and 1m aqueous solution d 1g mL of sulphuric acid respectively 1 A is more concentrated than B 2 B is more concentrated than A 3 Concentration of A conc of Bed 4 It is not possible to compare the entration

Physical Chemistry
Solutions200 ml of a sample of water required 2 94 mg of K Cr O eq wt 49 in the presence of H SO for the oxidation of dissolved organic matter in it The COD of the water sample is a 2 4 ppm b 4 8 ppm c 9 6 ppm d 16 ppm

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAIMS 2017 0 5g of an unknown solute is dissolved in 295 g solvent If molarity and density of solution are 47 0 05 M and 1 5 g cc respectively The molecular weight of unknown solute is 1 375 2 425 3 400 The depression in freezing poi Molality 4 500

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe mass of glucose that should be dissolved in 50 g of water in order to produce the same lowering of vapour pressure as is produced by dissolving 1 g of urea in the same quantity of water is a 1 g c 6 g b 3g d 18 g 2006
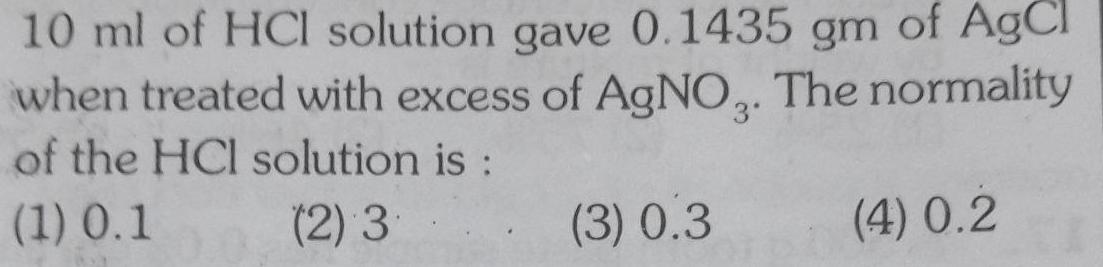
Physical Chemistry
Solutions10 ml of HCl solution gave 0 1435 gm of AgCl when treated with excess of AgNO3 The normality of the HCl solution is 1 0 1 2 3 3 0 3 4 0 2

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsSolvent which is better to be used during ebullioscopic measurement has 1 High K 3 K K 2 Low K 4 Unpredictable

Physical Chemistry
Solutions26 The molecular weight of benzoic acid in benzene as determined by depression in freezing point method corresponds to 1 Ionisation of benzoic acid 2 Dimerization of benzoic acid 3 Trimerization of benzoic acid 4 Solvation of benzoic acid

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsSingle The vapour pressure of pure benzene at 25 C is 639 7 mm Hg and the vapour pressure of solution of solute in benzene at 25 C is 631 9 mm Hg The molality of the solution is 7 Types A 0 156 C 0 518 B 0 108 D 0 815

Physical Chemistry
Solutions10 101 ei nijulpe to jaio emilion The cryoscopic constant for acetic acid is 3 6 K kg mol A solution of 1 g of a hydrocarbon in 100 g of acetic acid freezes at 16 14 C instead of the usual 16 60 C The hydrocarbon contains ositib 0 C01 di noitu 92 3 carbon What is the molecular formula 10120 0 70m

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsOn adding a non volatile solute to a solvent the vapour pressure of solvent decreases and becomes z x vapour pressure of solvent where z is 1 mole fraction of solvent 2 mole fraction of solute 3 molality 4 molarity

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsseparate 1 Chloroform and Aniline 2 Ether and Toluene 3 Hexane and Toluene

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA 0 0020 m aqueous solution of an ionic compound Co NH3 5 NO CI freezes at 0 00732 C Number of moles of ions which 1mol of ionic compound produces on being dissolved in water will be K 1 86 C m 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4

Physical Chemistry
Solutions1 00g of a non electrolyte solute molar mass 250g mol was dissolved in 51 2g of benzene If the freezing point depression constant K of benzene is 5 12 K kg mol 1 the freezing point of benzene will be lowered by 2 0 3 K 4 0 2 K 1 0 4 K 3 0 5 K

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsed K for benzene 5 12 kg mol K The molar volume of liquid benzene density 0 877 g ml increases by a factor of 2750 as it vaporizes at 20 C and that of liquid toluene density 0 867gml increases by a factor of 7720 at 20 C A Solution of benzene toluene has a vapour pressure of 46 0 torr Find the mole fraction of benzene in the vapour above the solution orallol glectrodes of cross section area 4cm

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsCane sugar underoges the inversion as follow C 2H 2O11 H O CH O CH 2O6 12 6 12 If solution of 0 025 moles of sugar in 200 gm of water show depresion in freezing point 0 37 then what sucrose has inverted K H O 1 86 K kg mol

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsand mole fraction of solute Calculate the amount of ice that will separate out of cooling a solution containing 50g of ethylene glycol in 200 g water to 9 3 C K for water 1 86 K mol kg A solution of crab hemocyanin a pigmented protein extracted from crabs was prepared by dissolving

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe density of 3 M solution of NaCl is 1 25 g ml Calculate molality of the 1 solution

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsmolecular formula K H O 0 52 K mol kg A complex is represented as CoCl xNH It s 0 1 molal solution in a solution show AT 0 558 C K for H O is 1 86 K mol kg Assuming 100 ionisation of complex an coordination no of Co is six calculate formula of complex Agolution containin

Physical Chemistry
Solutions3 2 mol of A is mixed with 3 mol of B to form an ideal solution such that the total vapour pressure over the solution becomes 500 mm Hg If 1 mol of B is further added vapour pressure becomes 450 mm Hg What is the vapour pressure of pure component B 1 675 mm Hg 2 950 mm Hg 3 200 mm Hg 4 575 mm Hg

Physical Chemistry
Solutions8 For an ideal solution with pAP which of the following is 02 to no aki elom ons o true gh to mm 05 at onderong of a XA liquid X4 vapour XA vapour b XA liquid XA liquid XA vapour 193 c d XA liquid and X with each other sdu 201 2018i0022s fonod noitulos Amih ati automaad an do not bear any relationship rob si 1 2 onesned 502 1 4 CF 0 XA vapour vapour Tom

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe freezing point of an aqueous solution of KCN containing 0 1892 mol Kg was 0 74 C On adding 0 095 mol of Hg CN the freezing point of solution was 0 53 C Assuming that complex is formed according to the equation Hg CN mCN Hg CN 2 The value of m is X then what is 2X 3

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsIn cold climate water freezes causing damage to the car radiator Ethylene glycol is used as antifreeze agent Calculate the amount of ethylene glycol to be added to 4 kg of water to prev it from freezing at 8 C K H O 1 86 K kg mot

Physical Chemistry
Solutions50 50 mL of 1 M oxalic acid is shaken with 0 5 g wood charcoal The final concentration of the solution after adsorption is 0 5 M What is the amount of oxalic acid adsorbed per gram of carbon b a 3 15 g c 6 30 g b 3 45 g d none of these vbmil Se

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsArtificial rain is caused by spraying a opposite charged collidal dust over a cloud b same charged collidal dust over a cloud c both d none of these

Physical Chemistry
Solutions0 7 g of Na CO xH O is dissolved in 100 ml 20 ml of which required 19 8 ml of 0 1 NHCI The value of x is 1 4 2 3 3 2 4 1 diluted bu

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe number of unit cells in a cube shaped ideal crystal of NaCl is 512 The number of unit cell along each edge of the ideal crystal is

Physical Chemistry
Solutions2 Benzene and naphthalene form an ideal solution at room temperature For this process the true statement s is are a AG is positive b AS is positive system c AS surroundings 0 d AH 0 2013 Adv

Physical Chemistry
Solutions28 When mercuric Iodide is added to the aqueous solution of potassium iodide 1 The boiling point does not change 2 Freezing point is raised 3 The freezing point is lowered 4 Freezing point does not change SOE


Physical Chemistry
SolutionsN 3 15 g of ice 4 Same in all 37 Concentrated aqueous sulphuric acid is 98 H SO4 w v and has a density of 1 80 gmL 1 Molarity of solution 1 1 M 2 1 8 M 3 10 M 4 1 5 M 38 An element X has the following isotopic composition 56X 90 57X 8 59X 2 0 The hic mass of the naturally 45 The numb 1 8 3 7 46 Mole frac NaOH 1 0 16 3 0 25 Imp fo Ass

Physical Chemistry
Solutions2 What is correct relation between mole fraction in vapour phase YA of A in terms of X If mole fraction in solution of A is X If PA is vapour pressure of A in pure state 1 1 XA PA 3 1 XAPO Y XA PA 2 1 XA 4 POXA

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe Henry s law constant for solubility of gas A in water at 25 C is 10 atm The by volume of gas A 50 in gaseous mixture The number of moles of A dissolved in 100 mol of water at 10 atm pressure 298 K is A 5 104 B 10 x 104 C 5 10 D 10 x 10