Solutions Questions and Answers

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAt a particular temperature, the solubility of H₂ in water is 0.0200 M when the partial pressure is 0.0900 atm. What will the solubility (in M) be when the partial pressure of H₂ is 1.54 atm?

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhat is the concentration in molarity of a solution which is 8.39 %m/v phenol (MM = 94.11 g/mol) in methanol (MM = 32.04 g/mol)?

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhat mass in grams of CH3OH (MM = 32.04 g/mol) would need to be added to 200.1 g of water in order to lower the freezing point of water by 12.0 °C? (Kf for water is 1.86 °C/m)

Physical Chemistry
Solutions(NH4)2SO4 has a van't Hoff factor of i = 2.3. What is the concentration of particles in a 0.6901 M solution of (NH4)2SO4?

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA 83.5 g sample of a nonelectrolyte is dissolved in 308.5 g of water. The solution is determined to have a boiling point of 102.3 °C. What is the molar mass of the compound? (Kb for water is 0.510 °C/m).

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsMgCl2 has a van't Hoff factor of 2.70. What would be the boiling point (in °C) of an aqueous solution containing 3.30 mol of MgCl2 in 1.00 kg of water? (Kb for water is 0.512 °C/m. The boiling point for water is 100.0°C.) As

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAt a particular temperature, the solubility of CO₂ in water is 0.13 M when the partial pressure is 1.5 atm. What partial pressure (in atm) of CO2 would give a solubility of 0.080 M?

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA 0.56 M solution of MgCl₂ is determined to have a concentration of particles of 1.51 M. What is the van't Hoff factor for MgCl2?

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsDuring the analysis, 0.163 g H₂O and 0.600 g CO₂ are produced. Calculate the amount (mol) H₂O formed by combustion of 0.400 g vitamin C.

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsSodium sulfate reacts with an excess barium chloride solution and forms barium sulfate:
BaCl₂(aq) + Na₂SO4(aq) ---> BaSO4(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
10.56 g BaSO4 of is precipitated from 500 mL of Na2SO4. What is the molarity of sodium sulfate?
0.18 m
0.18 M
0.09 M
0.09 m

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAniline, the molecule pictured above, is 0.125
M with a volume of 350 mL and is titrated
with 0.250 M hydrobromic acid. The Kb for
aniline is 4.0x10-10. Determine the pH at each
of the points listed below:
a. Initial pH
b.Midpoint
c. 200 mL of acid was added
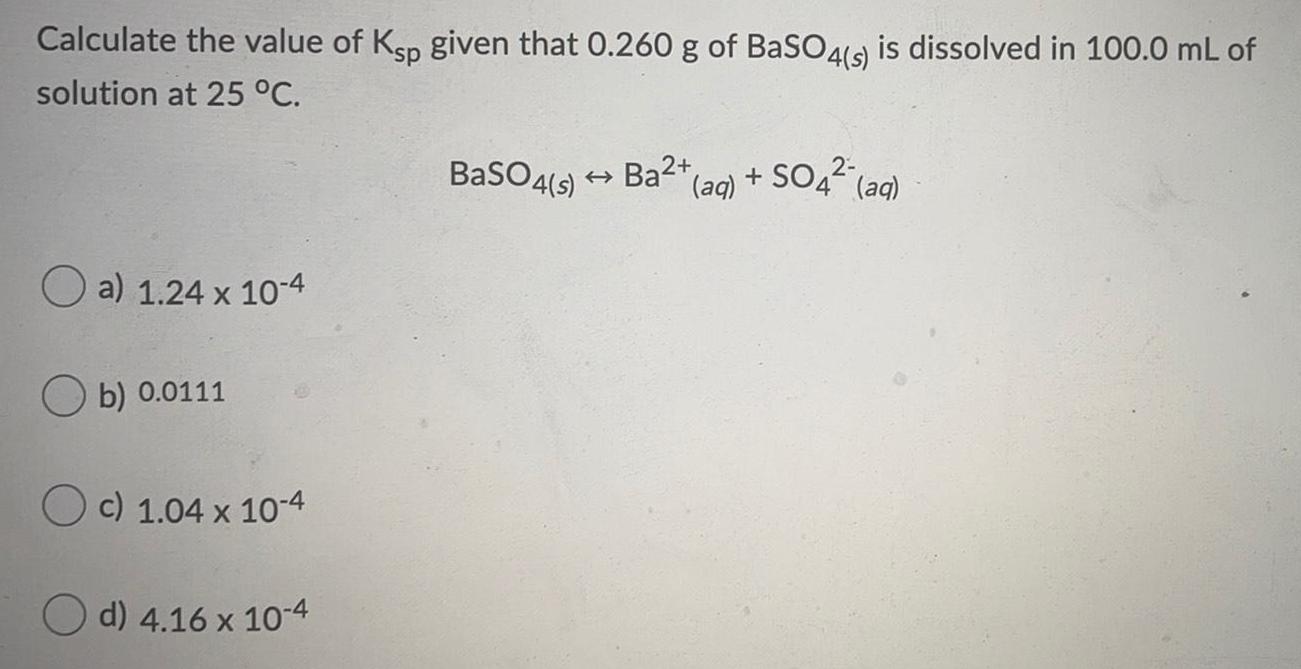
Physical Chemistry
SolutionsCalculate the value of Ksp given that 0.260 g of BaSO4(s) is dissolved in 100.0 mL of solution at 25 °C.
a) 1.24 x 10-4
b) 0.0111
c) 1.04 x 10-4
d) 4.16 x 10-4

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsIn order for a solute to dissolve in solution:
the solute-solvent forces must equal the solute-solute forces.
the solute-solute forces must be greater than the solute-solvent forces.
the solute-solvent forces must be greater than the solute-solute forces.
the polarity of the solute and solvent must be opposite.

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsHow many grams of potassium chlorate decompose to potassium chloride and 149 mL of O₂ at 128°C and 703 torr?
2 KCIO3(s)→ 2 KCl(s) + 3 0₂ (g)

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhat is the molarity of a solution prepared from 97.6 of NaCl in 222 mL of solution?
Report your answer with three significant figures. Do NOT include units in your answer.

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhich of the following aqueous solutions are buffer solutions?
(Select all that apply.)
[0.10 M HClO +0.22 M NaC1o
0.21 M HI+0.21 M KI
0.29 M NH4 Br + 0.35 M NH 3
0.13 M NaOH +0.25 M NaCl
0.33 M HF +0.20 M NaF


Physical Chemistry
SolutionsCalculate the molarity of 0.300 mol of Na₂S in 1.20 L of solution.
Calculate the molarity of 34.3 g of MgS in 943 mL of solution.

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAn aqueous potassium iodate (KIO3) solution is made by dissolving 554 grams of KIO, in sufficient water so that the final volume of the solution is 4.70 L. Calculate the molarity of the KIO, solution.

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsCalculate the molarity of the two solutions.
The first solution contains 0.550 mol of NaOH in 2.45 L of solution.
molarity:
The second solution contains 11.9 g of NaCl in 753 mL of solution.
molarity:

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsHow many grams of sodium hydroxide are present in 249.0 mL of a 0.600 M NaOH solution?
mass of sodium hydroxide =

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA 100.0 mL solution of oxalic acid (H2C204) was made using 6.93 g of solid oxalic acid. This solution is then used to titrate NaOH of unknown concentration.
A) Determine the molarity of the oxalic acid solution.
B) 12.53 mL of NaOH is titrated. It takes 21.38 mL of the acid solution to reach the endpoint of the titration. What is the concentration of the NaOH?

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsComplete the following road map for converting volume of A to volume of B for a
titration of aqueous solution A with aqueous solution B.
volume A (L)
multiply by the moles
of A per moles of B
divide by the
molarity of B
multiply by the moles
of B per moles of A
divide by the
molarity of A
multiply by the
molarity of A
multiply by the
molarity of B
moles A
moles B
volume B (L)

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsClassify each given species as a strong acid, weak acid, strong base or weak base.
Sr(OH)₂
H₂SO
CH₂COOH
Strong Acid
LIOH
NaOH
Ba(OH),
Weak Acid
NH,
Ca(OH)₂
H.PO
HCIO
HNO,
KOH
Strong Base
HF
HBr
HCI
Weak Base

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsCalculate the Molarity of a NaOH solution that contains 50 g of NaOH in 100 mLs of water.
(NaOH MW = 40 g/mol.)

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAbby calculated that a reaction between oxygen and hydrogen gas should yield 0.90 grams of water. However when she conducted the lab she only produced 0.45 grams of water. How efficient was her reaction?

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhat is the vapor pressure of 20.0 percent by mass CH3OH solution in C₂H5OH solution at 25 °C?
Vapor pressure of pure CH3OH is 30.0 torr and vapor pressure of C₂H5OH is 20.0 torr at the same temperature.
14.7 torr
22.6 torr
25.0 torr
28.2 torr
30.4 torr

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhat is the molality of 10.80 percent by mass C6H806 solution in water?
A. 0.386 m
B. 0.406 m
C. 10.6 m
D. 0.414 m
E. 0.688 m

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhich of the following will show lowest viscosity?
A. CH3CH2CH2OH
B. CH3CH2OH
C. CH3CH₂Br
D. HCH2CH2OH
E. CH3CH2CH2CH2OH

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhat is the molar mass of an enzyme if 15.0 g of enzyme dissolved in 250 ml solution produces an osmotic pressure of 1.50 torr at 27 °C?
A. 7.48 x 105 g/mol
B. 985 g/mol
C. 246 g/mol
D. 3.74 x 105 g/mol
E. 4.16 x 104 g/mol

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA chemist makes 940. mL of calcium sulfate (CaSO4) working solution by adding distilled water to 70.0 mL of a 6.67 mM stock solution of calcium sulfate in water.
Calculate the concentration of the chemist's working solution. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.
mM

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAn analytical chemist weighs out 0.173 g of an unknown triprotic acid into a 250 mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. She then titrates this solution with 0.2000 M NaOH solution. When the titration reaches the equivalence point, the chemist finds she has added 26.5 mL of NaOH solution.
Calculate the molar mass of the unknown acid. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA 0.207 mole sample of Mg(OH)2(aq) requires 50.0 mL of HCl(aq) for neutralization according to the reaction:
2HCl(aq) + Mg(OH)2(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + 2H2O(l).
The molarity (M) of the HCI is _mole/L-
(pay attention to the significant figures)

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA 0.261 g sample of NaHC₂O4 (one acidic proton) required 17.5 mL of sodium
hydroxide solution for complete reaction. Write the equation for this reaction and
determine the molar concentration of the sodium hydroxide solution.

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA chemist adds 65.0 mL of a 5.22 x 10 M mercury(II) iodide (HgI₂) solution to a reaction flask. Calculate the mass in milligrams of mercury(II) iodide the chemist has added to the flask. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe compound iron(III) chloride, FeCl3 is soluble in water. Write the net ionic equation for the dissociation reaction that occurs when solid iron(III) chloride dissolves in water:
Be sure to specify states such as (aq) or (s).
___⇒H₂O____+ ____

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhen chlorine reacts with sodium iodide, sodium chloride and iodine are produced. The balanced equation for this reaction is:
Cl₂(g) + 2Nal(s)→→ 2NaCl(s) + 1₂ (s)
If 2 moles of chlorine react,
The reaction consumes __moles of sodium iodide.
The reaction produces___ moles of sodium chloride and
moles of iodine.

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsIn the laboratory, a student dilutes 26.2 mL of a 8.80 M hydrobromic acid solution to a total volume of 300.0 mL. What is the concentration of the diluted solution?
Concentration=___M

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsCheck my work Enter your answer in the provided box.
To 1.73 L of 0.420 M HCl, you add 4.26 L of a second HCI solution of unknown concentration. The resulting solution is 0.810 M HCL. Assuming the volumes are additive, calculate the molarity of the second HCI solution.
__MHCI

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsGlycerol, C3H8O3 (molar mass = 92.09 g/mol, bp = 290 °C) is present in all lipids known as triglycerides. (i) What is the vapor pressure of a solution made by adding 164.0 g glycerol to 338 mL H₂O at 39.8°C? The vapor pressure of pure water at 39.8°C is 54.74 torr and its density is 0.992 g/mL. (Hint: Glycerol's boiling point of 290°C is very high compared to the boiling point of water. So, is glycerol a volatile liquid?) (ii) Would you expect the boiling point of this solution to be higher or lower than that of pure water? Concisely explain why. (iii) What is the freezing point of this solution? The Ky value of H₂O is 1.86 °C/m.

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsCalculate the following quantity: volume in liters of 0.327 M manganese(II) sulfate that contains
79.6 g of solute.

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAt 21.2°C the vapor pressure of methanol is 101 torr. If 75 g of aspirin (MM 180.15 g/mol) is dissolved in 65 g methanol (CH3OH) what is the vapor pressure of the solution?
17.2 torr
83.8 torr
123.5 torr
101 torr
247 torr

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsEnter your answer in the provided box.
Ordinary household bleach is an aqueous solution of sodium hypochlorite. What is the molarity of a bleach solution that contains 30.1 g of sodium hypochlorite in a total volume of 386 mL?

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA chemist makes 360. mL of silver perchlorate (AgC104) working solution by adding distilled water to 80.0 mL of a 13.3 M stock solution of silver perchlorate in water.
Calculate the concentration of the chemist's working solution. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits.

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsClassify each given species as a strong acid, weak acid, strong base or weak base.
NaOH
NH,
HCI
HF
CH₂COOH
H₂SO
KOH
Sr(OH)₂
HNO
LIOH
H₂PO
Ba(OH)₂
Ca(OH)₂
HCIO
HBr

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsCalculate the following quantity: final volume of a 0.0212 M solution prepared by diluting 19.2 mL of 0.138 M lithium carbonate with water.

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA chemist prepares a solution of iron(III) bromide (FeBr3) by measuring out 157. g of iron(III) bromide into a 300. mL volumetric flask and filling the flask
to the mark with water.
Calculate the concentration in mol/L of the chemist's iron (III) bromide solution. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits.

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA chemistry student needs 30.00 g of acetic acid for an experiment. He has available 150. g of a 29.7% w/w solution of acetic acid in water. Calculate the mass of solution the student should use. If there's not enough solution, press the "No solution" button. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits.

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA chemist makes 770. mL of mercury(II) iodide (HgI₂) working solution by adding distilled water to 240. mL of a 36.3 µM stock solution of mercury(II) iodide in water. Calculate the concentration of the chemist's working solution. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits.

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAn aqueous solution has a hydrogen ion concentration of 0.1 M (10^-1 M).
(1) What is the hydroxide ion concentration in this solution?
(2) What is the pOH of this solution?
(3) What is the pH of this solution?
M