Solutions Questions and Answers

Physical Chemistry
Solutions1 2 5 L 0 0025 M weak acid CH3COOH PKA 4 7 is added with 7 5 L 0 003 M CH3COOH PKA 4 7 what is the pH for the mixture Using numeric methods 2 f 2 5 L weak acid HOCI PKA 7 6 is found to have a pH of 4 5 what is HOCI concentration After 2 5 L water is added what is the pH now Using numeric methods

Physical Chemistry
Solutions3M M 37 Consider the following reaction M MOMO M2 a 2x 24 if 1 mol of MO oxidises 1 67 mol of M to b then the value of x in the reaction is b 3 c 4 2 4 5 38 In the mixture of NaHCO and Na CO the volum given HCl required is x ml with phenolphthalein in and further y mL required with methyl orange ind Hence volume of HCI for complete reaction of Nam e b y 9 10 mL of NaHCO is oxidised by 10 mL of 0 MnO Hence 10 mL of NaHCO is neutralised a 10 mL of 0 1 M NaOH b 10 mL of 0 02 M N e 10 mL of 0 1 M Ca OH d 10 mL of 0 05 N Ba 2

Physical Chemistry
Solutions10 The vapour pressure of a pure liquid A is 40 mm Hg at 310 K The vapour pressure of this liquid in a solution with liquid B is 32 mm Hg The mole fraction of A in the solution if it obeys Raoult s law is 1 0 8 3 0 2 2 0 5 4 0 4

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhen 5 litres of a gas mixture of methane and propane is perfectly combusted at 0 C and atmosphere 16 litre of oxygen at the same temperature and pressure is consumed The amount of heat released from this combustion in kJ AH comb CH 890 kJ mol AH comb C H 2220 kJ mol is NEET Kar 2013 a 32 c 317 b 38 d 477

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsColligative properties depend on a The nature of solute particle dissolve in solution b The number of solute particle dissolve in solution c The physical properties of solute particles dissolved in solution d The nature of solvent particles

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA solution of F is prepared by dissolving 0 0868 0 0004 g NaF molar mass 41 989 0 001 g mol in 160 00 0 08 mL of water Calculate the concentration of F in solution and its absolute uncertainty Significant figures are graded for this problem To avoid rounding errors do not round your answers until the very end of your calculations F M M

Physical Chemistry
Solutions7 The vapour pressure of n hexane at 350 K is 840 torr and that of cyclohexane is 600 torr Mole fraction of hexane in the mixture that boils at 350 K and 1 atm pressure assuming ideal behaviour is 1 0 67 3 0 50 2 0 80 4 2 2

Physical Chemistry
Solutions3 What is the concentration of ethylene in units of grams per liter dissolved in water at 25 C when the C2H4 gas over the solution has a partial pressure of 0 247 atm k for C H4 at is 4 8x10 3 mol L atm

Physical Chemistry
Solutions1 The boiling point elevation constant for benzene is 2 57 C m The boiling point of benzene is 81 C Determine the boiling point of solution formed when 10 g of C4H12 is dissolved in 20 g benzene 1 71 46 2 7 14 3 85 76 4 88 14

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsDiatomic gaseous species A2 g decomposes into atomic A by first order Kinetics as A g 2A g An empty flask was filled with A2 g and N g at an initial pressure of 800 mm of Hg at 600 K and sealed After a very long time gases in the flask developed 1400 mm of Hg If half life for the decomposition process is 2 h what was the pressure in the flask after 4 h Assume N 2 to be inert gas
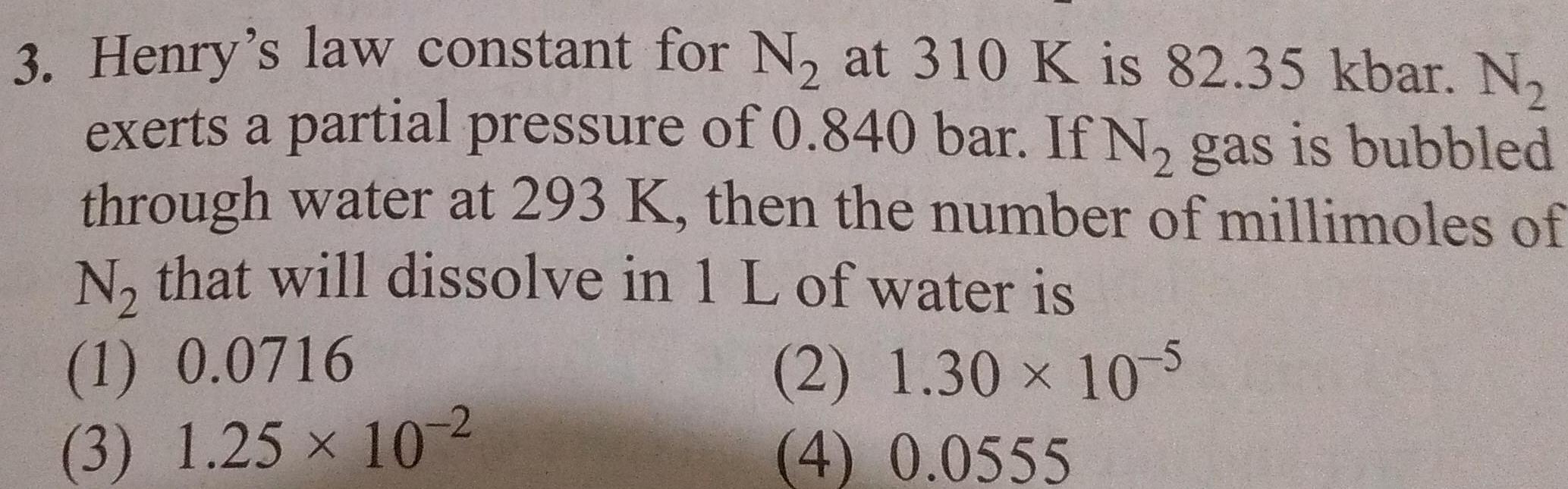
Physical Chemistry
Solutions3 Henry s law constant for N at 310 K is 82 35 kbar N exerts a partial pressure of 0 840 bar If N gas is bubbled through water at 293 K then the number of millimoles of N that will dissolve in 1 L of water is 2 1 30 10 5 4 0 0555 1 0 0716 3 1 25 10 2

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhen a gas is bubbled through water at 298 K a very dilute solution of gas is obtained Henry s law constant for the gas is 100 kbar If gas exerts a pressure of 1 bar the number of moles of gas dissolved in 1 litre of water is a 0 555 c 55 55 x 10 b 55 55 x 10 5 al d 5 55 x 10 500

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhich of the following is an incorrect property of colloids O Size of particle 1 to 1000 nm Values of colligative properties are high for colloidal solution then for true solution O Heterogenous and settle due to centrifuge Shows Brownian movement and Tyndall effect

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAn element X of atomic mass 25 0 exists as X4 in benzene to the extent of 100 When 10 30 g of saturated solution of X in benzene is added to 20 0 g of benzene the depression in freezing point of the resulting solution is 0 51 K If K for benzene is 5 1 K kg mol the solubility of Xin 100 g of benzene will be

Physical Chemistry
Solutions21 a A Sample of ferrous oxide has actual formula Fe0 9301 00 In this sample what fraction of metal ions are Fe ions What type of non stiochiometric defect is present in this sample b A solution prepared by dissolving 1 25 g of oil of winter green methyl salicylate in 99 0 g of benzene has a boiling point of 80 31 C Determine the molar mass of this compound B P of pure benzene 80 10 C and K for benzene 2 53 C kg mol

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe freezing point of a mixture containing 1 60 g of naphthalene molar mass 128 g mol and 20 g of benzene molar mass 78 g mol is 2 8 C and that of pure benzene is 5 5 C The value of the molal freezing point depression constant of benzene is A 4 3 C kg mol 1 4 3 C mol kg 1 C B D mol 1 4 3 C g 5 1 C mol g 1

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsHydrochloric acid is prepared by bubbling hydrogen chloride gas through water What is the molarity of a solution prepared by dissolving 261 L of HCI g at 37 C and 9 99 atm in 5 83 L of water Add 273 to convert to Kelvin R 0 0821 Latm mol K Report your answer to three significant figures Your Answer

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsColligative properties are very important properties of solution These are helpful in finding the molar mass of unknown compounds These properties are dependent on number of solute particles and not on its nature Consider the following curve 40 mmHg x X 1 12 W E mole fraction y 50 mmHg X 1 Read Less

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsa HCHO b CH3OH c C H5OH d C6H12O6 A 0 10 M solution of a monoprotic acid d 1 01 g cm is 5 dissociated What is the fre point of the solution The mol mass of the acid is 300 and K H O 1 86 C m

Physical Chemistry
Solutions2 51 A sample of clay was partially dried and then contained 50 silica and 7 water The original clay contained 12 water The percentage of silica in original sample is

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhich option correctly describes freezing point depression When salt is added to a mixture of ice and water salt will occupy some space in the liquid There are now fewer water particles per unit volume and the freezing point will go down Salt particles will have no effect on a solid the melting point of the ice will stay the same When salt is added to a mixture of ice and water the freezing point will increase since salt has a higher freezing point than water Salt particles will have a similar effect on the solid increasing its melting point since salt has a higher melting point than water When salt is added to a mixture of ice and water the freezing point will go down since salt has a lower freezing point than water Salt particles will have a similar effect on the solid increasing its melting point since salt has a higher melting point than water When salt is added to a mixture of ice and water salt will occupy some space in the liquid There are now fewer water particles per unit volume and the rate of freezing and melting will go down increasing the rate of melting but not the melting point

Physical Chemistry
Solutions6 Which of these statements is correct regarding a immiscible mixture of benzene 2 moles and water 3 moles at 80 oC Vapor pressure of pure benzene at 80 C 760 mm Hg Vapor pressure of pure water at 80 C 355 1 mm Hg I a Based on Dalton s law the total pressure will be 1115 1 mm Hg 1 47 atm The temperature is well above the boiling point b Based on Dalton s law the total pressure will be 517 1 mm Hg 0 68 atm The temperature is well below the boiling point c Based on Roult s law the total pressure will be 517 1 mm Hg 0 68 atm The temperature is well above the boiling point d Based on Dalton s law the total pressure will be 760 mm Hg 1 atm The temperature is exactly at the boiling point e Based on Roult s law the total pressure will be 760 mm Hg 1 atm The temperature is exactly at the boiling point

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA binary solution is prepared with 1 mole of liquid A P 50mm and 1 mole of liq B Pg 100mm If pressure over the mixture is reduced then the pressure in mm at which last trace of liquid will disappear will be

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsQ 55 Gold crystallizes in a face centered cubic lattice If the length of the edge of the unit cell is 407 pm The density of gold assuming it to be spherical is g cm Atomic mass of gold 197 amu 3

Physical Chemistry
Solutions1 Following solutions at the same temperature will be isotonic 3 42 g of cane sugar in one litre water and 0 18 g of glucose in one litre water 2 3 4 3 42 g of cane sugar in one litre water and 0 18 g of glucose in 0 1 litre water 3 42 g of cane sugar in one litre water and 0 585 g of NaCl in one litre water 3 42 g 3 42 g of cane sugar in one litre water and 1 17 g of NaCl in one litre water

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsnd the partial pressure in bar at 293K exerted by N gas over a saturated solution of 1 68mg of N dissolved in 900ml of water Given that Henry s law constant N at 293K is 78 kbar and density of water 1gm mL If the partial pressure is x x 10 bar Give x

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsDecomposition of non volatile solute A into another non volatile solute B and C When dissolved in water follows first order kinetics as H O A s 2B s C s If initially 2 mol of A is dissolved in 360 g of H O and left for decomposition at constant temperature 25 C Then Ps in the given table is assuming A B and C are miscible in water S N 1 2 Time 12 hr 80 hr The vapour pressure of solution 20 mm Hg Ps Vapour pressure mm Hg of H O at 25 C is 24 mm Hg log 2 0 30

Physical Chemistry
Solutions0 1 molar aqueous solution of NaCl and water are separated by semi permeable membrane at 27 C If external pressure of 3 atm is applied on solution side then L atm mol K R 1 12 O O Osmosis will continue O Reverse osmosis will occur Osmosis will stop Solute will move from solution to solvent

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsQNo 40 The conductivity of a saturated solution of CaF2 at 25 C is 6 x 106 Scm The conductivity of pure water is 2 x 10 Scm If A for Ca and Fions are 72 and 64 Scm mot then Kap of CaF is A C 4x 10 10 9 8 x 10 14 B D 3 2 x 10 14 D 9x10 10

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsOsmotic pressure of an aqueous solution of a non electrolyte solute is 300 mm of Hg at 27 C If certain volume of this solution is diluted by adding water and temperature is raised to 54 C then its osmotic pressure is found to be 300 mm of Hg Find increase in volume of solution after dilution

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsIf 100 ml of 1 M H SO4 solution is mixed with 100 ml of 9 8 w w H SO4 solution d 1 g ml then 1 Concentration of solution remains same 3 Mass of H S 04 in the solution is 98 g 4 Mass of H SO4 in the solution is 19 6 g

Physical Chemistry
Solutions78 Which of the following statements is are correct for the following graph vapour pressure P mole fraction D Pg x 1 1 Minimum boiling azeotrope is formed at point D 2 Liquid A is more volatile than B 3 A and B form ideal solution at point D 4 Both 1 3 are correct 3 of 4 mc 82 H

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA buffer solution cannot be prepared by mixing solution of O Potassium chloride and Potassium hydroxide O Ammonium hydroxide and Ammonium chloride Acetic acid and Sodium acetate vis BULL

Physical Chemistry
Solutions3 Using the Gibbs energy change AG 63 3 kJ for the following reaction Ag CO3 s 2Ag aq CO aq the Ksp of Ag CO3 s in water at 25 C is R 8 314 J K 1 mol 1 3 2 x 10 26 2 8 0 x 10 12 3 2 9 10 3 4 7 9 x 10 AIPMT 2014

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsing point 6 A solution containing 12 5 g of non electrolyte substance in 185 g of water shows boiling point elevation of 0 80 K Calculate the molar mass of the substance K 0 52 K kg mol a 53 06 g mol 1 b 25 3 g mol c 16 08 g mol 1 et d 43 92 g mol 1

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsSolveLancer Test In the following reaction to produce 89 6 L of ammonia at STP how many moles of N and H will be required respectively SolveLancer Test N g 3H g 2NH3 g a 1 3 b 2 6 c 3 9 d 0 5 1 5

Physical Chemistry
Solutions2 If in 0 2 mol CuSO4 aq solution 0 5 mol KI is added then freezing point of solution assume 100 ionization 1 Will increase 2 Will decrease 3 Remain same 4 Will decrease and becomes half

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAn azeotropic solution of two liquids has a point lower than either of the boiling points of th two liquids when it 1 Shows negative deviation 2 Shows positive deviation 3 Shows no deviation turated

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA 5 solution w W of cane sugar molar mass 342 g mol has freezing point 271 K What will be the freezing point of 5 glucose molar mass 18 g mol in water if freezing point of pure water is 273 15 K a 273 07 K c 273 15 K b 269 07 K d 260 09 K

Physical Chemistry
Solutions17 Equal moles of benzene and toluene are mixed the V P of benzene and toluene in pure state are 700 and 600 mm Hg respectively The mole fraction a benzene in vapour state is 1 0 7 3 0 50 2 0 47 4 0 54

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsTwo weak monobasic organic acids HA and HB have dissociation constants as 1 5 x 10 5 and 1 8 105 respectively at 25 C If 500 ml of 1 M solutions of each of these two acids are mixed to produce 1 litre of mixed solution what is the pH of the resulting solution

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe expression relating molarity M of a solution with its molality m is where d density Mg mol wt of solute 1000 M 1000d M MB 1 3 m m 1000d MMB M 2 m 4 m 1000 M 1000d M MB 1000d MMB 1000 M

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAt 323K the vapour pressure in mm of Hg of a methanol ethanol solution is represented as P 120X 140 Where X is the mole fraction of methanol in liquid solution at equilibrium The value of P ELOH is 260 mm 20 mm 120 mm 140 mm

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe mass of NaCl added in 100 g water to ma its boiling point 100 C is k 0 51 K kg mol 1 10 68 g 2 5 34 g 3 2 67 g

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAf solute and solvent interactions are more than solute solute and solvent solvent interactions then 1 It is ideal solution 2 It is non ideal solution with positive deviation 3 It is non ideal solution with negative deviation Con t predicted LA

Physical Chemistry
Solutions26 Density of 3M solution of NaCl is 1 25 g mL Calculate the volume of water required to make 1000 mL of t NaCl solution Consider the density of water as 1 g mL A 1074 5 mL B 1250 mL C 824 5 mL D 1000 mL

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsIf 2 4 g of a metal displace 1 12 litre hydrogen at norm temperature and pressure equivalent weight of metal would be 12 24 CORRECT ANSWER

Physical Chemistry
Solutions2 12 points total A wastewater pH 9 is contaminated with the following acid base 001 armiog latot In 152 maldos systems H3ASO4 H ASO4 HASO4 AsO4 pKa 1 2 3 pK a2 6 8 pK a 3 11 6 N2H6 N2Hs N H4 pK a 1 0 9 pK a 2 8 1 H SO4 HSeO4 SeO4 pK a 1 3 0 pK a2 1 7 Indicate predominant species for each acid base system justify your answer hawana Y VEZZO blow asinge lbsolontib

Physical Chemistry
Solutions2 When a non volatile solute A is added to solvent B its vapour pressure is reduced by 10 If molar mass of B is 30 of molar mass of A the mass ratio of B and A is a 0 33 c 3 0 b 6 0 d 0 66

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsEqual volume of 0 2 N Na2SO4 and 0 1 N BaCl solutions are mixed together Assume that BaSO4 is completely insoluble If K6 H O 0 52 K kg mol what would be the normal boiling point of the resulting solution Assume molality molarity O100 15 C 100 75 C 100 091 C 100 175 C