Organic Chemistry Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionWhat is the oxidation number for carbon in the ionic compound potassium carbonate (K₂CO3)?
-6
+4
-4
+3

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionWhich of the following statements about electrochemical cells is true?
Only oxidation half-reactions are useful
Oxidation occurs at the anode
Reduction occurs at the anode
An element with a strong attraction to electrons will be easily oxidized

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryM/Ch. In a hydration reaction, an alkene is converted to what type of compound?
an alkyne
an alcohol
an amide
an aldehyde

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryWhich species is oxidized in the following reaction?
2Hg²+ + N₂H4 → 2Hg + N₂ + 4H
This is a reduction reaction not an oxidation reaction
Nitrogen
Hydrogen
Mercury

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionWhich of the following statements is true about redox reactions?
Oxidation reactions always occur with reduction reactions because if one
element is losing electrons, another has to be gaining them.
An oxidizing agent is a species that is reduced.
An atom is reduced when it gains electrons.
All of the above are true.

Organic Chemistry
Halogen DerivativesClassify the electron donating group as one of the following.
Weak base - Poor nucleophile
Weak base - Good nucleophile
Strong base - Good nucleophile
Strong base Poor nucleophile

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryWhat are the intermolecular forces experienced by the interaction of the following molecules? NH3 and C6H6 (benzene)
only dispersion forces
dipole-induced dipole forces and dispersion forces
ion-induced dipole forces and dispersion foces
dipole-dipole and dispersion forces
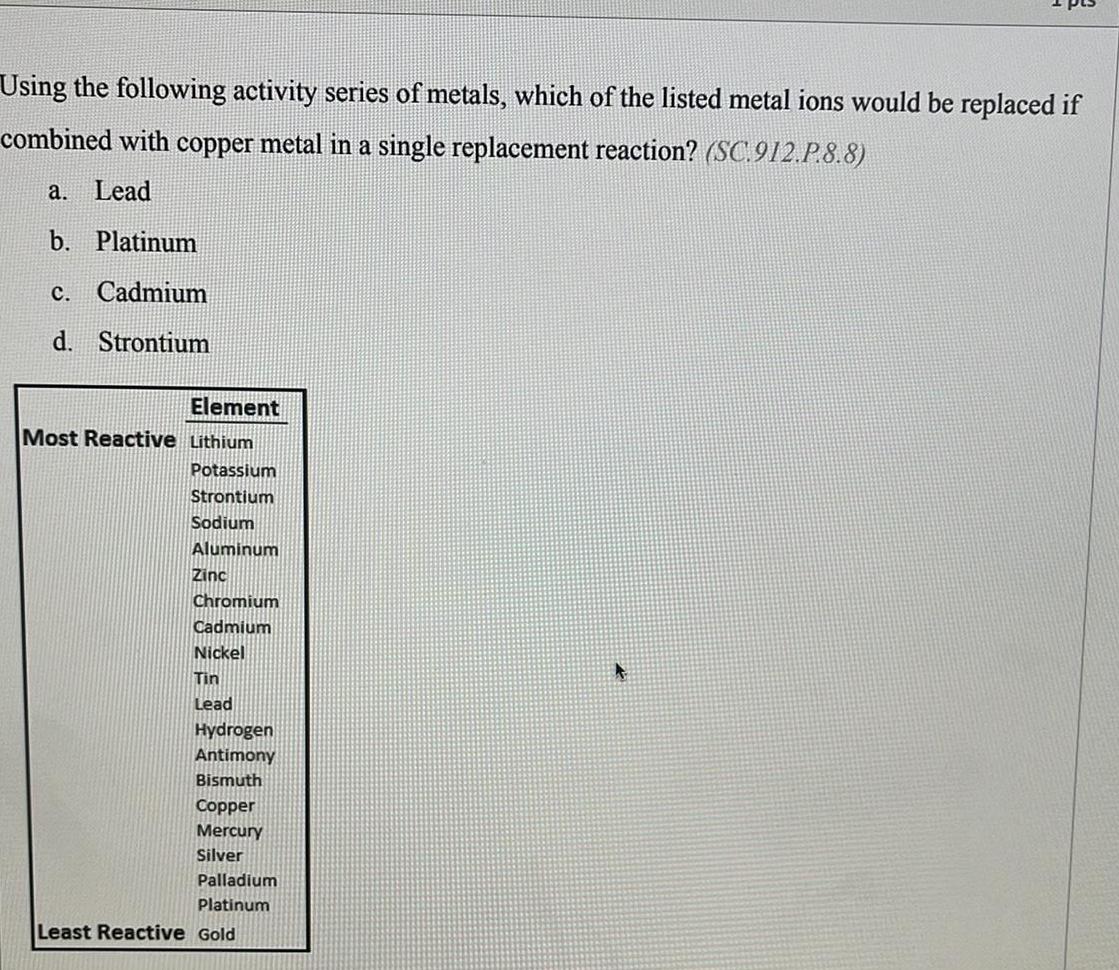
Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryUsing the following activity series of metals, which of the listed metal ions would be replaced if combined with copper metal in a single replacement reaction?
a. Lead
b. Platinum
c. Cadmium
d. Strontium

Organic Chemistry
Halogen DerivativesWhen (1R,2R,4S)-2-bromo-4-isopropyl-1- methylcyclohexane is reacted with sodium ethoxide only one product forms. Which alkene is it? (Chair conformations provided as a guide.)
Product 1)
Product 2)

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry in Daily LifeOn the basis of their electron configurations, predict the formula of the simple binary ionic compounds likely to form when the following pairs of elements reacts with each other.
a. aluminum, Al, and selenium, Se:
b. magnesium, Mg, and oxygen, O:
c. lithium, Li, and arsenic, As:

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryIdentify the best reagents to achieve the following transformation:
1. conc. H₂SO4, heat; 2. HBr, ROOR
1. NaOEt; 2. HBr, ROOR; 3. t-BuOK
1. NaOEt; 2. BH3 THF; 3. NaOH, H₂O2
1. conc. H₂SO4, heat; 2. HBr

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry in Daily LifeBaCO3 + 2HNO3 → Ba(NO3)2 + CO₂ + H₂O
What mass of barium nitrate can be formed by the reaction between 75.0 g barium carbonate
and 35.00 g nitric acid? Then calculate how much excess reactant is left over.

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryMetal Specific Heat (J/g°C)
Calcium 0.647
Iron 0.449
Silver 0.235
Gold 0.129
Ten grams of all four substances above are pulled from the same container of hot oil with a temperature of 250°C. Determine which substance will cool off fastest and explain how you know.

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryWrite balanced equations for the ionization of each of the
following carboxylic acids in water.
acetic acid

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionIt required 66.66 mL of 2.000 M Al(OH)3 to titrate (neutralize) 100.00 mL of an HBrO3 solution. What is the molarity. M, of the HBrO3 solution?
3 HBrO3+ Al(OH)3 --> 3 H₂O + Al(BrO3)3
A. 0.4000 M
B. 1.333 M
C. 2.000 M
D. 4.000 M

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryWhich of the following statements is (are) true for the compound (R)-2-butanol?
A) This compound is chiral.
B) This compound is optically active.
C) This compound has an enantiomer
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Organic Chemistry
PolymersIn an alkane series of hydrocarbons, as the number of carbon atoms increases in a chain, the normal boiling point of each
successive molecule -
increases
decreases
remains the same

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryGive the products for each of the following processes
Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins.
Product of
hydrogenation
palmitic acid
Br₂
0₂ alkane
Product of
hydrolysis
glycerol
the potassium salts of the fatty acids
Product of
saponification
ethylene glycol
Not a product of
these reactions
Reset

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryA compound is found to contain 45.71 % oxygen and 54.29 % fluorine by mass. What is the empirical formula for this compound?

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryThe saponification of an ester produced
isopropanol and sodum octanoate. What
ester underwent hydrolysis to give these
products
View Available Hint(s)
isopropyl octanoate
Isopropyl octanol
isopropyl octanoic acid)
octyl isopropanoate

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryA compound is found to contain 6.360 % silicon, 36.18 % bromine, and 57.46 % iodine by mass. What is the empirical formula for this compound? To answer the question, enter the elements in the order presented above.

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryEnter your answer in the provided box.
How many degrees of unsaturation are present in C8H₂CIO?
degrees of unsaturation

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryWhat is the total number of oxygen atoms present in Mg(CIO3)2?
2
6
3
5

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryShow the calculation of osmolarity for each of the following solutions. 3 points
a. 0.75 M magnesium nitrate solution has osmolarity of
b. 1.5 M sucrose solution has an osmolarity of
c. 0.952 moles of a copper (II) chloride in 806 mL of water has an osmolarity of

Organic Chemistry
Practical Detection25.0 g of HI(g) is injected into a 4.00 L reaction vessel that contains 20.0 g of l₂(g). When the system comes to equilibrium at 400°C, what will be the total pressure inside the reaction vessel?
2HI(g) H₂(g) + 12(g), K = 0.0156 at 400°C
a 2.43 atm
b. 3.78 atm
c.0.815 atm
d. 2.70 atm
e. 13.0 atm

Organic Chemistry
Hydrocarbons1,2-Dichloropentane reacts with excess sodium amide in liquid
ammonia (followed by water workup) to produce compound X. Com-
pound X undergoes acid-catalyzed hydration to produce a ketone.
Draw the structure of the ketone produced upon hydration of com-
pound X.

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryIncreasing pressure speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction because particles are compacted in a smaller volume, therefore increasing particle collisions.
Pressure only affects which phase?
aqueous
gas
liquid
solid

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionLook at the formula for the Heat of Reaction (ΔH).
ΔH is equal to the -
heat content of reactants minus the heat content of the products
Hydrogen reactants minus the Hydrogen products
heat content of the products minus the heat content of the reactants
Hydrogen products minus the Hydrogen the reactants
K

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry in Daily LifeHow does a catalyst alter a potential energy diagram?
it decreases the required activation energy
it decreases the heat of products
it decreases the heat of reaction
it decreases the heat of reactants

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionGiven the reaction at equilibrium:
NaCl(s) <--> Na+ (aq) + Cl-¹ (ag)
The addition of KCI to this system will cause a shift in the equilibrium to the
right, and the concentration of Na+(aq) ions will decrease
right, and the concentration of Na+(aq) ions will increase
left, and the concentration of Na+(aq) ions will increase
left, and the concentration of Na+(aq) ions will decrease

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryEnter the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of each of the following carboxylic acids with KOH
3-methylpentanoic acid (CH₂CH₂CH(CH3)CH₂COOH)
Express your answer as a chemical equation. Assume that there is no dissociation (.e., enter only whole compounds, not i

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryApply the Pauli exclusion principle.
(a) Indicate which orbitals in the following list fill before the 4p orbitals.
3d _4s _4d_ 5s
(b) What is the maximum number of electrons in the 4f subshell?
(c) An electron in an orbital has the following quantum numbers: n = 3, l = 2, m₁ = 0,
and ms = +1/2.
Identify the type of orbital.
What is the direction of the electron spin?

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryEstimate A proton's mass is estimated to be 1.6726 × 10-24 g, and the mass of an electron is estimated to be 9.1093 × 10-28 g. How many times larger is the mass of a proton compared to the mass of an electron?

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryCalculate ΔH for the reaction: C₂H4 (g) + H₂ (g) → C₂H6 (g), from the following data.
C₂H4 (g) +3O₂ (g) → 2 CO₂ (g) + 2 H₂O (l)
C2H6 (g) + 3 1/2O, (g) → 2 CO2 (g)+ 3 H2O (l)
H₂(g) + 1/2O₂(g) → H₂O (l)

Organic Chemistry
Carboxylic acidsIdentify the compound in the following group that is most soluble in water Rank compounds from most soluble in water to least soluble in water. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them.
hexane pentanoic acid
1-octanol

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryIf CO₂ is being produced in the solution at a faster
rate than H₂CO3, then the rate of the
reaction is faster than the rate of the
reaction.
a. forward / reverse
b. reverse / forward
c. neither A nor B is correct

Organic Chemistry
IsomerismIn water, HF dissociates partially in water according to the reaction HF + H₂O → H3O* + F. I would classify this compound as a:
Weak acid
Weak base
Strong acid
Strong base

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryA mixture of equal amounts of two enantiomers
A) is called a racemic mixture
B) is optically inactive
A) is called a C) implies that the enantiomers are meso forms
D) both A and B
E) none of the above

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionChoose the correct agent in each of these reactions:
Mg(s) + O2(g) → MgO Select the oxidizing agent:
CuO (s) + H2(g) →→ Cu(s) + H₂O(g) Select the reducing agent:
2 Na(s) + Cl2(g) →→→ NaCl(s) Select the reducing agent:

Organic Chemistry
PolymersWhat is the ratio of the average rate of effusion of NOF(g) to that of HBr(g) at 400 K?
YOU MUST WRITE THE CALCULATION FOR FULL CREDIT
81:49
The average rate of effusion is the same for the two gases.
7:9
9:7
49:81

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryPhotosynthesis uses 670-nm light to convert
CO₂ and
H₂O into glucose and
O₂. Calculate the frequency of this light.
Frequency: Hz

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry in Daily LifeYou just discovered a new element who has similar properties as Oxygen. Which of the
following would be TRUE?
The element is Joke and the symbol is Jo.
Jo²+
The ion would be Joke ion.
Jo²-
It is a transition metal.
Jo+

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionSodium hydroxide, NaOH, is a strong base that is used in industrial synthesis and processes such as making paper. What is the mass of 2.30×1022 formula units of NaOH (Molar mass = 40.0 g/mol)? Express the mass in grams to three significant figures.

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionHow will the presence or absence of the NH4+ ion be
detected in fertilizer?
Add hydrochloric acid (HCI) and look for a color
change with red litmus paper.
Add hydrochloric acid (HCI), followed by BaCl₂ and
look for the formation of a white precipitate.
Add silver nitrate (AgNO3) and look for a white
precipitate.
Add sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and look for a color
change with red litmus paper.
Add hydrochloric acid (HCI) and look for the
presence of bubbles.

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry in Daily LifeA chemist must dilute 92.8 mL of 14.1 mM aqueous calcium sulfate (CaSO4) solution until the concentration falls to 3.00 mM. She'll do this by adding distilled
water to the solution until it reaches a certain final volume.
Calculate this final volume, in liters. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionIn the following reactions, indicate if the species is oxidized or reduced
Mg2+ becomes Mg
O becomes O²-
Fe2+ becomes Fe³+
F becomes F-
Cu becomes Cu+
H becomes H+

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryMatch each of these acids or bases to their corresponding conjugate acid or base.
H3PO4 ⇒
CH3COOH →
H₂CO3 ⇒
OH ⇒>
CN ⇒
PO4³-

Organic Chemistry
Aldehydes & KetonesFor each chemically-distinct set of protons in the following molecule, predict its a) relative integration,
b) splitting pattern, and c) chemical shift (for example: 2H triplet @ 7.5 ppm).

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryHow many moles of water, H₂O, contain 2.0 x 1022 molecules of water? (See the hints for assistance in interpreting scientific notation.) Express the quantity in moles to two significant figures.

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry in Daily LifeAscorbic acid, or vitamin C (C6H806, molar mass = 176 g/mol), is a naturally occurring organic compound with antioxidant properties. A healthy adult's daily requirement of vitamin C is 70-90 mg. A sweet lime contains 2.86×10-4 mol of ascorbic acid.
To determine whether the ascorbic acid in a sweet lime meets the daily requirement, calculate the mass of ascorbic acid in 2.86×10-4 mol of ascorbic acid.
Express the mass in grams to three significant figures.