Organic Chemistry Questions
The best high school and college tutors are just a click away, 24×7! Pick a subject, ask a question, and get a detailed, handwritten solution personalized for you in minutes. We cover Math, Physics, Chemistry & Biology.

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryWrite the formula for the following compounds:
sodium fluoride; nitrous acid; carbon trioxide; calcium hydroxide; nitrogen tribromide; magnesium chloride; dinitrogen heptachloride; aluminum sulfate; sulfuric acid lithium sulfate; silver nitrate; calcium sulfate; iron (III) chloride disulfur tetrafluoride: mercury (II) nitrate: hydrochloric acid carbon tetrachloride; lead (IV) nitrate; magnesium iodide sodium nitride: trihydrogen monophosphide ; sodium carbonate; copper (II) sulfate; magnesium hydroxide; nitrogen pentoxide; barium nitrate

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryIf sodium peroxide is added to water, elemental oxygen gas is generated, consider this unbalanced equation:
Na₂O₂ (s) + H₂O(l)→ NaOH(aq) + O₂(g)
Suppose 4.70 g of sodium peroxide is added to a large excess of water. What mass of oxygen gas will be produced?

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionLead(II) oxide from an ore can be reduced to elemental lead by heating in a furnace with carbon.
PbO(s) + C(s)→ Pb(l) + CO(g)
Calculate the expected yield of lead if 50.0 kg of lead oxide is heated with 50.0 kg of carbon.

Organic Chemistry
PolymersPheromones are a special type of compound secreted by the females of many insect species to attract the males for mating. One pheromone has the molecular formula C10H16O. Normally, the amount of this pheromone secreted by a female insect is about 1.60 × 10^-12 g. How many molecules does this quantity contain?
Enter your answer in scientific notation.
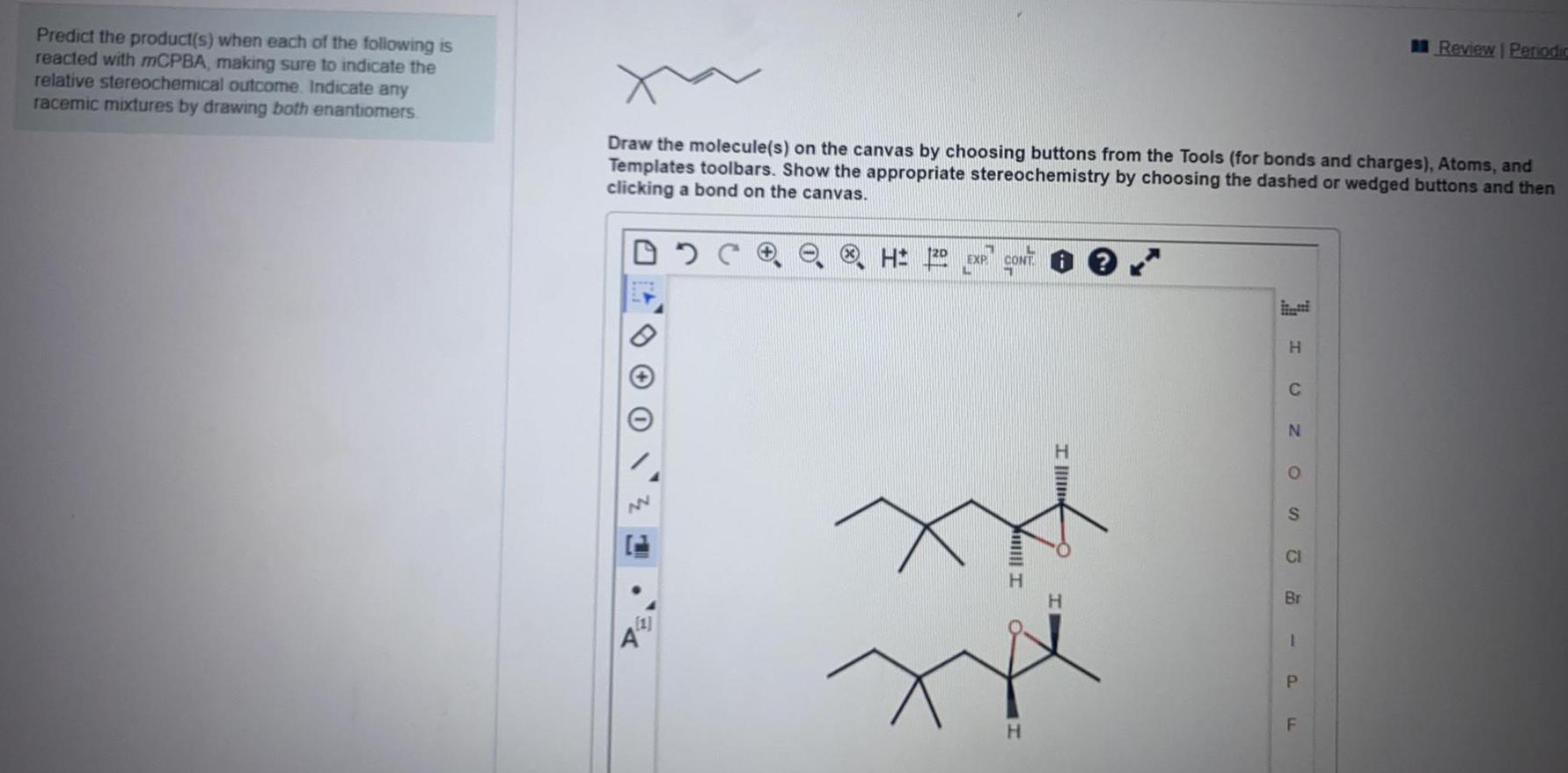
Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryPredict the product(s) when each of the following is reacted with mCPBA, making sure to indicate the relative stereochemical outcome. Indicate any racemic mixtures by drawing both enantiomers. Draw the molecule(s) on the canvas by choosing buttons from the Tools (for bonds and charges), Atoms, and Templates toolbars. Show the appropriate stereochemistry by choosing the dashed or wedged buttons and then clicking a bond on the canvas.

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryFor the following reaction, 33.0 grams of bromine are allowed to react with 13.1 grams of chlorine gas.
bromine(g) + chlorine(g) → bromine monochloride (g)
What is the maximum mass of bromine monochloride that can be formed?
What is the FORMULA for the limiting reagent?
What mass of the excess reagent remains after the reaction is complete?

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryFor the following reaction, 12.0 grams of sodium are allowed to react with 6.65 grams of water.
sodium(s) + water (l) ---> sodium hydroxide (aq) + hydrogen(g)
What is the maximum amount of sodium hydroxide that can be formed?
What is the FORMULA for the limiting reagent?
What amount of the excess reagent remains after the reaction is complete?

Organic Chemistry
PolymersThe illustration to the left represents a mixture of iodine (purple) and fluorine ( green) molecules.
If the molecules in the above illustration react to form IF3 according to the equation
I2+3 F₂ ---> 2 IF3
the limiting reagent is
the number of IF3 molecules formed is, and
the number of atoms/molecules in excess is

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry in Daily LifeAmmonium perchlorate (NH4ClO4) is the solid rocket fuel used by the U.S. Space Shuttle. It reacts with itself to produce nitrogen gas (N₂), chlorine gas (Cl₂), oxygen gas (O₂), water (H₂O), and a great deal of energy. What mass of oxygen gas is produced by the reaction of 2.37 g of ammonium perchlorate?

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryFor the following reaction, 6.18 grams of potassium hydroxide are mixed with excess potassium hydrogen sulfate. The reaction yields 17.0 grams of potassium sulfate.
potassium hydrogen sulfate (aq) + potassium hydroxide (aq) ---> potassium sulfate (aq) + water(l)
What is the theoretical yield of potassium sulfate?
What is the percent yield of potassium sulfate?

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistrySilicon carbide, SiC, is one of the hardest materials known. Surpassed in hardness only by diamond, it is sometimes known commercially as carborundum. Silicon carbide is used primarily as an abrasive for sandpaper and is manufactured by heating common sand (sillcon dioxide, SiO₂) with carbon in a furnace.
SiO₂ (s) + C(s) → CO(g) + SiC(s)
What mass of silicon carbide should result when 3.4 kg of pure sand is heated with an excess of carbon?

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryUrea, chemical formula (NH₂)₂CO, is used for fertilizer and many other things. Calculate the number
of N, C, O, and H atoms in 1.68 x 104 g of urea. Enter your answers in scientific notation.

Organic Chemistry
PolymersThe atomic masses of 35C1 (75.53%) and 37C1 (24.47%) are 34.968 amu and 36.956 amu, respectively.
Calculate the average atomic mass of chlorine. The percentages in parentheses denote the relative
abundances.

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryFor the following reaction, 23.9 grams of sulfur dioxide are allowed to react with 9.27 grams of oxygen gas.
sulfur dioxide (g) + oxygen (g) ---> sulfur trioxide (g)
What is the maximum amount of sulfur trioxide that can be formed?
What is the FORMULA for the limiting reagent?
What amount of the excess reagent remains after the reaction is complete? 46.35

Organic Chemistry
Halogen DerivativesWhat was the driving goal of the late nineteenth-century Can Vuong resistance
movement in what is now Vietnam?
to establish a communist republic in the region
to establish a democratic republic of ethnic Vietnamese only
to ally with the British as a means of expelling the French from the region
to bring the local king back to power and expel the French
to accept French control but extract far better terms for the local population
under French rule

Organic Chemistry
Halogen DerivativesWhich of the following most contributed to the formation of the mostly independent
Dominion of Canada?
pressure by the United States government for an end to British colonial control
in all of North America
ethnic-British nationalist sentiment after the war of 1812
voluntary British devolution of power in hopes of foregoing another war of
independence
threats by France of renewed hostilities in the Americas to protect their French-
speaking former colonists
increasingly costly battles between British troops and indigenous tribes

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry in Daily LifeAs you increase the temperature of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, the rate of the reaction initially
increases. It then reaches a maximum rate and finally dramatically declines. Keeping in mind that
enzymes are proteins, how do you explain these changes in reaction rates? Select the single best answer.
At first the reaction rate increases because the temperature increase causes the enzyme to
coagulate. At some point the rate of reaction dramatically decreases because the enzyme and
substrate collisions increase.
At first the rate of reaction increases because the temperature increase causes a decrease in
the number of collisions between the enzyme and the substrate. At some point the rate of
reaction dramatically decreases because the enzyme denatures due to the high temperature.
At first the reaction rate increases because the temperature increase causes the enzyme to
denature. At some point the rate of reaction dramatically decreases because the enzyme and
substrate collisions increase.
At first the rate of reaction increases because the temperature increase causes an increase in
the number of collisions between the enzyme and the substrate. At some point the rate of
reaction dramatically decreases because the enzyme denatures due to the high temperature.

Organic Chemistry
BiomoleculesWhich of the following statements about the lipoproteins given in the introduction are true?
Check all that apply.
Chylomicrons are the only lipoproteins that exclusively carry dietary lipids.
Lipoprotein densities increase in the following order: chylomicrons, VLDLs, LDLs, HDLs, IDLs.
Lipoproteins can be distinguished by their densities and composition.
HDL is termed "bad" cholesterol because it can deposit excess cholesterol in the arteries.
HDL has a high lipid-to-protein ratio.
Lipoproteins are complexes of lipids and proteins.
Lipoprotein densities vary because lipoproteins have different lipid-to-protein ratios.

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryName and Describe the interaction between polar molecules?

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryDetermine the number of moles of NaOH neutralized by 395 mL 0.610 M HNO3.

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryA pure sample of (R)-2-butanol has a specific rotation
of -13.5°. A sample of 2-butanol was found to have an
observed rotation of +6.75. What are the percentages
of (R)- and (S)-2-butanol in the sample (10 pts)?

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryDraw the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram for the N₂ molecule.
Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the molecule, including any core electrons.

Organic Chemistry
HydrocarbonsCompound X reacts with HI. The product of this reaction, when treated with KOH in ethanol, gives Y ( an isomer of X).
Ozonolysis of Y (H₂O2 workup) produces two compounds: a two carbon carboxylic acid, and a four carbon ketone.
What is X?
A) 2-methyl-2-pentene
B) 4-methyl-1-pentene
C) 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene
D) 3-methyl-1-pentene

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionAt 25° C, a solution containing 1.24 g of sucrose, dissolved in 3 mL of water,
was placed in a polarimeter cell that has a tube length of 10 cm.
The observed rotation of the solution was +39.0°.
What is the specific rotation of this solution?

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryWhat is another name for nonpolar molecules? Polar molecules?

Organic Chemistry
EthersHow many H₂ molecules are needed to completely hydrogenate the following triacylglycerol molecule? (Figure 2)
Express your answer numerically as an integer.

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry in Daily LifeA lead fishing sinker is immersed in a solution of Mg2+ and Cu²+ cations.
Which of the two cations will the lead metal react with?
Mg2+
Cu²+
Write the balanced reaction that will occur. Be sure to include the physical states of all species.
Balanced equation:

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryDraw the skeletal ("line") structure of a secondary alcohol with 6 carbon atoms, 1 oxygen atom, and no double or triple bonds.

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryPure (5R.6R)-5,6-di-tert-butyldecane has a specific rotation of +53. A student
tried to synthesize the compound in lab and found that her sample had a
specific rotation of -33.
a. What would be the specific rotation for an enantiomerically pure sam
of (55.6S)-5-6-di-tert-butyldecane?
b. What is the % of the solution? Which enantiomer is in excess?
c. What is the specific rotation of (5S,6R)-5,6-di-tert-butyldecane?

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryPure (5R,6R)-5,6-di-tert-butyldecane has a specific rotation of +53. A student tried to synthesize the compound in lab and found that her sample had a specific rotation of -33.
a. What would be the specific rotation for an enantiomerically pure sample of (5S,6S)-5,6-di-tert-butyldecane?
b. What is the %ee of the solution? Which enantiomer is in excess?
c. What is the specific rotation of (5S,6R)-5,6-di-tert-butyldecane?

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryGreen plants use light from the Sun to drive photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is a chemical reaction in which water (H₂O) and carbon dioxide (CO₂) chemically react to form the simple sugar glucose (C6H₁2O6) and oxygen gas (O₂). What mass of oxygen gas is produced by the reaction of 9.03 g of carbon dioxide? Round your answer to 3 significant digits.

Organic Chemistry
AminesDraw the condensed structure of a primary amine with 2 carbon atoms, and no double or triple bonds.

Organic Chemistry
Carboxylic acidsPredict the product of this organic reaction:
Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the structure of P.
If there is no reasonable possibility for P, check the No answer box under the drawing area.
Click and drag to start drawing a structure.

Organic Chemistry
Practical DetectionA metal sample weighing 43.5 g and at a temperature of 100.0 °C was placed in 39.9 g of water in a calorimeter at 25.1 °C. At equilibrium the temperature of the water and metal was 33.5 °C.
a. What was ΔT for the water? (ΔT = Tfinal - Tinitial)
b. What was ΔT for the metal?
c. Using the specific heat of water (4.184 J/g °C), calculate how much heat flowed into the water?
d. Calculate the specific heat of the metal.

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry in Daily LifeSolve each of the following. Remember to follow rules of rounding and significant figures
in your calculations.
In the complete reaction of 22.99 g of sodium with 35. 45g of chloride, what mass
of sodium chloride is formed?

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry in Daily LifeSome of the lipid groups appear similar, but changing a few components significantly alters their biological properties.
Identify the similarities and differences between glycerophospholipid and sphingolipid structures.
Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins.
phosphate group glycerol fatty acid
Glycerophospholipid Sphingolipid
Reset Help
sphingosine amino alcohol
Both lipids

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryUsing the equation Zeff = Z-S and assuming that the core electrons contribute 1.00 and valence electrons contribute nothing to the screening constant, S, calculate Zeff for these two ions.
Express your answers as integers. Enter your answers numerically separated by a comma.
Repeat this calculation using Slater's rules to estimate the screening constant, S, and calculate Zeff for these two ions.
Express your answers using two decimal places. Enter your answers numerically separated by a comma.

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryWhich of the following elements has the smallest atomic number?
sulfur, which has sixteen protons
lithium, which has three protons
scandium, which has twenty-one protons
helium, which has two protons

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryWhen we talk about the osmotic pressure
of a solution, what do we mean?
the temperature decrease when a
solvent freezes
water exerts a pressure in a closed
container
the partial pressure of the water
above a solution
the pressure that is needed to stop
the net flow of solvent across a
semipermeable membrane.

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryConcentrated sulfuric acid has a density of 1.84 g/ml.
A) What's the specific gravity of sulfuric acid?
B) Calculate the mass in grams of 1.00 liter sulfuric aci
Show your calculations for answer (B).

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryFor the chemical reaction
HCIO4 (aq) + NaOH(aq) → H₂O(l) + NaCIO4 (aq)
write the net ionic equation, including the phases.
net ionic equation:
Which ions are considered spectator ions for this reaction?
OH-
Na+
H+
CIO4-

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry in Daily LifeSome metal oxides, such as Sc₂ O3, do not react
with pure water, but they do react when the solution
becomes either acidic or basic.
Do you expect Sc₂ O3 to react when the solution becomes acidic or when it becomes basic?
The solution should be acidic.
The solution should be basic.
The reaction will occur in both cases.
Write a balanced chemical equation to support your answer.
Express your answer as a net ionic equation. Identify all of the phases in your answer.

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryOne of the alkali metals reacts with oxygen to form a solid white substance. When this substance is dissolved in water, the solution gives a positive test for hydrogen peroxide, H₂O₂.
When the solution is tested in a burner flame, a lilac-purple flame is produced. What is the likely identity of the metal?
Express your answer as a chemical symbol.
Write a balanced chemical equation for reaction of the white substance with water.
Express your answer as a chemical equation. Identify all of the phases in your answer.

Organic Chemistry
IsomerismPotassium superoxide, KO₂, is often used in oxygen masks (such as those used by firefighters) because KO₂ reacts with CO₂ to release molecular oxygen. Experiments indicate that 2 mol of KO₂ (s) react with each mole of CO₂ (g).
The products of the reaction are K₂CO3 (s) and O₂(g). Write a balanced equation for the reaction between KO₂ (s) and CO₂(g).
Express your answer as a chemical equation. Identify all of the phases in your answer.
Indicate the oxidation number for each atom involved in the reaction in part A. Before the reaction: Enter your answers numerically separated by commas.

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry in Daily LifeSolid potassium reacts with chlorine gas to produce solid potassium chloride. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction.

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryAqueous potassium nitrate (KNO3) and solid silver bromide are formed by the reaction of aqueous silver nitrate (AgNO3) and aqueous potassium bromide Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction.

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryFor this problem, identify the limiting reagent and calculate the grams of CO₂ obtained in the reaction of 140.0 grams of C7H12O5N3 with 120.0 grams of oxygen. If 125 grams of CO₂ is actually produced, what is the % yield. The equations are not balanced.
C7H12O5N3+ O2 -> CO₂ + H₂O + NH3
What is the limiting reagent?

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryHydrogen gas and aqueous sodium hydroxide (NaOH) are formed by the reaction of liquid water and solid sodium.
Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction.

Organic Chemistry
General organic chemistryWhat is the proper dissociation equation for Li3N, a strong electrolyte?
a. Li3N(s) <→ Li³+(aq) + 3N-(aq)
b. Li3N(s) → Li³+(aq) + 3N-(aq)
c. Li3N(s) <→ Li+(aq) + N³-(aq)
d. Li3N(s) <→ 3Li+(aq) + 3N-(aq)
e. Li3N(s) → 3Li+(aq) + N³-(aq)

Organic Chemistry
PolymersWhat is an autoimmune disease?
a disease caused by an immune system that cannot produce antibodies or T cell responses
a disease caused by an inappropriate immune response to self antigens
a disease caused by a severe immune response to a normally innocuous environmental antigen
a disease caused by an inappropriate immune response that overproduces cytokines to a toxic level