Chemical kinetics Questions and Answers

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kinetics6 A current of 1 40 ampere is passed through 500ml of 0 180 M solution of zinc sulphate for 200 seconds What will be the molarity of Zn ions after deposition of Zinc a 0 154 M b 0 177 M d 0 180 M c 2 M

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsThe numerical values of rate constants are same for first second and third order reactions Which one is true at a definite moment for rate of these three reactions if concentration of reactants is same and less than 1 M Question Type Single Correct Type 1 2 3 4 r r2 3 r1 12 13 r1 12 13 None of these

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsFor the reaction 2NO H2N2O H2O The values of dp dt was found to be 1 5 Torr sec for a pressure of 359 Torr of NO and 0 25 Torr sec for a pressure of 152 Torr the pressure of H2 being constant On the other hand when the pressure of NO was kept constant dp dt was 1 6 Torr sec for a hydrogen pressure of 289 Torr and 0 79 Torr sec for a pressure of 147 Torr Determine the order of the reaction 2 Points a overall order 3 for constant H2 pressure order 2 for constant NO pressure order 1 b overall order 3 for constant H2 pressure order 1 for constant NO pressure order 2 c overall order 2 for constant H2 pressure order 2 for constant NO pressure order 0 d overall order 2 for constant H2 pressure order 0 for constant NO pressure order 2 overall order 2 for constant H2 pressure order 1 for constant NO pressure order 1

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsIn a first order reaction the concentration 64 of the reactant decreases from 800 mol dm to 50 mol dm in 2 x 104 sec The rate constant of the reaction in s is 1 2 x 104 2 3 45 x 10 5 43 1 386 10 4 3 10 K 2 303 log t log 2 303 2x104 P 13 BG

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsWhich of the following is correct A B C D larger the activation energy high will be the value of temperature coefficient of reaction with increase in temperature in high temperature range k will increase more compare to low temperature range 1 Graph of k vs is a straight line with slope T Ea 2 303R Chemical reaction with low activation energy always occurs with fast rate compare to reaction with high activation energy

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsFor a reaction 2B products 6000 T log k M hr 20 life period is assuming initial conc of B as 1M 1 6 93 x 10 21 hr 2 1 15 x 10 4 hr 3 5 x 10 21 hr 4 1 x 10 20 hr The lower limit of ha

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsA rise of 10 C can cause the rate of some reactions to double This is best explained by A B C D The average velocity of the molecules has doubled The number of molecules with more than enough energy to overcome the activation energy barrier has doubled The activation energy has lowered The average kinetic energy of the particles has doubled

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticswhile VO For the decomposition of H O aq it was found that Vo t 15 min was 100 mL at 0 C and 1 atm maximum was 200 mL at 0 C and 2 atm If the same reaction had been followed by the titration method and if V CM t 0 had been 40 mL what would V CM t 15 min have been A 30 mL KMnO4 KMnO4 B 25 mL C 20 mL D 15 mL

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsIn a hypothetical reaction 2B aq C aq A aq 1st order decomposition A is optically active dextro rototory while B and C are optically inactive but B takes part in a titration reaction fast reaction with H O Hence the progress of reaction can be monitored by measuring rotation of plane of polarised light or by measuring volume of H O consumed in titration In an experiment the optical rotation was found to be 0 30 at t 20 min and 0 15 at t 50 min from start of the reaction If the progress would have been monitored by titration method volume of H O consumed at t 30 min from start is 30 ml then volume of H O consumed at t 90 min will be A 60 ml B 45 ml Le 5 52 5 ml D 90 ml

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsSO gas is entering the environment at a constant rate of 6 93 10 g L day due to emission of polluting gases from thermal power plant at Kota but at the same time it is decomposing and following first order kinetics with half life of 100 days Based on these details select the correct statement s from the following a Concentration of SO in Kota is 1 25 x 10 M assume SO present in air reaches steady state b If 10 L of air is passed through 1 L pure water assuming all SO is dissolved in it and the resulting solution is titrated against 1 N NaOH solution 15 ml of NaOH solution is required to reach the end point c An industry is manufacturing H SO4 at the rate of 980 kg per day with the use of SO in air and it should use 8 10 L air per day d If SO emission is stopped then after 1000 days its concentration will reduce to 1 22 x 108 M

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsConsider the oxidation of nitric oxide to form NO 2NO g O g 2NO g a Express the rate of the reaction in terms of changes in the concentration of NO O and NO b At a particular instant when 0 is decreasing at 0 2 mol L s at what rate is NO2 increasing at that instant

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsIn the Cannizzaro reaction given below 2Ph CHO Ph CH OH PhCOO in the presence of OH the slowest step is 1 The attack of OH at the carbonyl group 2 The transfer of hydride to the carbonyl group 3 The abstraction of proton form the carboxylic group 4 The deprotonation of pH CH OH

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kinetics16 Solubility curve of a hydrated salt in water with temperature is given The curve indicates that the solution process is Solubility g L 60 C Temperature a Exothermic b Endothermic c Endothermic till 60 C and endothermic after 60 C d Endothermic till 60 C and exothermic thereafter 17 Which of the following is not an endothermic reaction 21 An i to 1 1 x a C 27 22 Cha the a C 23 16 rev do a C

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsB is an reactant invovled in an reaction It is known that the reaction rate can be calculated by Rate dCB dt kCBb where CB is the concentration of B k is the apparent rate constant and b is the order of the reaction with respect to B When b 1 CB was measured as 8 7 3 31 and 1 45 mg L at 3 49 4 64 and 9 22 hours after the start of the reaction Please calculate the value of the apparent

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsIron 59 is a radioisotope that is used to evaluate bone marrow function The half life of iron 59 is 44 5 days If you begin with 35 8 mg of this isotope what mass remains after 87 2 days have passed

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsIt can be determined graphically by drawing a tangent at time ton either of the curves for concentration of R and P vs time t and calculating its slope Fig 4 1 So in problem 4 1 at 600s for example can be calculated by plotting concentration of butyl chloride as a function of time A tangent is drawn that touches the curve at t 600 s Fig 4 2 The slope of this tangent gives the instantaneous rate So instat 600 s At t 250 s t 350 s t 450 s 0 0165 0 037 800 400 s mol L 5 12 x 10 mal L s Finst 1 22 x 10 mol L s Finst 1 0 x10 mol L s 6 4 x 105 mol L g inst Now consider a reaction Hg l Cl g HgCl s Where stoichiometric coefficients of the reactants and products are same then rate of the reaction is given as A Hg A C1 A HgCl At At At Rate of reaction H nce of any of the reactants is same as the rate reaction two moles of

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsFor a reaction A g Products the half life was found to be 20 minutes when the initial pressure of A was 0 5 atm If the time needed for the pressure of A to become half starting from 1 atm is 14 14 minutes then what is the order of the reaction a Order 1 b Order 0 c Order 1 5 d Order 0 5

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kinetics26 In an evacuated vessel of 8 2 L capacity 0 2 moles of A g is taken vessel is sealed and heated to 127 C by which the following first order reaction occurred at constant volume and temperature A g 2 B g C s The vapour presure of C s is 0 1 atm at 127 C If the half life of reaction is 20 min then the correct information s related with reaction is are R 0 082 L atm K mol ID Q 529175 Options are A Ptotal 1 7 atm att B Ptotal 0 98 atm after 10 decomposition of A g C Ptotal 0 88 atm after 5 decompositon of A g D Ptotal 1 3 atm at t 20 min

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsThe reaction rate is defined as the rate at which the concentration of the reactants with time or the concentration of products with time O Increase increase O Decrease decrease O Decrease increase O Increase decrease
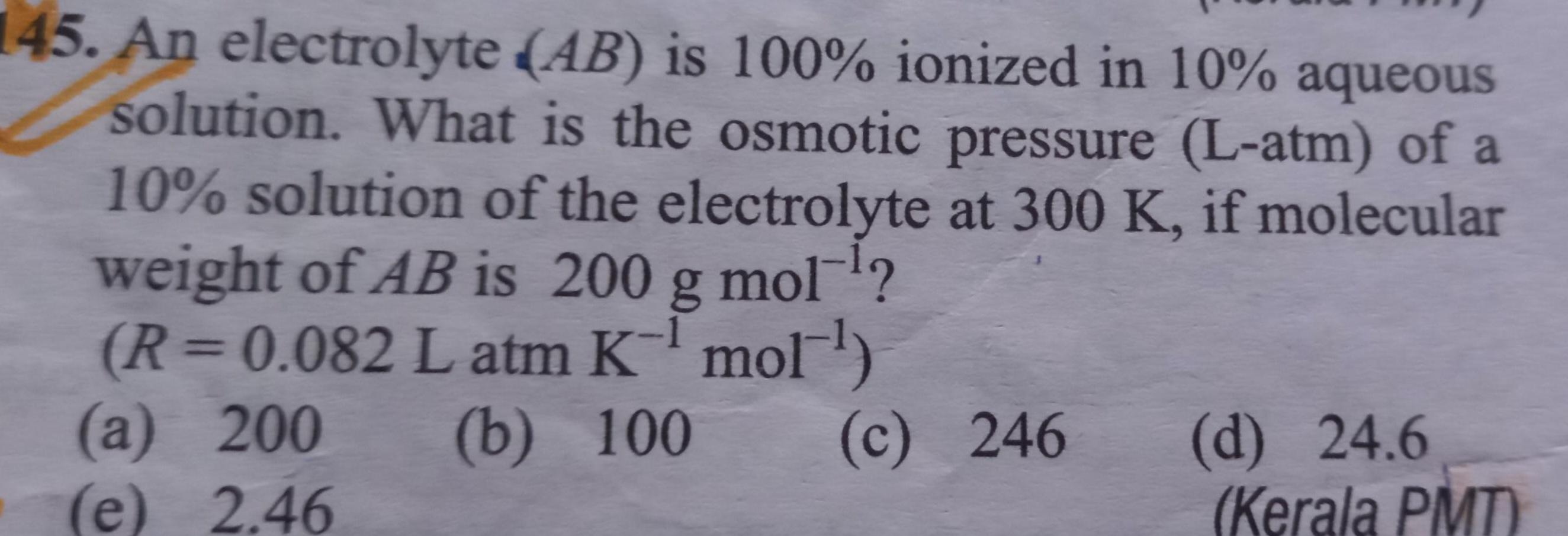
Physical Chemistry
Chemical kinetics145 An electrolyte AB is 100 ionized in 10 aqueous solution What is the osmotic pressure L atm of a 10 solution of the electrolyte at 300 K if molecular weight of AB is 200 g mol R 0 082 L atm K mol b 100 a 200 2 46 c 246 e d 24 6 Kerala PMT

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsA and B decompose via first order kinetics with half lives 54 0 min and 18 0 min respectively Starting from a equimolar non reactive mixture of A and B the time taken for the concentration of A to become 16 time that of B is min Round off t the Nearest Integer

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsA first order reaction is found to have a rate constant k 5 5 x 104 s Example 47 Find the half life of the reaction Half life for a first order reaction is Solution ty a T k 0 693 k 0 693 5 5x10 14s ty 2 T 1 26 x 10 s Show that in a first order reaction time required for completion of 99 9 is 10 times of half life t 2 of the reaction When reaction is completed 99 9 R R 0 999 R 2 303 R o log R t 2 303 t R o R 0 999 R log t 6 909 k For half life of the reaction t1 2 0 693 k 6 909 k 10 2 303 t log10 Example 4 8 Solution

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsA catalyst lowers the activation energy of a reaction in such a manner that the rate constant at 27 C for uncatalysed reaction equals the rate constant at 73 C for catalysed reaction By how many kJ mole activation energy barrier is reduced by catalyst Activation energy for the uncatalyzed reaction is 24 kJ

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsEXAMPLE 2 14 A solution containing 0 1 mol of naphthalene and 0 9 mol of benzene is cooled out until some benzene freezes out The solution is then decanted off from the solid and warmed upto 353 K where its vapour pressure was found to be 670 mm The freezing point and boiling point of benzene are 278 5 K and 353 K respectively and its enthalpy of fusion is 10 67 kJ mol Calculate the temperature to which the solution was cooled originally and the amount of benzene that must have frozen out Assume ideal behaviour

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsstraight line is obtained The points at which the line When a graph between log k and 1 T is drawn a cuts y axis and x axis respectively correspond to the temperatures 1 0 E 2 303R logA JogA 2 E R in A 4 log A

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsA substance A undergoes disproportionation reaction to form A and A obeying first order kinetics The rate constant is obtained by measuring volume of an oxidizing agent capable of oxidizing A A and A to A A A respectively From the following data calculate moles of A 6 minutes after starts of the reaction if initially 10 moles of A was taken Round off to nearest integer Time min Volume of oxidizing 20 21 5 r agent 0 4 min ml

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsIn the metal carbonyls of general formula M CO Which follows EAN rule if M is Ni Fe and Cr the value of x will be respectively 1 6 5 6 3 4 4 5 2 4 5 6 4 4 6 6

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsA solution contains Fe2 Fe and I ions This solution was treated with iodine at 35 C E for Fe 0 536 V The Fe is 0 77 V and E for 1 21 favourable redox reaction is AIPMT Mains 2011 1 I will be oxidised to I 2 Fe2 will be oxidised to Fe 3 I will be reduced to I 4 There will be no redox reaction ST

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsFor the reaction CH Br aq OH aq CH OH aq Br aq rate law is rate K CH3Br OH a How does reaction rate changes if OH is decreased by a factor of 5 b What is change in rate if concentrations of both reactants are doubled

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsCalculate the pH of buffer solution composed of 0 1M weak base BOH and 0 2M of its salt BA Kb 1 8 x 10 5 for weak base Define Pseudo first order reaction In a first order reaction 60 of reactant decomposes in 45 minutes Calculate the half life for the reaction

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsen pentoxide decomposes to O2 and O following first order kinetics N O g 2NO O g 0 2 mole of N Os was taken in 2 L vessel and heated at 200 K The concentration of N Os is measured at different intervals and the following graph was plotted 13 log N O Time Slope of straight line in graph A is 1 2 x 10 sec 1 what is half life of the reaction A 2 5 x 10 S B 2 5 x 10 3 S C 12 5 x 10 s D 2 5 x 104S

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsven ver A reaction has a half life of 1 min The time required for 99 9 completion of the reaction is min Round off to the Nearest Integer Use In 2 0 69 In 10 2 3

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kinetics25 At a certain temperature the half life periods for the catalytic decomposition of NH were found to be as follows Pressue mm Hg 50 100 200 Half life period hrs 3 52 1 76 0 88 What will be the pressure when the half life period 1 5 hours

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsHalf life of decomposition of a hydrocarbon at an initial pressure of 1 atm is 2 sec Half life increases to 20 sec on reducing the pressure to 0 1 atm The reaction is 1 Zero order 3 Second order 2 First order 4 Third order 1

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsA reaction mixture has been made by taken equal conc of two reactants It 40 minutes for the completion of 50 of the reaction For the completion of next 50 of reaction time taken is 80 min What is the order of reaction 1 2 3 3 2 0 4 1

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsThe rates of a certain reaction at different times are as follows Time 0 10 20 30 The reaction is 1 First order 3 Zero order Rate mol litre sec 2 8x10 22 2 78 10 2 2 81x10 2 79 10 2 Second order 4 Third order

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsWhich among the following plots are linear a x is the concentration of reactant remaining after time t 1 a x vs t for a first order reaction 2 a x vs t for a zero order reaction 3 a x vs t for a second order reaction 4 1 a x vs t for a second order reaction a 1 and 2 c 2 and 3 e 1 and 4 b 1 and 3 d 2 and 4 Kerala PMT 2008

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsWhich of the following statements are correct about catalyst at constant temperature A It does not alter AS of the reaction C It alters AS of the reaction B It does not alter AH of the react D none of these

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsThe pH at the second equivalent point of 30 ml of 0 124 M H3PO3 K 2 2 6 107 is tritated with 0 1 M NaOH solution is Given log 26 1 415 log 35 6 1 5514 A 10 57 B 11 57 C 9 57 D 12 57
Physical Chemistry
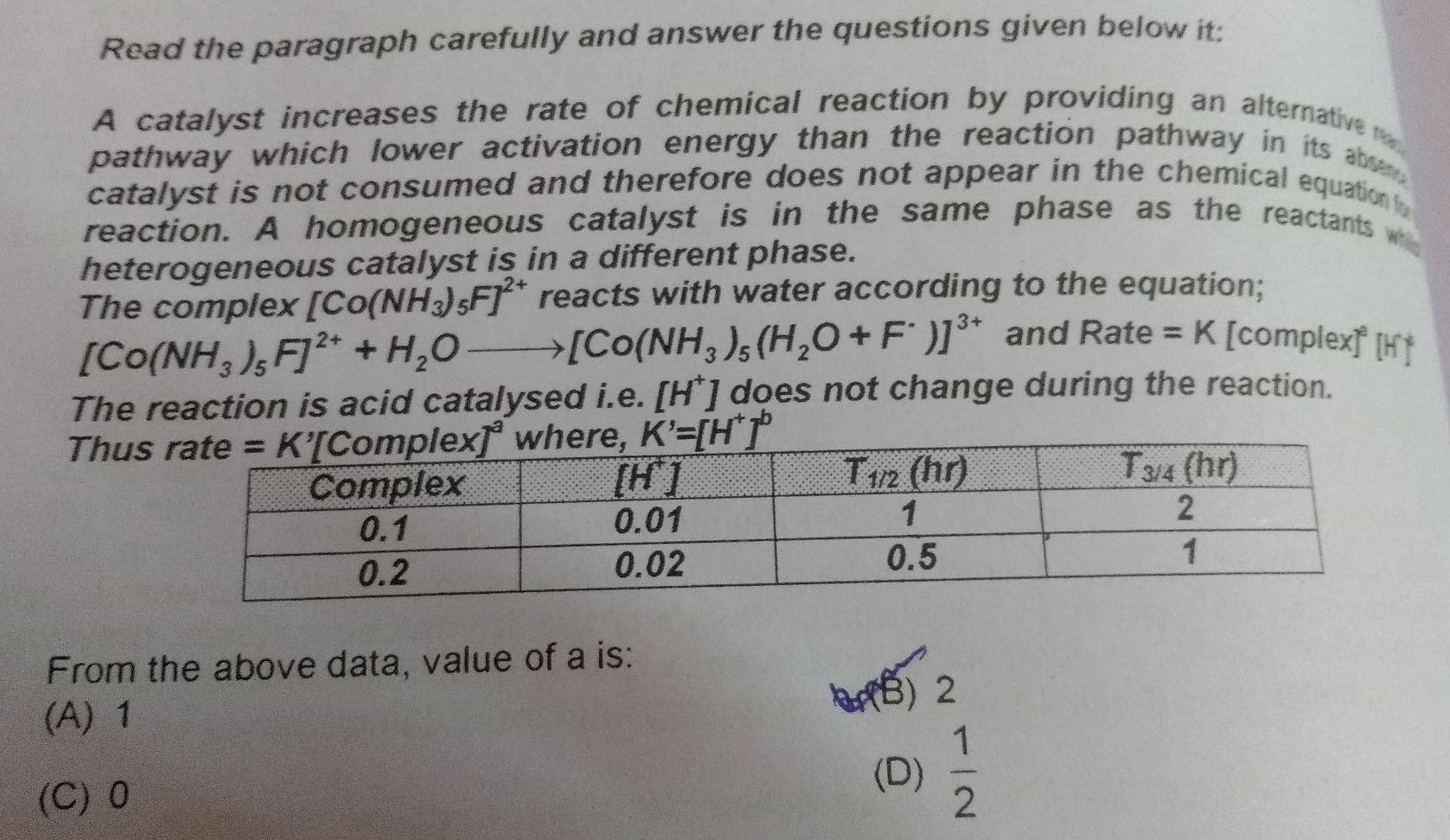
Chemical kineticsRead the paragraph carefully and answer the questions given below it TO A catalyst increases the rate of chemical reaction by providing an alternative pathway which lower activation energy than the reaction pathway in its absen catalyst is not consumed and therefore does not appear in the chemical equation fo reaction A homogeneous catalyst is in the same phase as the reactants heterogeneous catalyst is in a different phase The complex Co NH3 sF 2 reacts with water according to the equation Co NH3 H O F and Rate K complex H Co NH3 F 2 H O The reaction is acid catalysed i e H does not change during the reaction Thus rate K Complex where K H Complex 0 1 0 2 H 0 01 0 02 From the above data value of a is A 1 C O 3 T172 hr 1 0 5 BA 2 D NI 2 T3 4 hr 2 1

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsPre Medical Chemistry 12 The rate of first order reaction is 1 5 x 10 2 mol L 1 min at 0 5 M concentration of the reactant The half life of the reaction is 1 7 53 min 3 23 1 min 2 0 383 min 4 8 73 min 13 In a first order reaction the concentration of the from 0 8 M to 0 4 M in

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kinetics72 An ideal solution contains two volatile liquids A P 100 torr and B P 200 torr If the mixture contains 1 mole of A and 4 moles of B then total vapour pressure of the distillate is 1 150 torr 3 188 88 torr 4 198 88 torr 2 180 torr

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsUse the data provided to determine the rate law including the value of k of the following reaction 2 NO g O2 g 2 NO2 g Rate 1 7x103 M s NO 0 1 Rate 3 1 105 M s NO 0 1 Rate 57 M2s NO 0 Rate 3 8 M 1 2 1 NO 0 2 Rate 9 4 103 M2s NO 0 1 Rate 57 M s NO 0 NO M 0 030 0 030 0 060 02 M 0 0055 0 0110 0 0055 Initial Rate M 15 1 0 00855 0 0171 0 0342

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsThe following data is obtained during the first order thermal decomposition of 2 A g B g C B g at constant volume and temperature S No Time At the end of 10 minutes After completion 1 The rate constant in min is a 0 0693 c 0 00693 1 2 b 6 93 d 69 3 Total pressure in Pascal 300 200 KCET 2010

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsFor the reaction 3A 5B 2C 4D which reaction rate relationship is true a 4 B SA D 4 At O 3 Ob 4 B 4 A 5 3 Oc 4 A 4 B At O c At D A D 4 A A 3 At d 4 D A C 2 A B

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsDependence of rate constant of a reaction is given by Arrhenius equation k A e RT but originally it s derived from it s differential equation Reactions A B C D follows following rate law rate k A 1 2 B 1 2 Starting with initial conc of one mole of A and B each what is the time taken for amount of A of become 0 25 mole Given k 2 31 10 3 sec 1 300 sec 600 sec O900 sec

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsThe decomposition of H O can be followed by titration with KMnO and is found to be a first order reaction The rate constant is 4 5 x 10 2 In an experiment the initial titre value was 25 ml The titre value will be 5 ml after a lapse of

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kinetics1 25 2 50 3 75 4 100 1 In the synthesis of ammonia by Haber s process if 60 moles of ammonia is obtained in one hour then the rate of disappearance of nitrogen is 1 30 mo min 2 6 mol min 2 3 0 5 mol min 4 60 mol min The solubility product of Ag Cro is 32x10 What is the concentration of Cro ions in that solution

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kinetics1 The rate law for the reaction below is given by the expression K A B A B Product If the concentration of B is increased from 0 1 to 0 3 mole keeping the value of A at 0 1 m the rate constant will be 1 3K 2 9K 3 K 3 4 K

Physical Chemistry
Chemical kineticsConsider the reaction 2B C AH 15 kcal The energy of activation of backward reaction is 20 kcal mol In presence of catalyst the energy of activation of forward reaction is 3 kcal mol At 400 K the catalyst causes the rate of the forward reaction to increase by the number of times equal to 1 e 2 e 3 e2 4 201