Energetics Questions and Answers

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsA mixture of hydrogen gas and the theoretical amount of air at 25 C and a total pressure of 1 atm is exploded in a closed rigid vessel If the process occurs under dq 0 condition then using the given data answer the questions that follow Given i C 6 3 Cal deg mol ii C 9 3 Cal deg mol AH H O g 57 8 Kcal Take air as 80 N 20 O by volume What will be maximum temperature approx attained if the process occurs in above container A 298 K B 1900 K C 2665 K D 2940 K What will be the final pressure in atm approx A 0 85 B 5 46 C 7 6 D 8 5

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsIn an Otto cycle 33 3 air at 1bar and 290K is compressed isentropic ally until the pressure is 15bar The heat is added at constant volume until the pressure rises to 40bar Calculate the air standard efficiency for the cycle Take Cv 0 717 KJ Kg K and Runiv 8 314KJ Kg K 4 57 percent 5 pecent 3 87 percent 8 85 percent

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsYou are heating water in a pressure cooker provided with a temperature measuring device The initial water temperature is 30 C and the final steam temperature is 150 C Write down the changes step wise with relevant equations so as to calculate the total heat input required

Physical Chemistry
Energetics3 4 4x X Enthalpy change on freezing of 1 0 mol of water at 40 C to ice at 0 C is AfusH 6 kJ mol at 0 C CP H O 1 75 J mol K NCERT Pg 172 1 2 3 4

Physical Chemistry
Energetics6 If enthalpy of combustion of carbon to CO2 is 400 kJ mol 1 then how much heat will be released upon formation of 8 8 g CO2 from carbon and dioxygen gas NCERT Pg 176 1 40 kJ 2 80 kJ 3 400 kJ 4 800 kJ 7 A reaction is non temperatures when spontaneous at all NCERT Pg 186 O and A S 0

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsGases AHJ mole P A g B g C g Q C g E g D g F g B g C g R A g B g C g D g E g F g 30 20 40 60 80 100 1 2 3 Spontaneous at high temperatur Spontaneous at all temperature Spontaneous at low temperature

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsIn an isothermal process 3 moles of an ideal gas expands from pressure P1 to P2 against constant opposing pressure of P2 Calcu following Note Here P is constant but P is not ext a Change in enthalpy b Work done c Change in Internal energy d Heat transferred

Physical Chemistry
Energetics17 In which of the enlisted cases Hess s law is no applicable a Determination of lattice energy b Determination of resonance energy c Determination of enthalpy of transformation o one allotropic form to another d Determination of entropy 76n passing 3 Ampere of electricity for 50 minutes 1 8 metal is deposited The equivalent mass o

Physical Chemistry
Energetics5 For a free expansion of an ideal gas in an isolated chamber which of the following statements is true A Entropy of the system increases B Temperature of the system decreases C Internal energy of the system decreases D Positive work is done by the system

Physical Chemistry
Energetics28 The van der Waals coefficient a expressed in atm dm6 mol 2 for four different gases are He 0 0341 H 0 242 Kr 5 125 O 1 364 Based on the data given above the gas that will be expected to have the lowest critical temperature Te A He B H C Kr D 0

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsWater is gaseous in 5L volume at 130 C and adiabatically expands to 10L volume at a constant pressure of 0 80 atm Find the temperature work internal energy enthalpy and temperature change in this time assuming that it is 5 mol of gas

Physical Chemistry
Energetics3 If 60 of a first order reaction was completed in 60 minutes 50 of the same reaction would be completed approximately log 2 5 0 4 1 40 minutes 2 50 minutes 3 45 minutes

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsIn an coffee cup calorimeter experiment sodium hydroxide 8 16 g was dissolved in water 89 9 g The initial temperature of both were 6 5 C When the sodium hydroxide is dissolved the solution reached a maximum temperature of 26 6 C The specific heat of the solution is 3 98 J g 1 0c 1 Use NaOH as the limiting reactant calculate the molar enthalpy change of the solvation of NaOH in water A Hrxn in the unit of kJ mole Answer to 3 significant figures with the required unit as stated Do not answer in scientific notation

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsSir NCERT kay in 2 paragraph mai jo kuch bhi likha hai ple ase is ko pen paper mai sequence mai likh kr samjha dijiye bcz NCERT ki language mujhe bilkul samjh nhi aa rhi Naturally the resultant reaction will take place when the right hand side in equation 6 30 is negative In A G vs T plot representing the change Fe FeO in Fig 6 6 goes upward and that representing the change C CO C CO goes downward They cross each other at about 1073K At temperatures above 1073K approx the C CO line is below the Fe FeO line AGIA G So above 1073 K in the range of temprature 900 1500 K coke will reduce FeO and will itself be oxidised to CO Let us try to understand this through Fig 6 6 approximate values of AG are given At about 1673K 1400 C 4G value for the reaction Chemistry 150 Around 1400 C 2FeO 2Fe 0 2C 0 200 2FeO 2C 2Fe 200 FeO C Fe CO 1 AG 341kJ mol AG 447kJ mol AG 106kJ mol AG 53kJ mol 2Fe 0 2FeO C O CO 2FeO 2Fe O is 341 kJmol because it is reverse of Fe FeO change and for the reaction 2C 0 2CO 4G is 447 kJmol If we calculate 4 G value for overall reaction 6 27 the value will be 53 kJmol Therefore reaction 6 27 becomes feasible In a similar way the reduction of Fe O and Fe O by CO at relatively lower temperatures can be explained on the basis of lower lying points of intersection of their curves with the CO CO curve

Physical Chemistry
Energetics5 Concider the reaction AO BO CO D if AD B if unfavorable with 5 kcal mol and C D is favorable 8 kcal mol 1 The reaction forward is driven by 3 kcal mol 2 The reaction forward is driven by 11kcal mol 3 The reaction forward is driven by 8 kcal mol 4 The reaction forward is driven by 3 kcal mol

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsWhat is the heat of hydrogenation of ethene if the bond energies of C C C C H H and C H are 350 600 440 and 410 kJ mole respectively 1 130 kJ mol 3 400 kJ mol 2 260 kJ mol 4 450 kJ mol

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsMatch the enteries of column I with appropriate entries of column II and choose the correct option out of the four options A B C and D Column I Column II X Y Isobaric Z Adiabatic Isothermal P AT 0 q AV 0 r AP 0

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsWhen two phases of the same single substance remain in equilibrium with one another at a constant P and T their molar must be equal Which of the following will fit into the blank O Internal energy O Enthalpy O Entropy Gibb s free energy

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsIn which of the following entropy of the system decreases a Crystallization of liquid into solid b Temperature of crystalline solid is increased from 0 K to 115 K c H g 2H g d 2 NaHCO s Na CO s CO g H O g
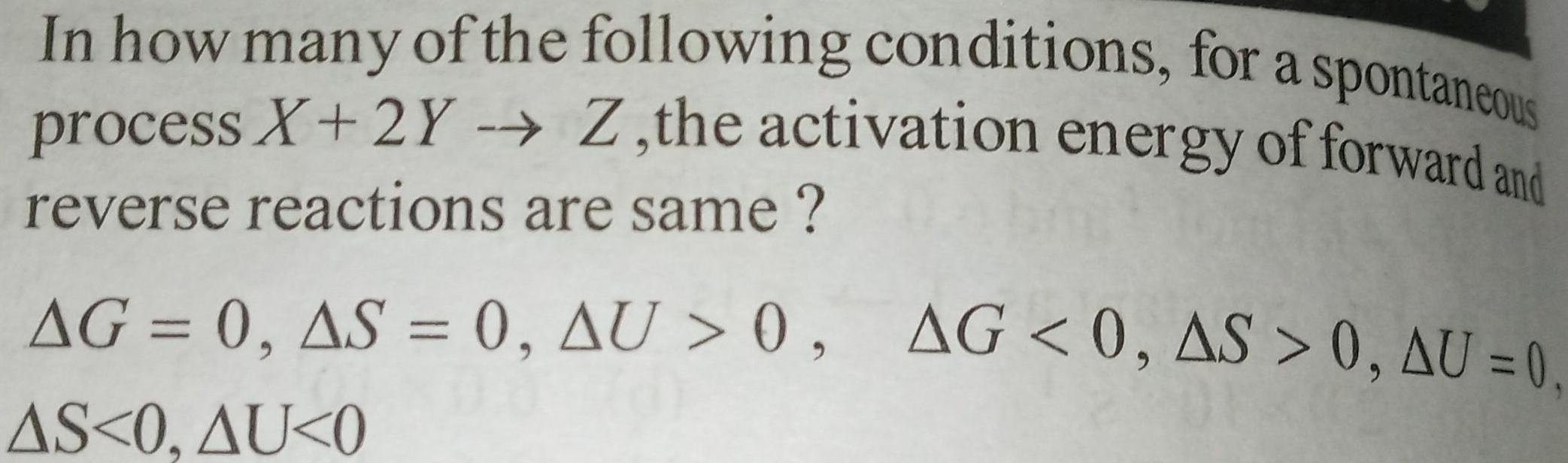
Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsIn how many of the following conditions for a spontaneous process X 2Y Z the activation energy of forward and reverse reactions are same AG 0 AS 0 AU 0 AG 0 AS 0 AU 0 DE AS 0 AU 0

Physical Chemistry
Energeticsvii If the standard enthalpy of formation of methanol is 238 9 kJ mol then entropy change of the surroundings will be a 801 7 J K c 0 8017 J K b 801 7 J K 1 d 0 8017 J K

Physical Chemistry
Energeticsa A gas is compressed isothermally at 400K from 0 3Mpa to 4Mpa is then cooled isobarically to 290K After that it is expanded adiabatically to 0 9 Mpa Later expanded at constant temperature to the initial value of pressure Finally heated isobarically to 400K Draw the PV diagram and calculate the overall work done change in internal energy and heat supplied Data Cp 3 7R and Cv 2 7R

Physical Chemistry
Energeticsii A gas is allowed to expand in a well insulated container against a constant external pressure of 2 5 bar from an initial volume of 2 5 L to a final volume of 4 5 L The change in internal energy AU of the gas will be

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsP B With reference to the above graph choose the correct option for fixed amount of an ideal gas in going from A to B VA VB T k O Volume firstly decreases TX

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsV E cell AG Keq of cell reaction 2 Questions 1 For a fuel cell 2H g O g 2H O E cell is 1 23 V the value of AGO and nature of the cell reaction is 1 23 7 kJ mol 1 feasible 2 237 3 kJ mol 1 non feasible 3 23 7 kJ mol 1 non feasible 4 237 3 kJ mol 1 feasible

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsHeat of combustion of ethyl alcohol carried out in a bomb calorimeter at 300K is 1350kJ mole Enthalpy of combustion of ethyl alcohol at the same temperature would be A 1347 5 kJ B 1350 kJ C 1349 6 kJ D 1352 5 kJ

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsIn a reversible compression process 1 mol of ideal gas in a piston cylinder device 3 undergoes a pressure change from 1 bar to pressure P and temperature increases from 400 K to 900 K The compression path is described by PV 3 constant Calculate the final pressure and heat transferred Given Heat capacity of gas Cp 30 84 J mol K

Physical Chemistry
Energetics1714 171 Which of the following conditions regarding a chemical process ensures its spontaneity at all temperature A AH 0 AG 0 C AH 0 AS 0 B AH 0 AS 0 D AH 0 AS 17

Physical Chemistry
Energetics17 Estimate the enthalpy of combustion for methane at 298 K and 1bar using the bond enthalpies in the textbook Compare your result with that calculated from the enthalpies of formation of products and reactants CH g 20 g CO g 2H O g

Physical Chemistry
Energetics7 The oxidation of malate to oxaloacetate can be coupled to the reduction of NAD to NADH Malate NAD oxaloacetate NADH H Mitochondrial concentrations of the reactants are as follows Oxaloacetate 5 0 x 10 mol L Malate 1 1 x 10 mol L NAD 7 5 x 10 mol L NADH 9 2 x 10 mol L What is the free energy change in the mitochondrion for the reaction

Physical Chemistry
Energetics0 1 kg of milk at 10 C is added to 0 3 kg of coffee in a cup of mass 0 3 kg both at 90 C Calculate the final temperature of the mixture in C Assume that there are no heat exchanges with the surroundings Assume that the specific heat of milk equals the specific heat of coffee 4200 J kg 1 0C 1 The specific heat of the cup is 840 J kg 1 0C 1 O 73 43 O 83 O 63 O 53

Physical Chemistry
Energeticsabove 138 Predict which of the following reaction s has a positive entropy change I Ag aq Cl aq AgCl s II NH CI s NH g HCI g N g 3H 9 III 2NH g A I and II C II and III B III D II

Physical Chemistry
Energeticso vapour But for the change of state to occur the wat er must absorb 540cal g of heat to change i nto vapour which is called latent heat of va pourization of water Do you think during evaporation the liquid a bsorbs this much heat to turn to vapour If no then how does it change to vapour T his cannot be by specific heat of water caus e specific heat of water is the amount of he at required to increase the temperature of 1 g of water by 1 C It doesn t change the stat e Lauess

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsAU of combustion of methane is 300 kJ mol The value of AH is Options 300 kJ mol 11 Greater than 300 kJ mol 0 kJ mol Less than 300 kJmol Solution Answer 4 NOF F 1 VI Dart 1 Dana Na 190

Physical Chemistry
Energetics139 Which of the following statement s is are correct Statement i The entropy of isolated system with P V work only is always maximized at equilibrium Statement ii It is possible for the entropy of close system to decrease substantially in an irreversible process 1 Statement iii Entropy can be created but not destroyed system Statement iv AS is zero for reversible process in an isolated system A Statement i ii iii B Statement ii iv C Statement i ii iv DYAll of these

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsIf Avap H for water at 298 K is 44 kJmol then how much heat is required to evaporate 9g of water at 298 K Options 11 KJ 22 kJ 99 kJ 396 kJ Solution Answer 2

Physical Chemistry
Energetics149 The combustion of benzene 1 gives CO g and H O I Given that heat of combustion of benzene at constant volume is 3263 9 kJ mol at 25 C heat of combustion in kJ mol of benzene at constant pressure will be R 8 314 JK mol A 3267 6 C 452 46 B 4152 6 D 3260 15

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsIf the standard enthalpy of combustion of solid phenol is 3054 kJ mol at 298 K and its standard molar entropy is 144 0 JK 1 mol 1 then the standard Gibbs energy of combustion of phenol is O a A Go 3084 kJ mol Ob A GO Oc A G Od4cG 3077 kJ mol 1 3074 kJ mol 3097 kJ mol 1

Physical Chemistry
Energeticsd P is the pressure of the gas when only one mole of gas is present Pure hydrogen sulphide is stored in a tank of 100 litre capacity at 20 C and 2 atm pressure The mass of the gas will be a 34 g b 340 g c 282 68 g d 28 24 g A weather balloon filled with hydrogen at 1 atm and 27 C has volume equal to 12000 litres On

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsCalculate the heat produced in kJ when 224 gm of CaO is completely converted to CaCO3 by reaction with CO at 27 C in a container of fixed volume Given AH CaCO3 s 1207 kJ mol AH CaO s 635 kJ mol AH CO g 394 kJ mol Use R 8 3 J K mol 85 702 04 kJ 2 721 96 kJ 3 712 kJ

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsWhen equal volumes of methanol CH3OH and water are mixed the temperature increases a What does this observation tell you about the value of H of mixing b Let s assume that hydrogen bonding is the only energetically significant non covalent interaction in both the pure liquids and in the mixture Based on your answer in part a will the total number of hydrogen bonds in the mixture be higher or lower than in the separate liquids Explain c If we have infinite time to observe the mixture will we ever see it revert to the

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsA monatomic ideal gas is the working substance for a refrigerator that undergoes the cyclic process ABCDA shown in the PV diagram The processes are all isochoric or isobaric with pressures between P and 2P and volumes between V and 2V What is the coefficient of performance for this refrigerator P 2P Po

Physical Chemistry
Energeticsc AG 0 AS 0 d AG 0 AS 0 52 The enthalpy of formation of ammonia is 46 0 kJ mol The enthalpy for the reaction 2N g 6H g 4 NH3 g is equal to a 46 0 kJ b 46 0 kJ c 184 0 kJ d 184 0 kJ

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsWhat is the change in chemical potential of a perfect gas when its pressure is increased isothermally from 92 0 kPa to 252 0 kPa at 50 C 2 71 kJ mol a b c d 4 5 kJ mol 3 1 kJ mol 71 kJ mol

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsCalculate the heat of formation of ethyl acetate from ethyl alcohol and acetic acid Given that heat of combustion of ethyl alcohol is 34 kcal and of acetic acid it is 21 kcal and of ethyl acetate it is 55 4 kcal 80212

Physical Chemistry
Energetics33 i H g Cl g 2HCl g AH x kJ ii NaCl H SO NaHSO HCI AH y kJ 4 4 iii 2H O 2Cl 4HC1 0 AH z kJ From the above equations the value of AH of HCl is a x kJ b y kJ c z kJ d x 2 kJ

Physical Chemistry
Energetics5 The value of AH in kJ for the reaction will be CS 1 4NOCI g CCI 1 2SO g 2N g if AH CS x AH CO z 1 x 4y z 2r AH NOCI Y AH SO r 2 r z 4y X 3 2r z 4y x 5 Wyd

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsWhich of the following relation is correct Question Type Single Correct Type 0 1 AH H 0 l AHC H g 2 AH CO g AHCO C graphite 3 4 AH CO g AH C AH CO g All of the above Your Answer 3 Status Incorrect graphite

Physical Chemistry
Energetics165 A box of 1L capacity is divided into two equal compartments by a thin partition which are filled with 2g H and 16gm CH4 respectively The pressure in each compartment is recorded as P atm The total pressure when partition is removed will be A P C P 2 B 2P D P 4

Physical Chemistry
EnergeticsThe molar heat of formation of NH4NO3 s is 367 54 KJ and those of N O g and H 0 e are 81 46 KJ and 285 78 KJ respectively at 27 C and 1 atm pressure What is AH for the reaction NH4NO3 S N O g 2H O l Question Type Single Correct Type 1 2 3 122 56 KJ 449 KJ 122 56 KJ