Equilibrium Questions and Answers

Physical Chemistry
Equilibrium10 95 According to Le Chatelier s principle adding heat to a solid and liquid in equilibrium will cause the 991 tot a temperature to increase b temperature to decrease c amount of liquid to decrease d amount of solid to decrease 96 0 1 M solution of which one of these substances 1993

Physical Chemistry
Equilibrium4 AH 0 and AS 0 53 For N O NO NO if total pressure is P atm and amount of dissociation is 50 the value of K will be 1 3P 2 2P 4 3 Match the column 3 AH 0 AS O 4 AH 0AS O 53 3N O NO NO afeg faci 50 K 1 3P 2 2P 3 54 aas 4

Physical Chemistry
Equilibrium7 The stoichiometric point of the titration of 25 0 mL 0 100 M HCIO with 0 10 M NaOH a H aq occurs when the molar concentration of NaClO is 0 050 M The pH of this solution is about given pKa of HCIO 7 43 log 0 05 1 301 A 2 63 C 10 10 B D 3 94 11 36

Physical Chemistry
Equilibrium5 In order to find the strength of a sample of sulphuric acid 10 g was diluted with water and a piece of marble weighing 7 g placed in it When all action had ceased the marble was removed washed dried and was found to weigh 2 2 What was the percentage strength of sulphuric acid

Physical Chemistry
Equilibrium20 Formation of ammonia in Haber s process N 3H 2NH3 AH ve can be increased by A increase in temperature and pressure B increase in temperature C increase in the concentration of ammonia D increase in pressure

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumThe equivalent conductivity of N 10 solution of acetic acid at 25 C is 15 ohm cm equiv What is the Degree of dissociation of acetic acid ACH COOH 400 ohm cm equiv 1 Question Type Single Correct Type 1 2 3 3 75 3 9 2 12 0 000

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumWhich of the following statement is correct 1 pK increases with increase in temperature 2 pK decreases with increase in temperature W 3 pk 14 at all temperature 4 pK pH at all temperature

Physical Chemistry
Equilibrium9 3 90 4 80 A2B K CD E K If degrees of dissociation 9 of A and C are same and K 2K then the ratio of total pressure P P 1 2 3 4 2 12 40 2 85 3 90 4 80 A B K C D E KAC 1 E 1 2 2 113 114 3 4 2 KKP Pa

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumTo 100 ml of an aqueous solution of 0 1 M CH COOH Ka 2 10 0 01 mol of HC1 g is passed Select correct options regarding the resulting solution A Degree of dissociation of acetic acid in resulting solution is 10 4 pH of resulting solution is nearly 1 S Degree of dissociation of water in resulting solution is 1 8 10 5 D Concentration of OH ions contributed by water is resulting solution is 10 7 M

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumConsider the following reaction 2NO 2H N 2H O The given reaction follows the mechanism 1 NO NO N O Fast and reversible II O H N O H O Slow III N O H N H O Fast Which of the following statement is incorrect If the concentration of NO becomes twice then rate of reaction becomes 4 times If the concentration of H becomes twice then rate of reaction becomes 4 times Overall order of reaction is 3 If the concentration of both NO and H becomes thrice then rate reaction becomes 27 times

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumVAVILOG G The equilibrium constant for the ionization of R NH g in water as RNH g H O RNH aq OH aq is 8 x 10 at 25 C Find the pH of a solution at equilibrium when pressure of R NH g is 0 5 bar The rate of react

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumFor the given sequential reaction A kiBk2 C Initial concentration of A is 20M Calculate the approximate concentration of C after 10 if k 2 108 min k 0 0693min 1

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumH g 1 g 2HI g in equilibrium for the forward reaction is 167 kJ mol 1 whereas for the reverse reaction is 180 kJ mol The presence of catalyst lowers the activation energy by 80 kJ mol Assuming that the reactions are made at 27 C and the frequency factor for forward and backward reactions are 4 104 and 2 10 3 respectively calculate K wold

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumIf pH and percentage degree of hydrolysis for the salt BA 0 1M are x and y respectively then x y is equal to given K HA 106 K BOH 106 a xMnO vPbO zHNO HMnO Pb NO H O then minimum integer

Physical Chemistry
Equilibrium53 For the reaction A g 2B g C g D g K A B Initial pressure of A and B are respectively 0 60 atm and 0 80 atm At a time when pressure o C is 0 20 atm rate of the reaction relative to the initial value is C A 6 B dx 1 48 D 1 24

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumSlope of the graph between log Keq and 1 T Tin Kelvin is 400 Which of the following change will ncrease the concentration of B g in an equilibrium mixture of A B and C 1 Addition of a gas which reacts with only A 2 Addition of inert gas at constant pressure 3 Increase in temperature at constant volume 4 Decrease in volume at constant

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumWhen AgCl is treated with a NH3 solution part of the precipitate dissolves to form a complex ion What weight of AgCl will dissolve in 1L of 1M NH3 solution Data ksp AgCl 1 82 10 10 B log 2 7 1 SOLUTION 6 86 gl 1

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumThe equilibrium constants of the following are N2 3H22NH3 K1 N2 O22NO K H 1 0 3 02 H 0 K3 5 The equilibrium constant K of the reaction 2NH3 2 1 K K3 K 2 K K3 K 3 K2 K3 K K 2NO 3H O will E 4 K K3 K

Physical Chemistry
Equilibrium4 9 The activation energy for the reaction 2 HI g H 1 g 2 is 209 5 kJ mol at 581K Calculate the fraction of molecules of reactants having energy equal to or greater than activation energy
Physical Chemistry
Equilibrium3 lon 85 100 mL of 0 02 M benzoic acid pK 4 20 is titrated using 0 02 M NaOH pH after 50 mL an 100 mL of NaOH have been added are a 3 50 7 b 4 2 7 c 4 2 8 1 d 4 2 8 25 86 What is the pH of a solution 10n

Physical Chemistry
Equilibriumoxidising agent react completely with acidified 0 1 M Kl aq then for which of the following oxidising agent equal moles of each oxidising agent will be used to produce one mole of 12 in each case An Question Type Single Correct Type 1 KMnO4 K Cr O7

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumA B C at 25 C k 2 5min k 5 5min k3 10 8 min and k 4 7 min The Arrhenius factor is 102 min for each reaction then AB is an endothermic process B C is an endothermic process O Activation energy for the conversion B Overall order of the reaction is 1 A is higher than the activation energy for the conversion B 2 O

Physical Chemistry
Equilibrium5 One mole of SO was placed in a litre vessel at a certain temperature When equilibrium was established in the 3 reaction 2SO3 the vessel was found to contain 0 4 moles of SO3 The value of equilibrium constant is 2SO 0 O a 0 13 c 0 68 b 0 36 d 0 45

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumKa HA 10 a 3 10 9 TAZI 1 732 x 10 c 8 3 When a salt of weak acid and weak base is dissolved in water at 25 C the pH of the resulting solution will always a be 7 c be less than 7 with 0 05 11 1 b be greater than 7 a b depend upon K and K values lution of 10 M ammonium formate

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumAgBr s 2S O aq 3 Ag S 03 2 aq Br aq Given Ksp AgBr 5 10 13 K Ag S 03 2 5 10 3 What is the molar solubility of AgBr in 0 1 M Na2S2O3 A B C D 0 5 M 0 45 M 0 045 M Correct Answer None of these

Physical Chemistry
Equilibrium4 T T 58 Calculate the pH on mixing 100 mL of 0 2M HCN with 400 58 25 C mL of 0 05 M KOH at 25 C pK for CN 8 1 4 7 2 9 3 3 5 7 4 8 3 1 4 7 2 9 3 3 5 7 4 8 3 400 mL 0 05 M KOH 0 2M HCN 10 pH pk for CN 8

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumA gas P at an initial pressure of 100 cm of Hg is taken in a container of capacity V L P dissociates as P g R g S g At equilibrium total pressure is found to be 150 cm of Hg Now another gas Q is taken in a container of same capacity at initial pressure of 100 cm of Hg Q dissociates as Q g 2R g T g At equilibrium total pressure is found to 150 cm of Hg Find the partial pressure of R g at equilibrium in cm of Hg if both containers are connected by a thin tube of negligible volume T constant throughout Give your answer after dividing it by 10

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumAn analytical chemist is titrating 235 8 mL of a 0 6700 M solution of hydrazoic acid HN3 with a 0 2500M solution of KOH The pK of hydrazoic acid is 4 72 Calculate the pH of the acid solution after the chemist has added 749 0 mL of the KOH solution to it a Note for advanced students you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of KOH solution added Round your answer to 2 decimal places

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumWhat is the equivalent mass of O2 in the following reaction H O O 2e 2 The amount of electricity which releases 2 0 g of gold from a gold salt is same as dissolves 0 967 g of copper anode during the electrolysis of copper sulphate soluti the oxidation number of gold in the gold ion At mass of Cu 63 5 Au 197 When a molten salt was electrolysed for 5 min with 9 65 A current 0 18 g of the deposited Calculate the Eq mass of metal og nohoubad During the electrolysis of a concentrated brine solution calculate the moles of produced by the passage of 4F electricity Calculate the cell potential in M if AG 965kl mol and n 1

Physical Chemistry
Equilibrium7 Which one of the following information can be obtained on the basis of Le Chatelier principle a Dissociation constant of a weak acid b Entropy change in a reaction c Equilibrium constant of a chemical reaction d Shift in equilibrium position on changing value of a constraint 1992 98 Aqueous solution of acetic acid contains a CH3COO and H

Physical Chemistry
Equilibrium91 The solubility of AgCl will be minimum in a 0 01 M CaCl c 0 001 M AgNO3 b pure water d 0 01 M NaCl 1995 92 In liquid gas equilibrium the pressure of

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumFor the dissociation A B3 g 2AB g B g 2 If M Molecular mass of A B3 g D Vapour density of equilibrium mixture po Initial pressure of A B3 g then identify the CORRECT statement s A Equilibrium pressure can be expressed as B Equilibrium pressure can be expressed as 2P D M P M 2D M 2D 3D C Degree of dissociation of A B3 g can be expressed as D Increase in temperature will increase the magnitude of D

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumAcid lonization Equation H PO4 aq H aq HPO4 aq HPO4 aq H aq PO4 aq Acid lonization Constants Ka 6 3 10 8 Ka 4 5 x 10 13 pK 7 20 12 35 A buffer was prepared by mixing 200 0 mL of 0 500 M NaH PO4 and 50 00 mL of 0 400 M Na HPO4 1 Calculate the pH of the buffer Round off your answer until the second digit after the decimal point 2 Calculate the molar concentration of the buffer Observe rules on significant figures
Physical Chemistry
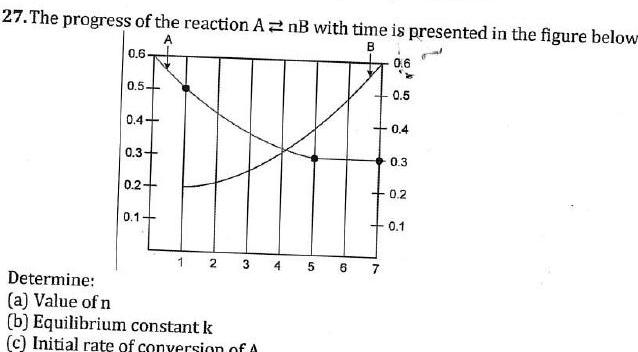
Equilibrium27 The progress of the reaction AnB with time is presented in the figure below A B 0 6 0 5 0 4 0 3 0 2 0 1 2 3 Determine a Value of n b Equilibrium constant k c Initial rate of conversion of A 4 5 6 0 6 7 0 5 0 4 0 3 0 2 0 1

Physical Chemistry
Equilibrium30 Which among the solutions given below will not show a change in pH on dilution I 0 1 M NH COOCH II 0 1 M NaCl III 0 1 M NH OH IV 0 01 M H SO4 A I and II B I II and IV C I and III D III and IV

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumVEE MAIN EVUTJuly Soon Shin memory Based Paper Discussion Chemistry Ba OH 5 x 10 mol L dissociate 100 find conc of H O AX Bolo H 5x10 M OH 2x5x15 16 M Topic name lonic Equilibrium DBa OH Ba 2OH 2 H 0 OH 15 4 llent 16 4 1 12 M H EA BY CHO

Physical Chemistry
Equilibrium4 The solubility product of BaCrO is 2 4 x 10 10 M The 24 BaCro fact 2 4 x 10 M IK x 10 M ff Ba maximum concentration precipitation in a 6 x 10 1 4 x 10 7 M 2 1 2 10 0 M 3 6 10 M 4 3 10 M of Ba NO3 possible without MK CrO solution is fat 1 4 x 10 7 M 2 1 2 x 10 0 M 3 6 10 M 4 3 10 M

Physical Chemistry
Equilibrium4 6 25 10 atm 3 Match List I and List II List I a The limits of pH values of buffer solution b Concentration of H 0 in 0 001 M Ba OH c The buffer capacity of a soultion is maximum when concentration of salt to that of acid is d Ionic product of water is A B C 1 iv 2 Iv 3 1 List II 1 5 10 2 11 Equal i 10 4 iv pka 1 D 11 4 6 25 10 atm 43 111 w gew I a was first pH b 0 001 M Ba OH H O C for t A 1 iv 2 Iv 3 1 B il

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumWhen the MnO reacts with HCl the chlorine gas is evolved according to the equation MnO 4HCI MnCl Cl 2H O Which are correct regarding this equation 1h factor of HCI is 0 5 Equivalent mass of HCI will be equal to molecular mass of HCI Equivalent mass of MnO is half of its molecular mass 4 It is redox reaction

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumIn the system 2SO2 0 2SO3 2 moles of SO 1 mole O and 2 moles SO3 are present at equilibrium What is the number of moles of O to be introduced into the vessel to increase the equilibrium moles of SO3 to 3 moles A 4 5 B 2 0 C 6 0 D 8 5

Physical Chemistry
Equilibrium8 According to Langmuir model of adsorption there is an equilibrium between adsorption and desorption as given below A g S s A S S where A S represent the adsorbate and the solid surface sites and A S is the adsorbed species The adsorption coefficient K is defined as kalka where ka and ka are the rate constants for adsorption and desorption respectively Which of the following is correct I K II K A S A S A S A S III A large value of K indicates strong adsorption IV A large value of K indicates strong desorption A I and III B II and III C I and IV D I and II

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumFor an equilibrium the equilibrium constants at 27 Cand 127 C are respectively K and K if AH for the reaction in the above temperature range is 4576cal then log10 K K is A 5 6 B 5 6 C D 4576 300 400 4576 10

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumThe solubility of MX MX2 and MX3 is 10 mole per litre Hence their solubility products are respectively O O O O 10 6 4 x 10 27 10 2 10 8 4 x 10 2 27 10 16 10 8 x 108 32 10 12 none of these

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumFor the endothermic reaction 3 A g B g C g select the option s by which equilibrium concentration of A g can be decreased Decreasing the temperature O O Decreasing the volume of the container Increasing the volume of the container Adding Bla at equilibrium

Physical Chemistry
Equilibriumlat 37 The balanced MnO4 aq SO g Mn aq HSO aq 3 form of the given Texn 1 2MnO4 aq 5SO g 5H aq 2Mn 5HSO aq 2 2MnO4 aq 5SO g 2H O 1 H aq 2Mn aq 5HSO aq 3 5MnO4 aq 2SO g 5H O 1 H aq 2Mn 2 aq 5HSO aq 4 MnO4 aq 5SO g 2H O 1 H aq Mn 2 aq TUT ows 1 FUGO 1 12

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumWhat will be hydrolysis constant of anilinium hydrochloride Pt H 1 atm H 1 M PhNH C1 M 32 H 1 atm Pt if cell potential of the cell is 0 188 volt at 298 K a 1 352 x 10 5 b 4 32 x 10 6 c 8 72 x 10 5 d 7 98 10 4

Physical Chemistry
Equilibrium67 An aqueous solution contains 0 10 M H S and 0 20 M HCl If the equilibrium constants for the formation of HS from H S is 1 0 x 10 7 and that of S2 from HS ions is 1 2 x 10 13 then the concentration of S ions in aqueous solution is A 5 x 10 19 C 3 x 10 20 B 5 x 10 8 D 6 x 10 21

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumA solution contain equal moles of CH COOH and CH3COONa The pH will ch significantly if 1 small amount of CH3 COONa is added without changing volume pot pla 2 small amount of CH3COOH is added without changing volume 3 the solution is diluted 4 moles of CH3COOH equal to moles of CH3COONa are added

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumpH of a saturated solution of Ba OH is 12 The value of solubility product Ksp of Ba OH is AIPMT Prelims 2012 2 5 0 10 6 4 5 0 10 7 1 4 0x10 6 10 7

Physical Chemistry
EquilibriumNO3 NO2 acidic medium E 0 79V NO3 NH OH acidic medium E 0 731V At what pH the above two half reaction will have same E values Assume the concentration of all other species to be unity