General Questions and Answers

Physical Chemistry
GeneralIf 0.850 g of glucose are burned in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the 700. g of water in the calorimeter increases from 15.30 °C to 19.00 °C. If the heat capacity of the calorimeter is 660 J/°C what is the value of q for the combustion of the glucose sample? Use Cwater = 4.184J/g °C Report your answer using three significant figures.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralState what would happen to red blood cells if placed in a 5% glucose solution? hypotonic hypertonic crenation hemolysis no change

Physical Chemistry
GeneralA system releases heat to the surroundings and no work is done on or by the system. What are the signs of system and
Select the correct answer below:
O system <0 and Wsystem > 0
system
> 0 and Wsystem > 0
O 9system >0 and Wsystem = 0
O 9system <0 and Wsystem = 0
FEEDBACK

Physical Chemistry
General3.0 mol PbS
Express your answer using two significant figures.
V=
Submit
Part B
AΣO
V =
Request Answer
Express your answer using two significant figures.
VAE
ESSAY
?
?
mol PbO
mol SO₂

Physical Chemistry
GeneralA subunit of an organic compound that confers particular chemical and physical properties is termed.
Select one:
a.
a monomer.
b. an oligomer.
c. a functional group.
d.
a synthetic unit.
e. an isomer.

Physical Chemistry
General8. Fill in the following table, converting the following number of atoms to moles and moles to
atoms as needed. (3 points per problem, 12 points total)
Atoms
a.
3.4 x 1026 atoms
C.
9.0 x 1020 atoms
Moles
0.1250 moles
b.
0.0015 moles
d.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralWhat is a cultural trait?
OA
OB.
O C.
OD.
a behavior common to all cultures
an element of culture that depends on people
an element of culture that is adopted from other cultures
a behavior unique to a cultural group

Physical Chemistry
GeneralWrite the correct chemical formula on the blanks:
• Potassium bicarbonate
. Carbon tetrafluoride
.
.
. Nickel II Oxide
Aluminum Hydroxide
Hydrogen Fluoride
. Nickel III Oxide
.
• Silicon dioxide
.
.
Sulfur hexafluoride
Dinitrogen monoxide
Cobalt II Chloride
I
• CoCl₂
• FeSO4
• Mg(OH)2
. CF4
• SiO2
• N₂O
• Ni2O3
• HNO3
• FeS
• AICI3
• NiO
• SF6
• H2SO4
。
Al(OH)3
(5 points)
• HF
• KHCO3
• CoCl3

Physical Chemistry
GeneralCompound Mass Moles
H₂O
N₂O
SO₂
CH₂Cl₂
113
6.11 g
2.72
0.0784
Number of
molecules
Complete the fourth column of the table..
Enter your answers numerically separated by commas.
Nho,
NN₂0
Nso₂
NCH₂Cl₂
Submit
VAXO
?
45.34 1026,0.837 1023, 16.379 1023, 0.67211023
Previous Answers Request Answer

Physical Chemistry
GeneralUsing the two tables below and your knowledge of the shapes of molecules, identify whether each
of the compounds below are polar or nonpolar by writing polar or nonpolar next to the compound.
(3 points per compound 9 points total)
a.
b.
C.
SeO₂
NBr3
CO₂

Physical Chemistry
General13. For the following equations and the number of grams of starting materials given, determine the
limiting reactant and the number of grams of the designated product actually produced. 20 points)
2 Na3PO4 + 3 MgCl2 →Mg3(PO4)2 + 6 NaCl
starting materials 250. grams MgCl2 and
Limiting reactant =
Grams of Mg3(PO4)2
200. grams Na3PO4

Physical Chemistry
GeneralCombine the following pairs of reactants in test tubes by using the stock solutions in the lab. Use
about 1-2 mL of each solution. Describe each reaction.
(NH4)2CO3(aq) + CaCl₂(aq)
(NH4)2CO3(aq)
+ K₂SO4(aq)
Ba(NO3)2(aq) + CaCl₂(aq)
Ba(NO3)2(aq) + K₂SO4(aq) ->
You will be using a glass pipette and a pipette bulb. Do not invert or turn the pipette
sideway or the chemical inthe pipet will touch the pipet bulb. And when you reuse the
pipet bulb, you contaminate all chemical. (watch video 7 on the first page please)
FAJORT
1
1
Lab Report
Write balanced molecular equations and balanced net ionic equations for the four
reactions. Include designations for state of matter, e.g. (aq) and (s). Write N.R. if no
reaction occurred.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralWhich of the following exists as separate ions and
should thus be split up in a net-ionic equation? (Choose
all that should be split and be aware of the state)
O₂(aq)
HCI(g)
KBr(aq)
✔aqueous ethanol - CH₂CH₂OH(aq)
NaCl(s)
HF(aq)

Physical Chemistry
GeneralAn unknown metal absorbs 23.8 J of heat, and its temperature increases by 15.4°C. What is the heat capacity of the metal?
• Round your answer to two decimal places.
Provide your answer below:
J/degrees C
FEEDBACK

Physical Chemistry
GeneralSelect the single best answer.
Arrange the compounds NaF, MgO, and AIN in order of increasing lattice energy.
MgO, AIN, NaF
MgO, NaF, AIN
NaF, AIN, MgO
NaF, MgO, AIN
AIN, MgO, NaF
AIN, NaF, MgO

Physical Chemistry
GeneralAmmonium nitrate (NH4NO3) dissolves readily in water eventhough the dissolution is endothermic by 26.4kj/mol. The solution process is spontaneous because
1. of the increase in enthalpy upon dissolution of this strong electrolyte
2. the vapor pressure of the water decreases upon addition of the solute
3. of the increase in disorder upon dissolution of this strong electrolyte
4. osmotic properties predict this behavior
5. of the decrease in enthalpy upon addition of the solute

Physical Chemistry
GeneralA chemist must dilute 64.0 mL of 2.29 M aqueous sodium carbonate (Na₂CO3) solution until the concentration falls to 2.00 M. She'll do this by adding distilled water to the solution until it reaches a certain final volume.
Calculate this final volume, in milliliters. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralHow many moles of NH3 can be produced from 3.04 moles of nitrogen in the following reaction:
N₂ (g) + 3 H₂ (g) → 2 NH3 (g)

Physical Chemistry
GeneralCalculate the mass (in grams) of CO2 produced by the reaction of 0.130 mol of HCl with excess NaHCO3. Do not include units in your answer.
HCI (aq) + NaHCO3(aq) → NaCl (aq) + H₂O () + CO₂(g)
Answer:

Physical Chemistry
GeneralWhen solutions of lead(II) nitrate and sodium sulfate are mixed, a white precipitate forms.
Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction.
Phases are optional. Do not write an ionic equation (i.e., the answer should not show any charges).

Physical Chemistry
GeneralPart A
For the reaction, calculate how many moles of the product form when 1.83 mol of H₂ completely reacts.
Assume that there is more than enough of the other reactant.
H₂ (g) + Cl₂ (g) → 2 HCl (g)
VHCI =
Part B
For the reaction, calculate how many moles of the product form when 1.95 mol of O2 completely reacts.
Assume that there is more than enough of the other reactant.
2 H₂ (g) + O2 (g) → 2 H₂O (1)
VH2O=

Physical Chemistry
GeneralThe rust that appears on steel surfaces is iron(III) oxide. If the rust found spread over the surfaces of a steel boat hull contains, a total of 1.324 x 1023 oxygen atoms, how many grams of rust are present on the boat hull?
mass:

Physical Chemistry
GeneralA double bond between two atoms, A and B, _______________.
arises when two electrons are
transferred from A to B.
is longer than a single bond between
the same two atoms.
has a lower bond energy than a single
bond between the same two atoms.
consists of four electrons shared
between A and B.
consists of two electrons shared
between A and B.
![Give the chemical symbol for the element with the ground-state electron configuration [Ar]4s²3d².
symbol:
Determine the quantum numbers n and and select all possible values for me for each subshell of the element.
4s n =
4s =
The possible values of me for the 4s subshell are
0
-3,-2,-1,0, +1, +2, +3
-2,-1,0, +1, +2
-1,0, +1](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/57326990-1659465135.7392194.jpeg?w=256)
Physical Chemistry
GeneralGive the chemical symbol for the element with the ground-state electron configuration [Ar]4s²3d².
symbol:
Determine the quantum numbers n and and select all possible values for me for each subshell of the element.
4s n =
4s =
The possible values of me for the 4s subshell are
0
-3,-2,-1,0, +1, +2, +3
-2,-1,0, +1, +2
-1,0, +1

Physical Chemistry
GeneralUpon mixing a clear colorless BaCl 2 solution with a
clear, colorless Na 2SO 4 solution according to the
reaction below, a student observes a white
cloudiness form. What is responsible for the
cloudiness that is observed?
BaCl 2(aq) + Na 2SO 4(aq) → BaSO 4(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
Na2SO4
NaCl
BaCl2
BaSO4
It is impossible to tell without doing the reaction oneself.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralWhat is the most likely cause of a large Portuguese-speaking population in Brazil?
A. Brazil is surrounded by Spanish-speaking countries.
B. Portugal and Brazil have developed good trade relations.
C. Portugal had established a colony in Brazil in the past.
D. Portugal and Brazil have engaged in wars in the past.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralWrite the balanced net ionic equation for the reactions that occur when the given aqueous solutions are mixed. Include the physical states.
A. nitric acid, HNO3, and calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2
net ionic equation:
B. lead(II) nitrate, Pb(NO3)2, and potassium iodide, KI
net ionic equation:

Physical Chemistry
GeneralMnO₂ (s) + HCl(aq) → Cl₂ (g) + MnCl₂ (aq) + H₂O(1)
Express your answer as a chemical equation. Identify all of the phases in your answer.
A chemical reaction does not occur for this question.
Part B
CO2 (g) +BaSiO3 (s) + H₂O(1)→ SiO2 (s) + Ba(HCO3)2 (aq)
Express your answer as a chemical equation. Identify all of the phases in your answer.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralAssuming reactions between the following pairs of
elements, which pair is most likely to form an ionic
compound?
fluorine and iodine
chlorine and oxygen
copper and tin
carbon and chlorine
cesium and iodine

Physical Chemistry
GeneralBe sure to answer all parts.
Rank the following compounds in order of increasing strength of intermolecular forces:
A. CH3CH₂CH₂CHO (butanal)
B. CH3CH₂CH₂CH₂CH3
(pentane)
C. CH3CH₂CH₂CH₂OH (1-butanol)

Physical Chemistry
GeneralA gas occupies a volume of 25.0 mL at a pressure of 760.0 mmHg and 27.0°C. What is the
volume of the gas when the pressure is changed to 500.0 mmHg and the temperature to 400 K?
760 mm Hg = 1 atm.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralFe(NO3)3(aq) + (NH4)2S (aq) → Fe2 S3 (s) + NH4NO3(aq)
Express your answer as a chemical equation. Identify all of the phases in your answer.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralNitrogen and hydrogen combine at a high temperature, in the presence of a catalyst, to produce ammonia.
N₂(g) + 3 H₂(g) → 2 NH3(g)
Assume 0.280 mol N₂ and 0.901 mol H₂ are present initially.
After complete reaction, how many moles of ammonia are produced?
NH3: mol
How many moles of H₂ remain?
H₂: mol

Physical Chemistry
GeneralGaseous hydrogen and oxygen can be prepared in the laboratory from the decomposition of gaseous water.
The equation for the reaction is
2 H₂O(g) →2H₂(g) + O₂(g)
Calculate how many grams of O₂(g) can be produced from 66.8 g H₂O(g).
mass: g 0₂

Physical Chemistry
GeneralFor the reaction shown, calculate how many moles
of NO₂ form when each amount of reactant
completely reacts.
2 N₂O5 (g) →4 NO2 (g) + O2(g)
Part D
1.009 x 10-³ mol N₂O5
Express your answer using four significant figures.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralWrite the new moles ratios for the following equations based on the information given
1. 2Na+ O₂ → Na₂O using 3 moles O₂
2. Pb(NO3)2 + 2KIPbl2 + 2KNO3 starting with 4
moles KI
3. 2Al + 3CuCl₂ ⇒ 2AlCl3 + 3Cu starting with 0.05
moles CuCl2
4.2H₂O → 2H₂ + O₂ making 760 moles of H₂.
5. CH4 + 202 CO2 + 2H₂O making 51 moles H₂O

Physical Chemistry
GeneralConsider the following reaction at equilibrium:
2NO₂(g) ⇒ N₂O4(g)
The AH' for this reaction is <0. If the volume of the container is decreased by
while the temperature is kept constant, how will K(eq) change?
A) increase
B) decrease
C) stay the same

Physical Chemistry
GeneralList the number of each type of atom on the right side of the equation
2 Na3PO4 (aq) + 2 CoCl₂ (aq) → 2C03 (PO4)2 (s) + 6NaCl(aq)
Enter your answers separated by commas (the order of the numbers is the same as the
order of the elements on the left side of the equation).

Physical Chemistry
GeneralWhich statement best describes the process of Alpha and Beta Decay? (Pick 2)
In Alpha Decay the atom gains 2 protons and 2 neutrons.
In Alpha Decay the atom loses 2 protons and 2 neutrons.
In Beta Decay one of the atoms neutrons splits into a proton and electron.
In Beta Decay one of the atoms protons and electrons combine to form a neutron.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralList the number of each type of atom on the left side of the equation
C2H6 (g) + 7 O2 (g) → 3 CO2 (g) + 6 H₂O(g)
Enter your answers separated by commas (the order of the numbers is the sam
order of the elements on the left side of the equation).
Part E
List the number of each type of atom on the right side of the equation
C2H6 (g) + 7O2(g) → 3CO2 (g) + 6H₂O(g)
Enter your answers separated by commas (the order of the numbers is the same as
order of the elements on the left side of the equation).

Physical Chemistry
GeneralWhich of the following molecules are aliphatic hydrocarbons?
CH3CH3
CH3CH₂OH
CH2=CH₂
I
Multiple Choice
I and III
I, II, III
II
II and IV
II, III, IV
III
CH3OCH3
IV

Physical Chemistry
GeneralAs the separation distance between two charges of the same sign increases, what happens to the
electrostatic potential energy?
It becomes more negative (i.e., lower)
It becomes less positive (i.e., lower)
It becomes more positive (i.e., higher)
It becomes less negative (i.e., higher)
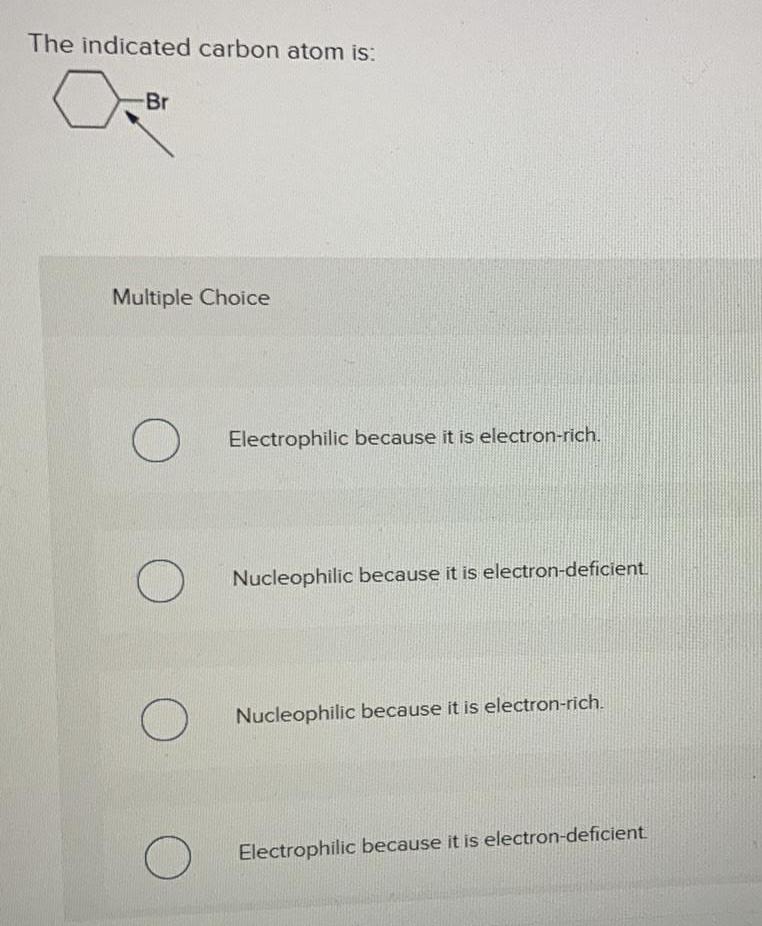
Physical Chemistry
GeneralThe indicated carbon atom is:
-Br
Multiple Choice
O
O
O
Electrophilic because it is electron-rich.
Nucleophilic because it is electron-deficient.
Nucleophilic because it is electron-rich.
Electrophilic because it is electron-deficient.
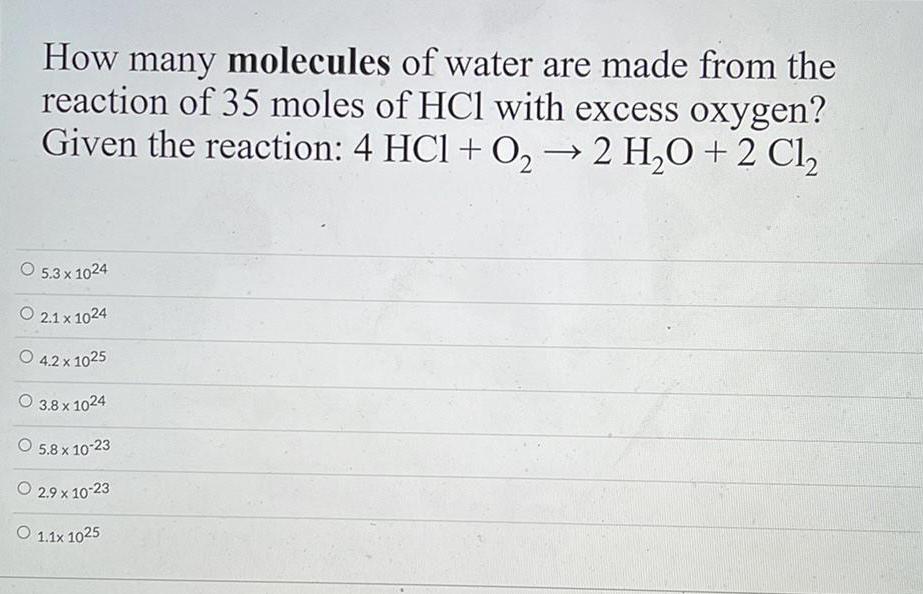
Physical Chemistry
GeneralHow many molecules of water are made from the
reaction of 35 moles of HCl with excess oxygen?
Given the reaction: 4 HCl + O₂ → 2 H₂O + 2Cl₂
O 5.3 x 1024
O 2.1 x 1024
O 4.2 x 1025
O 3.8 x 1024
5.8 x 10-23
2.9 x 10-23
O 1.1x 1025

Physical Chemistry
GeneralWhich atomic orbitals overlap to form the carbon-carbon σ and TT bonding molecular orbitals of ethylene, H₂C=CH2?
Multiple Choice
O
O
O
Csp³ + Csp³, and C2p+C2p
Csp³ + Csp³, and Csp² +Csp²
Csp²+Csp², and Csp²+ Csp²
Csp²+Csp², and C2p+C2p

Physical Chemistry
GeneralReturn to the balanced equation O₂ 1-2 H₂ → 2H₂O
(1pts)
16. a. How many moles are in 39 grams of O₂?
(1pts) b. Using the calculated moles of O₂ from 16a, how many moles of H₂O can
you make?
(1pts) c. Using the calculated moles of H₂O from 16b, how many grams of H₂O
can you make?
Now we will use the chemical equation N₂ + 3 H, -> 2NH,
(1pts)
17. If you begin with 18.3 grams of N₂, how many grams of NH3 can you
make?

Physical Chemistry
GeneralOne way the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) tests for chloride contaminants in water is by titrating a sample of silver nitrate
solution. Any chloride anions in solution will combine with the silver cations to produce bright white silver chloride precipitate.
Suppose an EPA chemist tests a 250. mL sample of groundwater known to be contaminated with tin(II) chloride, which would react with
silver nitrate solution like this:
SnCl₂(aq) + 2 AgNO3(aq)
-
mg
2 AgCl(s) + Sn(NO3)₂(aq)
The chemist adds 32.0 mM silver nitrate solution to the sample until silver chloride stops forming. She then washes, dries, and weighs the
precipitate. She finds she has collected 8.2 mg of silver chloride.
Calculate the concentration of tin(II) chloride contaminant in the original groundwater sample. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralCalculate the solubility at 25 °C of CaF2 in pure water and in a 0.0170 M NaF solution. You'll find Ksp
Round both of your answers to 2 significant digits.
data in the ALEKS Data tab.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralO
Resonance structures have the same placement of electrons but different arrangement of atoms.
Resonance structures have the same placement of atoms but different arrangement of electrons.
Resonance structures have the same placement of atoms and the same arrangement of electrons.
Resonance structures have different placement of atoms and different arrangement of electrons.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralAqueous solutions of the following reactants are mixed. Calculate the concentration (in mol/L) of calcium ions in solution after the reaction has gone to completion.
75.0 mL of 1.50 M AgNO3 are mixed with 75.0 mL of 4.5 M CaCl₂
Do NOT include units in your answer. If you round during your calculation, be sure to keep at least four (4) decimal places. Report your answer to two (2) decimal places.
Answer: