General Questions and Answers

Physical Chemistry
GeneralWhat would be the molarity of a solution made from 82.5 g Ca(OH)₂ in 500.0 mL of solution?
Select the correct answer below:
O 2.23 x 10-³ M
O 1.22 x 104 M
O 2.23 M
O 12.2 M

Physical Chemistry
GeneralIdentify the strongest attractive forces between the particles of each of the following.
Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins.
Dipole-dipole attraction
CH3 Cl
lonic bonding
CH3NH₂ H₂
CBR4
Dispersion forces
Hydrogen bonding
Reset
Help

Physical Chemistry
GeneralWhich of these accurately describes the halogens?
O mostly gases, low density, insulators, reactive
O solids, luster, high density, conductors
O solids, soft, brittle, conductors
O solids, luster, brittle, conductors, reactive

Physical Chemistry
GeneralQUESTION 24 1 POINT
The end point in a titration of a 35 mL sample of aqueous HC1 was reached by the addition of 17 mL of 0.76 M NaOH
titrant. The reaction proceeds by the following equation.
HCl(aq) + NaOH (aq) → NaCl(aq) + H₂O(1)
What is the molar concentration of HCl?
• Report your answer with two significant figures.
Provide your answer below:
M

Physical Chemistry
GeneralWhat are the columns on the periodic table called? Select the TWO that apply.
Ocolumns
periods
families
groups

Physical Chemistry
GeneralFluorine (F) has a melting point of 53.53 K and a boiling point of 85.03 K. Draw what Fluorine would look like on the molecular
level at 40 K. Be sure to indicate (and label) what types of interactions and/or bonds are present.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralWhich is a neutralization reaction?
Select the correct answer below:
O Cl₂(aq) + H₂O(l) → HCl(aq) + OH¯(aq)
O HCl(aq) + LiOH(aq) → LiCl(aq) + H₂O(1)
O CaCl₂(aq) → Ca²+ (aq) + 2Cl(aq)
O HCl(aq) + H₂O(l) → H₂O+ (aq) + Cl¯ (aq)

Physical Chemistry
GeneralWhich statement best explains a way in which a cell gets rid of wastes?
A. The nucleus provides the instructions for making proteins from
amino acids.
OB. A chloroplast converts energy from sunlight into organic matter.
OC. Vacuoles merge with the cell membrane and then open.
D. Mitochondria change energy stored in organic compounds into a
usable form.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralWhen a 7.00 g sample of KCl is dissolved in water in a calorimeter that has a total heat capacity of 3.30 kJ
temperature decreases by 0.490 K. Calculate the molar heat of solution of KC1.
AH soln=

Physical Chemistry
GeneralCalculate the volume of a stock solution of Ba(OH)₂, with a concentration of 0.10 M, needed to prepare 8.0 L of 0.072 M
Ba(OH)₂.
Select the correct answer below:
0 072 L
O 58L
0.58 L
OIL

Physical Chemistry
GeneralFor each of the following unbalanced equations, calculate how many moles of the second reactant would be required to react completely with 0.364 moles of the first reactant.
Co(s)+F2 (g) → CoF3 (s)
a.
b.
C.
mol F₂
Al(s) + H₂SO4 (aq) → Al₂(SO4)3 (8) + H₂(g)
mol H₂SO4
K(s) + H₂O(1)→ KOH(aq) + H₂(g)
mol H₂O

Physical Chemistry
General1. Provide the chemical formula for the substance described in each of the chemical reactions.
Refer to pages 94-95 for the substance described in each reaction.
(a) the white smoke produced from reaction A.1
(b) the strong odor produced from reaction A.2
(c) the colorless gas produced from reaction B.1
(d) the flame-extinguishing gas from reaction B.2
(e) the gray solid produced from reaction C.1
(f) the colorless gas produced from reaction C.2
(g) the white ppt produced from reaction C.3
(h) the cream ppt produced from reaction D.1
(i) the blue-white ppt produced from reaction D.2
(1) the white ppt produced from reaction D.3
(k) the yellow ppt produced from reaction D.4
(1) the blue-white ppt produced from reaction D.5
(m) the white ppt produced from reaction D.6
(n) the acid reacting in reaction E.1
(o) the acid reacting in reaction E.2
(p) the acid reacting in reaction E.3
(q) the base reacting in reactions E.1-E.3
mincode o
(0)
Refer to the Activity Series for Metals in Appendix F and indicate reaction (Rxn) or no
reaction (NR) when a piece of zinc metal is dropped into the following aqueous solutions.
(a) Al(NO3)3(aq)
(b) Cr(NO3)3(aq)
(c) Mg(NO3)2(aq)
(d) Fe(NO3)2(aq)
(e) Cu(NO3)2(aq)
(f)
HNO3(aq)

Physical Chemistry
GeneralA sample of nitrogen gas at a pressure of 926 mm Hg and a temperature of 31 °C, occupies a volume of 4152.6 ml.. If the gas is heated at constant
pressure to a temperature of 79 °C, the volume of the gas sample, in liters, will be

Physical Chemistry
GeneralQUESTION 10 1 POINT
An aqueous solution contains the following ions: Cl-, Na+, Mg2+, CO3, and HCO3. Is a precipitate likely to form? If so,
give the formula of the precipitate.
Select the correct answer below:
O Mg(HCO3)2
O Mg(CO3)2
O NaCl
No precipitate will form.
B

Physical Chemistry
GeneralSuppose the quantum number rule for the angular momentum quantum number, I was
1 = 0,1,2,...,l
L = 0,1,2,...,l-1
Drag the text components into the boxes to create the Ar electron configuration for the new rule.
Instead of
Number of electrons
Orbital
Orbital Energy

Physical Chemistry
GeneralFor the following reaction, 4.01 grams of hydrogen gas are allowed to react with 46.4 grams of iodine.
hydrogen(g) + iodine(s) hydrogen iodide(g)
What is the maximum mass of hydrogen iodide that can be formed?
What is the FORMULA for the limiting reagent?
What mass of the excess reagent remains after the reaction is complete?
grams
grams

Physical Chemistry
General1. Provide the key term that corresponds to each of the following definitions.
(a) a substance undergoing a chemical reaction
(b) a substance resulting from a chemical reaction
(c) a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction
(d) a relative order of metals arranged in a list according to their ability to
undergo reaction
(e) a solution of a substance dissolved in water
(f) an insoluble solid substance produced from a reaction in aqueous solution
(g) the solution above a precipitate after insoluble particles separate
Key Terms: aqueous solution, activity series, catalyst, precipitate (ppt), product, reactant,
supernate

Physical Chemistry
GeneralCopper will take on many forms during the course of this experiment. This will lead to color changes, solution formation (where the copper cation is hydrated in water),
formation of a precipitate, etc.). Look up the physical properties of the copper containing substance in each step and match it to the description.
Cu(s)
A. Solid, reddish-orange color, shiny.
Copper(II) nitrate
Copper(11) oxide
Copper(11) hydroxide
Copper(11) sulfate
B. Blue crystalline solid. Water soluble.
C. Blue, blue-green solid. Nearly insoluble in water.
D. Black/brown powder. Insoluble in water.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralA 6.0 M solution of KNO3 has a volume of 0.60 L. If the solution is diluted to 3.0 L, what is the new concentration?
Select the correct answer below:
O 0.12 M
O 15 M
O 30. M
O 1.2 M

Physical Chemistry
GeneralThe end point in a titration of a 35 mL sample of aqueous HCI was reached by the addition of 17 mL of 0.76 M NaOH
titrant. The reaction proceeds by the following equation.
HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) -
What is the molar concentration of HCI?
• Report your answer with two significant figures.
Provide your answer below:
-> NaCl(aq) + H₂O(1)

Physical Chemistry
General(a) A GaAs semiconductor resistor is doped with donor impurities at a concentra-
tion of N = 2 x 10¹5 cm-3 and has a cross-sectional area of 5 x 10-5 cm². A current
of 1 = 25 mA is induced in the resistor with an applied bias of 5 V. Determine the
length of the resistor. (b) Using the results of part (a), calculate the drift velocity of
the electrons. (c) If the bias applied to the resistor in part (a) increases to 20 V, deter-
mine the resulting current if the electrons are traveling at their saturation velocity of
5 x 10 cm/s.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralA solution is made by adding 9.00 g of iron sulfate to 57.0 g of water. What is the mass percentage of iron sulfate in this solution?

Physical Chemistry
GeneralThe compound sodium thiosulfate pentahydrate, Na2S2O3.5H2O, is important commercially to the photography business as "hypo", because it has the ability to dissolve unreacted silver salts from photographic film during development. Sodium thiosulfate pentahydrate can be produced by boiling elemental sulfur in an aqueous solution of sodium sulfite. S8 (s) + Na₂SO3(aq) + H₂O(l) → Na2S₂O3.5H₂O(s) (unbalanced) What is the theoretical yield of sodium thiosulfate pentahydrate when 2.90 g of sulfur is boiled with 13.9 g of sodium sulfite? Theoretical yield = Sodium thiosulfate pentahydrate is very soluble in water. What is the percent yield of the synthesis if a student doing this experiment is able to isolate (collect) only 5.18 g of the product?

Physical Chemistry
GeneralWhat is the molarity of CaCl₂ when 1.92 mol of CaCl₂ is dissolved in water to form 515 mL of solution?
Select the correct answer below:
3.73 M
0.268 M
3.73 x 10-³ M
0.989 M

Physical Chemistry
General75.0 mL of 1.50 M AgNO3 are mixed with 99 mL of 1.00 M CaCl2
Do NOT include units in your answer. If you round during your calculation, be sure to keep at least four (4) decimal places.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralNed decides to use instrumental methods to analyze trace evidence found at a crime scene. Which Items might
A test tubes
B. Bunsen burner
C. mass spectrometer
D. lifting tape
E. forceps

Physical Chemistry
GeneralWhen covalent compounds, such as water (H₂O),
form covalent bonds, they share valence electrons. A
Lewis dot structure or electron dot structure is a
drawing that represents chemical bonds between
atoms as shared or transferred electrons, where the
valence electrons are represented as dots. For
example, notice the Lewis structure of NC13 (Figure
1). When a pair of electrons is shared between two
atoms, a line is drawn to indicate a bond.
For neutral molecules, which statements about covalent Lewis structures are true?

Physical Chemistry
GeneralA sample of 13.2 g of Fe₂O3 reacts with 15.2 g Cto yield Fe and CO₂. The balanced chemical equation is
Fe₂O3(s) + 3 CO(g) → 2 Fe(s) + 3 CO₂(g)
Which substance is the limiting reactant?
CO₂
Fe
CO
Fe₂0,

Physical Chemistry
GeneralWhich term is used to describe when a solid goes directly into the gas state?
heat of vaporization
evaporation
condensation
sublimation

Physical Chemistry
GeneralIf 28 moles of NO combine with 45 moles of H₂, how many moles of NH3 can form? What is the limiting reagent?
2 NO(g) + 5 H₂(g) → 2 NH3(g) + 2 H₂O(g)
Step 1: Find the number of moles of NH3 each starting material could form.
Step 2: Determine the limiting reagent.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralIn the presence of aqueous ammonia, cobalt(III) forms the complex ion Co(NH3)6³+. Determine the molar concentration of free cobalt(III) ion in solution when 0.150 mole of Co(NO3)3 is dissolved in a liter of 2.50 M aqueous ammonia. x 10 M Enter your answer in scientific notation.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralGive the IUPAC name of the product that would form when the following alkene undergoes catalytic hydrogenation.
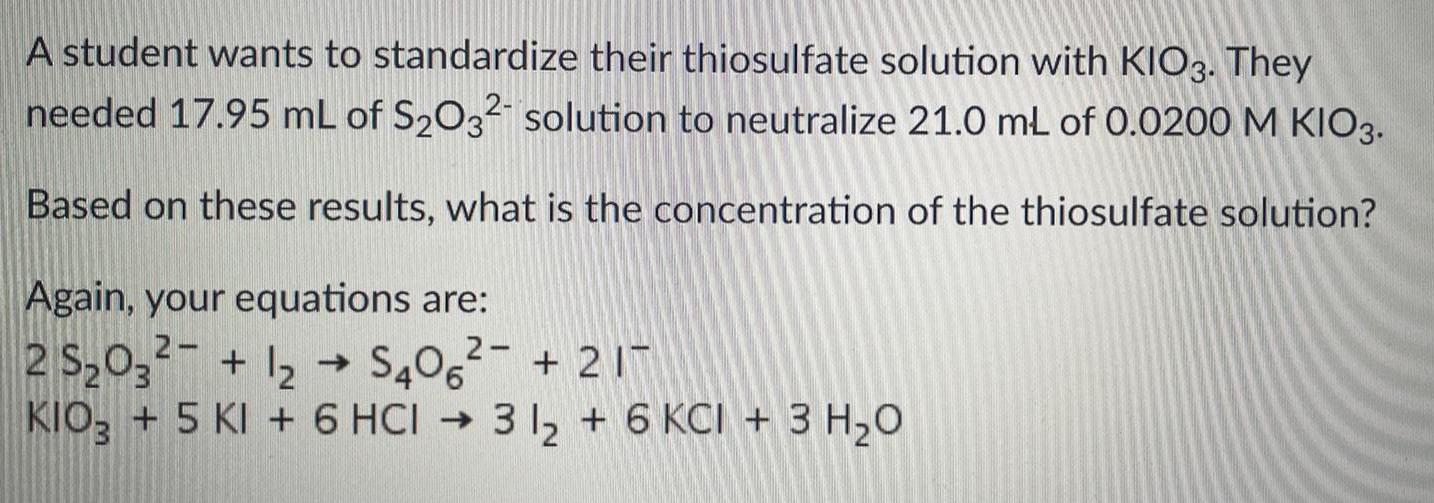
Physical Chemistry
GeneralA student wants to standardize their thiosulfate solution with KIO3. They needed 17.95 mL of S₂O32 solution to neutralize 21.0 mL of 0.0200 M KIO3. Based on these results, what is the concentration of the thiosulfate solution? Again, your equations are:

Physical Chemistry
GeneralExamine the following sentence and then identify the rule that governs the comma.
For the lab session, please bring forceps, a scalpel, pins, and your spiral notebook.
Rule 1, comma in a series
Rule 4, comma with appositives
Rule 5, comma with speaker tag

Physical Chemistry
GeneralChoose the sentence with the correct punctuation.
This modernized car according to the latest reports, has won the national award for
stability.
This modernized car, according to the latest reports has won the national award for
stability.
This modernized car, according to the latest reports, has won the national award for
stability.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralChoose the sentence with the correct punctuation.
Mr. Wilson the man with the British accent teaches yoga, at the high school.
Mr. Wilson, the man with the British accent, teaches yoga at the high school.
Mr. Wilson the man with the British accent, teaches yoga at the high school.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralSolid lead (II) sulfide reacts with aqueous hydrochloric acid to form solid lead (II) chloride and dihydrogen sulfide gas.

Physical Chemistry
General"Tomorrow," sally said, "you should travel North to get to New york city."
Sally...north...New York City
sally...North...New york city
Sally... North... New York City

Physical Chemistry
GeneralMatch the number with its corresponding numerical prefix used for molecular/covalent compound naming.
mono-
penta-
octo-
hexa-
quadra-
bi-
nona-
tri-
di-
tetra-
hepta-

Physical Chemistry
GeneralAn analytical chemist is titrating 167.6 mL of a 0.09400 M solution of ethylamine (C₂H5NH₂) with a 0.1200 M solution of HNO3. The PK, of ethylamine is 3.19. Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 154.8 mL of the HNO3 solution to it. Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HNO3 solution added.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralSuppose a 0.23 M aqueous solution of oxalic acid (H₂C₂O4) is prepared. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of C₂0. You'll find information on the properties of oxalic acid in the ALEKS Data resource. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.


Physical Chemistry
GeneralHow many grams of Ar are there in a sample of Ar that contains the same number of moles as a 64.1 gram sample of K? grams of Ar

Physical Chemistry
GeneralA certain mass of nitrogen gas occupies a volume of 6.85 L at a pressure of 5.52 atm. At what pressure will the volume of this sample be 9.23 L? Assume constant temperature and ideal behavior.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralA 0.5998 g sample of a new compound has been analyzed and found to contain the following masses of elements: carbon, 0.2321 g; hydrogen, 0.05842 g; oxygen, 0.3093 g. Calculate the empirical formula of the compound.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralA sample of air at room temperature (298.15 K) in a 4.00 L container holds approximately 0.562 moles of O, and 2.11
moles of N₂ along with other trace elements to total 2.67 moles. What is the partial pressure of O₂ in the mixture?
• Your answer should have three significant figures.
• Use R = 0.08206 L atm/mol K

Physical Chemistry
GeneralA coffee-cup calorimeter contains 50.0 mL of distilled water at 22.7°C. Solid ammonium bromide (3.14 g) is added and the solution is stirred, giving a final temperature of 20.3°C. Using the same assumptions as in Example 6.7.1, find AHsoln for NH4Br (in kilojoules per mole).

Physical Chemistry
GeneralMost carbonates are insoluble in water. Which of the following will dramatically increase the solubility of
calcium carbonate in water?
Heat the solid in water
Add H₂SO4
Add NH,
Add NaOH
Add CaCl₂

Physical Chemistry
GeneralSuppose a 0.040 M aqueous solution of sulfuric acid (H₂SO4) is prepared. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of SO4 of sulfuric acid in the ALEKS Data resource.

Physical Chemistry
GeneralMISSED THIS? Read Section 6.6. You can click on
the Review link to access the section in your e Text.
Copper (II) fluoride contains 37.42% F by mass.
Use this percentage to calculate the mass of fluorine in grams contained in 39.0 g of copp fluoride.