Solutions Questions and Answers

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsCalculate the a Normality and b Molarity of sulphuric acid solution prepared by dissolving 13 3 mL of sulfuric acid in 500 mL water specific gravity for concentrated sulfuric acid is about 1 84 g mL

Physical Chemistry
Solutionstheory of electrolyte solutions d You are given an aqueous NaCl solution of 1 0 mol kg at 25 C If you are asked to calculate the activity coefficient of the solution which theory or expression do you think would be the most suitable State the reason

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsOn addition of 0 25 mol of a non volatile solute HA mono basic acid in 5 mol of benzene solute gets partially dimerised an the pressure of solution measured is 581 11 mm Hg On further titration of this solution 200 mL of 1 25 M NaOH required to reach end point NaOH 1 21 g mL PBenzene 600 mm Hg PH O 23 76 mm Hg 2HA HA 2 Degree of association of solute a in solution is

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAn ideal solution made by mixing two volatil components A and B If the vapour pressure c solution is 170 mm Hg then mole fraction of A i vapour phase is P 200 mm Hg P 100 mm Hg 1 0 72 3 0 68 2 0 82 4 0 50

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsConsider the case of Arsenic acid H3AsO4 Sketch a species distribution diagram a versus pH for this acid in water The first second and third acid dissociation constants for this case are Kal 5 8E 3 K 2 1 1E 7 K 3 3 2E 12 H3ASO4 H H ASO4 H AsO4 H HASO4 HASO4 H AsO4 a Label the species for any lines that you put on the plot

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe solubility of salicylic acid at 10 C is 0 14 g per 100 mL of water Based on the total amount of water or other solutions added for the hydrolysis precipitation and filtration of salicylic acid estimate the amount in grams of salicylic acid that was lost in the filtrate for this step of the reaction Assume that the solution was at 10 C during filtration 40 mL were used

Physical Chemistry
Solutions3 Consider the following graph depicting of total vapour pressure and vapour pressure of components of a solution with mol fraction v p po A XB 0 A B po B XB 1 XB D mol fraction Which of the following is correct regarding the plot 1 A is more volatile than B 2 B will be more in liquid phase starting from equal mole fractions of A and B 3 AD BD CD 4 AD BC CD

Physical Chemistry
Solutions4 A gas exerts a partial pressure of 0 2 atm over water The Henrys law constant is 104 atm The solubility of the gas in millimol per litre will be approximately 1 2 75 10 5 3 1 1 x 10 5 2 1 1 10 3 4 27

Physical Chemistry
Solutions3 The total vapour pressure of a solution of methanol and ethanol in an ideal solution is given by P 135 100 where a mole fraction of methanol Pure state vapour pressure of methanol is 1 235 mm g 3 35 mm q 2 100 mm g 4 135 mm g

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAssertion At equilibrium vapour phase will be always rich in component which is more volatile Reason The composition of vapour phase in equilibrium with the solution is determined by the partial pressures of the components

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsIf a patient is receiving 155 mL of 5 00 m v glucose solution every 3 0C hours how many grams of glucose does the patient receive in 14 0 hours Select the appropriate items from the menus to show how to calculate the answer using dimensional analysis and then select the correct answer 14 0 hours 14 0 hours 100 mL 100 mL

Physical Chemistry
Solutions12 Two pure liquids A and B have vapour pressures in the ratio 1 3 The mol fraction of A in vapou phase when A and B are mixed in 1 3 molar rati in a solution will be 1 0 1 3 0 3 2 0 2 4 0 5

Physical Chemistry
Solutions22 In the following graph vapour against mole fraction of the components Which of the following statement is correct A vapour pressure C X 1 E 1 F H XB Mole fraction of B B D X 1 1 AD represents variation of vapour pressure liquid A with XA 2 BC represents variation of vapour pressure liquid B with XB 3 GH FH EH

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsN 24 What is the weight of available oxygen from a solution of H O if 20 ml of this solution needs 25 ml KMnO for complete oxidation 1 59 30 01 g 2 4 0 25 g 0 5 g

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA mixture of liquids A and B exhibits ideal behavior At 74 C the total vapor pressure of a solution containing 1 6 moles of A and 2 7 moles of B is 321 mmHg Upon the addition of another mole of B to the solution the vapor pressure increases to 338 mmHg Calculate the vapor pressures of pure A and B at 74 C

Physical Chemistry
Solutions3 5 Concentration of glucose C6H 2O6 in normal blood is approximately 90 mg per 100 mL What is the molarity of the glucose solution in blood 1 5 M 2 0 005 M 3 0 05 M 4 1 M

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA Molarity Imole in slit Sol MATB 1 Molar V L 20 166 X 480 Imole in 980 Solut mole of solut volunce u seln m1 Soluti 50 wen 20gm y 1 45 M AB C MATA x 1000 X1000 molal Imole in sing of solvent v y 2 IND I more concentrated 1 202 Imole in Ike solut

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA mixture of 20 ml of methane and 20 ml of O is exploded and cooled at room temperature If the reaction between the two substance is written as CH4 20 CO H O then final volume of the gaseous mixture is 1 10 ml 2 20 ml 3 30 ml 4 60 ml

Physical Chemistry
Solutions500 mL of 61 W V urea solution is mixed with 500 mL of 18 w V gluc ose solution and final volume of mixtur e becomes 2 L after addition of water The osmotic pressure of final 2 L soluti on at 27 degrees C is 5yR The value o fy is R universr gas constant

Physical Chemistry
Solutions12 10 gm of a sample of CaCO is treated with 200 ml of 0 1 N HCI Calculate the purity of CaCO 1 50 2 10 3 65 4 90 13 The number of moles of potassium permagnet required to oxidise 2 moles of oxalic acid in acidic medium is 1 3 1 6 11 2 is 4 14 The number of moles of ferrous oxalate oxidised completely by 1 mole of K Cr O in acidic medium 3 2 4 2 7 2 12 4 7 5 2 3 2 ANSWER 3 8 2 3

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsM 0 If 300 mL of HCI is mixed with 100 mL of 10 M Ca OH 2 then nature of resulting solution 10 and molarity of excess of reactant left is 1 Basic 0 1 M 3 Acidic 0 25 M 2 Acidic 0 025 M 4 Basic 0 01 M

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe vapour pressure of a solution having 2 0 g of solute X gram atomic mass 32 g mol in 100 g of CS vapour pressure 854 torr is 848 9 torr The molecular formula of the solute is 1 X 3 X 2 X 4 X8

Physical Chemistry
Solutionsa Define conductivity and molar conductivity for the solution of an electrolyte b Define Kohlrausch law A for NaCl HCI and CH3COONa respectively are 126 426 91 S cm mol 1 Calculate A for CH3COONa

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsA SALT SOLUTION IS OBTAINED BY DISSOLVING 40g OF SA LT IN 60g OF WATER WHAT MUST BE DONE TO MAKE THIS SALT SOLUTION 50 OPTIONS 1 ADD 20g OF WATER TO THE SOLUTION 2 ADD 20g OF SALT TO THE SOLUTION 3 ADD 10g OF SALT AND 10g OF WATER TO THE SOLUTION 4 BOTH 1 AND 2 PLEASE EXPLAIN CLEARLY AND STEP BY STEP WI TH FULL EXPLANATION

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhen 0 1 m CH3COOH is present in a solvent it shows elevation in boiling point of 0 75 C Acid dissociation constant will be K 5 K Kg mol 1M 1m 1 5 x 10 2 5 X 10 3 3 10 2 4 10

Physical Chemistry
Solutions6g urea is dissolved in 1kg solvent Value of T T will be K 2 kg K mol Solvent Vapour pressure Solid Solvent 1 0 2 C 2 0 2 C 3 0 1 C Solution T T Temperature K

Physical Chemistry
Solutions40 g NaOH i 2 is dissolved in 1L volatile solvent vapour pressure of this solution becomes equal to its solid phase at 300K What is the freezing point of pure solvent Density 1g mL kf 1 8 k kgmol 1 296 4 K 2 303 6 K 3 297 5 K 4 302 4 K

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAn aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid 1 obeys Raoult s law 2 Shows negative deviations from Raoult s law 3 Shows positive deviations from Raoult s law 4 Obeys Henry s law at all compositions

Physical Chemistry
Solutions27 A 20 litre container at 400 K contains CO2 g at pressure 0 4 atm and an excess of SrO neglect the volume of solid SrO The volume of the container is now decreased by moving the movable piston fitted in the container The maximum volume of the container when pressure of CO2 attains its maximum value will be Given that SrCO3 s SrO s CO2 g a 5 litre c 4 litre b 10 litre d 2 litre Kp 1 6 atm NEET 2017

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsSolution which shows positive deviation from Raoults law is CHCl3 C6H6 HCI H O CH3COCH3 C H5OH ICH

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhich of the following aqueous solutions has the least freezing point 0 2 m CaCl2 0 1 m AlCl3 1 m Glucose hr m 0 3 m Al2 SO4 3

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsIf the limiting molar conductivities of KCI HCI and KAc are x y and z S cm mol respectively then the limiting molar conductivity of HAc is x y z x y z y z x x y z

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsThe weight of 25 w w aqueous solution of HCI required to react completely with 50 g of CaCO3 is 146 g 71 g 106 5 g 35 5 g

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsBuild Up Your Understanding A football bladder contains equimolar proportions of H and O The composition by mass of the mixture effusing out of punctured football is in the ratio H O

Physical Chemistry
Solutions0 For WA WB type of salt pH is given by this formula 1 pH 7 pK pk pK The pH of solution can be greater than 7 if the difference between pK and pK is 2 neutral 4 None 1 Negative 3 positive

Physical Chemistry
Solutions110 In the volumetric estimation of HCl if we make use of phenolphthalein as an indicator which base is unsuitable for the titration 1 NaOH 3 KOH 2 RbOH 4 NH OH

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsIE0116 97 Following five solution of KOH were prepare as 0 1 moles in 1 L 0 2 moles in 2 L 0 3 moles in 3 L 0 4 moles in 4 L First Second Third Fourth Fifth The pH of resultant solution is 1 2 2 1 3 13 0 5 moles in 5 IE0118 Session dissok Its pH 1 Fo 2 For 3 For 4 Fo TH

Physical Chemistry
Solutions05 0 001 mol of the strong electrolyte M OH has been dissolved to make a 20 mL of its saturated solution Its pH will be K 1 10 1 13 2 3 3 3 11 4 9 8 150138

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsTotal vapour pressure of mixture of 1 mol X P 150 torr and 2 mol Y X Pa 300 torr is 240 torr In this case Y 1 There is a negative deviation from Raoult s law 2 There is a positive deviation from Raoult s law 3 There is no deviation from Raoult s law 4 Can not be decided

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsMarks 4 0 00 At a given temperature total vapour pressure in Torr of a mixture of volatile components A and B is given by P 120 75 XB Where XB is mole fraction of B in liquid Calculate the sum of vapour pressure of pure A and B respectively in Torr

Physical Chemistry
Solutionser Pre Medical Chemistry 183 101 How many moles of HCI must be removed from

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsIn which of the following pairs of solutions will the values of the vant Hoff factor be the same A 0 05 M K4 Fe CN 6 and 0 10 M FeSO4 B 0 10 M K4 Fe CN 6 and 0 05 M FeSO4 NH4 2SO4 6H2O C 0 20 M NaCl and 0 10 M BaCl2 D 0 05 M FeSO4 NH4 2SO4 6H2O and 0 02 M KCI MgCl2 6H2O

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsExample 17 In a solvent 50 of benzoic acid dimerises while rest ionises determine molar mass of acid which is observed and also its yan t Hoff fontor

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsWhich of the following statements is not true about ideal solutions A B C There is no enthalpy change on mixing There is no volume change on mixing The interactions between the components are similar to those in the pure components The components show positive and Dnegative deviations from

Physical Chemistry
Solutions15 The molar conductivities and at infinite 20 dilution in water at 25 C are 91 0 and 426 2 S cm mol respectively To calculate Ho the additional value required is 1 2 0 3 C Aka 4 ANOH EC0020 The d and C 1 fro 2 from 3 frem 4 in

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsANCH EC0020 6 The molar conductance of AgNO AgCl and NaCl at infinite dilution are 116 5 121 6 and 110 3 S cm mol respectively The molar conductance of NaNO is 1 111 4 S cm mol 3 130 6 S cm mol NaCl H O 3 AKC 2 105 2 S cm mol 4 150 2 S cm met em FC0021 21 Son

Physical Chemistry
SolutionsAn aqueous solution of sugar is taken in a beake At freezing point of solution 1 Crystals of sugar separated 2 Crystals of glucose and fructose are separat 3 Crystals of ice separated 4 Mixture of ice and some sugar crystals separa
Physical Chemistry
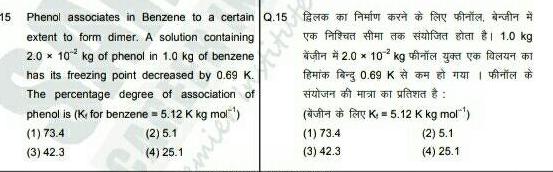
Solutions15 Phenol associates in Benzene to a certain Q 15 extent to form dimer A solution containing 2 0 x 10 kg of phenol in 1 0 kg of benzene has its freezing point decreased by 0 69 K The percentage degree of association of phenol is K for benzene 5 12 K kg mol 1 73 4 2 5 1 3 42 3 4 25 1 Kitu y fay f fafted 2 0 10 kg fr 0 69 K f uff K 5 12 K kg mol 1 73 4 2 5 1 3 42 3 4 25 1 1 1 0 kg

Physical Chemistry
Solutions3 2000 J 4 2000 J 152 In a U tube as shown in figure water and oil Q 152 for rent and st are in the left side and right side of the tube respectively The heights from the bottom for water and oil columns are 15 cm and 20 cm respectively The density of the oil is e fag tr 15 cm 20 cm1 da a 152 15cm 30 cm Water take Pa 1000 kg m 1 1200 kg m 2 750 kg m 3 1000 kg m 4 1333 kg m W Copper of fixed volume V in drown into wire 20 am ut Water Pat 1000 kg m faforg 1 1200 kg m 2 750 kg m 3 1000 kg m 4 1333 kg m se

Physical Chemistry
Solutions4 Both Zn and Cu will remain in the solution IE0086 74 What will happen if the pH of the solution of 0 001 M Mg NO solution is adjusted to pH 9 KMg OH 8 9 x 10 2 1 precipitation will take place 2 precipitation will not take place 3 Solution will be saturated 4 None of these